Joint Special Issues on Perovskite Optoelectronics

Please find here a collection of contributions to the dual Special Issues on "Halide Perovskites for Optoelectronics Applications" published in Energy Technology and ChemSusChem following the symposium on this topic at the ICMAT 2017 Conference in Singapore (http://icmat2017.mrs.org.sg). Perovskite optoelectronics make up one of the most exciting topics in energy research today, and multidisciplinary collaborations are pushing to make a real impact on our not-too-distant energy future. The topics covered here include solar cell device characterization and engineering, fundamental physics and chemistry of perovskite materials, interface characterization and energy band engineering, solar cell device processing improvements, and perovskite light-emitting diode fabrication. Special thanks go to the symposium organizers for their efforts in coordinating these issues: Henk Bolink, Subodh G. Mhaisalkar, Damodaran Bahulayan, Tze Chien Sum, Anders Hagfeldt, and Connie Chang-Hasnain. On behalf of the editorial offices of both journals and these guest editors, we wish you happy reading!
Preface to Special Issue of Energy Technology on Perovskite Optoelectronics

Subodh G. Mhaisalkar*, Henk J. Bolink*
Optoelectronic arts: This Editorial introduces one of two companion Special Issues on “Halide Perovskites for Optoelectronics Applications” in Energy Technology and ChemSusChem following the ICMAT 2017 Conference in Singapore. More information on the companion Special Issue can be found in the Editorial published in ChemSusChem.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1731–1733 [Editorial]
Recent Advances in Metal Halide-Based Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes
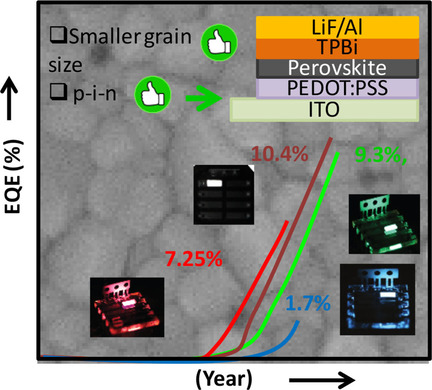
Naresh K. Kumawat, Dhritiman Gupta*, Dinesh Kabra*
Enlightening the perovskites: Recent developments of perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) based on metal-halide perovskite semiconductors are discussed with an emphasis on size of the crystallites and its consequence on optical properties, device architectures, and the corresponding PeLED performance parameters. A uniform pinhole-free morphology with small grain size is essential for high-performance PeLEDs The emerging technology of quasi-2D perovskites with high efficiency and stability is also highlighted along with the inorganic PeLEDs.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1734–1749 [Review]
Impact of Interfacial Layers in Perovskite Solar Cells
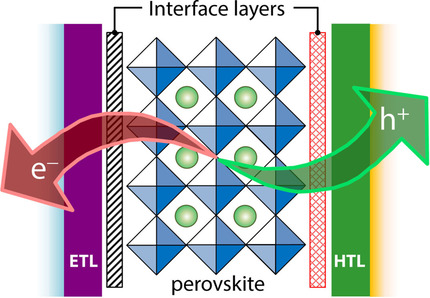
An-Na Cho, Nam-Gyu Park*
Upping the face: Interfacial engineering in perovskite solar cells is beneficial to improving photovoltaic performance because of the effective charge collection by changing the work function and/or dipole moment and reducing trapping states and recombination by improving electronic coupling through chemical binding. Bifunctional organic materials or nonstoichiometric approaches are effective methods to passivate grain boundaries of perovskite films.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3687–3704 [Review]
Application of Methylamine Gas in Fabricating Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Perovskite Solar Cells
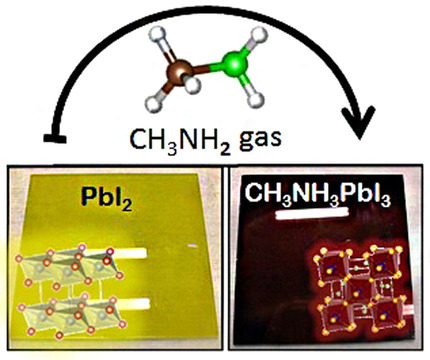
Sonia R. Raga, Yan Jiang, Luis K. Ono, Yabing Qi*
MAGIC, or methylamine gas-induced conversion of perovskite is a very versatile technique for solar-cell fabrication. It can rapidly form high-quality perovskite films by exposing lead halide precursors to methylamine gas and can improve the morphology and electrical properties of perovskite layers by short exposures. Ultra-smooth and pinhole-free films over large areas can be easily fabricated with methylamine gas.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1750–1761 [Review]
Polaronic Charge Carrier–Lattice Interactions in Lead Halide Perovskites
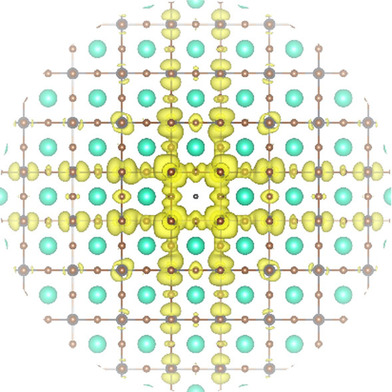
Christoph Wolf, Himchan Cho, Young-Hoon Kim, Tae-Woo Lee*
Shake it like a polaron: The importance of charge carrier–lattice interactions in lead-halide perovskites is reviewed under the aspect of efficient radiative charge-carrier recombination for light-emitting applications. The charge carriers at room temperature are accurately described by a Fröhlich polaron model leading to an exciton–polaron picture that is able to explain the temperature dependence of physical properties across a range of experiments.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3705–3711 [Minireview]
Effect of TiO2 Surface Treatment on the Current–Voltage Hysteresis of Planar-Structure Perovskite Solar Cells Prepared on Rough and Flat Fluorine-Doped Tin Oxide Substrates
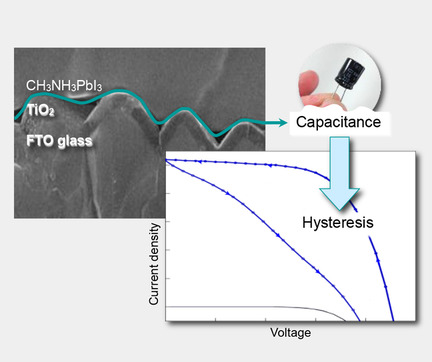
Ludmila Cojocaru*, Satoshi Uchida*, Piyankarage V. V. Jayaweera, Shoji Kaneko, Haibin Wang, Jotaro Nakazaki, Takaya Kubo, Hiroshi Segawa*
Rough or flat? The evolution of current–voltage hysteresis of perovskite solar cells and the effect of surface treatment (TiCl4 and vacuum ultraviolet radiation) of compact TiO2 layer prepared in two conductive substrates with specific two different roughness values is analyzed. The results reveal that the reduction in hysteresis observed after treatment is due to better contacts at the TiO2/CH3NH3PbI3 interface, which facilitates the electron transfer by suppressing traps or/and electron recombination.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1762–1766 [Communication]
Low-Dimensional Organic–Inorganic Halide Perovskite: Structure, Properties, and Applications
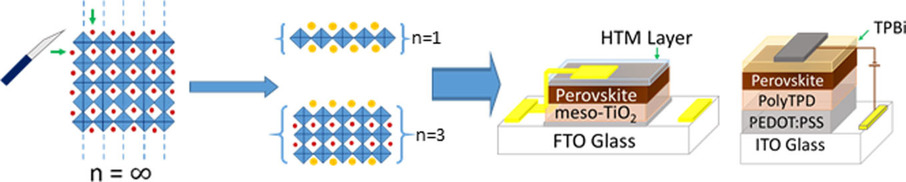
Ravi K. Misra, Bat-El Cohen, Lior Iagher, Lioz Etgar*
Peeling back the layers: The synthesis, properties, and structural orientation of low-dimensional perovskite are surveyed. Controlling the number of perovskite layers can provide a confined structure with chemical and physical properties that are different from those of 3 D perovskite. The use of low-dimensional perovskite in photovoltaic solar cells is discussed, as is its use in light-emitting diodes and photodetectors.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3712–3721 [Minireview]
Tunneling-Assisted Trapping as one of the Possible Mechanisms for the Origin of Hysteresis in Perovskite Solar Cells
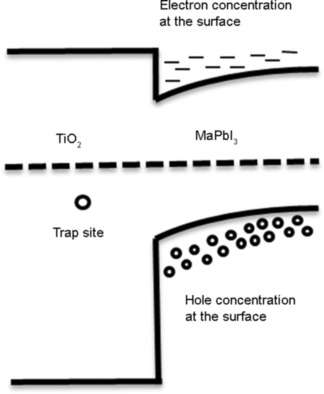
Samy Almosni, Ludmila Cojocaru, Debin Li, Satoshi Uchida*, Takaya Kubo, Hiroshi Segawa
Funny, these traps: In this paper, we have shown that by combining trapping in compact titanium oxide (c-TiO2) and recombination at the c-TiO2/methylammonium lead triiodide (MAPbI3) interface, the hysteresis phenomenon can be reproduced for parameters such as scan rate and voltage preset. These results suggest that tunnelling-assisted charge trapping combined with interface recombination could be at the origin of the hysteresis phenomenon.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1767–1774 [Full Paper]
Synthetic Manipulation of Hybrid Perovskite Systems in Search of New and Enhanced Functionalities
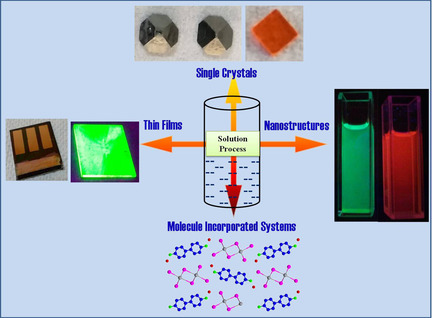
Rounak Naphade, Satyawan Nagane, Umesh Bansode, Mukta Tathavadekar, Aditya Sadhanala, Satishchandra Ogale*
The manipulation approach: We discuss the advances of synthetic manipulations of organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite-based systems, covering the areas of thin films, single crystals, and quantum nanostructures (0 D quantum dots, 1 D nanowires, nanorods). We also discuss the challenges and the opportunities in this rapidly evolving field.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3722–3739 [Minireview]
Secondary Hydrothermally Processed Engineered Titanium Dioxide Nanostructures for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells
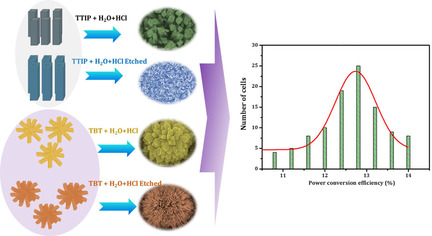
Sawanta S. Mali, Chang Su Shim, Hyungjin Kim, Chirayath A. Betty, Pramod S. Patil, Chang Kook Hong*
Flower power: A secondary hydrothermal process is used to synthesize hollow rutile TiO2 nanostructures for the electron-transport layer of perovskite solar cells. The prepared nanostructures are used in combination with methylammonium lead iodide, and their photovoltaic properties are studied. The core–shell architecture of a perovskite enveloped by TiO2 provides an enhanced surface area, better contact with the perovskite, and effective light penetration.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1775–1787 [Full Paper]
Factors Influencing the Mechanical Properties of Formamidinium Lead Halides and Related Hybrid Perovskites
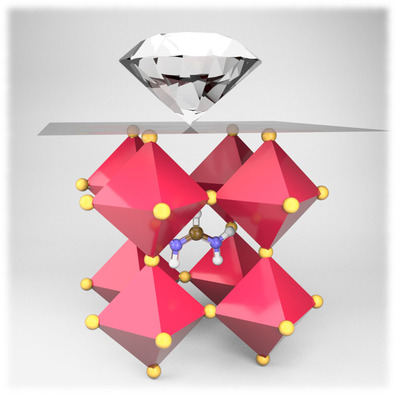
Shijing Sun, Furkan H. Isikgor, Zeyu Deng, Fengxia Wei, Gregor Kieslich, Paul D. Bristowe, Jianyong Ouyang, Anthony K. Cheetham*
Hard or soft? Nanoindentation on single crystals of FAPbX3 (X=Br or I) is used to study the mechanical properties of formamidinium lead halide perovskites. The effects of hydrogen bonding are evaluated by ab initio molecular dynamics and calculating radial distribution functions.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3740–3745 [Communication]
Thiophene–Arylamine Hole-Transporting Materials in Perovskite Solar Cells: Substitution Position Effect
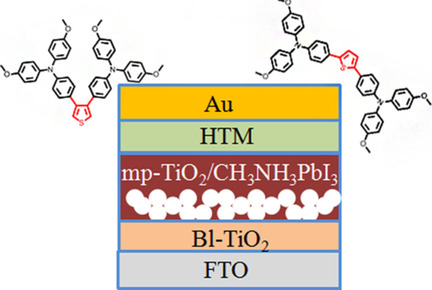
Xuepeng Liu, Fantai Kong*, Rahim Ghadari, Shengli Jin, Wangchao Chen, Ting Yu, Tasawar Hayat, Ahmed Alsaedi, Fuling Guo, Zhan'ao Tan, Jian Chen, Songyuan Dai*
Right move: Two new hole-transporting materials (HTMs) with substituents in different positions are investigated. The 2,5-substituent shows significantly better performance than that of the 3,4-substituent in a perovskite solar cell; the former is comparable to that of 2,2′,7,7′-tetrakis(N,N-di-p-methoxyphenylamine)-9,9′-spirobifluorene (spiro-OMeTAD).
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1788–1794 [Full Paper]
CsPb2Br5 Single Crystals: Synthesis and Characterization
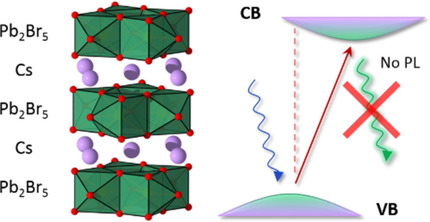
Ibrahim Dursun, Michele De Bastiani, Bekir Turedi, Badriah Alamer, Aleksander Shkurenko, Jun Yin, Ahmed M. El-Zohry, Issam Gereige, Ahmed AlSaggaf, Omar F. Mohammed, Mohamed Eddaoudi, Osman M. Bakr*
The antisolvent paradox: Ternary halogen-plumbate compounds like CsPb2Br5 are capturing the attention of the optoelectronic community. However, fundamental knowledge of their intrinsic properties is still missing. Here, we present the synthesis of CsPb2Br5 single crystals by an antisolvent-vapor crystallization method and their characterization.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3746–3749 [Communication]
Silicon-Based Inorganic–Organic Hybrid Nanocomposites for Optoelectronic Applications
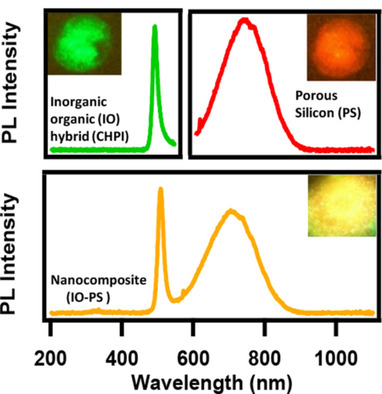
Pawan K. Kanaujia, Ajay Singh, G. Vijaya Prakash*
The combination makes the difference: Nanocomposites consisting of porous silicon and an inorganic-organic hybrid perovskite are prepared using a simple three-step electrochemical method. The nanocomposite shows photoluminescence (PL) in the orange–yellow range, which is the average of its constituents (red for silicon and green for the perovskite). Thus, by carefully selecting each component, the emitted light can be fine-tuned.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1795–1799 [Full Paper]
Plasmonic Gold Nanostars Incorporated into High-Efficiency Perovskite Solar Cells

Munkhbayar Batmunkh, Thomas J. Macdonald, William J. Peveler, Abdulaziz S. R. Bati, Claire J. Carmalt, Ivan P. Parkin, Joseph G. Shapter*
Golden star: Plasmonic gold nanostars are incorporated into mesoporous TiO2 photoelectrodes to fabricate high efficiency perovskite solar cells. A power conversion efficiency of 17.72 % is achieved using TiO2-AuNSs photoelectrode-based device.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3750–3753 [Communication]
Towards All-Inorganic Transport Layers for Wide-Band-Gap Formamidinium Lead Bromide-Based Planar Photovoltaics

Anand S. Subbiah, Neha Mahuli, Sumanshu Agarwal, Maikel F. A. M. van Hest, Shaibal K. Sarkar*
On inorganic grounds: Photovoltaic devices utilizing a perovskite absorber based on large-band-gap formamidinium lead bromide (FAPbBr3) are fabricated by using inorganic charge-transport layers in a planar architecture. Nickel oxide prepared by atomic layer deposition and sputtered zinc oxide are used as hole- and electron-transport layers, respectively. The use of stable oxide-based transport layers improves the performance of the FAPbBr3 device in comparison to its organic counter parts.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1800–1806 [Full Paper]
Photovoltaic Rudorffites: Lead-Free Silver Bismuth Halides Alternative to Hybrid Lead Halide Perovskites
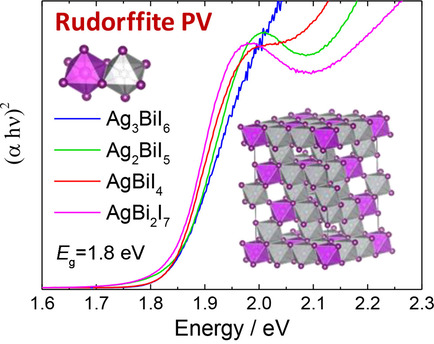
Ivan Turkevych*, Said Kazaoui, Eisuke Ito, Toshiyuki Urano, Koji Yamada, Hiroshi Tomiyasu, Hideo Yamagishi, Michio Kondo, Shinji Aramaki
Move over perovskite: Optoelectronic properties of several highly stable silver iodobismuthates with rudorffite structure reveal them as alternative nontoxic and solution-processable photovoltaic materials that feature direct band gaps of around 1.8 eV. The proof-of-concept solar cell with FTO/c-m-TiO2/Ag3BiI6/PTAA/Au (c: compact; m: mesoporous; PTAA: poly[bis(4-phenyl)(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)amine]) architecture shows a promising power conversion efficiency of 4.3 %.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3754–3759 [Communication]
One-step Solution-Processed Formamidinium Lead Tribromide Formation for Better Reproducible Planar Perovskite Solar Cells
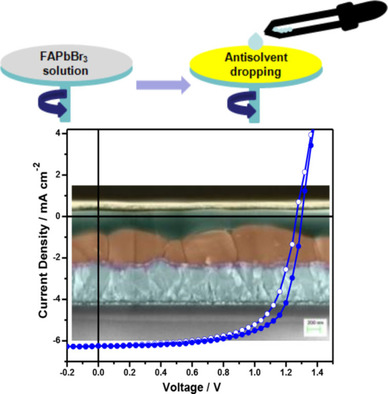
Jaykrushna Das, Anand S. Subbiah, Neha Mahuli, Roja Singh, Shaibal K. Sarkar*
Magic of antisolvent: A single-step method for the preparation of regular planar solar cells based on formamidinium lead tribromide (FAPbBr3) is demonstrated by performing an antisolvent-assisted crystallization process. This results in a considerably improved film quality of the perovskite layer in terms of uniformity, coverage, crystallinity, and light absorption, which gives rise to improved photovoltaic performance with better reproducibility compared to conventional one-step process.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1807–1813 [Full Paper]
Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers Increase the Stability of Methylammonium Lead Iodide Perovskite Against Light and Oxygen
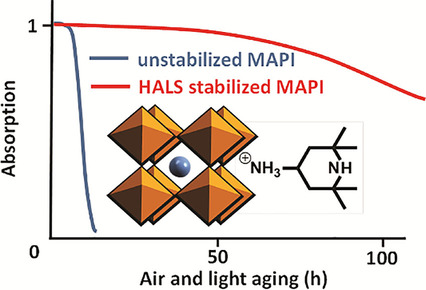
Nevena Marinova*, Marius Franckevičius*, Ieva Matulaitienė, Andrius Devižis, Gediminas Niaura, Vidmantas Gulbinas, Juan Luis Delgado*
Hindered reasons: A hindered amine light stabilizer (HALS) exerts a stabilization effect methylammonium lead iodide perovskite (MAPI), a promising material for photovoltaic devices, against photooxidation. The incorporation of HALS in MAPI films significantly extends their resistivity against photodegradation in ambient air, while causing no significant changes in key properties.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3760–3764 [Communication]
Addition of Lithium Iodide into Precursor Solution for Enhancing the Photovoltaic Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells
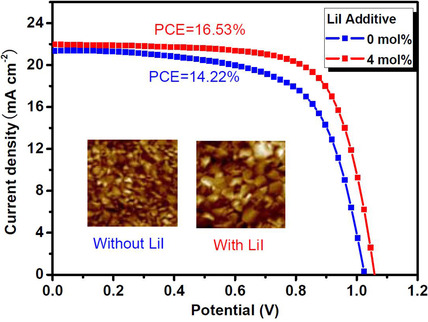
Hui Luo, Jihuai Wu*, Quanzhen Liu, Jianling Huang, Yongguang Tu, Jianming Lin, Miaoliang Huang
Into the Mix: Lithium iodide is introduced as an additive to the perovskite precursor solution. The addition effects the crystal growth of perovskite film, giving rise to increased crystallinity, which improves the quality and conductivity of the perovskite film and speeds up the charge transport in the device. The perovskite solar cell utilizing LiI gives rise to a power conversion efficiency that is considerably higher than a device based on a perovskite without added LiI.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1814–1819 [Full Paper]
Broadband-Emitting 2 D Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Perovskite Based on Cyclohexane-bis(methylamonium) Cation
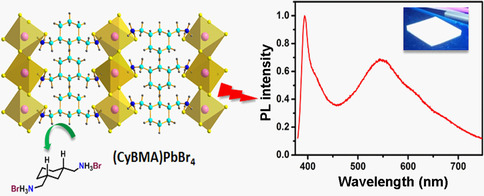
Ishita Neogi, Annalisa Bruno*, Damodaran Bahulayan, Teck Wee Goh, Biplab Ghosh, Rakesh Ganguly, Daniele Cortecchia, Tze Chien Sum, Cesare Soci, Nripan Mathews*, Subodh Gautam Mhaisalkar*
Cis or trans? A new 2 D hybrid perovskite ((CyBMA)PbBr4) based on highly flexible cis-1,3-bis(methylaminohydrobromide)cyclohexane (CyBMABr) core presenting a broad emission spanning from 380 to 750 nm is presented here. Its design, synthesis, and photophysical properties are investigated, highlighting the effects of stereoisomerism of the templating cation on the formation and properties of the resulting perovskite.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3765–3772 [Full Paper]
Tuning the Fermi Level of TiO2 Electron Transport Layer through Europium Doping for Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells
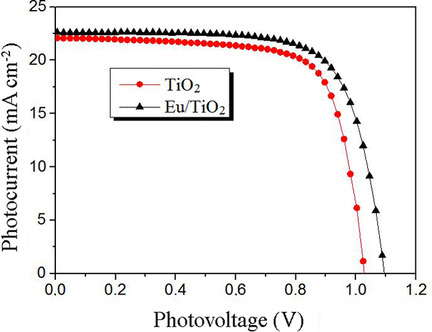
Zhe Xu, Jihuai Wu*, Tongyue Wu, Quanlin Bao, Xin He, Zhang Lan, Jianming Lin, Miaoliang Huang, Yunfang Huang, Leqin Fan
Europia′s best achievement: A mesoporous TiO2 layer is doped with the rare-earth ion Eu3+ to tune the Fermi level and improve charge transportation in the layer. A perovskite solar cell based on the Eu3+-doped TiO2 electron-transport layer achieves a power conversion efficiency of 17.90 % whereas the device based on pure-TiO2 electron-transport layer has an efficiency of 15.85 % under the same conditions.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1820–1826 [Full Paper]
High Efficiency MAPbI3 Perovskite Solar Cell Using a Pure Thin Film of Polyoxometalate as Scaffold Layer
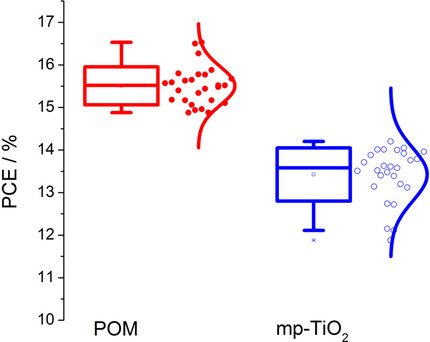
Mohammad Khaledi Sardashti, Mahmoud Zendehdel*, Narges Yaghoobi Nia, Davud Karimian, Mohammad Sheikhi
Pure POM: A high-efficiency MAPbI3 perovskite solar cell is fabricated with a pure layer of [SiW11O39]8− polyoxomethalate (POM) structure as a thin-film scaffold layer. A smooth nanoporous surface of POM causes outstanding improvement of the photocurrent density, external quantum efficiency, and overall power conversion efficiency (PCE).
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3773–3779 [Full Paper]
Identifying the Cause of Voltage and Fill Factor Losses in Perovskite Solar Cells by Using Luminescence Measurements

Nandi Wu*, Yiliang Wu, Daniel Walter, Heping Shen, The Duong, Dale Grant, Chog Barugkin, Xiao Fu, Jun Peng, Thomas White, Kylie Catchpole, Klaus Weber
Characterizing loss: Luminescence-based techniques reveal that high band gap solar cells, such as perovskite, can have a reduced open-circuit voltage and fill factor (FF) due carrier transport limitations within the cell, especially at interfaces. By reconstructing current–voltage curves without limiting transport layers, the contributions of recombination, series resistance, and shunt resistance in the cell can be determined.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1827–1835 [Full Paper]
Diphenyl-2-pyridylamine-Substituted Porphyrins as Hole-Transporting Materials for Perovskite Solar Cells
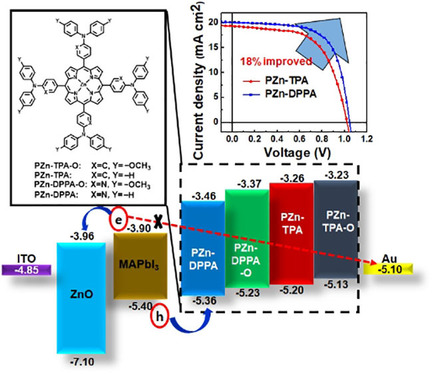
Un-Hak Lee, Randi Azmi, Septy Sinaga, Sunbin Hwang, Seung Hun Eom, Tae-Wook Kim, Sung Cheol Yoon*, Sung-Yeon Jang*, In Hwan Jung*
A hole new world: A series of porphyrin-based hole-transporting materials (HTMs) has been developed for low-temperature perovskite solar cells (PSCs). Diphenyl-2-pyridylamine (DPPA)-substituted porphyrin HTM provides high hole mobility and well-matched energy levels with MAPbI3 perovskite active layers, which improve the charge-extraction properties of PSCs, demonstrating performances comparable to those of spiro-OMeTAD-based devices.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3780–3787 [Full Paper]
Efficient and Stable Inverted Planar Perovskite Solar Cells Employing CuI as Hole-Transporting Layer Prepared by Solid–Gas Transformation
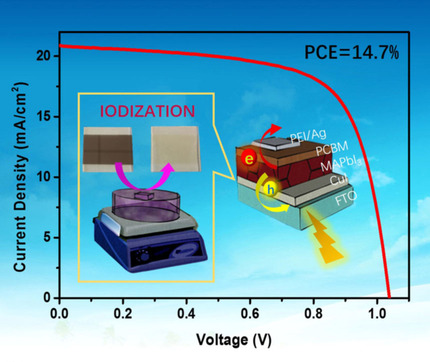
Haoxin Wang, Ze Yu*, Xiao Jiang, Jiajia Li, Bin Cai, Xichuan Yang*, Licheng Sun
Copperfinger and Iodine: Herein, we adopt a simple solid–gas reaction method to fabricate a uniform CuI film by exposing a thermally evaporated copper film to iodine vapor and apply it as a hole-transporting layer (HTL) in inverted planar perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The best device displays a promising power conversion efficiency (PCE) together with good air stability.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1836–1843 [Full Paper]
High Photoluminescence Quantum Yields in Organic Semiconductor–Perovskite Composite Thin Films
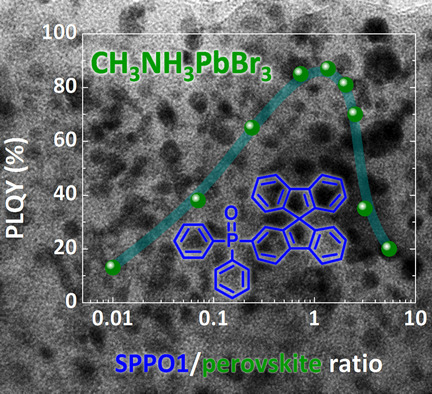
Giulia Longo, Maria-Grazia La-Placa, Michele Sessolo*, Henk J. Bolink
LED-ing by example: Highly luminescent, solution-processed perovskite–organic semiconductor composite thin films were developed. By tuning the relative concentration of the components, photoluminescent quantum yields as high as 85 % were obtained. This opens new avenues for the preparation of simple perovskite LEDs.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3788–3793 [Full Paper]
Interface Engineering of electron Transport Layer-Free Planar Perovskite Solar Cells with Efficiency Exceeding 15 %
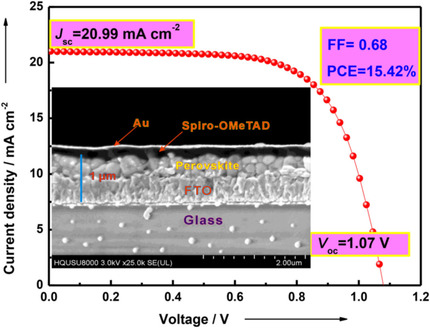
Feiyue Huang, Yuelin Wei*, Lin Gu, Qiyao Guo, Hui Xu, Dan Luo, Shao Jin, Xiaomin Yang, Yunfang Huang*, Jihuai Wu
Direct growth: We present excellent performing electron selective layer (ESL)-free perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The perovskite films with high electronic quality are directly grown on fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) substrates, which are pretreated by ultraviolet–ozone and plasma cleaning. The ESL-free PSCs based on the FTO substrates with plasma-cleaning pretreatment achieve the best photovoltaic performance.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1844–1851 [Full Paper]
Effects of Self-Assembled Monolayer Modification of Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles Layer on the Performance and Application of Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells

Qin Wang, Chu-Chen Chueh, Ting Zhao, Jiaqi Cheng, Morteza Eslamian*, Wallace C. H. Choy, Alex K.-Y. Jen*
Engineered layers: Low-temperature solution-processed NiOx nanoparticle film is usually accompanied with defect formation. Here, we find that 4-bromobenzoic acid can form a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) on the NiOx film and effectively tune the interfacial properties, resulting in high perovskite solar cells (PSCs) efficiency. Also, we incorporate the above-mentioned SAM into flexible PSCs
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3794–3803 [Full Paper]
Quinoidal 2,2′,6,6′-Tetraphenyl-Dipyranylidene as a Dopant-Free Hole-Transport Material for Stable and Cost-Effective Perovskite Solar Cells
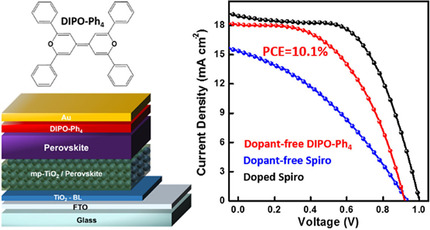
Chao Shen, Marc Courté, Anurag Krishna, Shasha Tang, Denis Fichou*
Small, but smart: In this manuscript, the use of a new hole-transport material, namely 2,2′,6,6′-tetraphenyl-dipyranylidene (DIPO-Ph4), in perovskite solar cells (PSC) is reported. This quinoidal π-conjugated heterocycle is a simple molecule, easy-to-synthetize and inexpensive, and possesses all required electronic properties to perfectly fit a PSC as a hole-transport material.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1852–1858 [Full Paper]
Effect of Formamidinium/Cesium Substitution and PbI2 on the Long-Term Stability of Triple-Cation Perovskites
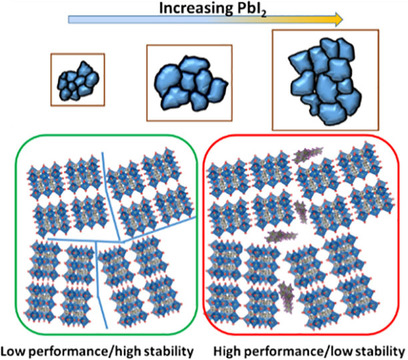
Shashwat Shukla, Sudhanshu Shukla, Lew Jia Haur, Sai S. H. Dintakurti, Guifang Han, Anish Priyadarshi, Tom Baikie, Subodh G. Mhaisalkar*, Nripan Mathews*
Addition and multiple cations: In triple-cation mixed-halide perovskite films, the addition of excess PbI2 is known to benefit the performance, but its impact on the degradation kinetics of the perovskite is less well known. In this study, the amount of PbI2 in the triple-cation perovskite films is varied and the degradation kinetics monitored. The inclusion of excess PbI2 adversely affects the stability of the material but also leads to enhanced grain sizes and better optical absorption.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3804–3809 [Full Paper]
Enhanced Coverage of All-Inorganic Perovskite CsPbBr3 through Sequential Deposition for Green Light-Emitting Diodes
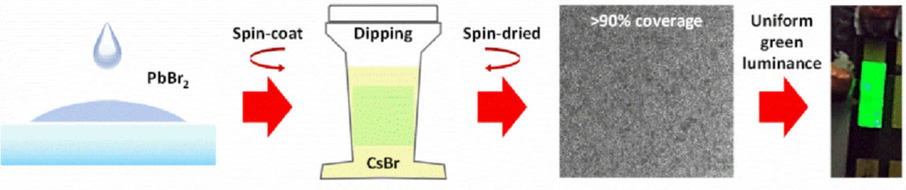
Yan Fong Ng, Wei Jian Neo, Nur Fadilah Jamaludin, Natalia Yantara, Subodh Mhaisalkar, Nripan Mathews*
It′s good to be green: Cesium-based halide perovskites are attracting heavy interest due to their thermal stability in optoelectronic applications (e.g., light-emitting diodes). However, film coverage issues with single-step spin-coating can lead to leakage losses in device operation. Here, we report the use of a sequential deposition process to boost the perovskite film coverage up to more than 90 %, with proof-of-concept devices showing bright green emission.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1859–1865 [Full Paper]
Al2O3 Underlayer Prepared by Atomic Layer Deposition for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells
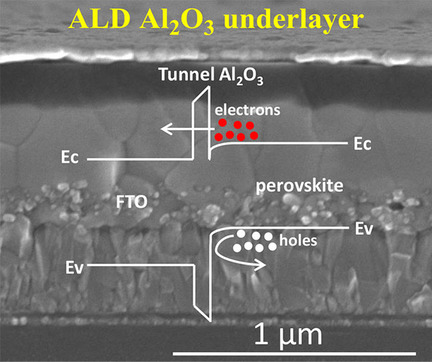
Jinbao Zhang, Adam Hultqvist, Tian Zhang, Liangcong Jiang, Changqing Ruan, Li Yang, Yibing Cheng, Marika Edoff*, Erik M. J. Johansson*
Tunneling through the underlayer! Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is used to prepare a compact Al2O3 underlayer for perovskite solar cells. The thickness of the Al2O3 layer can be controlled well by adjusting the deposition cycles during the ALD process. The Al2O3 layer can effectively block electron recombination at the perovskite/fluorine-doped tin oxide interface and can sufficiently transport the electrons through tunneling.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3810–3817 [Full Paper]
Simplified Architecture of a Fully Printable Perovskite Solar Cell Using a Thick Zirconia Layer
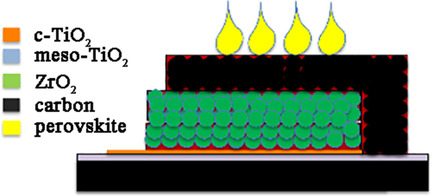
Anish Priyadarshi, Amna Bashir, Johana T. Gunawan, Lew J. Haur, Annalisa Bruno, Zareen Akhter, Nripan Mathews*, Subodh G. Mhaisalkar*
In print: A fully printable, hole-conductor-free perovskite solar cell (PSC) with a simple and low-cost fabrication route and high stability is well placed for commercialization. We aim to simplify the fabrication process of these solar cells by replacing the mesoporous TiO2 layer with a thick ZrO2 layer.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1866–1872 [Full Paper]
Modulating Excitonic Recombination Effects through One-Step Synthesis of Perovskite Nanoparticles for Light-Emitting Diodes
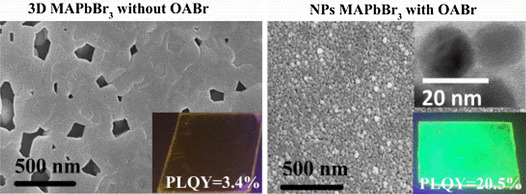
Sneha A. Kulkarni, Subas Muduli, Guichuan Xing, Natalia Yantara, Mingjie Li, Shi Chen, Tze Chien Sum, Nripan Mathews*, Tim J. White, Subodh G. Mhaisalkar*
I′m so excitonic! A process to form MAPbBr3 perovskite nanoparticle (NP) films formation directly on substrate surface through one-step in situ deposition method is described, avoiding the pitfalls of forming thin films from preformed NPs. Partial substitution of the MABr with OABr regulates the NP growth rate. The NPs film is highly luminescent (photoluminescence quantum yield=20.4 %) and displays an excitonic emission signature.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3818–3824 [Full Paper]
Regulated Film Quality with Methylammonium Bromide Addition in a Two-Step Sequential Deposition to Improve the Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells
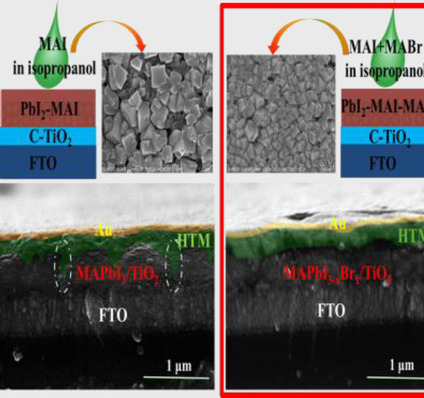
Guohua Dong, Debin Xia, Yulin Yang*, Li Sheng, Ruiqing Fan*, Lele Qiu
Fantastic films: The perovskite film quality, optical properties, and corresponding perovskite solar cells performance can be improved substantially by the suitable addition of methylammonium bromide (MABr) into the methylammonium iodide (MAI) solution in isopropanol with a two-step sequential deposition route.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1873–1879 [Full Paper]
Low-Cost Perovskite Solar Cells Employing Dimethoxydiphenylamine-Substituted Bistricyclic Aromatic Enes as Hole Transport Materials
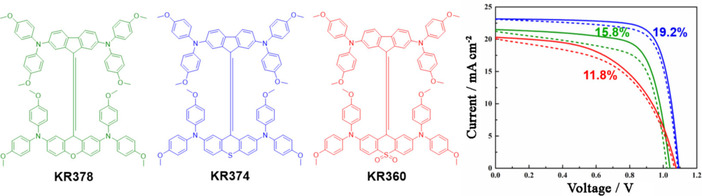
Kasparas Rakstys, Sanghyun Paek, Giulia Grancini, Peng Gao, Vygintas Jankauskas, Abdullah M. Asiri, Mohammad Khaja Nazeeruddin*
Bridge to success: We report the synthesis of three new hole transport materials (HTMs) using a cost-effective procedure and the impact of different atoms in heteromerous bistricyclic aromatic ene scaffolds. S-bridged KR374 shows a a significantly improved hole-drift mobility leading to enhanced photovoltaic performance in mixed-ion perovskite solar cells and reduced hysteresis owing to the improved interface between the perovskite and HTM caused by stronger Pb–S interaction.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3825–3832 [Full Paper]
Effect of Excess PbI2 in Fully Printable Carbon-based Perovskite Solar Cells
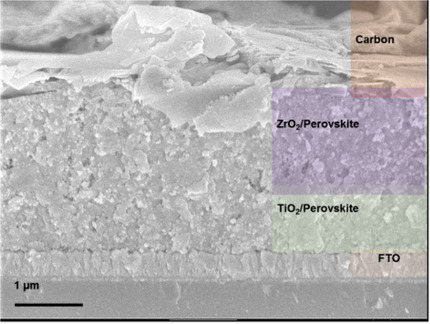
Vishakha Kapoor, Amna Bashir, Lew J. Haur, Annalisa Bruno, Sudhanshu Shukla, Anish Priyadarshi*, Nripan Mathews, Subodh Mhaisalkar*
PbI2 INXS: The effect of having excess PbI2 in fully printable carbon-based perovskite solar cells is studied with excess amounts of PbI2 ranging from 0 % to 15 % added to the equimolar perovskite solution for use in the solar cell. The device containing 15 % excess PbI2 shows degradation under continuous illumination, whereas there is no degradation with an equimolar ratio of perovskite precursors.
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1880–1886 [Full Paper]
Replacement of Biphenyl by Bipyridine Enabling Powerful Hole Transport Materials for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells
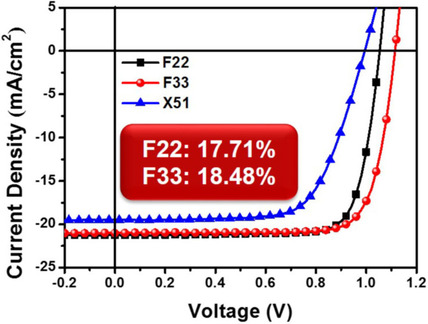
Fei Wu, Yahan Shan, Jianhui Qiao, Cheng Zhong, Rui Wang, Qunliang Song*, Linna Zhu*
Bip, bip: Bipyridine is introduced for the first time as the core structure for new hole transport materials (HTMs). Remarkable power conversion efficiencies of 17.71 and 18.48 % are achieved in conventional planar perovskite (CH3NH3PbI3−xClx) solar cells by using the newly devised HTMs.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3833–3838 [Full Paper]
CH3NH3Br Additive for Enhanced Photovoltaic Performance and Air Stability of Planar Perovskite Solar Cells prepared by Two-Step Dipping Method
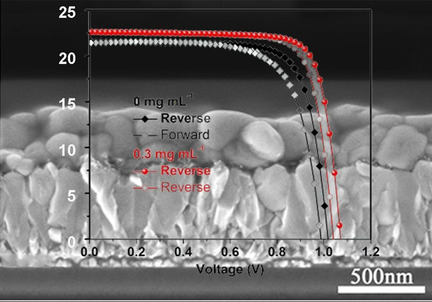
Lei Zhang*, Xuezhen Zhang, Xiaoxia Xu, Jie Tang, Jihuai Wu, Zhang Lan*
Two-step dipping: We report a facile CH3NH3Br (MABr) additive route to achieve both high power conversion efficiency (PCE) and good long-term stability of the devices by the typical two-step dipping method. The application of MABr additive can greatly improve the quality of perovskite film, enhance electron transport rate, suppress recombineation and finally improve photovoltaic performance. The best-performance device achieves an average PCE of 18.61 % (by forward and reverse scans).
Energy Technology 2017, 5, No. 10, 1887–1894 [Full Paper]
Molecular Self-Assembly Fabrication and Carrier Dynamics of Stable and Efficient CH3NH3Pb(1−x)SnxI3 Perovskite Solar Cells
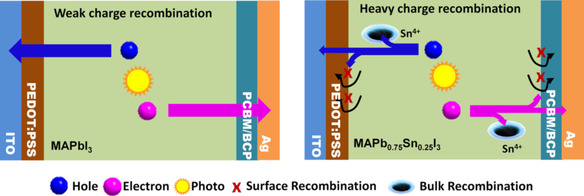
Jiandong Fan*, Chong Liu, Hongliang Li, Cuiling Zhang, Wenzhe Li*, Yaohua Mai*
Toward lead-free: We employ a molecular self-assembly approach to obtain a series CH3NH3Pb(1−x)SnxI3 (0≤x≤1) perovskite with high stability and efficiency. The reasons that limit its further efficiency improvement are provided by means of studying the carrier dynamics in the device.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3839–3845 [Full Paper]
Towards Extending Solar Cell Lifetimes: Addition of a Fluorous Cation to Triple Cation-Based Perovskite Films
Manuel Salado, M. Asunción Fernández, Juan P. Holgado, Samrana Kazim, Mohammad Khaja Nazeeruddin, Paul J. Dyson, Shahzada Ahmad*
The fast and the fluorous: The addition of a fluorous-functionalized imidazolium cation during the preparation of triple cation-based perovskite Cs0.05(MA0.15FA0.85)0.95Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3 has been shown to influence its stability. The resulting materials display prolonged tolerance to atmospheric humidity (>100 days) along with power conversion efficiencies exceeding 16 %.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3846–3853 [Full Paper]
High-Efficiency Perovskite Solar Cell Based on Poly(3-Hexylthiophene): Influence of Molecular Weight and Mesoscopic Scaffold Layer
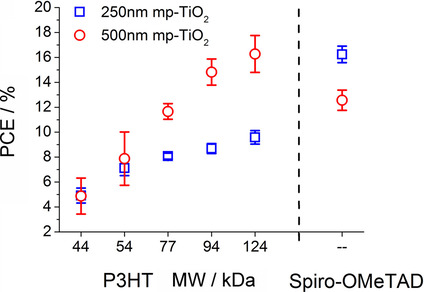
Narges Yaghoobi Nia, Fabio Matteocci, Lucio Cina, Aldo Di Carlo*
Molecular weight matters! High efficiency perovskite solar cells fabricated in ambient conditions by controlling of mesoporous (mp)-TiO2 thickness and investigation of poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT) molecular weight (MW) as hole-transport layer. The best efficiencies are achieved for a MW of 124 kDa and for a thickness of mp-TiO2 of 500 nm. Efficiency enhancement is mainly related to the increase of Jsc and FF as P3HT MW increases.
ChemSusChem 2017, 10, No. 19, 3854–3860 [Full Paper]




