Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Spider minor ampullate silk protein nanoparticles: an effective protein delivery system capable of enhancing systemic immune responses
- First Published: 15 June 2024
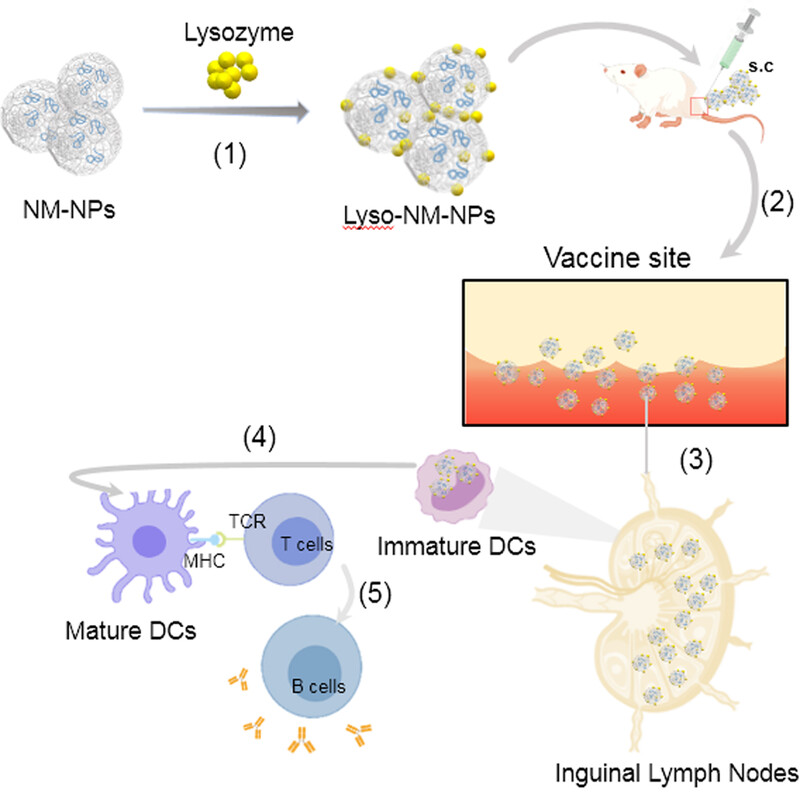
This study displayed the potential use of spider MiSp-derived NM-NPs as a nanocarrier for protein antigens. The mechanisms underlying how NM-NPs act as a vaccine carrier to promote antigen-specific immune responses are multifaceted. (1) High loading efficiency of antigen, (2) the nanoparticles establish an antigen depot at the injection site, (3) efficient uptake by APCs in the draining lymph node, (4) promote DC maturation in the draining lymph nodes and promoting cross-presentation, and (5) significant increases in specific antibodies levels and cellular immune responses.
Structural basis of neuropeptide Y signaling through Y1 and Y2 receptors
- First Published: 15 June 2024
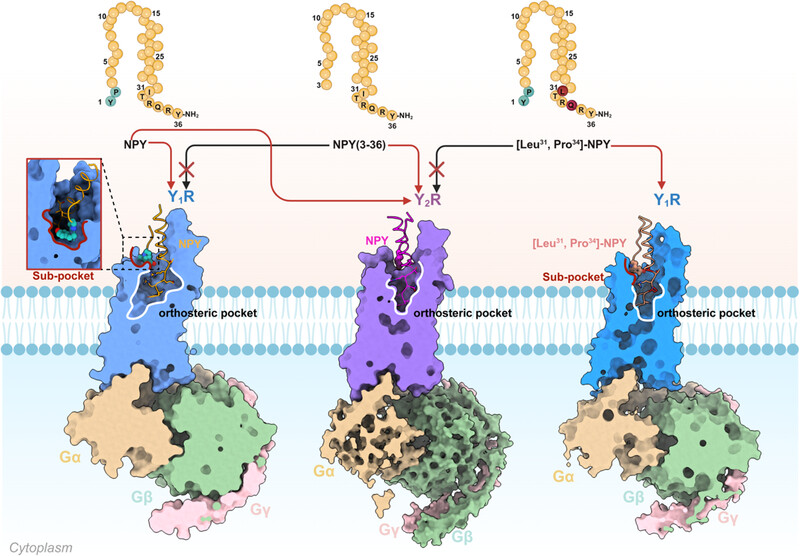
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) serves a critical role in modulating a variety of physiological processes. Gaining comprehensive understanding of structural mechanisms through which Y1R and Y2R interact with NPY is indispensable for the rational design of selective drugs. We offer detailed molecular maps depicting the binding of NPY peptides to NPY receptor subtypes, thereby shedding light on subtype-specific interaction patterns.
HIGHLIGHTS
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants from BA.2 to BA.2.86 and JN.1: strong lung infection ability and evolving immune escape capacity
- First Published: 15 June 2024
REVIEWS
Natural killer cells in cancer immunotherapy
- First Published: 15 June 2024
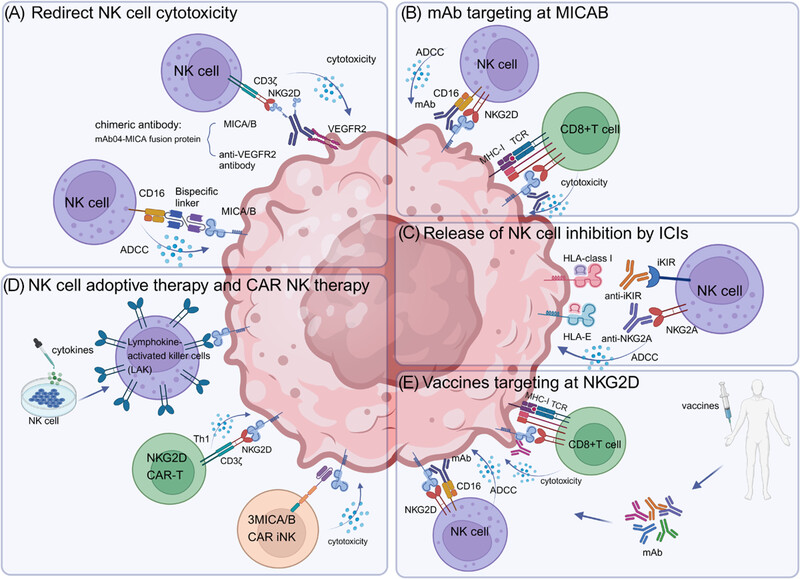
NK cells have cytotoxic functions against tumor cells especially through NKG2D receptor. This article reviews the mechanisms how tumors escape NK-mediated killing and therapeutic strategies with NK cells and especially MICA/B–NKG2D axis. Finally, the recent innovative CAR-NK/NKG2D CAR-T and MICA/B vaccines in tumor were summarized.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Association between Hepatitis B virus infection and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer
- First Published: 17 June 2024
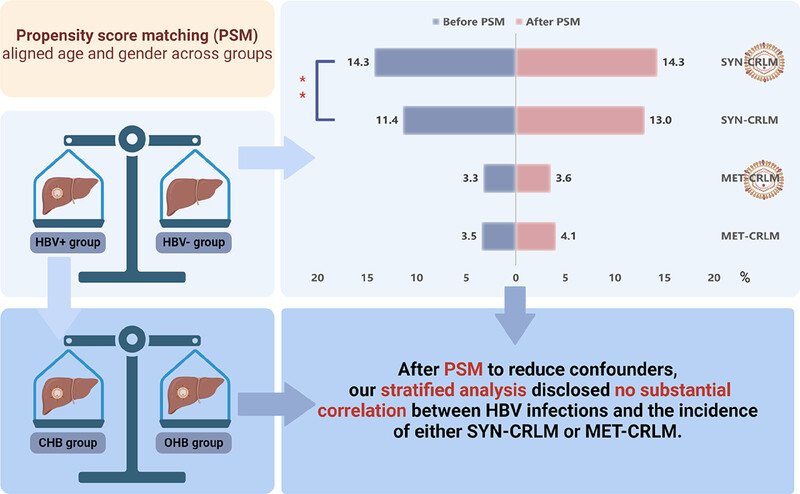
In a retrospective cohort of 5871 colorectal cancer patients, we aimed to investigate the association between both previous and current Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections and colorectal liver metastasis (CRLM). Propensity score matching (PSM) was applied to harmonize age and sex disparities within HBV+ (n = 1696) and HBV- (n = 4175) groups and further within HBV+ subgroups of chronic (CHB, n = 474) and occult (OHB, n = 1222) infections. We observed that null association between HBV infection status and synchronous CRLM in participants after PSM. Furthermore, there was no significant association between HBV infection and metachronous CRLM.
Metabolic shifts during coffee consumption refresh the immune response: insight from comprehensive multiomics analysis
- First Published: 17 June 2024
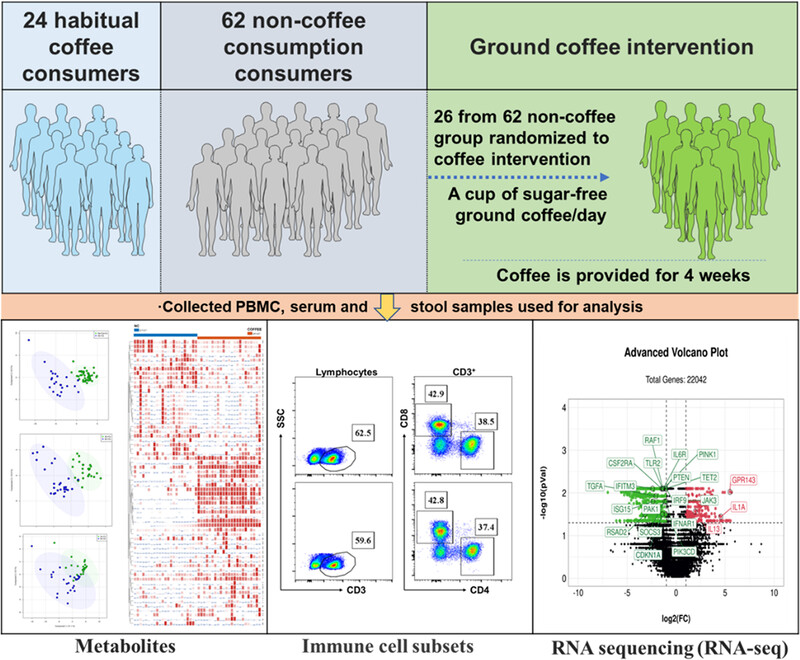
Coffee, a widely consumed beverage, has shown benefits for human health but lacks sufficient basic and clinical evidence to fully understand its impacts and mechanisms. In this study, our findings provide novel evidence of coffee in the anti-inflammatory and anti-immunosenescence effects, suggesting that coffee consumption could be considered as one healthy suggestion for healthcare.
Comparison of genetic and epigenetic profiles of periodontitis according to the presence of type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 19 June 2024
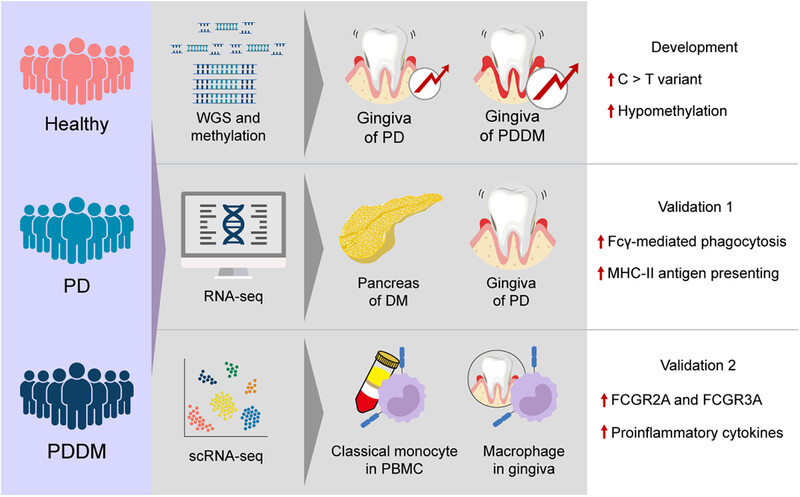
Periodontitis accompanied by type 2 diabetes exhibits significant hypomethylation of Fc gamma receptor-related genes compared with periodontitis.
Periodontitis accompanied by type 2 diabetes shows a notable increase in C>T base substitutions within Fc gamma receptor-related genes compared with periodontitis.
Hypomethylation and C>T base substitutions display a linear correlation, with a stronger correlation observed in periodontitis accompanied by type 2 diabetes.
Fc gamma receptor-related genes are significantly upregulated in monocytes of patients with periodontitis accompanied by type 2 diabetes.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer with trastuzumab emtansine resistance: insights from a multicenter retrospective real-world study
- First Published: 19 June 2024
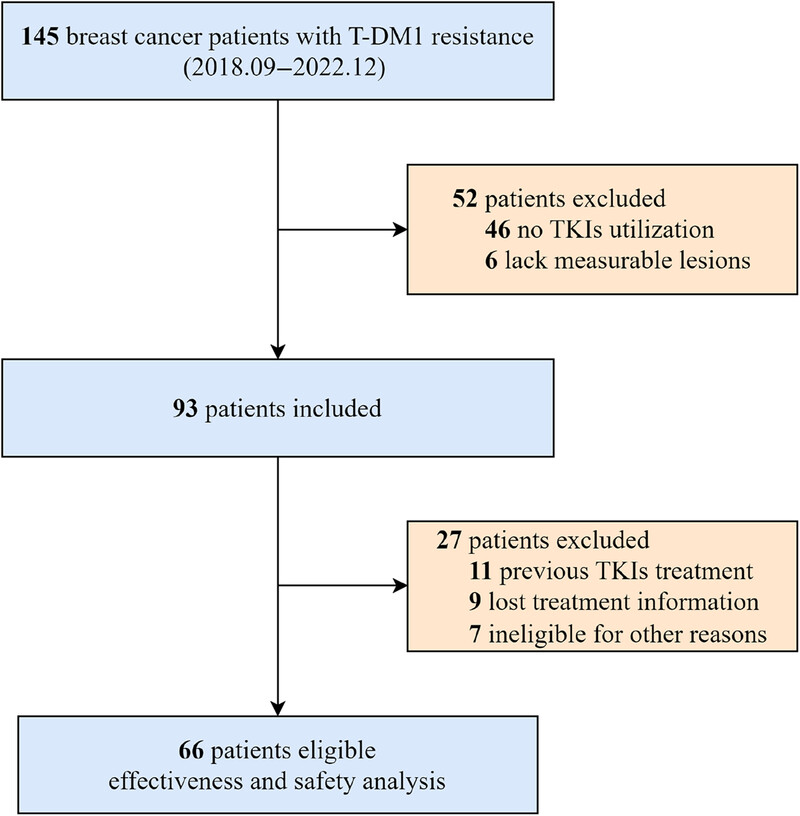
TKIs-based therapy could become an alternative treatment option for overcoming T-DM1 resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer.
Patients who benefited from previous T-DM1 treatment ≥6 months and featured acquired resistance to trastuzumab might achieve a better survival in subsequent TKIs treatment.
HIGHLIGHTS
Targeting RNA-binding motif protein 39 for arginine reduction: unveiling metabolic vulnerability in arginine-dependent liver cancer
- First Published: 19 June 2024
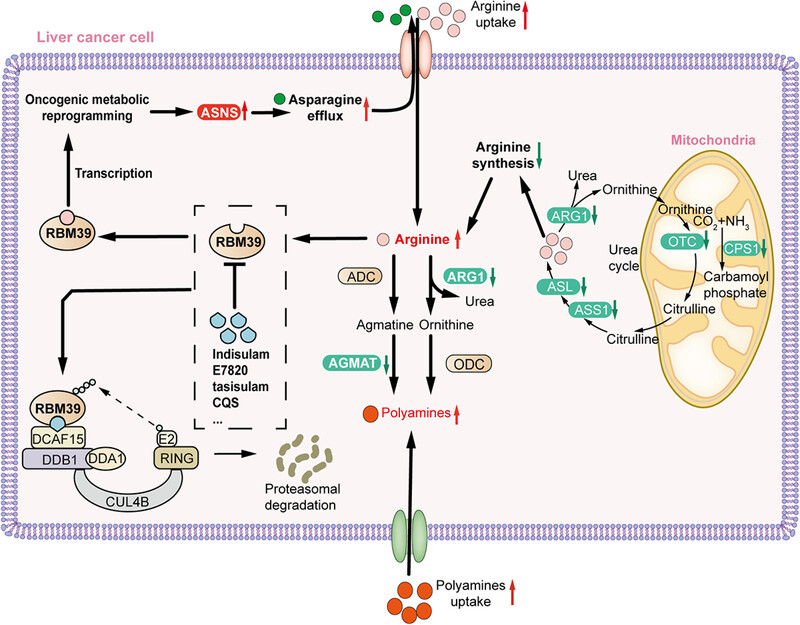
In a recent publication in Cell, Mossmann and colleagues presented a study uncovering arginine's role as a molecule with characteristics akin to second messengers, reshaping metabolism to promote tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Their investigation demonstrated that the RNA-binding motif protein 39 (RBM39) drives heightened asparagine synthesis, leading to elevated arginine absorption. This sets up a reinforcing cycle that supports sustained arginine levels and promotes oncogenic metabolic alterations. This finding introduces a fresh therapeutic approach for arginine-dependent liver malignancies.
REVIEWS
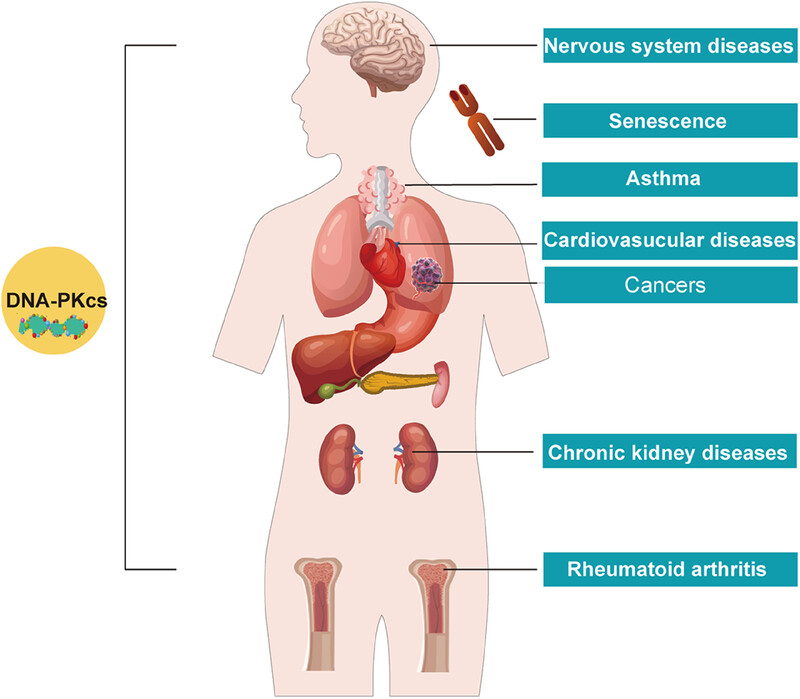
The multifaceted functions of DNA-PKcs: implications for the therapy of human diseases
- First Published: 19 June 2024
HIGHLIGHT
Targeting CD300ld to normalize the tumor microenvironment: an emerging insight in cancer immunotherapy
- First Published: 20 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics analysis for prediction of treatment response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and clinical outcome in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer: A large multicentric and validated study
- First Published: 20 June 2024
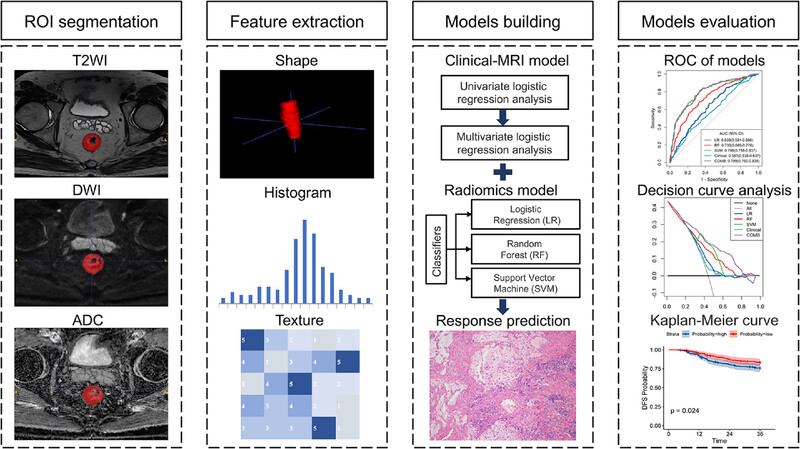
This study constructed a combined model with clinical MRI features and radiomics signature generated by Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm, and showed promising discrimination for the prediction of treatment response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) patients. The model was then validated in two external validation datasets and a prospective validation dataset, exhibited moderate performance for predicting good response, and was valuable for prognosis prediction.
Integrin αM promotes macrophage alternative M2 polarization in hyperuricemia-related chronic kidney disease
- First Published: 22 June 2024
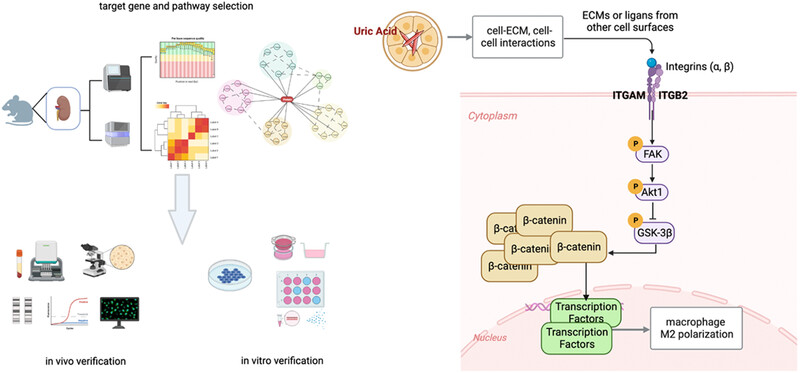
Schematic diagram of macrophage ITGAM and related mechanisms in hyperuricemia-related chronic kidney disease in mice. Through the integration and analysis of transcriptomic and phosphoproteomic data from renal tissue stimulated by hyperuricemia, we identified ITGAM as a central node. ITGAM on macrophages activates FAK/AKT/GSK-3β, resulting in the stabilization of β-catenin, and promotion of M2 polarization and kidney fibrosis in hyperuricemic CKD mice. The findings were confirmed through both in vivo and in vitro experiments by manipulating Itgam, p-FAK, and p-AKT1.
HIGHLIGHT
Targeting polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment for cancer immunotherapy
- First Published: 22 June 2024
REVIEWS
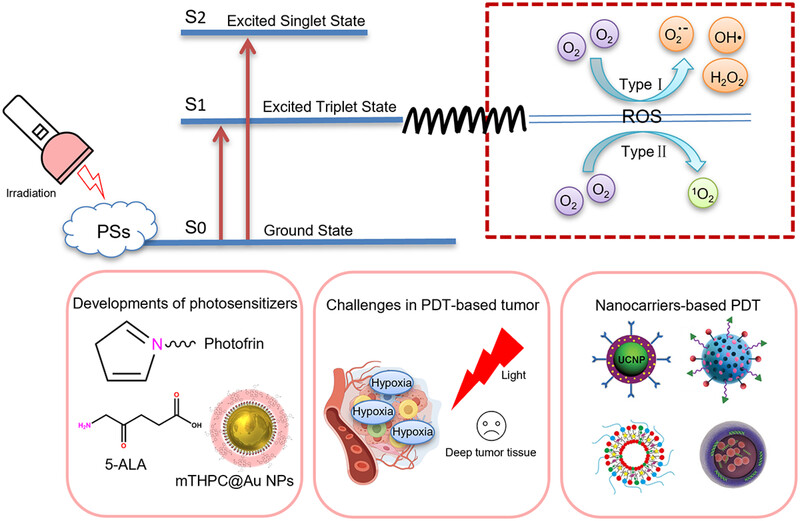
Photodynamic therapy for cancer: mechanisms, photosensitizers, nanocarriers, and clinical studies
- First Published: 22 June 2024
HIGHLIGHT
Phospholipids with two polyunsaturated fatty acyl tails: an important driver of ferroptosis
- First Published: 25 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
UV radiation-induced peptides in frog skin confer protection against cutaneous photodamage through suppressing MAPK signaling
- First Published: 25 June 2024
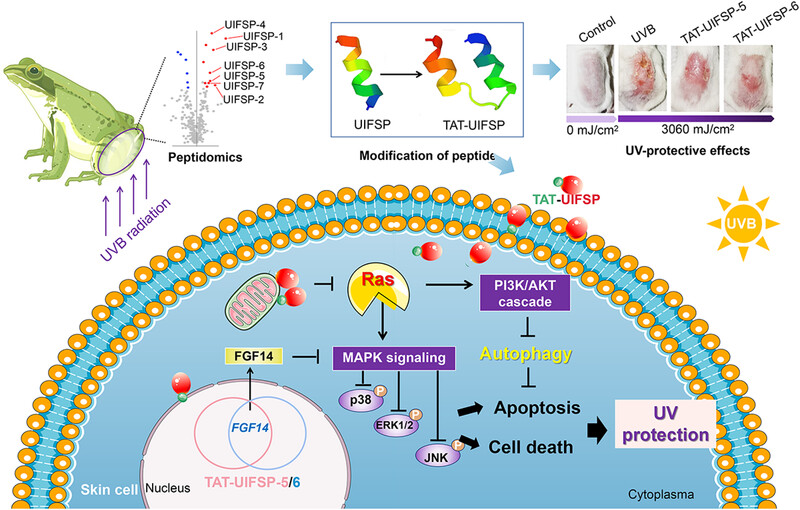
We found a series of UV-induced frog skin peptides (UIFSPs) from P. nigromaculatus. These peptides conferred significant protection against UVB-induced skin damage, and the photo-protective efficacy of UIFSPs was enhanced by UIFSPs modification with TAT protein transduction domain. Mechanistically, TAT-conjugated UIFSPs internalized into skin cells and suppressed UVB-induced activation of Ras/PI3K/AKT and Ras/MAPKs pathways, thereby preventing skin photodamage.
REVIEWS
Nanoliposomes as nonviral vectors in cancer gene therapy
- First Published: 25 June 2024
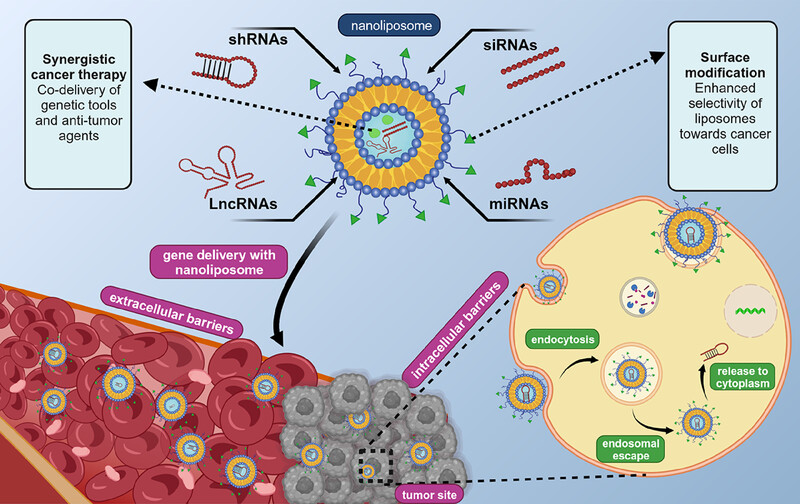
Cancer gene therapy is a promising approach; however, more investigations are needed to improve its efficiency, liposomes are nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery, and display enhanced intracellular accumulation, targeted delivery and high biocompatibility. Their surface modification of nanoparticles by ligands enhances selectivity of gene delivery to cancer cells.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
5,7,4′-Trimethoxyflavone triggers cancer cell PD-L1 ubiquitin–proteasome degradation and facilitates antitumor immunity by targeting HRD1
- First Published: 27 June 2024
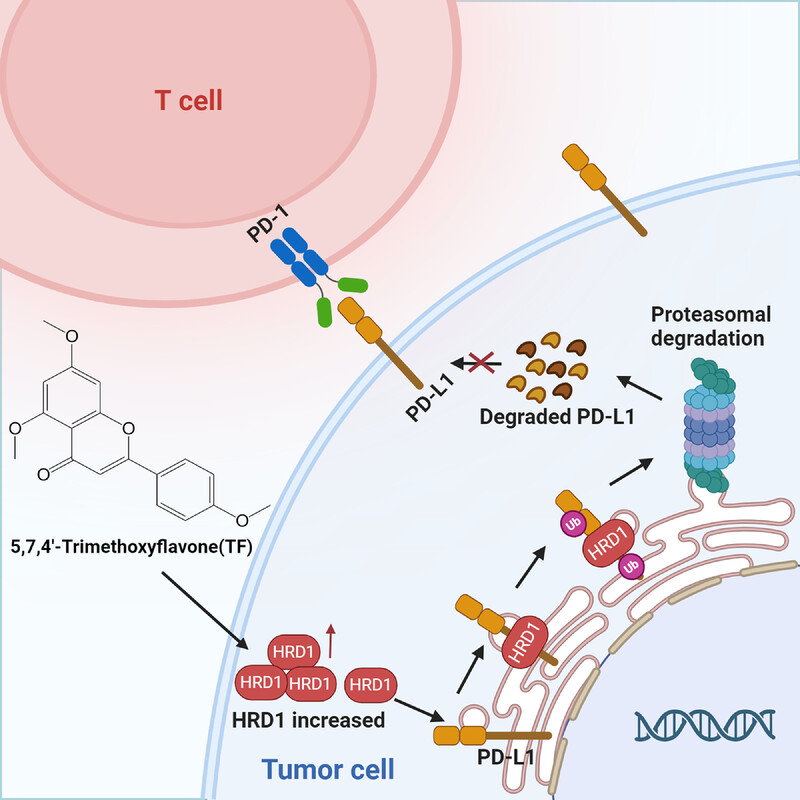
A brief description of the role of TF in promoting PD-L1 degradation in colorectal cancer (CRC). TF binds specifically to and stably expresses HRD1, thereby increasing the ubiquitination of PD-L1 and leading to its degradation via the proteasome, which enhances T cell activity and activates the tumor immune microenvironment.
Airway epithelial-derived exosomes induce acute asthma exacerbation after respiratory syncytial virus infection
- First Published: 27 June 2024
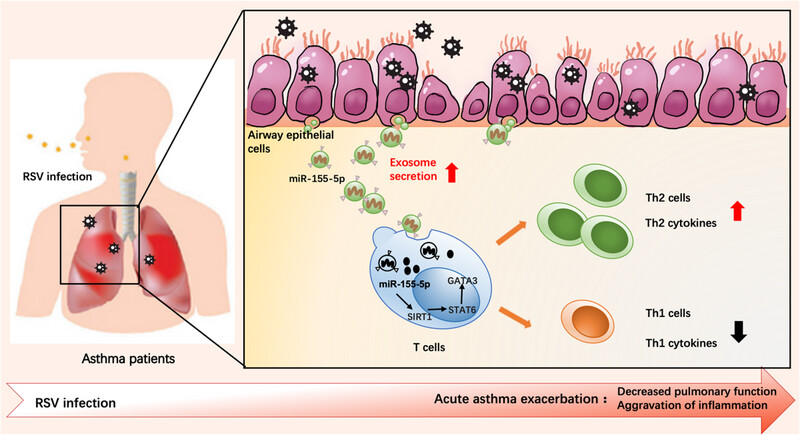
Acute asthma exacerbation is sudden or aggravated asthma symptoms in asthma patients, which is induced by outside stimulants. During acute asthma exacerbation after RSV infection, AEC-Exos promote the enhanced Th2 inflammation by transporting increased hsa-miR-155-5p, which was mediated partly through SIRT1-mediated pathway. hsa-miR-155-5p is a potential biomarker for early prediction of acute asthma exacerbation.
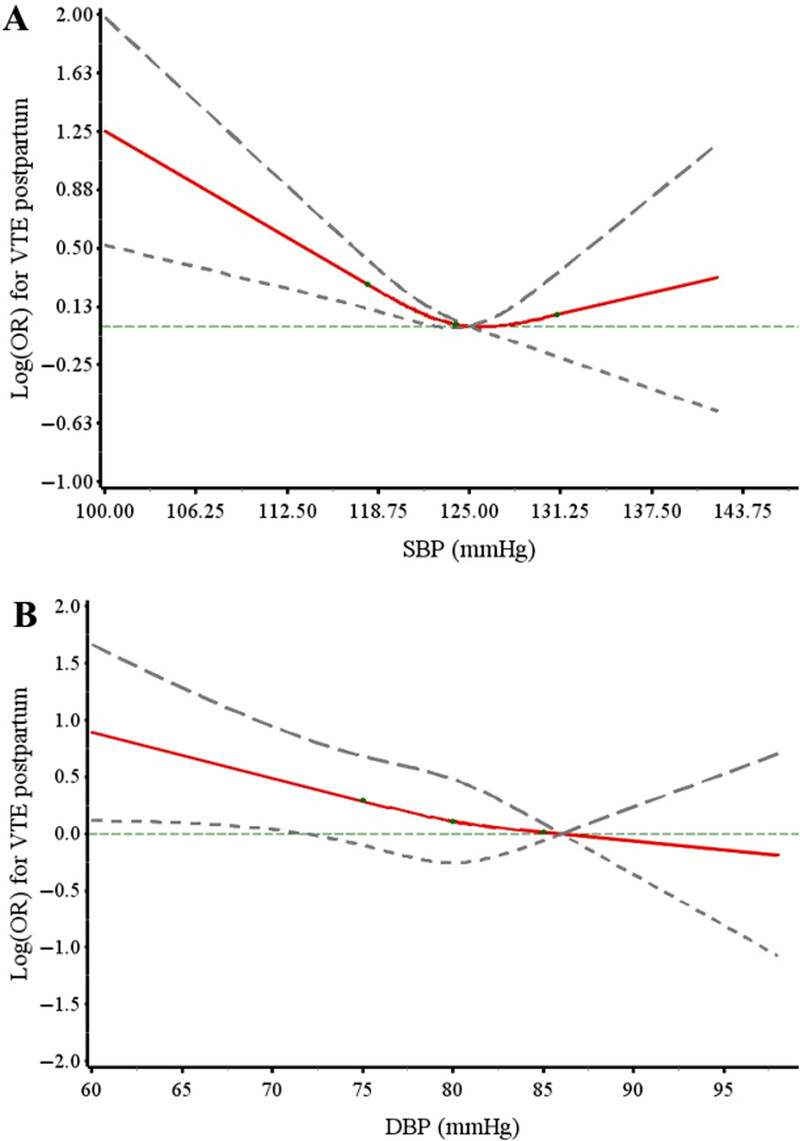
Associations of blood pressure in the third trimester and risk of venous thromboembolism postpartum
- First Published: 27 June 2024
REVIEW
Membranous nephropathy: pathogenesis and treatments
- First Published: 29 June 2024
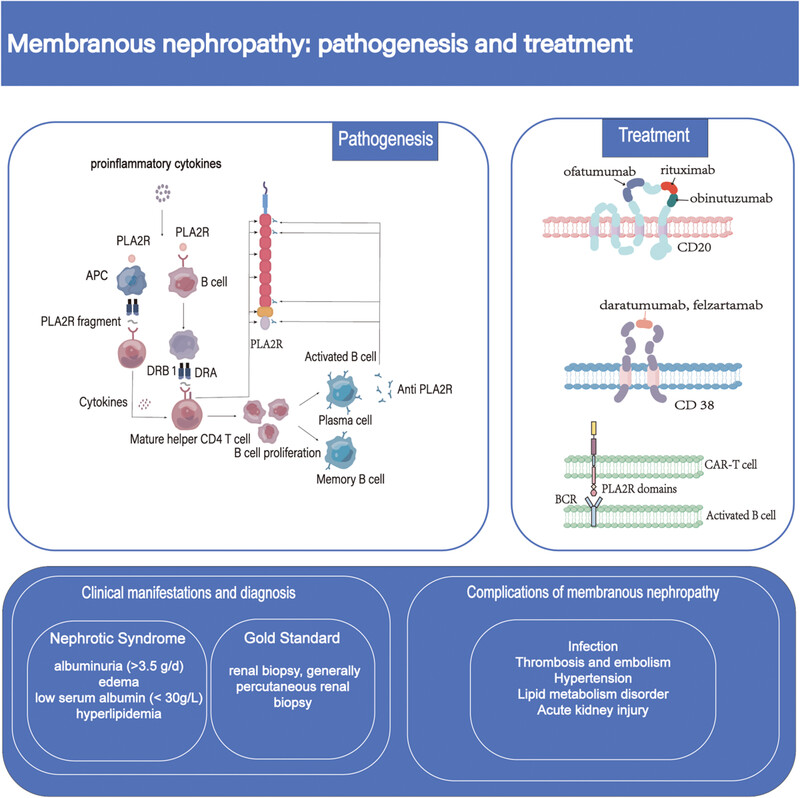
Membranous nephropathy, an autoimmune disease, can manifest at any age and is among the most common causes of nephrotic syndrome in adults. This review explores recent advancements in the pathophysiology of MN, encompassing pathogenesis, clinical presentations, diagnostic criteria, treatment options, and prognosis, with a focus on emerging developments in pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies aimed at halting disease progression .
HIGHLIGHTS
Disulfidptosis: disulfide stress-induced novel cell death pathway
- First Published: 29 June 2024
REVIEW
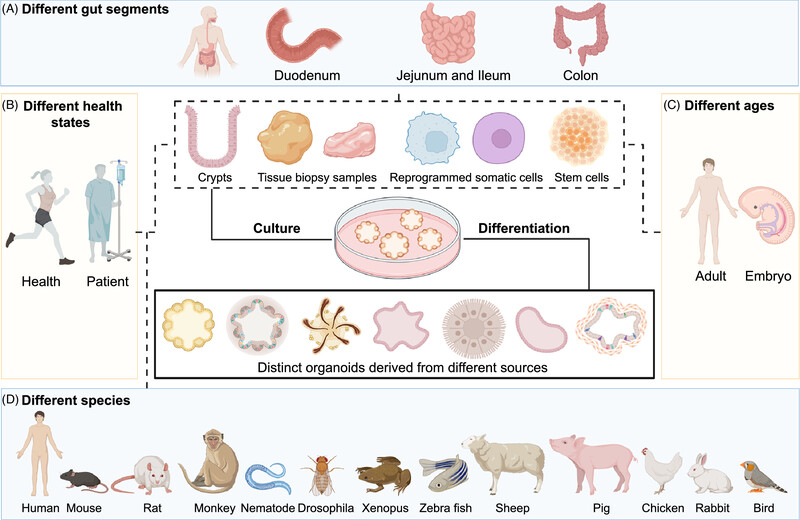
Organoids in gastrointestinal diseases: from bench to clinic
- First Published: 29 June 2024
HIGHLIGHT
Engineered CARD11–PIK3R3 T-cell therapies as weapons of cancer mass destruction
- First Published: 01 July 2024
Dopamine release after acute sleep deprivation: culprit of affective state transitions
- First Published: 01 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
CREB3 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by depressing AKT signaling through competitively binding with insulin receptor and transcriptionally activating RNA-binding motif protein 38
- First Published: 01 July 2024
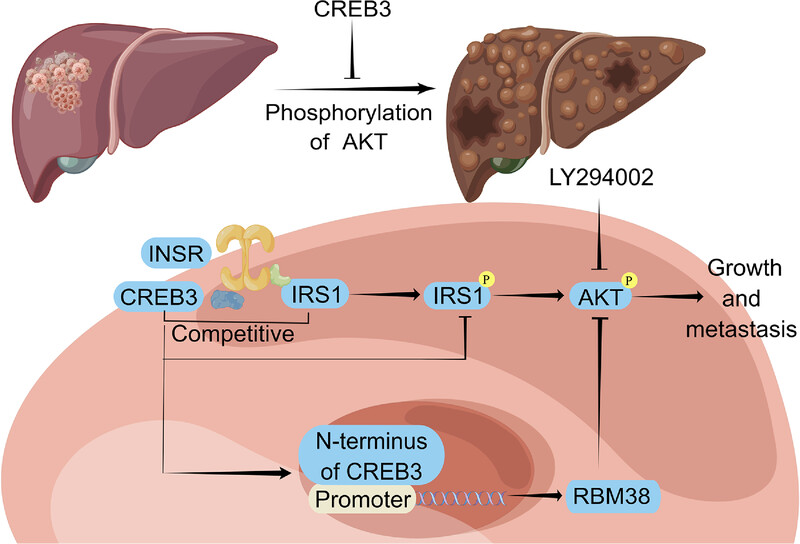
cAMP responsive element binding protein 3 (CREB3) hinders the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by suppressing the phosphorylation of AKT signaling through binding competitively with insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) to insulin receptor (INSR). Meanwhile, N-terminal of CREB3 inhibits AKT activation by transcriptionally promoting RNA-binding motif protein 38 (RBM38) expression in nucleus. Our findings provide novel insight into HCC therapy.
Epidermal growth factor receptor‑targeted antibody nimotuzumab combined with chemoradiotherapy improves survival in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a propensity score matching real-world study
- First Published: 02 July 2024
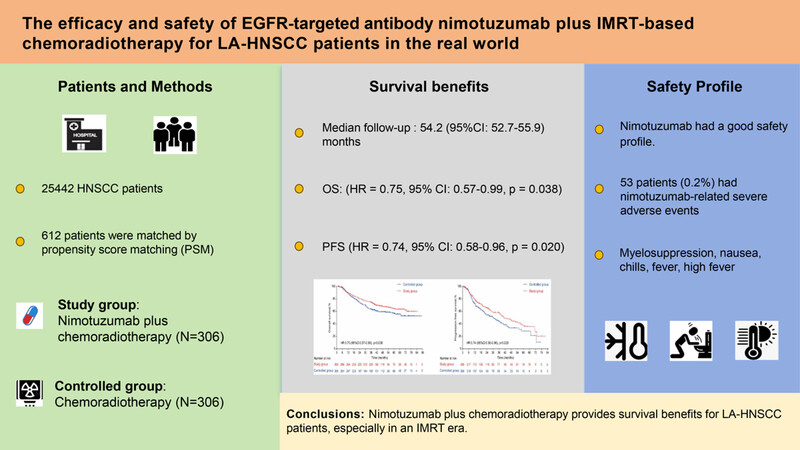
Nimotuzumab plus chemoradiotherapy provided manageable safety and survival benefits with improved OS and PFS for LA-HNSCC patients in an IMRT era. And subgroup analysis revealed that patients with aged 50–60 year, stage IV, N2, radiotherapy dose ≥60 Gy, without previous surgery, and neoadjuvant therapy have a trend of survival benefit with nimotuzumab.
Single-cell transcriptome dissecting the microenvironment remodeled by PD1 blockade combined with photodynamic therapy in a mouse model of oral carcinogenesis
- First Published: 02 July 2024
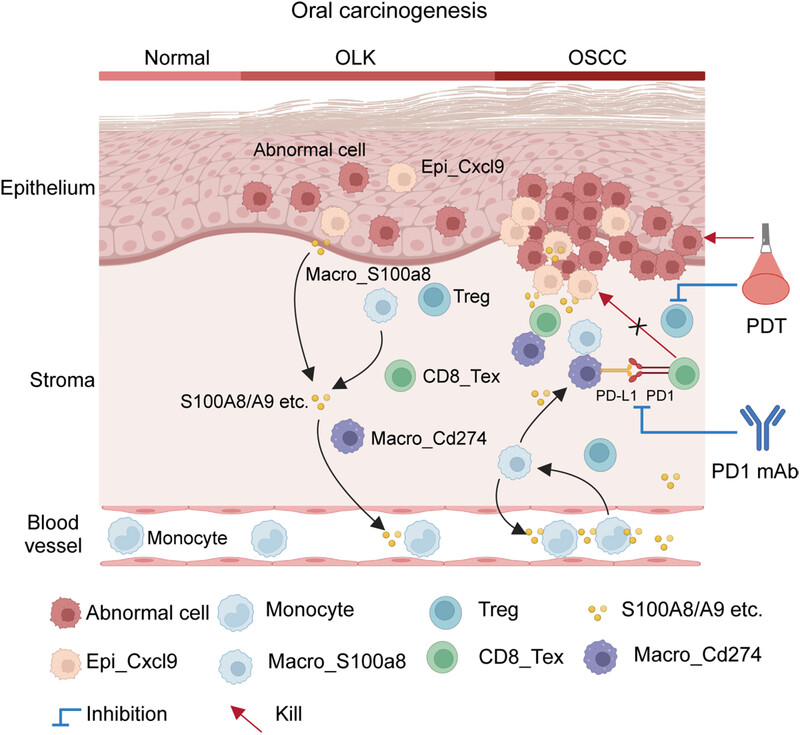
In oral carcinogenesis, various cell types, including epithelial cells (Epi_Cxcl9) and macrophages (Macro_S100a8), exhibit significant expression of inflammatory-related cytokines such as S100A8/S100A9. The overexpressed inflammatory cytokines recruit numerous immunosuppressive cell subsets (Tregs, Macro_Cd274, CD8_Tex, etc.). PD1 monoclonal antibody (PD1 mAb) can specifically block the functional inhibition of CD8_Tex by Macro_Cd274, but simultaneously accompanied by an increase in Treg proportion. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) not only directly kills abnormal cells but also reduces the proportion of Treg. Compared with monotherapy, the combination of PD1 mAb and PDT can reshape the microenvironment and induce a stronger therapy-related inflammatory response, thereby preventing oral carcinogenesis.
PERSPECTIVE
COVID-19 vaccine: recent advancements and future prospects
- First Published: 05 July 2024
REVIEW
Gene editing therapy for cardiovascular diseases
- First Published: 05 July 2024
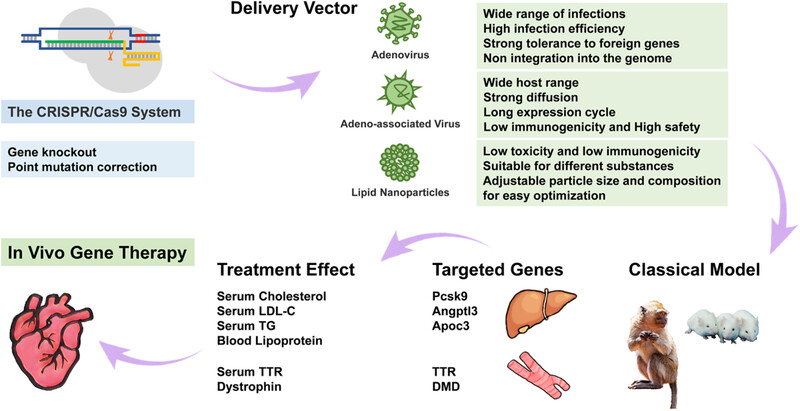
The application of the CRISPR/Cas system for gene editing therapy in CVD
Several gene editing systems have been utilized to target crucial genes associated with cardiovascular disease in different animal models through diverse delivery methods, all of which have displayed encouraging outcomes. Recent clinical trials have showcased notable advancements in multiple gene editing therapeutic strategies for cardiovascular disease. Both preclinical and clinical gene editing therapies for cardiovascular diseases establish a strong groundwork for further research and the development of novel therapeutic interventions for cardiovascular diseases .
Congenital heart disease: types, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment options
- First Published: 05 July 2024
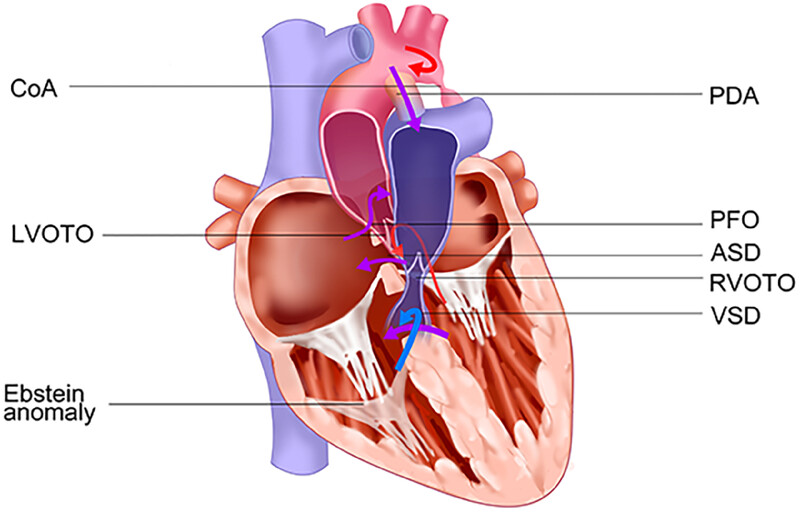
In this review, we provide an update of the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment in most common type of CHD, including patent foramen ovale, atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus, coarctation of the aorta, transposition of the great arteries, corrected transposition of the great arteries, coronary anomalies, left and right ventricular outflow tract obstruction, tetralogy of Fallot and Ebstein anomaly.
HIGHLIGHTS
Type-I-interferon-responsive microglia: participates in cerebral development and disease
- First Published: 05 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
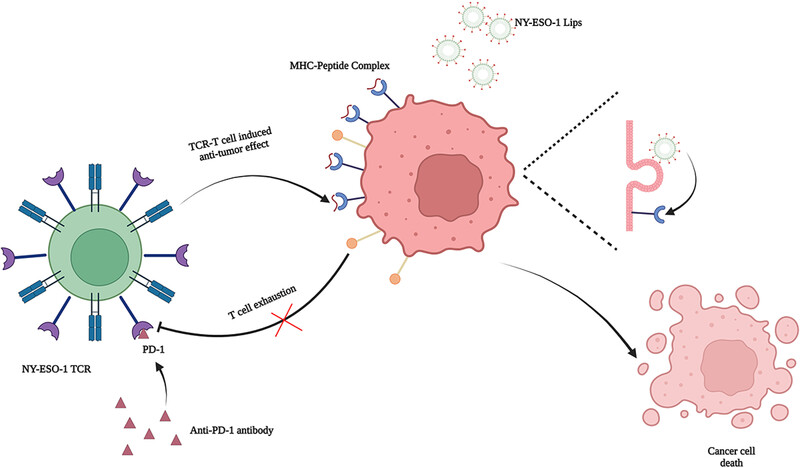
Liposome-based in situ antigen-modification strategy for “universal” T-cell-receptor engineered T cell in cancer immunotherapy
- First Published: 07 July 2024
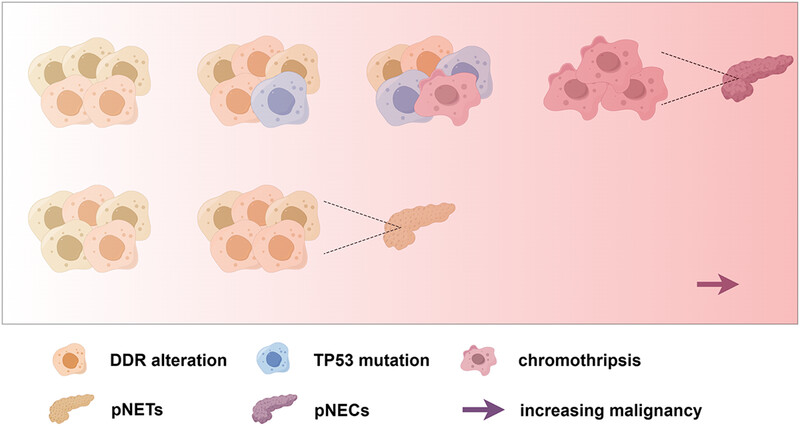
Chromothripsis is a novel biomarker for prognosis and differentiation diagnosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms
- First Published: 10 July 2024
The ischemia-enhanced myocardial infarction protection-related lncRNA protects against acute myocardial infarction
- First Published: 10 July 2024
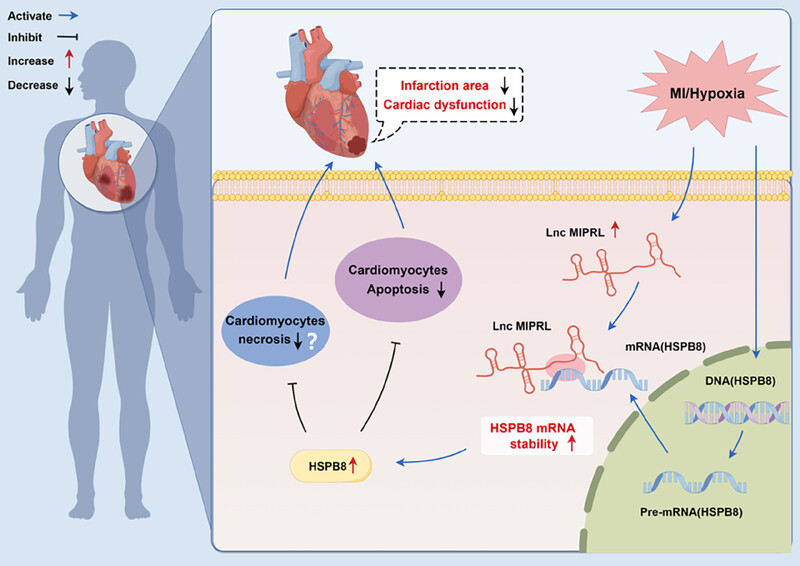
Myocardial infarction protection-related lncRNA (MIPRL) expression is increased in hearts after acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and in cultured cardiomyocytes after hypoxia. The upregulated MIPRL increases the expression of heat shock protein beta-8 (HSPB8) by enhancing the stability of HSPB8 messenger RNA. MIPRL protects against AMI via HSPB8-mediated inhibition of cardiac cell apoptosis and necrosis during AMI.
REVIEW
Skeletal muscle: molecular structure, myogenesis, biological functions, and diseases
- First Published: 10 July 2024
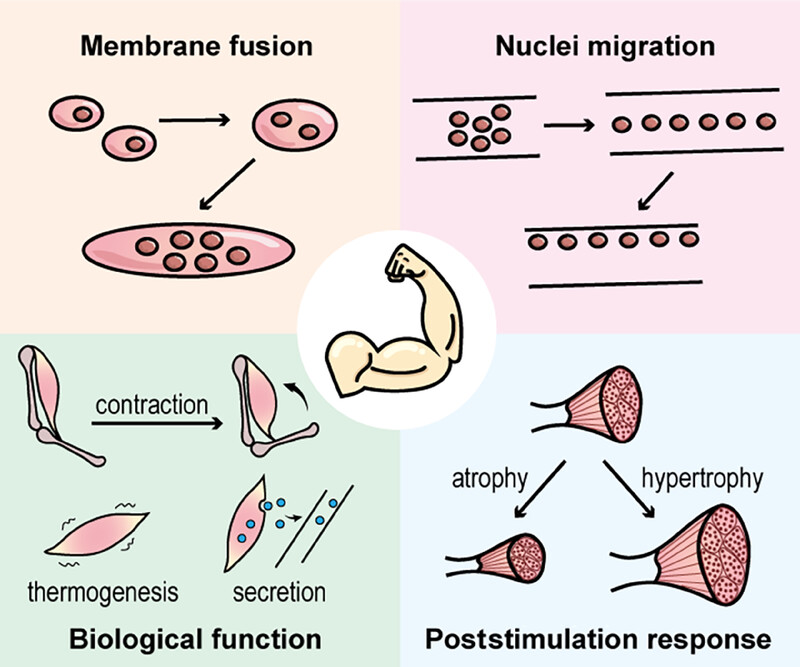
The article systematically and comprehensively reviews the physiological and pathological processes associated with skeletal muscles from five perspectives: molecule basis, myogenesis, biological function, poststimulation response, and myopathy. We primarily focus on nuclei-related behaviors of skeletal muscle, cell–cell fusion, and nuclei migration in the first two sections and discuss the three biological functions of skeletal muscle (muscle contraction, thermogenesis, and myokines secretion) and its response to stimulation (atrophy, hypertrophy, and regeneration), and finally settle on myopathy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
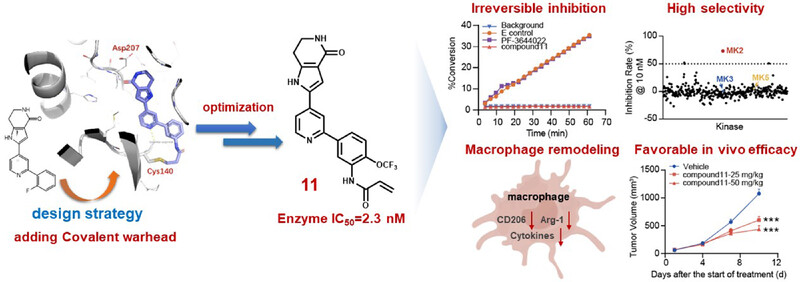
Remodeling tumor-associated macrophage for anti-cancer effects by rational design of irreversible inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2
- First Published: 10 July 2024
Unraveling dynamic immunological landscapes in intracerebral hemorrhage: insights from single-cell and spatial transcriptomic profiling
- First Published: 10 July 2024
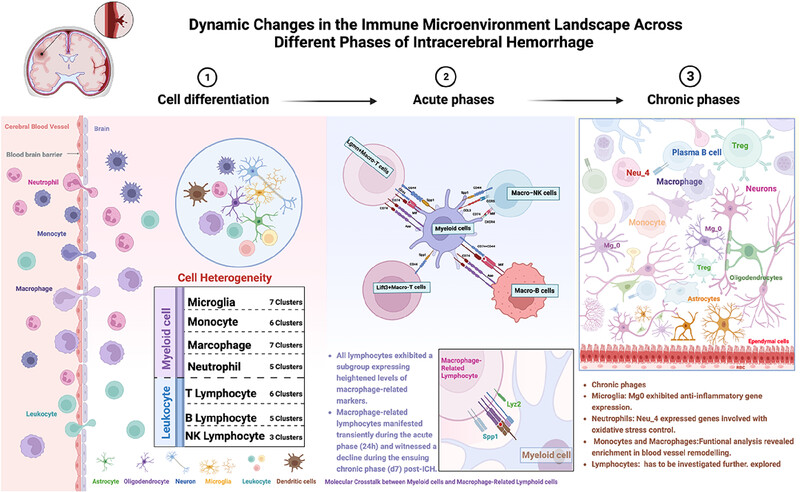
Using single-cell transcriptomics, we explored post-ICH cellular changes and intercellular dynamics. We identified distinct myeloid and lymphocyte subclasses. Early after ICH (≤24 h), myeloid cells dominated, while a lymphocyte subset showed heightened macrophage-related markers. These findings highlight myeloid-lymphocyte interactions, crucial in ICH pathogenesis. Further studies are warranted to explore subacute phase cellular engagements.
Identification of an alternative ligand-binding pocket in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and its correlated selective agonist for promoting beige adipocyte differentiation
- First Published: 10 July 2024
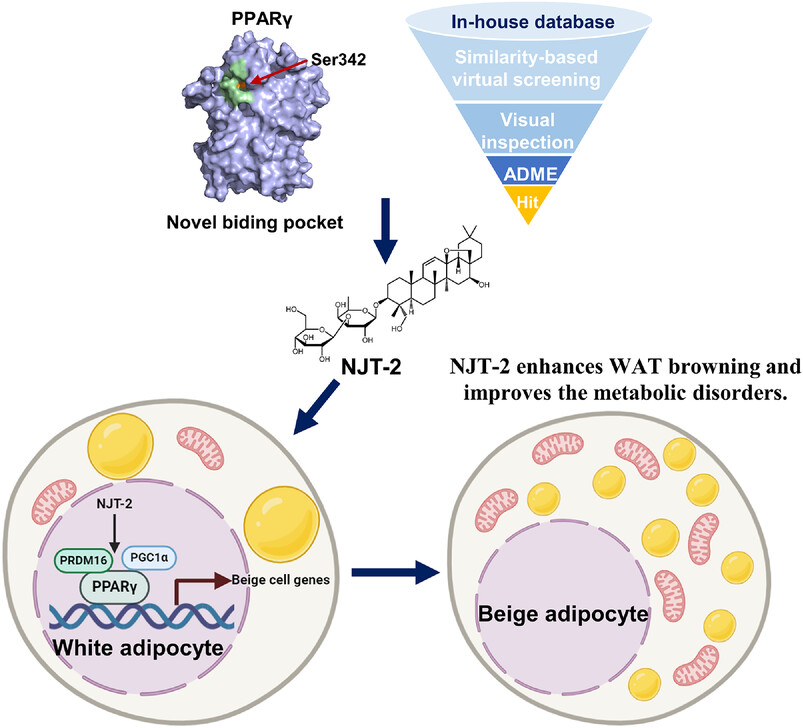
Identification of an alternative ligand-binding pocket in proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), and screening out NJT-2, a natural compound derived from Bupleurum chinense DC, binds in this pocket, induces the coactivator recruitment, guides the PPARγ binding to the promotors of beige adipocyte-related genes, thus enhances white adipose tissue browning and improves the metabolic disorders without the similar adverse effects observed with thiazolidinediones.
DNMT3A dysfunction promotes neuroinflammation and exacerbates acute ischemic stroke
- First Published: 14 July 2024
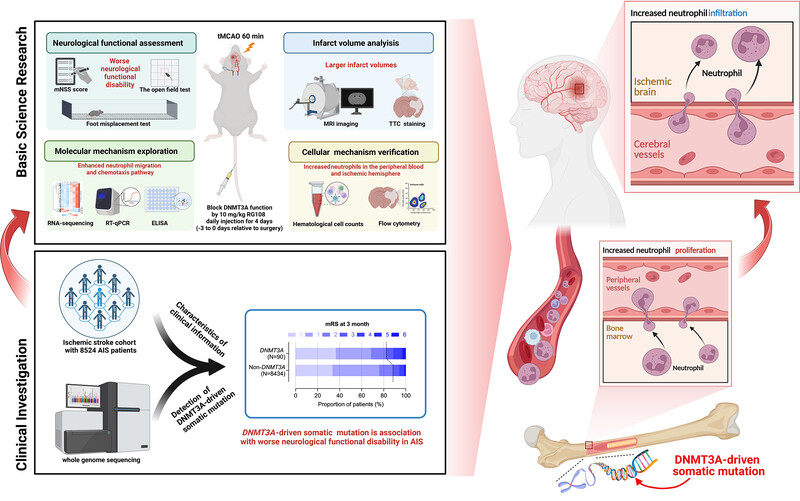
•Evaluate the association of DNMT3A-driven clonal hematopoiesis and worse neurological functional disability in ischemic stroke patients in a well-characterized cohort of 8524 patients with AIS.
•Use a molecular inhibitor of DNMT3A RG108 to confirm that DNMT3A-dysfunction increases infarct volume and worsens neurobehavioral deficits in a tMCAO mouse model.
•The potential mechanism is an increase in neutrophil proliferation and infiltration into the ischemic brain region, resulting in proinflammatory activation and more damage to the brain tissue .
Risk of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis following COVID-19: a nationwide cohort study
- First Published: 14 July 2024
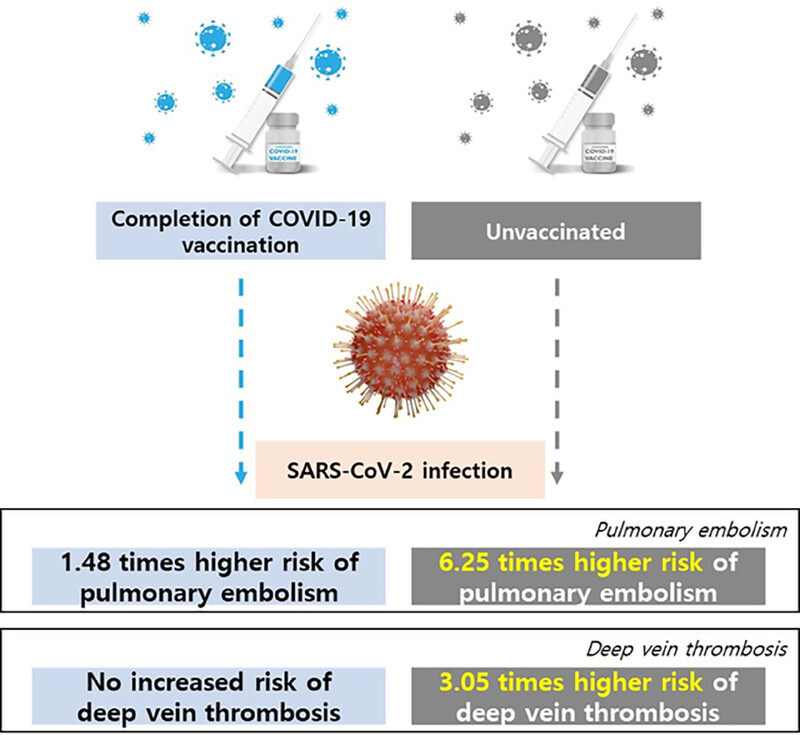
COVID-19 was associated with an increased risk of PE (aHR, 6.25; 95% CI, 3.67–10.66; p < 0.001) and DVT (aHR, 3.05; 95% CI, 1.75–5.29; p < 0.001) in unvaccinated participants. Even in those with complete COVID-19 vaccination, a smaller but significant risk of PE was observed (aHR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.15–1.88; p < 0.001). However, COVID-19 did not increase DVT risk in those with complete vaccination.
REVIEW
Cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases: an emerging research frontier
- First Published: 13 July 2024
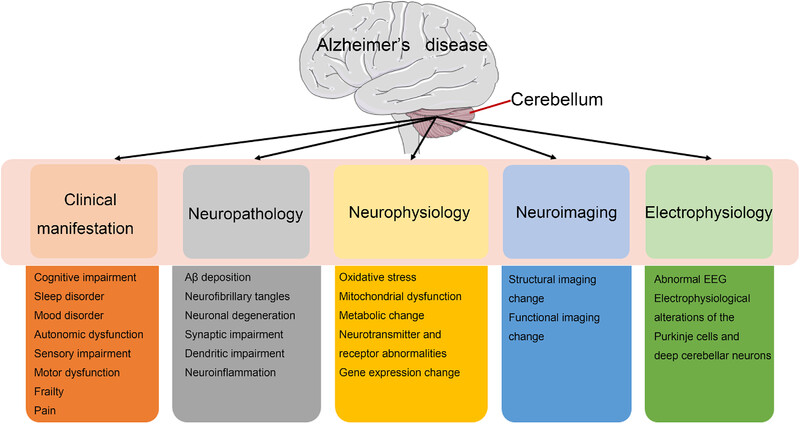
The cerebellum has a highly organized laminar flow structure and tightly anatomical circuits connecting with the cerebral cortex and subcortical regions, through which it is involved in the regulation of movement, balance, and cognition. To understand the role of the cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease (AD), we propose a comprehensive review highlighting a succinct synopsis of the clinical manifestation, neuropathology, neurophysiology, neuroimaging, and electrophysiology features associated with cerebellar dysfunction in AD, thereby underscoring the cerebellum as an emerging frontier for AD research. Abbreviations: Aβ, amyloid-β; EEG, electroencephalography.
Liquid–liquid phase separation in diseases
- First Published: 13 July 2024
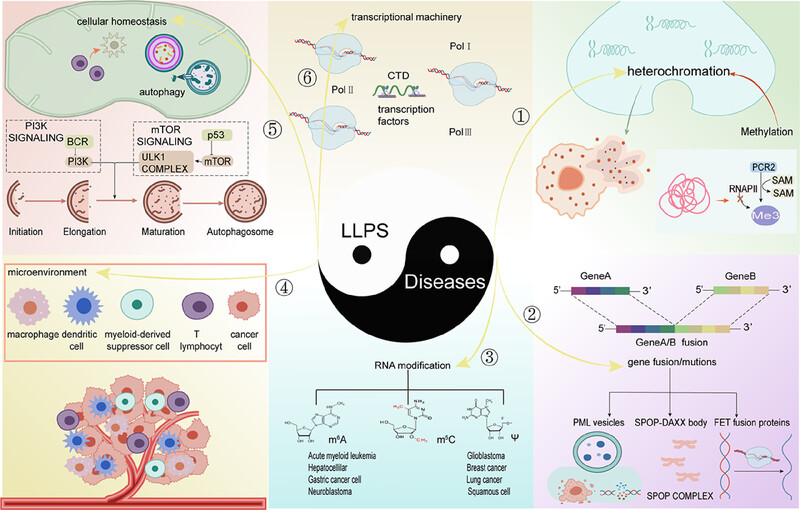
Liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) as a rising molecular entity in the cytoplasm regulates diseases progression via a variety of ways. For example, the relationship between LLPS and cancer can be summarized into six aspects: gene fusions/mutations, heterochromatin formation, transcriptional machinery, cellular homeostasis, microenvironment, and RNA modification. In particular, the behavior and mechanism of LLPS in RNA modification may point to new directions for diagnostics and therapy for some of the most dangerous and hard-to-treat tumors.