Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
A Low Temperature Self-Assembled ZrO2 Layer as a Surface Modification for High Energy Density Ni-Rich Cathode Materials in a Lithium-Ion Battery
- First Published: 05 February 2021
The surface modification for Ni-rich cathode materials is required to be homogeneous without Ni2+/Li+ cation mixing in the reheating section. Herein, homogeneous ZrO2 layer forms on the surface of NCM82 Ni-rich cathode materials through self-combustion reaction, leading to the ZrO2 layer is formed at a low temperature, whereby the bulk structure of Ni-rich material is preserved. More details can be found in article number 2000800 by Junyoung Mun and co-workers.
Back Cover
Interface Engineering for High-Performance Photoelectrochemical Cells via Atomic Layer Deposition Technique
- First Published: 05 February 2021

A short overview of atomic layer deposition (ALD) application in the interface engineering of photoelectrochemical (PEC) cells is given. The results of ALD technology-based interface and surface engineering for high-performance PEC cells in recent years are summarized and the challenges and opportunities of the development of ALD-based interface engineering for high-performance PEC cells in the near future are discussed. More details can be found in article number 2000819 by Zhuo Kang, Yue Zhang, and co-workers.
Masthead
Reviews
The Insights of Lithium Metal Plating/Stripping in Porous Hosts: Progress and Perspectives
- First Published: 05 December 2020
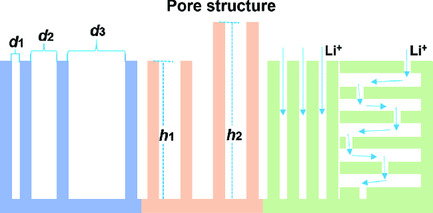
The pore structure of hosts in composite Li anode determines the distribution of electric and Li-ion concentration fields, thus regulating Li plating/stripping behavior. Herein, the recent progress and perspectives in investigating the behavior of Li plating/stripping in a pore is summarized from the aspects of pore diameter, depth, and tortuosity to promote the development of composite Li anodes.
Recent Progress in Electrocatalytic Glycerol Oxidation
- First Published: 01 December 2020
The present review focuses on summarizing the recent progress of electrolytic glycerol oxidation, aiming to provide an overview on fundamentals, reaction mechanisms, application in fuel cells and electrolyzers, and electrocatalysts development regarding the topic of glycerol oxidation reaction (GOR).
Molten-Salt Technology Application for the Synthesis of Photocatalytic Materials
- First Published: 12 January 2021
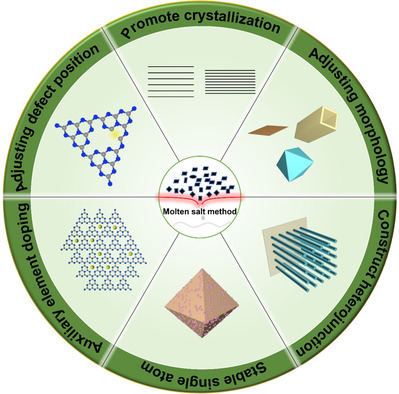
This review focuses on the application of molten salt technology in photocatalytic synthesis, including promote crystallization, adjusting morphology, accelerating the construction of heterostructure, auxiliary element doping, stable single atom, and adjusting defect position. The key challenges and opportunities are also discussed, indicating the development potential for the synthesis of photocatalysts in the future.
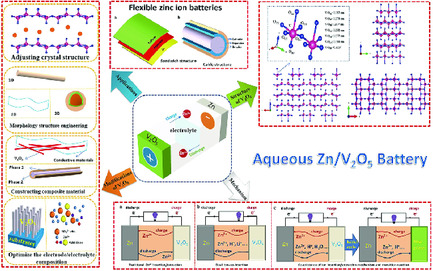
The Current Developments and Perspectives of V2O5 as Cathode for Rechargeable Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 17 November 2020
Interface Engineering for High-Performance Photoelectrochemical Cells via Atomic Layer Deposition Technique
- First Published: 20 November 2020
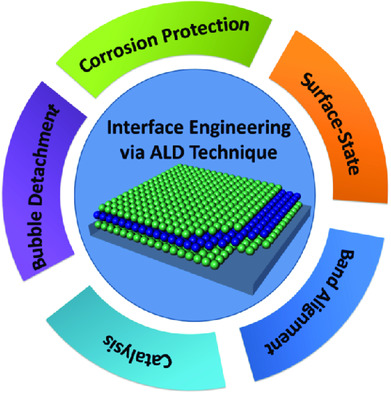
A short overview of atomic layer deposition (ALD) application in the interface engineering of photoelectrochemical (PEC) cells is given. The results of ALD technology–based interface and surface engineering for high-performance PEC cells in recent years are summarized and the challenges and opportunities of the development of ALD-based interface engineering for high-performance PEC cells in the near future are discussed.
Recent Developments of Preintercalated Cathodes for Rechargeable Aqueous Zn-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 20 November 2020
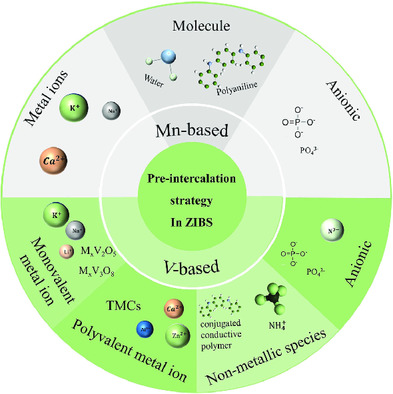
Preintercalation is an effective strategy to solve the structure collapse and slow zinc-ion diffusion kinetics of cathode in rechargeable aqueous Zn-ion batteries (ZIBs). This study reviews the preinterclalation strategy in manganese- and vanadium-based cathode of ZIBs, and summarizes the different effect and reaction mechanisms caused by various preintercalated species, including metal ions, nonmetallic species, molecule, and anionic.
Review on Synthesis and Catalytic Coupling Mechanism of Highly Active Electrocatalysts for Water Splitting
- First Published: 22 December 2020
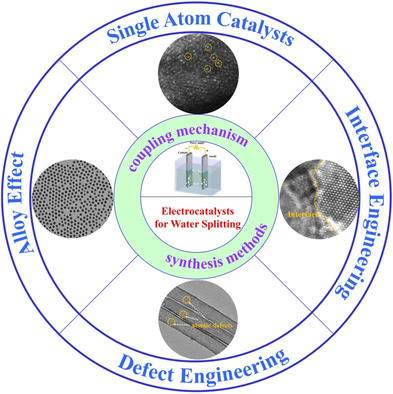
Herein, synthesis methods and catalytic coupling mechanisms of metal-based electrocatalysts for water splitting are reviewed. Importantly, alloy effect, interface construction, various defects, and doping effects in electrocatalysts are believed to be the main reasons for improving the intrinsic catalytic activities. This review prospects an important impact on the development of hydrogen generation.
Essay
Toward Large-Scale Hydrogen Production from Water: What Have We Learned and What Are the Main Research Hurdles to Cross for Commercialization?
- First Published: 12 December 2020
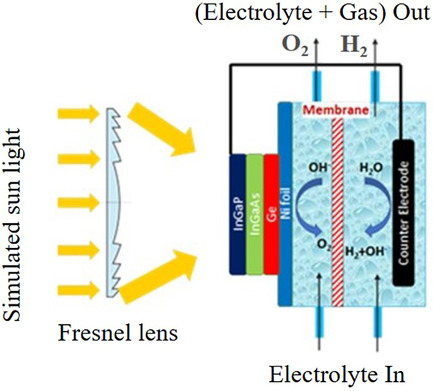
Research methodologies of hydrogen production from water are addressed. Priorities are given for methods suitable for largescale applications. The planned production capacity globally is orders of magnitudes lower than that needed to make an impact on the environment. Hydrogen as a fuel (not as a chemical) stands to decrease CO2 emission. A considerable investment in research and development is needed.
Full Papers
Probabilistic Steady State Voltage Stability Assessment Method for Correlated Wind Energy and Solar Photovoltaic Integrated Power Systems
- First Published: 10 December 2020
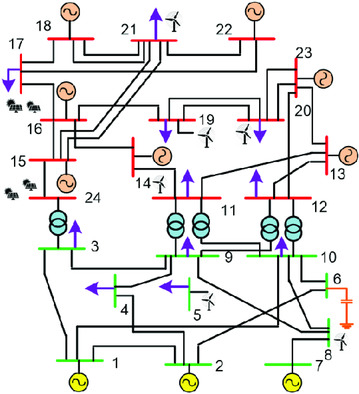
Herein, a method is reported for probabilistic assessment of the voltage stability margin (VSM) in power systems. The wind and solar photovoltaic power plants are integrated with standard power grid systems. The probabilistic VSM is jointly analyzed through continuous power flow and the three point estimation method. The statistical distribution of the VSM is obtained using Cornish–Fisher expansion series.
A Low Temperature Self-Assembled ZrO2 Layer as a Surface Modification for High Energy Density Ni-Rich Cathode Materials in a Lithium-Ion Battery
- First Published: 23 December 2020
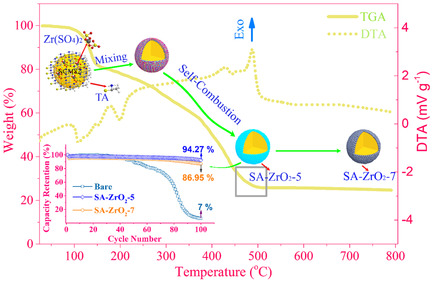
The surface modification for Ni-rich cathode materials is required for homogeneous coating layers, without Ni2+/Li+ cation mixing in the reheating process. Herein, a homogeneous ZrO2 layer forms on the surface of NCM82 Ni-rich cathode materials through self-combustion reaction, leading to the ZrO2 layer forming at a low temperature, whereby the bulk structure of NCM82 materials is preserved.
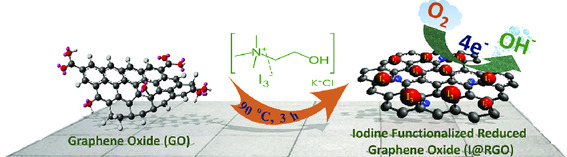
Synthesis of Iodine-Functionalized Graphene Electrocatalyst Using Deep Eutectic Solvents for Oxygen Reduction Reaction and Supercapacitors
- First Published: 20 November 2020
Enhanced Reversible Capacity and Cyclic Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries Using SnO2 Interpenetrated MXene V2C Architecture as Anode Materials
- First Published: 23 November 2020
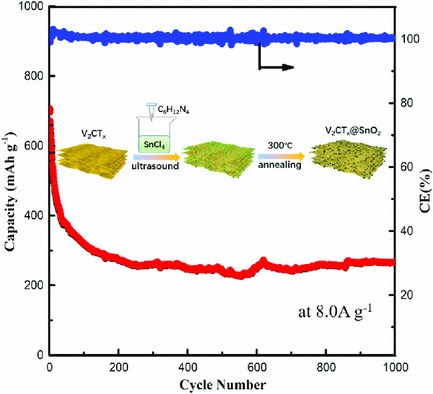
A sandwich structure MXene V2CTx@SnO2 heterogeneous nanocomposite is successfully prepared, which combines the advantages of MXene and SnO2 nanomaterial. As the anode material in Li-ion batteries, it has large reversible capacity of ≈260 mAh g−1 at high current density of 8000 mA g−1 after 1000 cycles, showing superior reversible capacity, high Coulombic efficiency, excellent cycling stability, and superior rate capability.
An Effective Way of Improving the Performance of Ni-Rich LiNi0.82Co0.12Mn0.06O2 Cathode in Lithium-Ion Battery via Borate Coating
- First Published: 10 December 2020
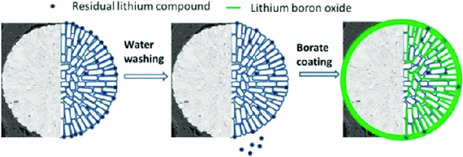
The strategy combining water washing with borate-coating can effectively reduce residual lithium compounds and pH value. The boron forms a membrane to act as an artificial solid-state electrolyte interface (SEI) and diffuses into the whole particle to form lithium transfer network. A minimal amount of boron modification improves the discharge capacity and cycle performance of cathode materials.
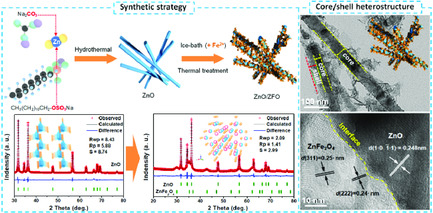
Designing Hierarchical Porous ZnO/ZnFe2O4 Hybrid Nanofibers with Robust Core/Shell Heterostructure as Competitive Anodes for Efficient Lithium Storage
- First Published: 21 November 2020
A General Template-Induced Sulfuration Approach for Preparing Bifunctional Hollow Sulfides for High-Performance Al- and Li-ion Batteries
- First Published: 21 November 2020
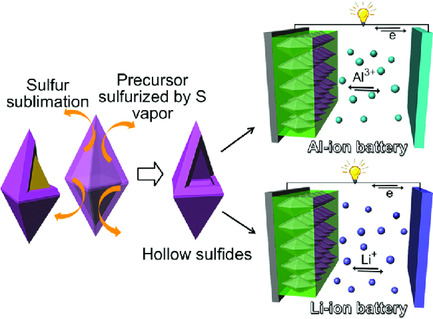
A general template-induced sulfuration method which is applicable for preparing a broad set of hollow sulfides is developed. As a demonstrating study, a hollow nickel disulfide is prepared which has been confirmed extendable for other sulfides. The nickel disulfide exhibits bifunctional properties using as aluminum-ion battery cathode and lithium-ion battery anode with good electrochemical performances.
A Metal–Organic Framework-5-Incorporated All-Solid-State Composite Polymer Electrolyte Membrane with Enhanced Performances for High-Safety Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 26 November 2020

Herein, a metal–organic framework-5 (MOF-5)-incorporated composite solid polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state Li-metal batteries is prepared. The fluorinated polymer (PTFEMA-co-PPEGMA) matrix provides good film-forming properties. Furthermore, the MOF-5 nanoparticles play an important role in the enhancement of electrochemical performance. A high tLi+ (0.51) and a wide electrochemical window (5.38 V) are achieved after the incorporation of MOF-5 fillers into matrix.
Mixed Polyanion Na-Mn-V-P Glass–Ceramic Cathode Network: Improved Electrochemical Performance and Stability
- First Published: 21 November 2020
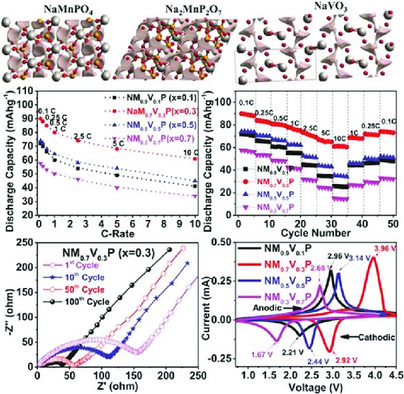
The electrochemical performance of mixed polyanion NaMn1−x(VO)xPO4 glass and glass–ceramic cathode systems is superior to current amorphous-based counter parts. The deliverables are as mentioned: a) bulk conductivity (σb) = 5.92 × 10−07 S cm−1; b) charge capacity = 80.55 mAh g−1; and c) discharge capacity = 81.19 mAh g−1 at various current rates due to the lowest resistance over particle–electrolyte.
Fabrication of the Oxygen Vacancy Amorphous MnO2/Carbon Nanotube as Cathode for Advanced Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 01 December 2020
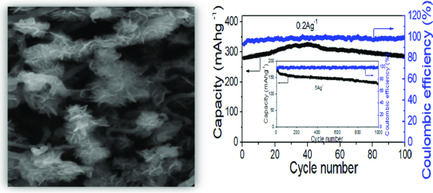
A simple coprecipitation method at room temperature is used to prepare oxygen vacancy MnO2, which are thin nanosheets uniformly distributed on the carbon nanotube (Vo-MnO2/CNT). The high-performance zinc-ion battery (ZIB) is fabricated with faster reaction kinetics, higher capacity of 314 mAh g−1 at 0.2 A g−1, and better long-term cycles of 81% retention after 1000 cycles at 5 A g−1.
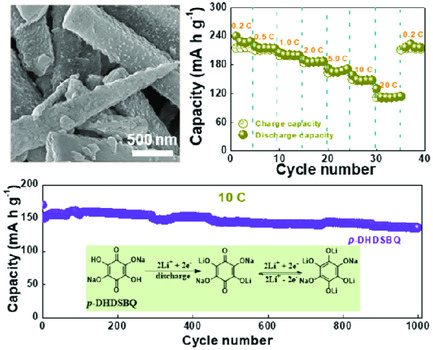
Disodium-Substituted Tetrahydroxybenzoquinone Salt as an Organic Electrode for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 26 November 2020
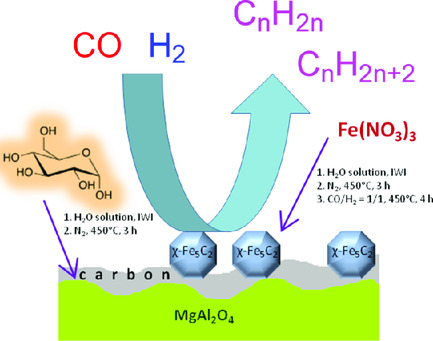
Unusual Effect of Support Carbonization on the Structure and Performance of Fe/Mgal2o4 Fischer–Tropsch Catalyst
- First Published: 03 December 2020
Investigation of Drying Curves of Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes with a New Gravimetrical Double-Side Batch Dryer Concept Including Setup Characterization and Model Simulations
- First Published: 11 December 2020
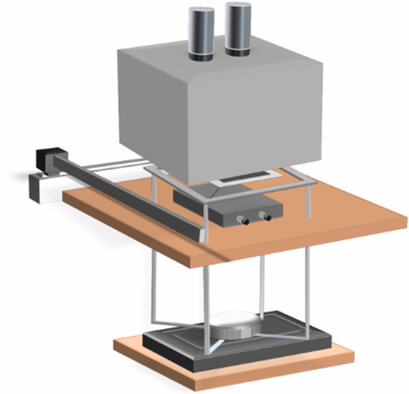
An experimental setup to measure the drying process of anodes for lithium-ion batteries in situ is introduced, using a combination of gravimetric and thermal measurements. Experiment is compared to simulation, showing good agreement, enabling the prediction of the drying process of battery electrodes under the knowledge of the drying conditions and the properties of the wet electrode.
Ternary Polymer Solar Cells Using Two Polymers P1 and P3 with Similar Chemical Structures and Nonfullerene Acceptor Attained Power Conversion Efficiency Over 15.5% with Low Energy Loss of 0.55 eV
- First Published: 09 December 2020
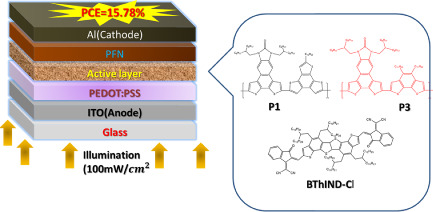
Ternary polymer solar cells using two polymers P1 and P3 with similar chemical structures and a nonfullerene acceptor are fabricated. The attained power conversion efficiency is over 15.5% with low energy loss of 0.55 eV, which is larger than that for binary counterparts processed under identical conditions.
Reduction of Dust Deposition on Solar Photovoltaic Cells by Self-Cleaning Coating: Experimental Study of Influencing Factors
- First Published: 21 December 2020
Dust deposition reduction on solar photovoltaic cells by superhydrophobic coating is investigated experimentally. Different influencing factors are considered to examine the performance of self-cleaning coating. Better self-cleaning performance can be found for larger tilt angle of solar cell, dry dust particles, and dust with higher Young's module.
Solid-State Reoxidation Kinetics of A/B-Site Substituted LaMnO3 During Solar Thermochemical CO2 Conversion
- First Published: 11 December 2020
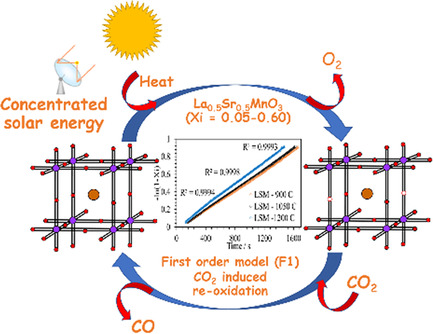
Solid-state kinetics of perovskite structured oxygen carriers for solar thermochemical CO2 splitting are found to be influenced both by the composition and the extent of conversion. A multistep mechanism with low or negative values of kinetic parameters exhibiting an anti-Arrhenius behavior is observed.
Plasma Synthesized Trilayered Rhodium−Platinum−Tin Oxide Nanostructures with Enhanced Tolerance to CO Poisoning and High Electroactivity for Ethanol Oxidation
- First Published: 11 December 2020
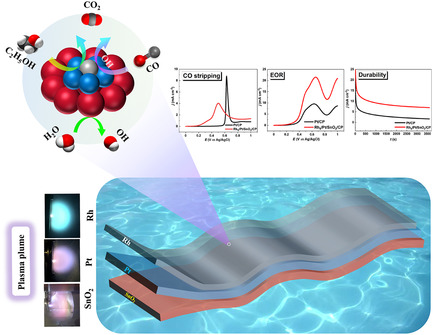
Herein, trilayered binderless nanostructured RhPtSnO2 is presented. The RhPtSnO2 electrocatalysts with different thicknesses of Rh are grown directly onto the carbon paper substrate at room temperature through pulsed laser deposition. These multilayered catalysts exhibit outstanding tolerance toward carbon monoxide poisoning and high electrocatalytic performance for ethanol oxidation reaction.
A Double-Deep Q-Network-Based Energy Management Strategy for Hybrid Electric Vehicles under Variable Driving Cycles
- First Published: 22 December 2020
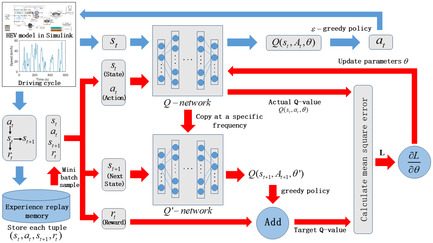
Herein, a double-deep Q-networks-based energy management strategy for hybrid electric vehicles is proposed. The distance traveled of driving cycle is introduced as states to enhance the adaptability of the algorithm. Two different neural networks are designed for action selection and target value calculation respectively to avoid overestimation in the process of model training.
Apples and Apples: A Shortcut Assessment Framework for Early-Stage Carbon Capture and Utilization Technologies Based on Efficiency, Feasibility, and Risk
- First Published: 24 November 2020
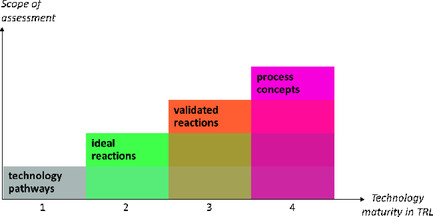
A shortcut assessment framework for early-stage carbon capture and utilization technologies is proposed, based on the perspectives of efficiency, feasibility, and risk (Efferi). The scope of the Efferi framework increases over technology maturity. The Efferi framework implements the Global CO2 Initiative's Guidelines, enables comparisons at different technology maturities, and systematically reduces subjective judgments.
Enhancement of Electron Collection and Light Trapping of Inclined GaN and AlGaN Nanowire Arrays
- First Published: 24 December 2020
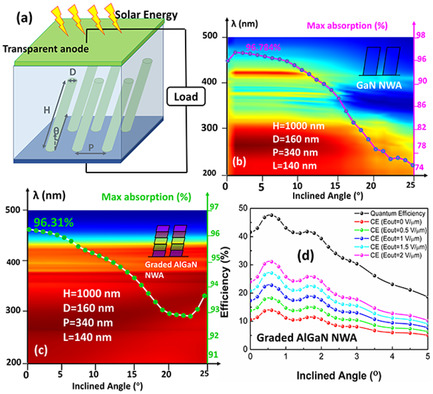
Optical absorption and photoemission of the inclined GaN and graded compositional AlxGa1−xN nanowire array (NWA) photocathode under external electric field are investigated. The inclined AlxGa1−xN NWA photocathode can obtain light absorption of 97%, quantum efficiency of 47.57%, and collection efficiency of 31.09%.
Carbon-Based Printable Perovskite Solar Cells with a Mesoporous TiO2 Electron Transporting Layer Derived from Metal–Organic Framework NH2-MIL-125
- First Published: 28 December 2020
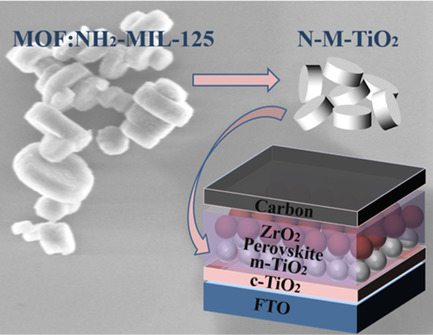
A novel mesoporous TiO2 nanocrystalline with pie morphology, large specific surface area (SSA), and outstanding wettability is successfully prepared by sintering the NH2-MIL-125. The TiO2 derived from NH2-MIL-125 possesses excellent penetration and crystallinity of perovskite in the electron transporting layer (ETL). Meanwhile, the power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) of the two perovskite solar cell (PSC) devices based on the as-prepared TiO2 are 13.49% and 12.55%.
A Design of Flexible Triboelectric Generator Integrated with High-Efficiency Energy Storage Unit
- First Published: 28 December 2020
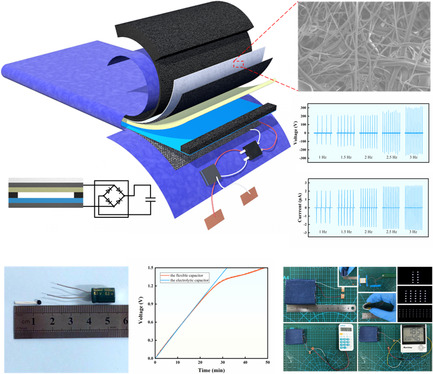
Herein, a design of flexible triboelectric generator integrated with high-efficiency energy storage unit is proposed. The polyvinylidene fluoride layer prepared by ectrospinning is added to improve output performance. The flexible solid-state capacitor made of chemical cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol)–H2SO4 hydrogel and activated carbon can make energy storage more efficient.
Thermodynamic Analysis of a Peak Shaving Power Station based on the Liquid Air Energy Storage System with the Utilization of Liquefied Natural Gas in the Liquefied Natural Gas Terminal
- First Published: 28 December 2020
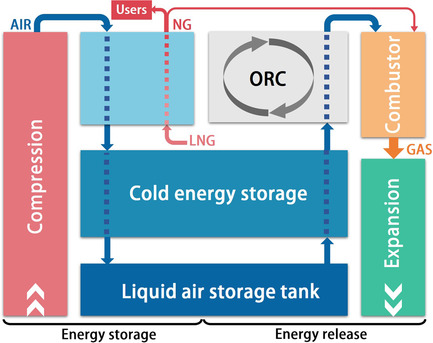
Herein, a large-power bidirectional peak shaving power station based on liquid air energy storage is proposed and the influence of the cold energy storage efficiency on the system is analyzed. Comparative analyses of four different systems are carried out. Furthermore, decoupling mechanism between the energy storage and release process with liquefied natural gas (LNG) cold energy is clarified.
Sulfur-Implanted Carbon Dots-Embedded Graphene as Ultrastable Anode for Li-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 23 December 2020
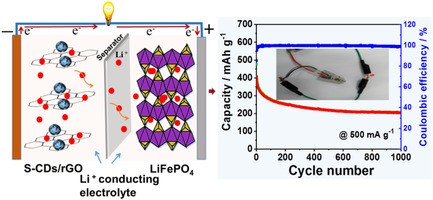
Sulfur-implanted carbon dots (S-CDs) improve the specific capacity and cycling stability of rGO as anode material for LIBs. Moreover, the full cell assembled with the prepared S-CDs/rGO as anode and commercial LiFePO4 as cathode exhibits good rate capabilities and excellent cycling performance (a low fading rate of 0.049% per cycle) in a voltage range of 1.5–3.9 V.
Embedded Growth of Li2O2 Achieved by a Rational Designed Three-Dimensional Fe2O3@CNS-CNTs Sandwich Structure for Improving the Performance of Li–O2 Batteries
- First Published: 19 December 2020
A Novel Receiver Design for Energy Packet-Based Dispatching
- First Published: 14 January 2021
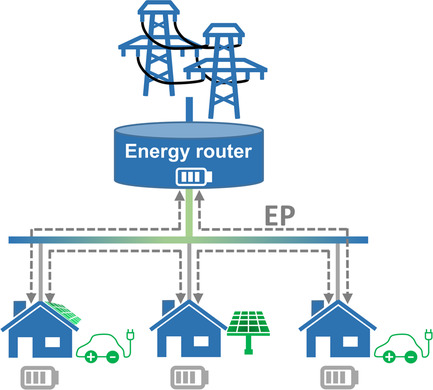
Packet-based energy dispatching has recently been introduced as an innovative solution to ensure the reliability of future electricity supply. However, the concepts presented so far assume a central synchronicity provision unit for energy packet (EP) dispatching. The present contribution focuses on a design of an EP receiver that recovers the required synchronicity information directly from the received signal itself.
Hydrogen-Bromine Redox-Flow Battery Cycling with Bromine Complexing Agent: on the Benefits of Nanoporous Separator Versus Proton Exchange Membrane
- First Published: 22 December 2020
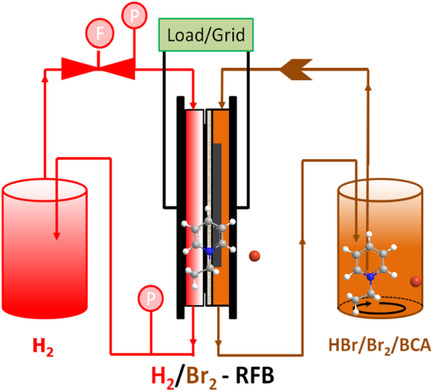
Bromine complexing agents (BCA) bring safety to electrochemical systems, in this case, a redox-flow hydrobromic acid (HBr) battery. It is demonstrated that BCA strongly interacts with perfluorinated sulfonic acid membranes and impedes the battery cycling; nanoporous separators are more tolerant and can offer a solution to safe and efficient HBr redox-flow batteries.
Research Articles
Optimization and Analysis of Minimizing Exergy Loss in Ironmaking System
- First Published: 19 December 2020

To obtain the minimum exergy loss, this study establishes an optimization model of the ironmaking system. Exergy loss minimum is taken as the optimization objective, and the material and energy system of ironmaking are optimized and analyzed. The optimization result shows that the minimum exergy loss of the ironmaking system is 4605.80 MJ t-HM−1.