Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Issue Information
Review
Organic and Inorganic Photoactive Absorbers for Wavelength-Selective Transparent Photovoltaic Devices: Focus Review
- First Published: 06 September 2024
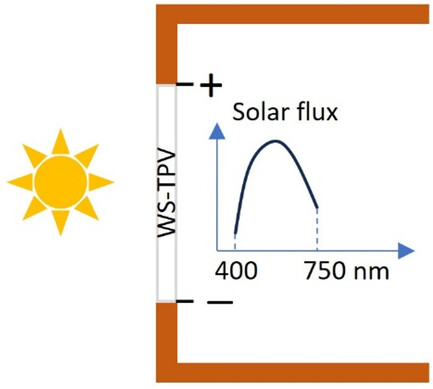
The current state of wavelength-selective transparent solar cells is reviewed. IR-selective devices based on organic bulk heterojunctions have demonstrated >60% transparency. The color rendering limitation of transmitted light can be addressed by an asymmetric block copolymer molecular design. UV-selective devices have high transparency and stability. However, power conversion efficiency and power output need further improvement.
Single-Crystal Perovskite Halide: Crystal Growth to Devices Applications
- First Published: 03 October 2024
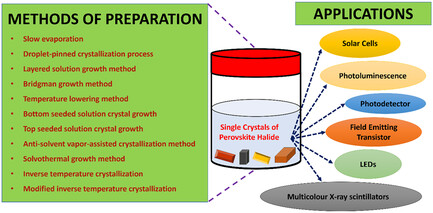
Advanced crystal growth techniques enable the production of high-quality perovskite single crystals with exceptional properties. These crystals exhibit tailored stoichiometry, crystal phases, and morphologies, facilitated by variations in halide composition. The absence of grain boundaries in perovskite single crystals significantly enhances their stability and reduces carrier trap density. This, in turn, leads to longer carrier diffusion lengths, making them ideal candidates for a wide range of multifunctional electronic applications. The perovskite halide structure serves as a crucial link between crystallization methods and device performance. By understanding the relationship between crystal growth techniques and the resulting material properties, researchers can continue to push the boundaries of energy conversion, light emission, and electronic device capabilities.
Recent Advances in Desiccant Materials for Energy-Efficient and Sustainable Heat Transfer Systems
- First Published: 25 October 2024
Research Article
Assessment of Ecofriendly Zeotropic Working Fluids in Organic Rankine Cycle for Renewable Energy Harvesting
- First Published: 19 May 2024
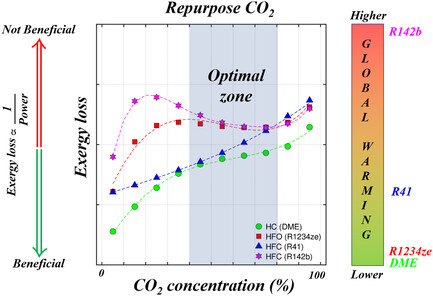
Organic Rankine thermodynamic cycle is best suited for utilizing renewable energy. The choice of working fluid has a great influence on the environmental impact and sustainability. Often, alternative working fluids are assessed solely based on thermodynamic performance. Herein, a holistic approach focusing on exergy, economics, environmental impact, and sustainability is performed, and the results favor ecofriendly working fluids.
Study of Budding Snubber Quality Deterioration in Solid Oxide Fuel Cell-Fed Inverter Used in Microgrid Energy Conversion
- First Published: 05 July 2024
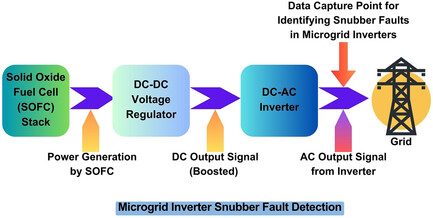
The article addresses the critical issue of snubber quality deterioration in microgrid inverters. It presents a nascent snubber resistance fault (NSF) detection technique for solid oxide fuel cell-powered three-phase inverters in microgrids. Using the fast Fourier transform, the study analyzes the inverter output current signal to detect faults, proposing an algorithm for effective NSF detection and presenting a comparative analysis.
Flexible Nanocarbon Electrodes for Holistically Engineered Solar Cell and Battery Integrated Piezoresistive Sensor
- First Published: 21 August 2024
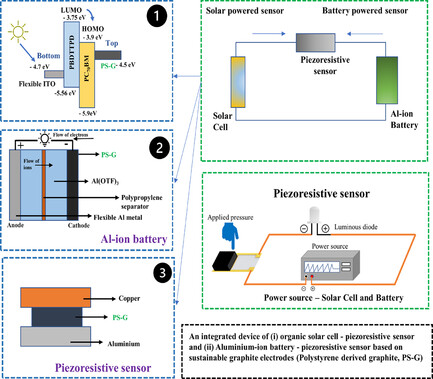
An integrated system of solar cell and battery-powered piezoresistive sensors using flexible polystyrene-derived graphite (PS-G) electrodes is developed. Components include a solar cell (indium tin oxide and PS-G electrodes), an Al-ion battery (aluminum foil and PS-G electrodes), and a piezoresistive sensor (PS-G and copper electrodes). This system leverages sustainable PS-G electrodes for integrated energy harvesting, storage, and sensing.
Substrate and Step Rate Dependence Electrodeposition of Nickel–Cobalt–Molybdenum–Phosphorous Alloy for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 22 October 2024
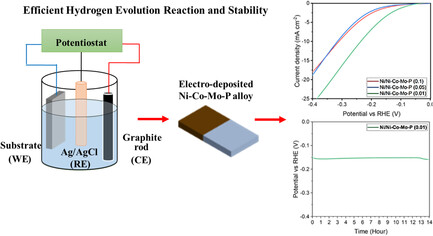
Electrodeposited microcrystalline nickel–cobalt–molybdenum–phosphorous (Ni–Co–Mo–P) alloys grown on nickel sheets and copper sheets have shown efficient catalytic properties for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in an alkaline medium. The deposited quaternary alloy exhibits the lowest overpotential of −163 mV at 10 mA cm−2 for copper substrate with a Tafel slope of 154 mV dec−1 and their inherent stability is also recorded.
A Self-Powered and Self-Absorbing Wireless Sensor Node for Smart Grid
- First Published: 19 November 2024
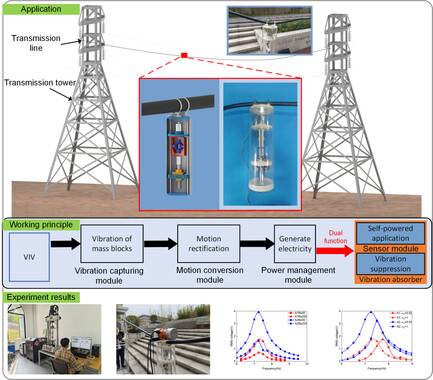
This article introduces a dual-functional energy harvester to harvest vibration energy and achieve vibration suppression for the transmission line. An innovative mechanism combining the vibration system and mechanical rectification mechanism is proposed. The experiments show that the prototype can generate a maximum of 183.96 mW and provides enough power for the wireless sensor module to continuously return the environmental data.
Review
Review on Synthesis Methods of Carbon Nanotubes as Activated Carbon Composites Based on Biomass for Supercapacitors in Electric Vehicles
- First Published: 05 September 2024
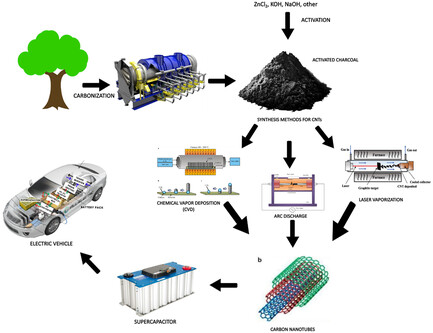
This work reviews various methods to synthesize carbon nanotubes and analyzes the best methods to produce composites for supercapacitors for electric vehicles. Chemical vapor deposition is found to be the best method because the produced CNTs can be used directly without purification unless the catalyst particles need to be removed. However, further studies are required to determine the optimal conditions.
Research Article
Evolving Thermal Energy Storage Using Hybrid Nanoparticle: An Experimental Investigation on Salt Hydrate Phase Change Materials for Greener Future
- First Published: 14 April 2024
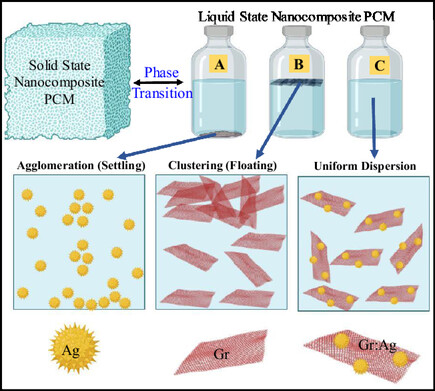
In the realm of energy storage, materials engineering is crucial. Specifically, materials engineered at the nanoscale have special qualities that lead to high optical absorbance, thermal conductivity, and potential energy storage. This research highlights the following influence of hybrid nanomaterial graphene:silver with inorganic phase change material (PCM) with experimental characterization (morphological, chemical, thermal, and optical) and numerical analysis.
Exploring the Thermal Potential of Shape Stabilized Graphene Nano Platelets Enhanced Phase Change Material for Thermal Energy Storage
- First Published: 21 May 2024
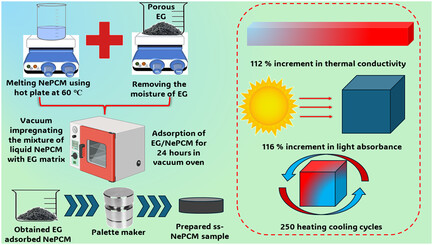
Nanoscale materials play a pivotal role in energy storage. This research investigates the impact of graphene nano platelets on organic phase change materials (PCMs), combining experimental characterization (morphological, chemical, thermal, and optical) with numerical analysis. The addition of expanded graphite (EG) ensures shape stability, enhancing efficiency and affordability. Finally, the prepared EG-impregnated nano composite undergoes leakage test.
Enhanced Heat Transfer Efficiency through Formulation and Rheo-Thermal Analysis of Palm Oil-Based CNP/SiO2 Binary Nanofluid
- First Published: 01 June 2024
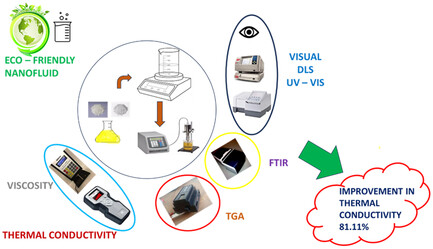
The study introduces an innovative hybrid nanofluid combining silicon dioxide (SiO2) and cellulose nanoparticles (CNP) into analytical-grade Palm oil, adopting a two-step methodology. This endeavor represents a significant advancement in exploring SiO2–CNP-Palm oil hybrid nanofluids, positioning them as promising candidates for advanced heat transfer media. The formulated nanofluid containing 0.1 w/v% SiO2/CNP nanoparticles exhibits a significant enhancement in thermal conductivity, showcasing an impressive 81.11% improvement.
Influence of Different Melting Points of Phase Change Material on Photovoltaic Phase Change Materials System Performance: An Energy, Exergy, and Environmental Point of View
- First Published: 04 June 2024
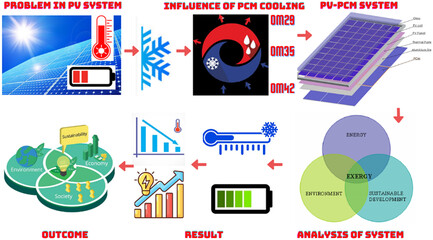
The photovoltaic (PV) system has poor conversion efficiency due to a rise in solar cell temperature. As a solution, PV panels must be cooled to generate more electricity. PV panel cooling is done by integrating the phase-change material (PCM) underneath the panel. The influence of different melting points of PCM on the PV-PCM system is investigated based on 4E performance characteristics.
Experimental Investigation for Enhancement of Solar Still Performance for Wastewater Treatment with the Influence of Encapsulated Phase Change Material
- First Published: 02 August 2024
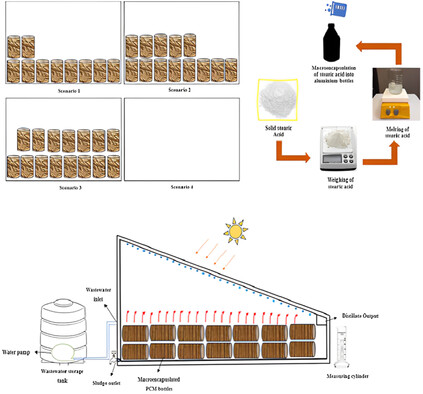
The present study aims to increase the productivity and thermal efficiency of single-basin solar still using stearic acid as a phase change material to treat industrial wastewater. Stearic acid has been macroencapsulated in aluminum bottles eliminating issues of cost, leakage, and problems in separation from the wastewater. Optimization studies are conducted by varying masses of stearic acid.
Separation Study of Magnesium–Lithium from Low-Mg/Li Brine
- First Published: 05 August 2024
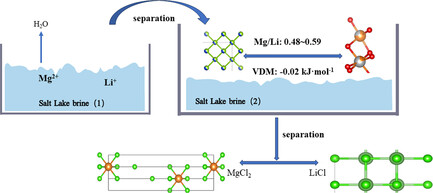
In the process of extracting lithium resources from salt lakes, the Mg/Li ratio is a crucial factor that constrains lithium extraction. Natural evaporation to the optimal Mg/Li ratio range increases the repulsive force between magnesium and lithium and reduces the clustering phenomenon, which is conducive to the efficient separation of magnesium and lithium.
Examining the Thermophysical Impact of Low Concentrated Nanoparticles Hexagonal Boron Nitride Embedded in Phase Change Material for Photo to Thermal Energy Conversion
- First Published: 30 July 2024
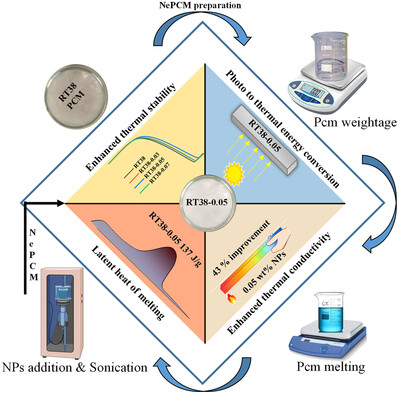
The low concentration of h-BN nanoparticles is integrated in RT38 PCM for thermophysical characterization and photo to thermal energy conversion. The optimal nanocomposite exhibits 43% thermal conductivity improvement by adding 0.05 wt% h-BN nanoparticle with RT38 PCM. Further, the optimal nanocomposite improves the thermal degradation property of composite along with enhanced photo to thermal energy conversion.
Investigating Long-Term Durability of Nanofillers (TiO2) Embedded Organic Eutectic Phase Change Composites
- First Published: 13 August 2024

The present study explores the durability of eutectic phase change composite loaded with TiO2 nanoparticles. The reliability of nanoenhanced eutectic phase change composite (M2) is confirmed by accelerated thermal cycling and a comprehensive morphological thermophysical analysis after 4000 melt-freeze cycles. Thermophysical characterization of the thermally cycled (M2) proves the thermal stability of the (M2), is adequate for its usage in medium-temperature thermal energy storage systems.
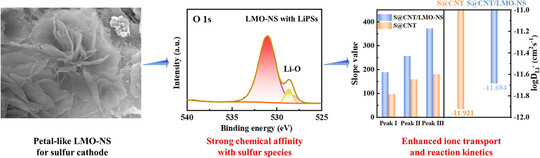
Adsorption and Catalysis Effects of LaMnO3 Nanosheets for High-Performance Li–S Batteries
- First Published: 07 October 2024
Enhancing Supercapacitor Performance of NiCoMn-Layered Double Hydroxide with Ag–Citrate/Polyaniline Nanocomposites
- First Published: 17 November 2024
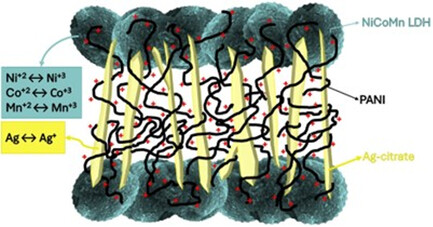
The NiCoMn-layered double hydroxide (LDH)/Ag/polyaniline (PANI) nanocomposite enhances supercapacitor performance by combining Ag–citrate, which improves conductivity and pseudocapacitance, with PANI, which boosts electrical conductivity and electric double-layer capacitor behavior. Situated between NiCoMn LDH layers, Ag–citrate and PANI work together to enable efficient energy storage through a blend of pseudocapacitive and electrochemical double-layer mechanisms.
Facile Surface Chemical Tailoring of Industrial Carbon Waste for Improved Sodium Storage
- First Published: 13 January 2025
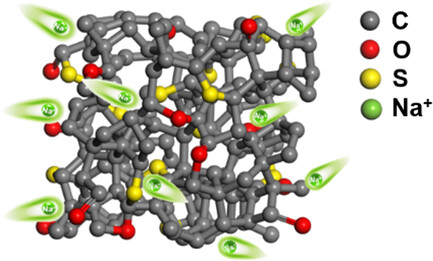
Carbon-based materials are widely used as anodes for sodium-ion batteries, while small interlayer distances limit their performance. This study uses heteroatom-doped petroleum coke to enlarge interlayer distances, thus achieving better cycling capacity (209 mAh g−1) and improved initial coulombic efficiency (51.3%). The findings highlight the potential of heteroatom doping and microstructural tailoring for advancing sustainable energy storage solutions.
Developing Hybrid TiO2–Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Photoanodes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
- First Published: 30 March 2025
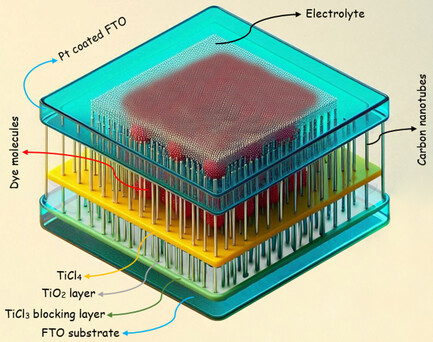
Multiwalled carbon nanotubes are incorporated to the extra thin mesoporous TiO2 layer to obtain a high short-circuit density in dye-sensitized solar cells. With increasing electron diffusion length, charge collection efficiency, and decreasing serial resistance, the power conversion efficiency of a solar device is enhanced remarkably.
Optimized Mixed Halide Triple Cation Perovskite Based Indoor Photovoltaic Device Architecture with Ultrahigh Open Circuit Voltage and Efficiency > 42%
- First Published: 24 April 2025
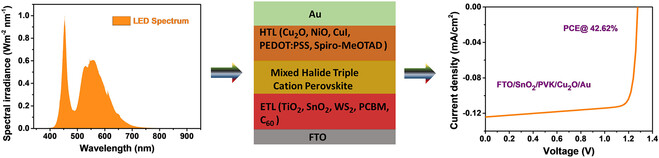
The SCAPS-1D software was used to simulate a FTO/ETL/PVK/HTL/Au device under a 3 W m−2 light-emitting diode spectrum. Optimization involved tuning layer thickness, doping levels, absorber and interface defect densities, and series/shunt resistances. The optimized configuration of FTO/SnO2/PVK/Cu2O/Au demonstrates the highest performance, achieving a PCE of 42.62%.