Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 4/2020
- Page: 595
- First Published: 24 March 2020

Hydrogen: A Clean and Green Fuel of the Future. Copyright: Sonil Nanda
Hydrogen is a clean energy vector and carrier. It shows not only a high heating value, but also releases water upon combustion. Moreover, hydrogen can be used as direct gaseous fuel in fuel cells or catalytically transformed into liquid hydrocarbon fuels such as green diesel and alcohols. Hydrogen is also used during the upgrading of alternative and synthetic hydrocarbon fuels by several hydrotreating technologies. Currently, most of the commercial hydrogen is produced from the catalytic reforming of natural gas and other fossil fuels, which results in significant levels of greenhouse gas emissions leading to global warming. However, hydrogen can be produced from waste biomasses, organic residues, and alternative resources through biological, thermochemical, hydrothermal, photoelectrochemical, electrochemical, photocatalytic, and other cleaner technologies. Over the long term, these sustainable processes for hydrogen production can have less environmental impacts and lead to a clean hydrogen-powered energy sector.
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 4/2020
- Page: 596
- First Published: 24 March 2020
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 4/2020
- Page: 597
- First Published: 24 March 2020
Highlights
Editorial
Hydrogen Energy Production from Advanced Reforming Processes and Emerging Approaches
- Page: 600
- First Published: 24 March 2020
Reviews
Biohydrogen Production Through Dark Fermentation
- Pages: 601-612
- First Published: 08 January 2020
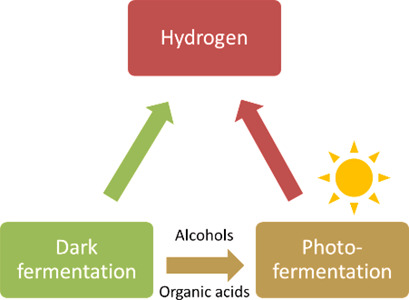
Hydrogen is an excellent energy vector and carrier. Dark fermentation as well as integrated dark fermentation and photofermentation are environmentally benign routes for biological hydrogen production. Optimization of fermentation parameters as well as employing versatile microorganisms can result in maximizing biohydrogen production from a wide variety of organic residues.
Overview on the Current Status of Hydrogen Energy Research and Development in India
- Pages: 613-624
- First Published: 22 January 2020
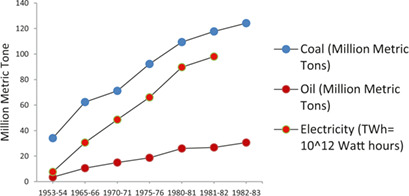
Hydrogen is currently proving its potency as a sustainable and clean energy carrier with high specific energy and zero polluting energy sources. The progress of hydrogen energy research and development regarding production and storage techniques in India is reviewed discussing current studies and ongoing projects. Challenges related to the promotion of hydrogen in India are highlighted.
Hydrogen Production from Catalytic Steam Reforming of Bio-Oils: A Critical Review
- Pages: 625-640
- First Published: 22 January 2020
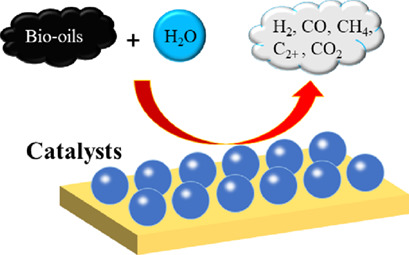
Maintaining the activity and stability of the catalysts is the key issue in steam reforming of bio-oils. The most important factors in catalyst design are the elemental composition, the structures, and the interactions of the catalytically active species and supports. The operation conditions can extend the catalyst lifetimes by affecting the coke morphology or by promoting coke gasification.
Catalytic Hydrogen Production from Methane Partial Oxidation: Mechanism and Kinetic Study
- Pages: 641-648
- First Published: 22 January 2020
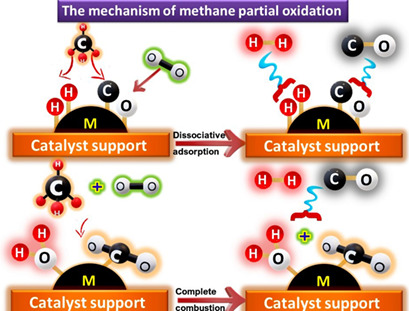
An overview is given on the multifunctional potential of a transition and noble metal catalyst supported on either single support or combined oxide support in the catalytic partial oxidation of methane. The factors influencing the oxidation reaction along with the mechanism and recent kinetic studies are reported. The deactivation of the catalytic partial oxidation of methane catalysts is evaluated.
Flowsheet Modeling and Simulation of Biomass Steam Gasification for Hydrogen Production
- Pages: 649-660
- First Published: 04 February 2020

Hydrogen production from biomass steam gasification as well as equilibrium modeling and simulation studies using various techniques for effective hydrogen production are reviewed. Heat integration, economic analysis of the hydrogen production, and systematic design algorithms for energy-efficient and economic hydrogen production from various biomass feedstocks are discussed.
High-Performance Bimetallic Catalysts for Low-Temperature Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
- Pages: 661-671
- First Published: 04 February 2020
Recent developments in bimetallic catalysts in catalytic dry reforming of methane are reviewed focusing on the evaluation of catalysts, deactivation studies, and reaction mechanisms of developed bimetallic catalysts. The latest insights in catalyst characteristics are given together with strategies on coke management and mechanism of bimetallic catalysts on catalytic dry reforming of methane.
Effect of Supports and Promoters on the Performance of Ni-Based Catalysts in Ethanol Steam Reforming
- Pages: 672-688
- First Published: 04 February 2020
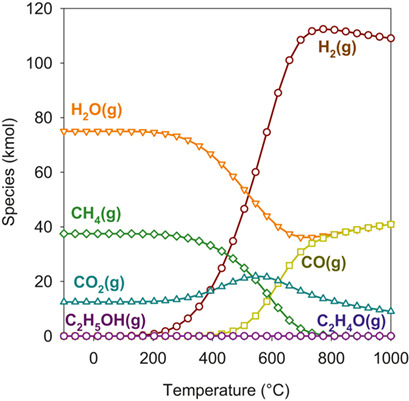
Hydrogen produced from ethanol steam reforming (ESR) can be an excellent alternative to fossil fuels. The ESR process has been well studied, also using transition metals as catalysts coupled with both acidic and basic oxides as supports. This review discusses the influences of the supports and promoters of Ni-based catalysts on the ESR process.
Research Articles
Hydrogen Production by Steam Reforming of Fusel Oil Using a CeCoOx Mixed-Oxide Catalyst
- Pages: 689-697
- First Published: 25 November 2019
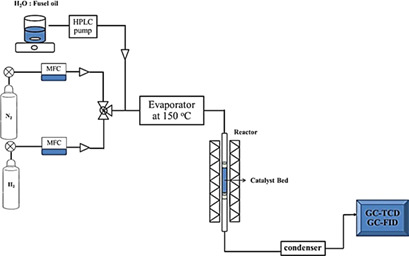
CeCoOx mixed oxides prepared from CeO2 and Co3O4 proved to be effective catalysts for H2 production from the steam reforming of fusel oil. The optimum catalyst composition Ce0.6Co0.4Ox exhibited a higher H2 yield and fusel oil conversion level and a narrower distribution of by-products compared to pure oxides. It converts fusel oil into clean and more versatile H2 for various applications.
A Comparative Study of Hydroxyapatite- and Alumina-Based Catalysts in Dry Reforming of Methane
- Pages: 698-704
- First Published: 22 January 2020

Dry reforming of methane has been intensively studied during the last decade, but it is still not deployed on the industrial scale. One of the main challenges of the process is the development of an active and stable reforming catalyst. Hydroxyapatite is reported as a new promising material to design highly active and stable catalysts for this process.
Kinetic and CFD Modeling of Exhaust Gas Reforming of Natural Gas in a Catalytic Fixed-Bed Reactor for Spark Ignition Engines
- Pages: 705-718
- First Published: 22 January 2020
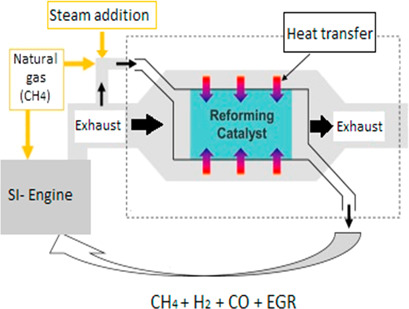
Exhaust gas reforming is a fuel conversion technology that can enhance engine efficiency and reduce emissions in internal combustion engines. A catalytic reactor integrated in the exhaust recirculation loop uses exhaust heat and gas for on-board production of hydrogen-rich syngas. Herein, exhaust gas reforming of natural gas in a catalytic fixed-bed reactor was modeled under different conditions.
Bimetallic Ru-Fe Nanoparticles Supported on Carbon Nanotubes for Ammonia Decomposition and Synthesis
- Pages: 719-730
- First Published: 04 February 2020
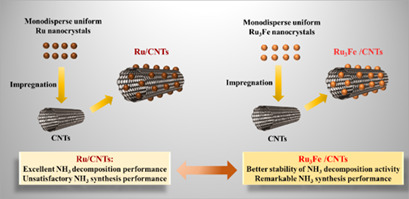
Monodispersed Ru and Ru3Fe nanoparticles were prepared by liquid-phase reduction followed by impregnation with multiwall carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to prepare Ru/CNTs or Ru3Fe/CNTs catalysts. The synthesized Ru3Fe/CNTs catalysts can effectively facilitate the synthesis and decomposition of ammonia and yield a superior catalytic stability for ammonia decomposition as compared to Ru/CNTs catalysts.
Zeotype SAPO-34 Synthesized by Combination of Templates for the Gasification of Biomass
- Pages: 731-741
- First Published: 04 February 2020
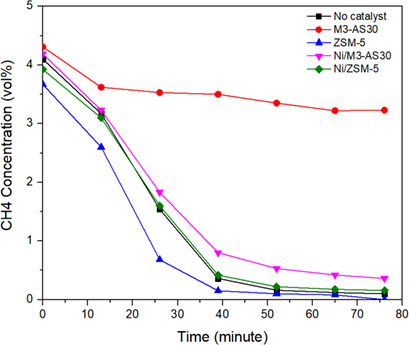
Microporous silicoaluminophosphate (SAPO) zeotype materials are potential catalysts for biomass gasification to fuels. A SAPO-34 catalyst synthesized from colloidal silica with a combination of three organic templates exhibited high total acidity, small particle size, and high surface area, and produced a large amount of light hydrocarbons in biomass gasification in a fixed-bed reactor.
Response Surface Optimization of Hydrogen-Rich Syngas Production by Greenhouse Gases Reforming
- Pages: 742-751
- First Published: 04 February 2020
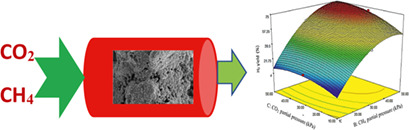
The interaction effects of methane partial pressure, carbon dioxide partial pressure, and reaction temperature on hydrogen-rich production by methane dry reforming were investigated. The process parameters were optimized using response surface methodology to obtain maximum hydrogen yield. The optimum conditions were validated to check the robustness of the response surface model.
Advanced Surface of Fibrous Activated Carbon Immobilized with FeO/TiO2 for Photocatalytic Evolution of Hydrogen under Visible Light
- Pages: 752-761
- First Published: 07 February 2020
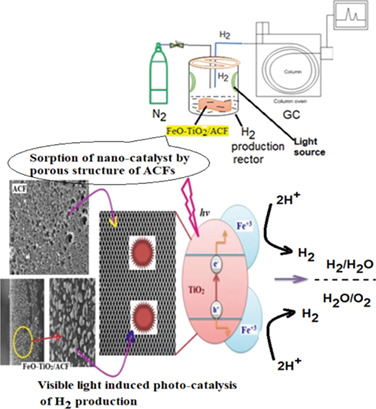
Hydrogen production and stability of catalytic materials still suffer from low efficiency due to the fast rate of recombination of electron-holes in the photocatalytic process. Fibrous activated carbon (ACF) served as surface immobilizer to capture co-doped FeO/TiO2 for improving the sorption of a nanocatalyst onto the porous surface. Stable FeO/TiO2 nanoparticles were immobilized on the ACF surface.
Enhanced Hydrogen Generation from Empty Fruit Bunches by Charcoal Addition into a Downdraft Gasifier
- Pages: 762-769
- First Published: 07 February 2020
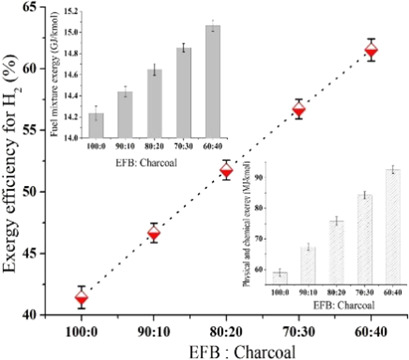
The bioenergy potentiality of mixtures of empty fruit bunches (EFBs) with varying percentages of charcoal was evaluated. Hydrogen generation through co-gasification of EFBs could be significantly enhanced by adding charcoal. Carbon-based nanoparticles were found to be responsible for bioenergy production. Heating value and hydrogen-based exergy were increased by charcoal addition.
Adsorption Properties of Activated Tire Pyrolysis Chars for Phenol and Chlorophenols
- Pages: 770-780
- First Published: 25 February 2020

Pyrolysis has experienced a renaissance in recent years. It has also become a more frequently used method for end-of-life tire processing. Nowadays, the pyrolysis products are valorized to improve process sustainability. This work demonstrates upgrading tire pyrolysis char for efficient adsorption of phenol and its chlorinated derivatives from aqueous solutions.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 4/2020
- Pages: 781-782
- First Published: 24 March 2020










