Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Issue Information
Research Article
Modification and Optimization Study of ZIF-8 with Branched Polyethyleneimine Modified Polysulfone Membrane
- First Published: 14 April 2025
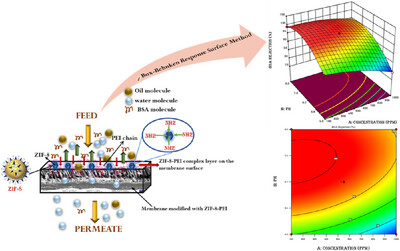
Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) and modified ZIF-8 with polyethyleneimine (PEI) were incorporated into the polysulfone membrane. The electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged membrane surface and the BSA and oil-water emulsion causes them to be retained on the membrane, while the positively charged water molecules permeate through. As a result, the water flux is excellent. Thus, this study expected that oil-water separation would be possible due to the hydrophilic character of the membrane produced by the precise loading of ZIF-8 and PEI particles. The Box–Behnken Design (BBD) statistical method was used to optimize the membrane's performance. This technique helps to determine a suitable combination of parameters (feed pH, feed concentration, and additive loading) for achieving the greatest rejection and flux recovery ratio (FRR) for BSA and oil-water emulsion.
Insights into CO2 Hydrogenation to DME: In Situ DRIFTS Study of Reaction over Cu/ZSM-5 Catalyst
- First Published: 15 April 2025
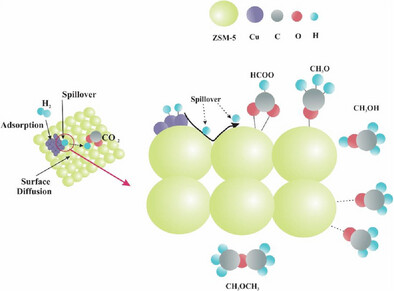
This manuscript explores the intricate mechanisms of CO2 hydrogenation to MeOH and DME. We detail the reaction pathway, emphasizing the formation of key intermediates. The application of in situ DRIFTS is highlighted as a powerful tool for monitoring surface species and understanding catalytic processes. Our findings advance catalyst design and performance, contributing to sustainable energy solutions and carbon capture efforts.
Use of Fenton-Oxidation and a Helicoidal Flux Reactor in the Removal of Doxycycline: Optimization and By-Products Identification
- First Published: 30 March 2025
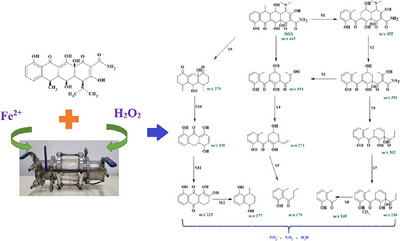
Fenton, photo-Fenton, and a helicoidal flow reactor were assessed in the removal of doxycycline. Effects of Fe2+, H2O2, and the volumetric flow through the reactor were evaluated. Additionally, the samples total organic carbon and nitrates were determined. Twelve possible by-products were identified, and a reaction route was proposed.
Unlocking Potential: Vegetable Oil Effects on Lactic Acid Extraction
- First Published: 30 March 2025
This study investigates the recovery of lactic acid from aqueous solutions using tri-n-octylamine (TOA) and various vegetable oils. The highest separation efficiency (74.54 %) and distribution coefficient (2.93) were achieved with rice bran oil. PCA analysis reveals that sesame and rice bran oils are highly similar, offering efficient extraction performance.
Dense Coconut Oil-in-Water (CO-Water) Emulsification via a Vortex-Based Cavitation Device
- First Published: 15 April 2025
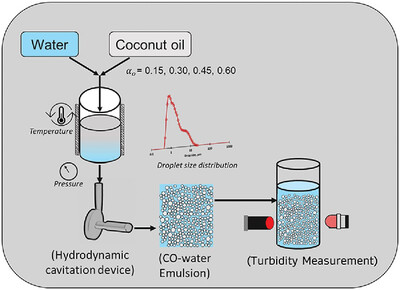
This study investigates the emulsification of coconut oil-in-water (CO-water) emulsions using a vortex-based hydrodynamic cavitation (HC) device. The present study explores the influence of dispersed phase on produced O/W emulsions without changing the surfactant type and concentration. Emulsification of CO-water presents unique challenges due to its higher melting point of 23.16 °C, necessitates operation at constant temperature to ensure it remains fully liquid state during process. Emulsions were produced at a controlled temperature of 25 °C with coconut oil volume fractions (αo) of 0.15, 0.30, 0.45, and 0.60, and the influence of αo on the droplet size distribution (DSD), Sauter mean diameter (d32), other characteristic diameters, and droplet breakage efficiency (η) was investigated. Additionally, this study validates the application of a turbidity-based method for estimating droplet size in CO-water emulsions, demonstrating its reliability across different oil-in-water systems. The findings offer valuable insights into the role of oil phase properties in HC emulsification, with direct relevance to personal care and food product formulations, where coconut oil is a commonly used ingredient.
Development of Process Control Strategy for Acid Gas Sweetening Process
- First Published: 14 April 2025
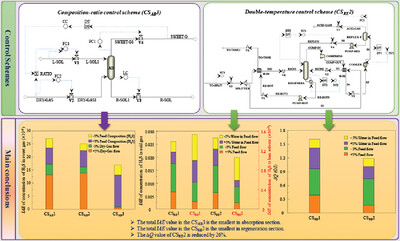
Dynamic behavior of a novel acid gas sweetening process was simulated using ASPEN, IAE and ∆Q were used to evaluate the stability and controllability of dynamic control. Novel composition-ratio control scheme for absorption process and new double-temperature control scheme for regeneration process were developed, and the optimized control strategy obtained matched the acid sweetening process developed.
Green Synthesis of Fe3O4-Crataegus tanacetifolia (Lam.) Biochar Magnetic Nanocomposites for Adsorption of Naproxen
- First Published: 15 April 2025
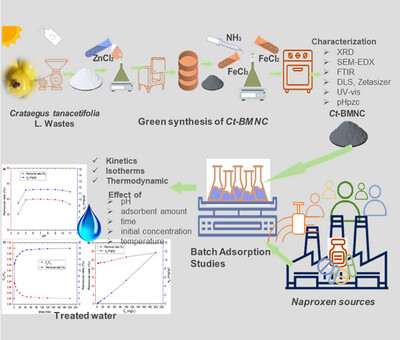
Biochar was obtained from Crataegus tanacetifolia (Lam.) plant wastes by green synthesis, and magnetic properties were imparted with Fe3O4. Characterization of Ct-BMNC was performed by XRD, SEM-EDX, FTIR, DLS, Zetasizer, TGA-DTA, BET, UV–Vis, and pHpzc. Also, batch adsorption tests of naproxen were performed. The results were processed in kinetic and isotherm models, and error functions.
Thermodynamic Analysis of the Oxidation of Ethane to Ethylene with Carbon Dioxide
- First Published: 14 April 2025
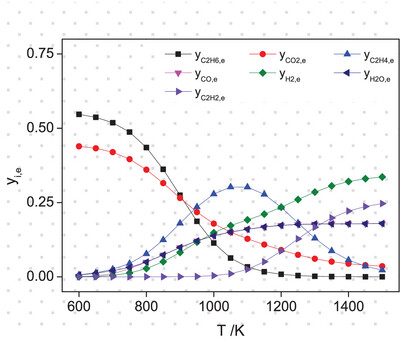
The study demonstrated the oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane with CO2 did not significantly reduce the Gibbs free energy compared to the direct dehydrogenation of ethane. However, the dehydrogenation was facilitated by the reverse water-gas shift reaction. The increase in CO2 in feed enhanced ethane conversion and ethylene yield, but this resulted in a reduction in CO2 conversion.
Compact Temporal Causal Algorithm for Modeling Prediction in the Green Ammonia Production Process
- First Published: 21 April 2025
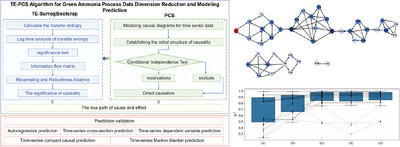
Advanced causal inference optimizes green ammonia production by extracting key variable relationships from high-dimensional data. The TE-PCS algorithm, integrating transfer entropy and direct causal identification, builds a compact temporal network. Industrial validation confirms high accuracy (R2 ∼ 0.89) with reduced variables, enabling scalable solutions for sustainable synthesis.
A Technical Analysis of Biofuel Production from Dairy Waste Sludge for Sustainable Environment
- First Published: 15 April 2025
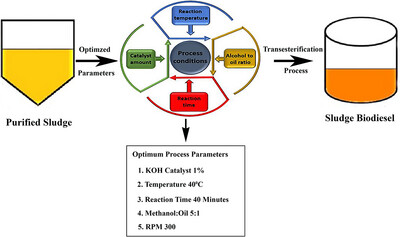
By heating dairy waste sludge at a 5:1 molar ratio to 40 °C and maintaining that temperature for 40 min while 1 % KOH was present, the ideal kinematic viscosity (3.4 cSt) with ester recovery (78.93 %) was achieved. Kinematic viscosity and biofuel recovery measurements served as a basis for these conclusions.
Kinetics Research and Process Development for the Intensification of the Fully Continuous Flow Synthesis of 3-Amino-1-Adamantanol
- First Published: 14 April 2025
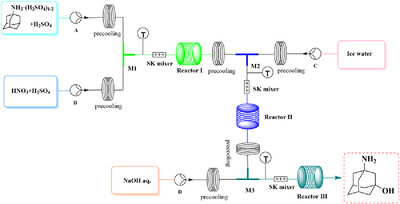
A fully continuous flow reaction system combining nitration, hydrolysis and neutralization was established for the synthesis of 3-amino-1-adamantanol. Compared with the batch method, the reaction time was greatly shortened from 8 h to 36 min, the side reactions were significantly inhibited, and the yield increased from 87.8 % to 95.2 % by continuous flow strategy.
Pore Size Effects over Hierarchical Pore Hβ via Two-Stage Crystallization in Benzene Hydroalkylation
- First Published: 15 April 2025
Copper Removal with Zeolite/Polylactic Acid Beads: Neural Networks and Fixed-Bed Column Insights
- First Published: 19 April 2025
PNZ/PLA composite beads were synthesized for Cu2+ removal in fixed-bed columns. Their structural changes before and after adsorption were analyzed. Adsorption efficiency was optimized using RSM and ANN, with ANN showing higher accuracy. Breakthrough models were applied, and reusability was assessed through multiple adsorption–desorption cycles.
Effect of Operating Velocity of Mass Transfer in a Fluidized Bed Using a Bubble-Based Approach
- First Published: 15 April 2025
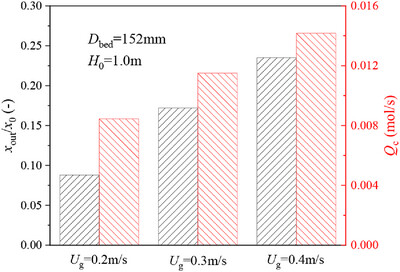
A bubble-based mass transfer model is applied to evaluate the interphase mass transfer behaviors in a bubbling fluidized bed under different operating conditions. The dependence of gas–solid contact and mass transfer on operating parameters is analyzed. The results reveal that the increase of operating velocity will reduce the gas residence time and conversion rate. The contact efficiency between gas and particles is enhanced so as to increase the total ozone decomposition amount in the reactor.