Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Alterations in the axon initial segment plasticity is involved in early pathogenesis in Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 14 October 2024
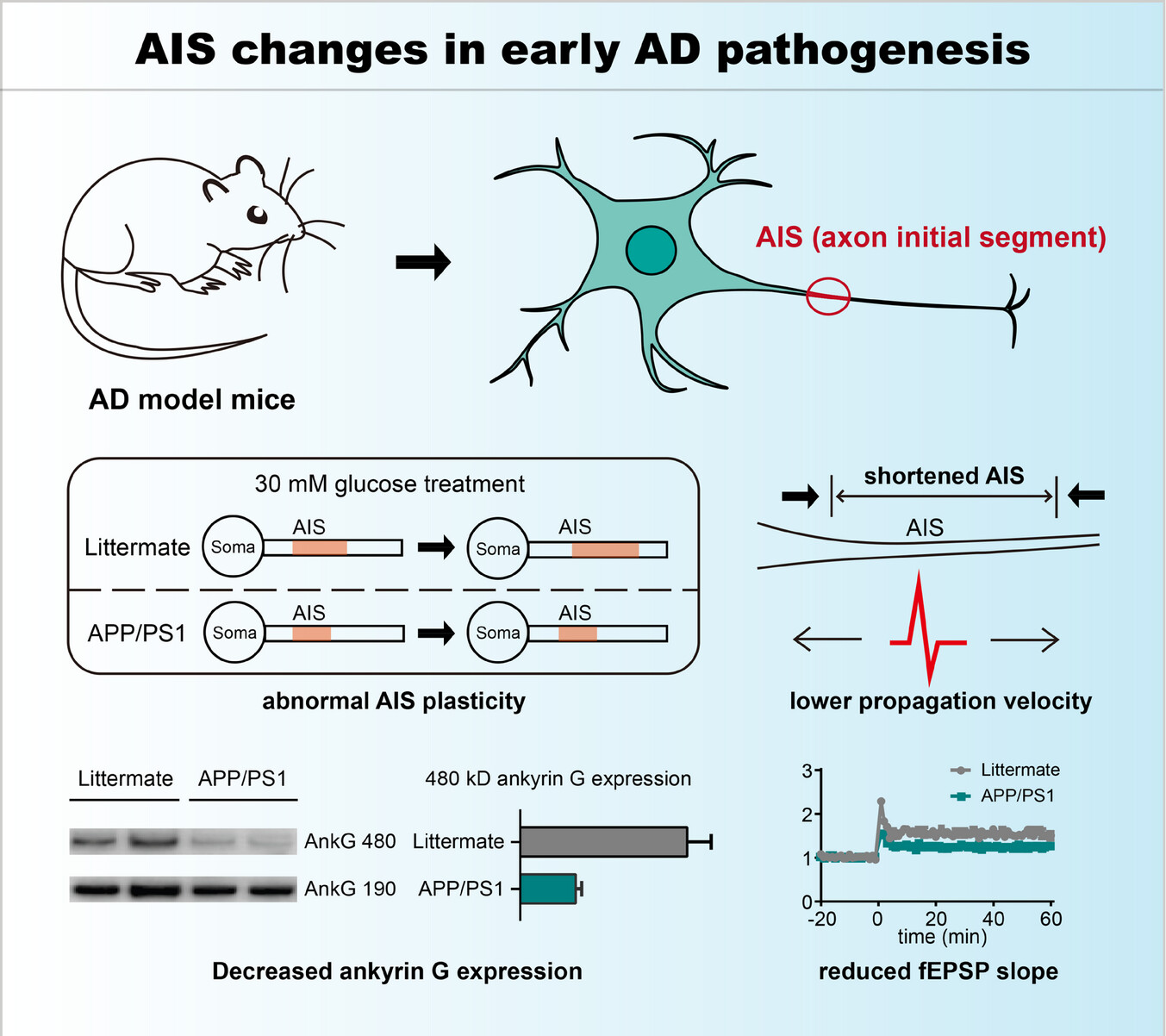
• The length of the AIS is reduced in neurons from AD patients or animal models, which slows down the velocity of action potential propagation on the axon.
• The structural plasticity of the AIS is damaged in neurons from APP/PS1 mice.
• Ankyrin G (AnkG), the key organizer of the AIS, is down-regulated in APP/PS1 mice, especially the 480 kD isoform. The overexpression of 480 kD AnkG could restore the plasticity of AIS and normal LTP in AnkG−/− mice.
Vitamin B12 protects necrosis of acinar cells in pancreatic tissues with acute pancreatitis
- First Published: 15 October 2024
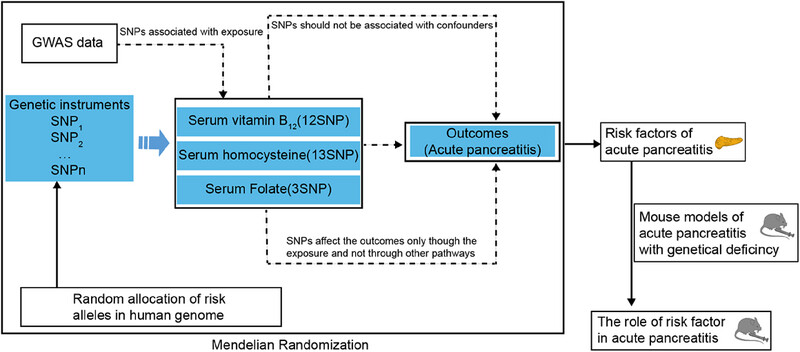
Combined with Mendelian randomization analysis and acute pancreatitis mouse models, this study uncovered that vitamin B12 prevents necrosis of pancreatic acinar cells in the progression of acute pancreatitis via ATP pathway. This finding offers a promising and accessible therapeutic option for acute pancreatitis.
REVIEW
Targeting esophageal carcinoma: molecular mechanisms and clinical studies
- First Published: 15 October 2024
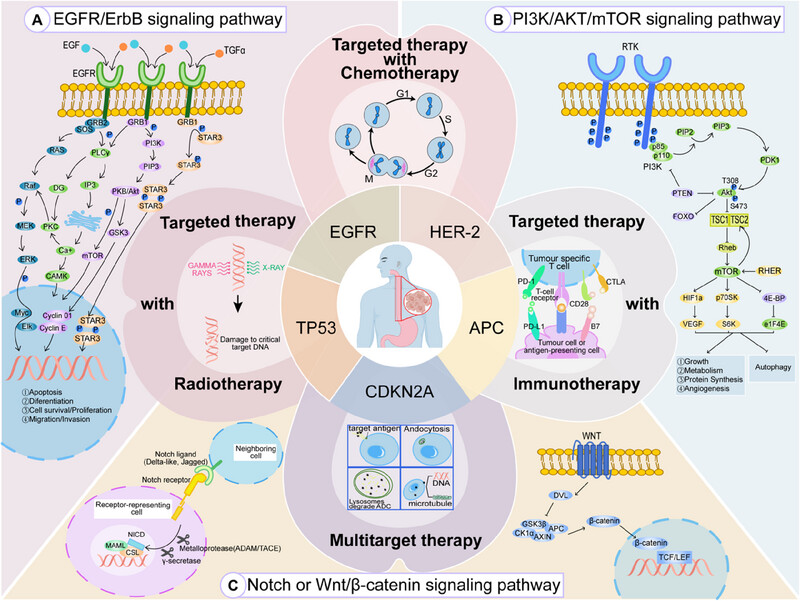
Potential strategies and potential targets for treating EC. Current the EC's research focuses on pivotal genes EGFR, HER2, TP53, CDKN2A, and APC, targeting key pathways in cell regulation and signaling. We highlight four novel therapeutic strategies: combined targeted therapy with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and multitarget approaches. Mechanistic insights into esophageal carcinogenesis underscore alterations in EGFR/ErbB, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, and Notch/Wnt/β-catenin pathways, driving proliferative and survival signaling cascades.
CDKN2A, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; EC, esophageal cancer; EGFR, endothelial growth factor receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; TP53, tumor protein 53.
Hypoxia and aging: molecular mechanisms, diseases, and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 15 October 2024
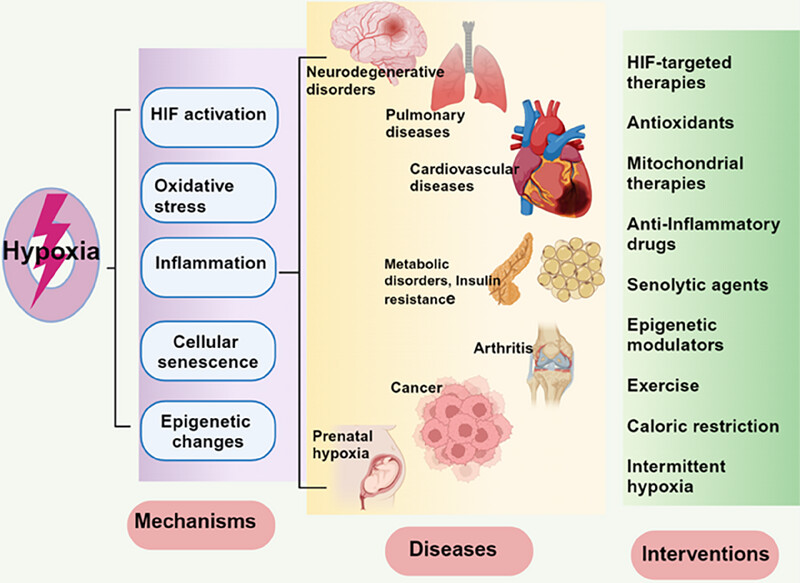
Aging involves the decline of cellular functions and increased disease susceptibility. Hypoxia, or reduced oxygen availability, accelerates aging by influencing pathways like hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), oxidative stress, and inflammation. This review highlights how hypoxia exacerbates cellular damage, promotes senescence, and contributes to age-related diseases. Emerging therapies, such as HIF modulators and senolytics, show promise in mitigating hypoxia's impact on aging.
Inducing disulfidptosis in tumors:potential pathways and significance
- First Published: 15 October 2024

Exploring the mechanisms of disulfidptosis reveals potential pathways to induce tumor cell death. Tumor cells with high SLC7A11 expression uptake a large amount of cystine to meet their metabolic needs. The reduction of cystine requires the involvement of the Trx system and NADPH. When NADPH is deficient or the Trx system is dysfunctional, cystine and other disulfides induce actin cytoskeleton disulfide stress, leading to disulfidptosis. Rac-WRC-Arp2/3 mediates actin polymerization, facilitating disulfidptosis. In this process, targeting NADPH metabolism-related enzymes and the Trx system is the most promising method to induce disulfidptosis.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Structural insights into the mechanotransducing mechanism of FtsEX in cell division
- First Published: 20 October 2024
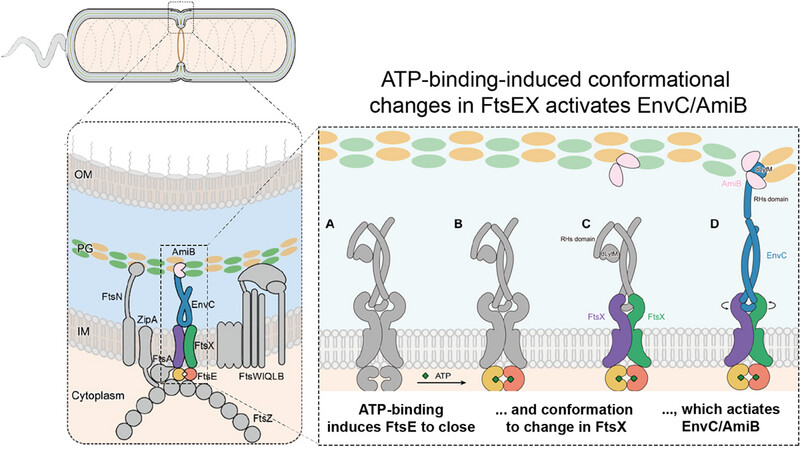
FtsEX plays a pivotal role in cell division by facilitating the activation of peptidoglycan hydrolysis through the adaptor EnvC. By characterizing the structures of FtsEX and EnvC in different states using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and homology modeling, we propose a mechanotransducing mechanism for FtsEX: ATP binding brings the FtsEX dimer close together, inducing a rotary shift in the periplasmic loop domains (PLDs), which results in activating conformational changes in EnvC.
REVIEW
Nanomedicine for cancer patient-centered care
- First Published: 20 October 2024
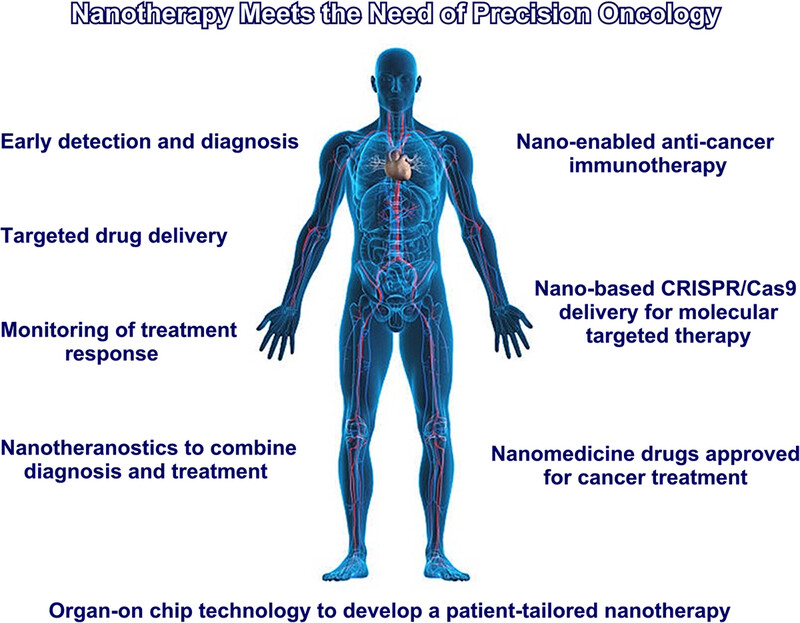
Nanomedicine can satisfy the need for developing precision oncology, promote modern early diagnostic systems, monitoring the therapy based on the response of the individual patient, and provide precision antitumor immunotherapy and gene therapy, which can be developed with sophisticated experiments such as those made with organ-on-chip technology.
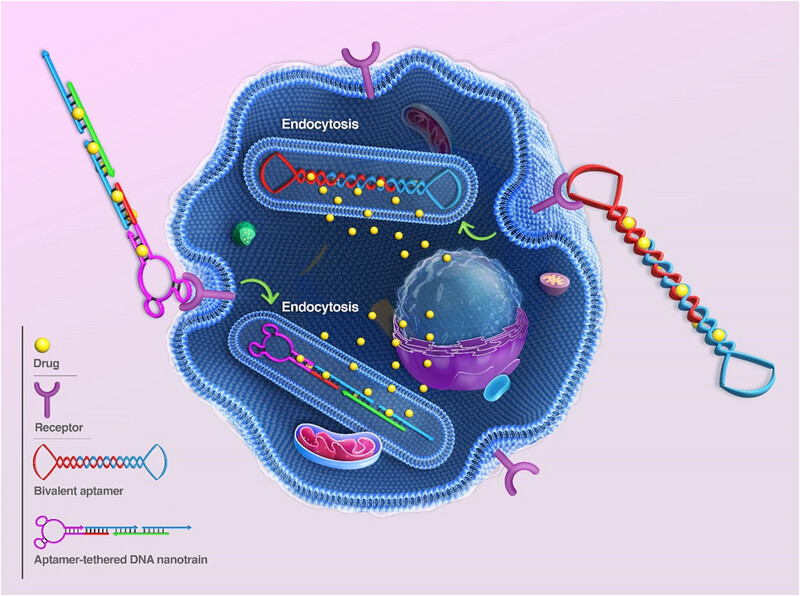
Progressive cancer targeting by programmable aptamer-tethered nanostructures
- First Published: 20 October 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Feedback loop LINC00511–YTHDF2–SOX2 regulatory network drives cholangiocarcinoma progression and stemness
- First Published: 22 October 2024
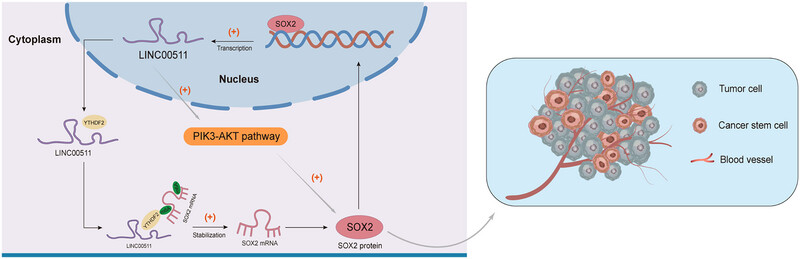
LINC00511 significantly infected cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. The interaction of LINC00511, YTHDF2, and SOX2 in CCA. LINC00511 formed a complex with YTHDF2, affecting the stability of SOX2 mRNA and thus influencing SOX2 expression. LINC00511 further modulated the expression of SOX2 through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Meanwhile, SOX2 can also promote LINC00511 expression as an upstream transcription factor, thereby confirming a positive feedback loop formed by LINC00511, YTHDF2, and SOX2, which plays a significant role in the occurrence and development of CCA.
REVIEW
The dysfunction of complement and coagulation in diseases: the implications for the therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 23 October 2024
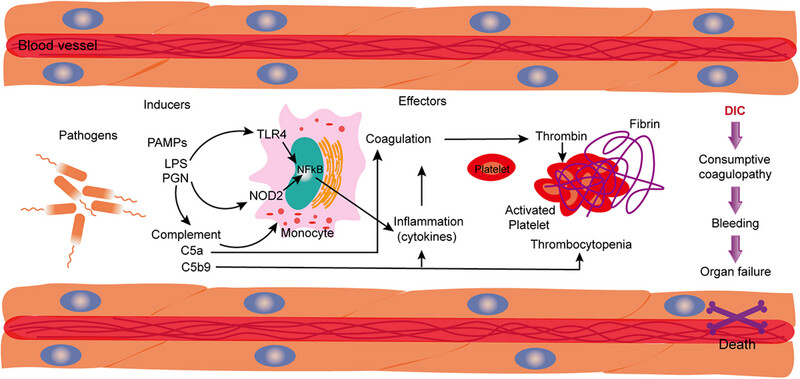
Understanding the alterations in complement and coagulation systems could aid in the creation of novel therapeutic approaches to tackle the dysfunction of complement and coagulation in diseases. The unacceptably high mortality rate of sepsis has prompted further research into the molecular pathogenesis of sepsis and therapeutic interventions. The present review aims to treat diseases by targeting complement and coagulation pathways .
RNA modification in normal hematopoiesis and hematologic malignancies
- First Published: 23 October 2024
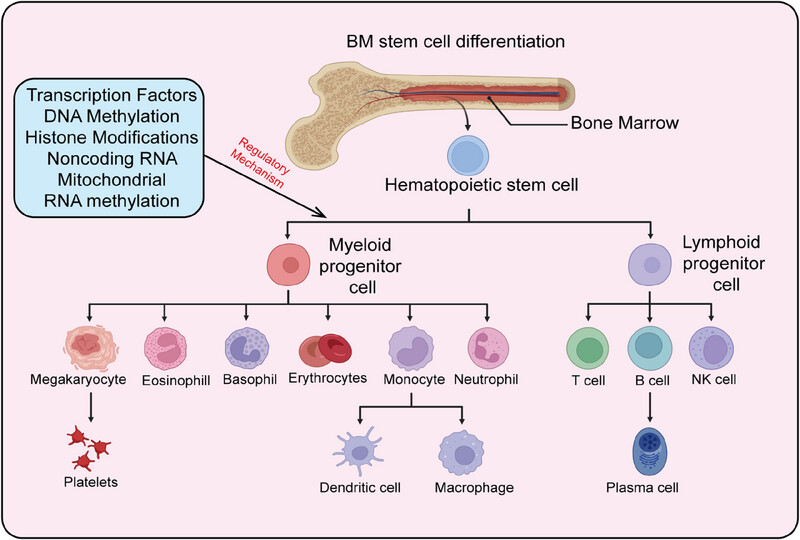
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant RNA modification in eukaryotic cells. Previous studies have shown that m6A plays a critical role under both normal physiological and pathological conditions. This review systematically reviews the latest research advancements on the roles and mechanisms of m6A regulatory factors in normal hematopoiesis and related malignant diseases. Targeting m6A modification may hold promise for achieving more precise and effective leukemia treatments.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
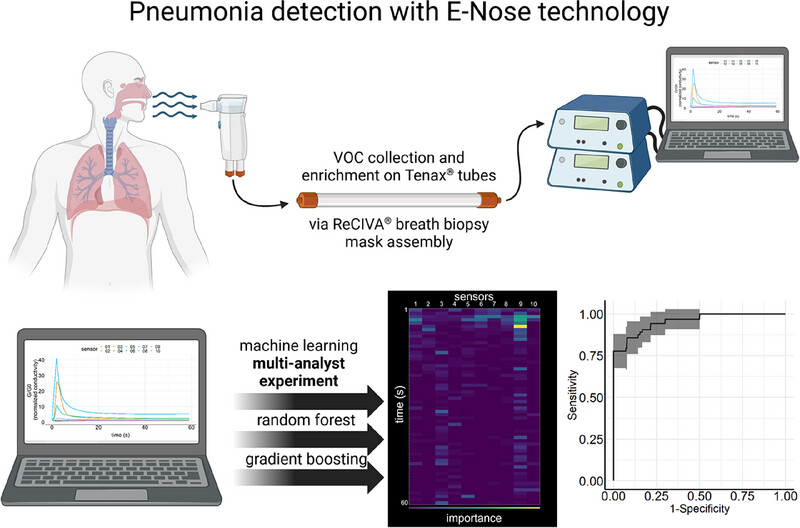
Point-of-care breath sample analysis by semiconductor-based E-Nose technology discriminates non-infected subjects from SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia patients: a multi-analyst experiment
- First Published: 24 October 2024
Robust tetra-armed poly (ethylene glycol)-based hydrogel as tissue bioadhesive for the efficient repair of meniscus tears
- First Published: 24 October 2024
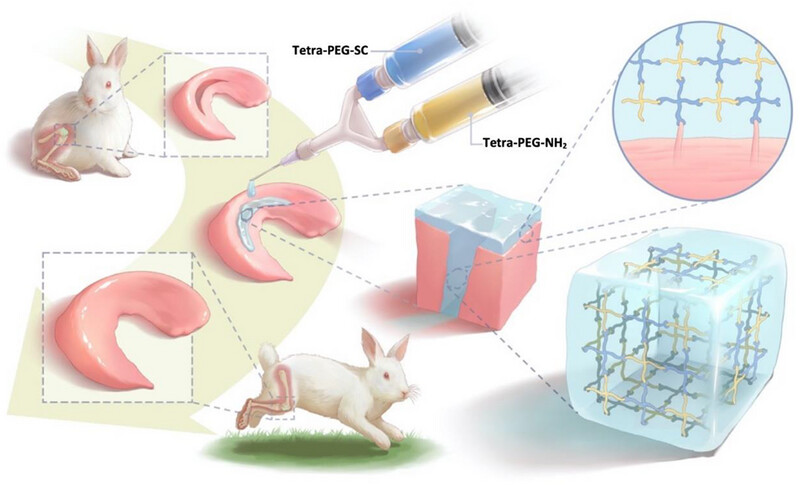
Tetra-PEG hydrogel bioadhesive schematic diagram for meniscal repair. More specifically the key points of our study are:
1. Facile construction of the applicable tetra-PEG bioadhesive. Once synchronously sprayed onto the injured meniscus tissues, NHS-active tetra-PEG-SC solution can simultaneously be reacted with amine groups of tetra-PEG-NH2 solution and tissue proteins of the cartilage surfaces within seconds, contributing to the high mechanical toughness and long-term tissue adherence.
2. Of particular collaborative mechanism of strengthened hydrogel‒meniscus adhesion. In views of the synergistic effects of robust chemical anchor between the amine-abundant proteins and NHS-active ester hydrogels and strong physical entanglements between the meniscus fibers and polymeric chains, this bioadhesive can support higher interfacial toughness by dissipating a substantial amount of mechanical energy when there are outside forces after clinical application.
3. A progressive option for the clinical complex meniscus injury. Without tedious manipulation procedure and specialized clinical skills, this novel bioadhesive can be tightly integrated with the surrounding cartilage tissue to withstand a hydraulic pressure of 29.4 kPa when flushed with water, far exceeding the clinically arthroscopic surgery (∼10 kPa) and existing commercial adhesives, which can be clinically applied to promote meniscus healing and chondroprotection.
Partial reduction of interleukin-33 signaling improves senescence and renal injury in diabetic nephropathy
- First Published: 24 October 2024
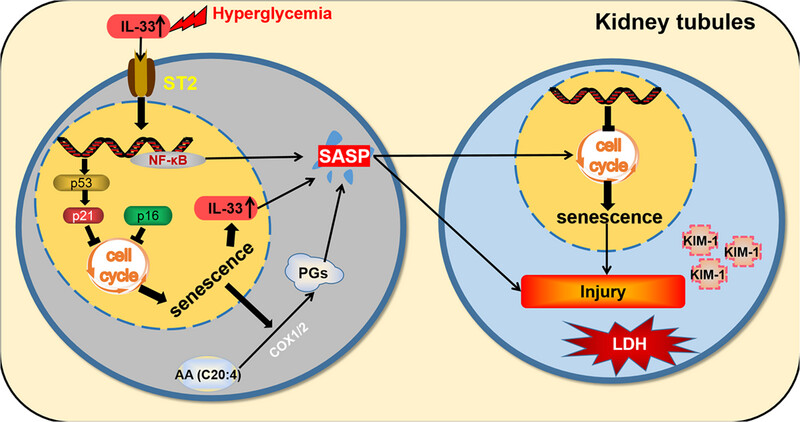
Sustained hyperglycemic stimulation increases the production of IL-33, which promotes the senescence of tubular epithelial cells through the regulation of cell cycle factors. The senescent cells then release SASP components, such as IL-33 and prostaglandins, which further exacerbate cellular senescence and renal lesions.
REVIEW
Cardiomyopathy: pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 25 October 2024
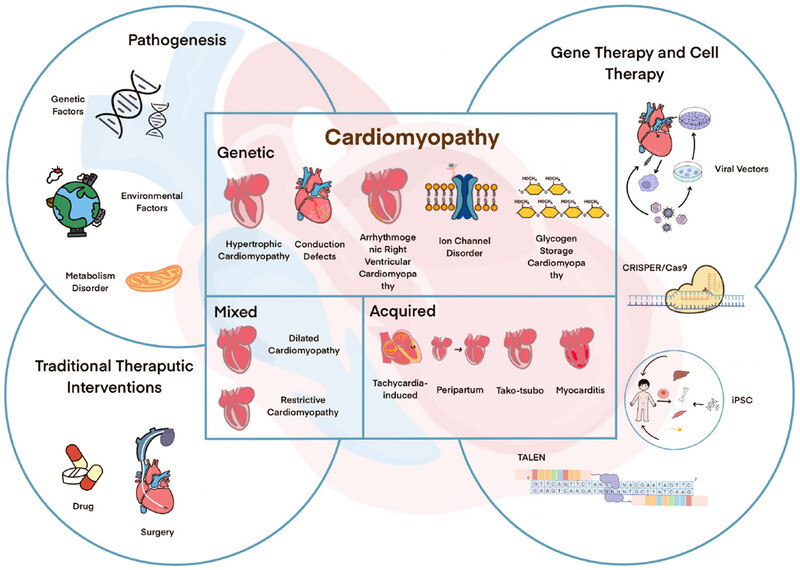
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases characterized by structural and functional damage to the myocardium. Many specific gene mutations, environmental factors, and metabolic disorders may cause cardiomyopathy. Traditional therapeutic includes drug and surgery. With the growing comprehension of the molecular mechanisms underlying cardiomyopathy. Gene therapy and cell therapy has become a tool for the clinical treatment of disease.
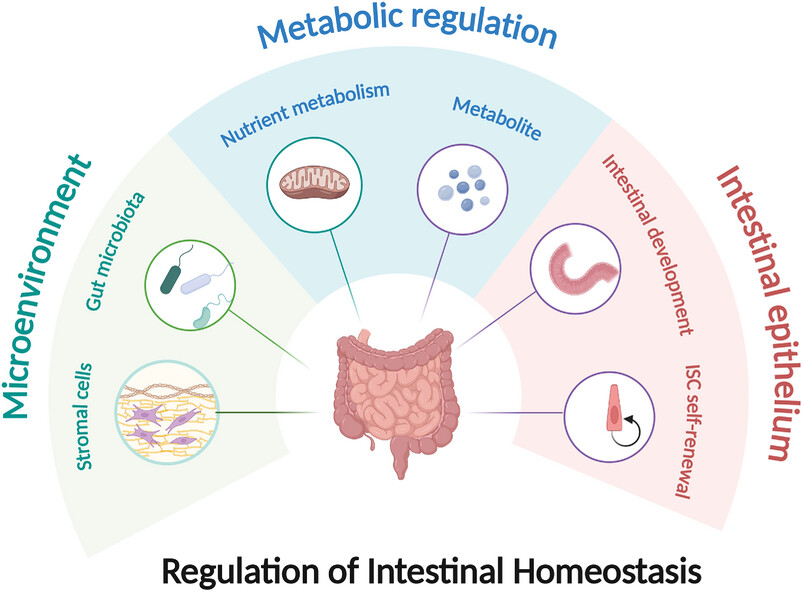
Metabolic regulation of intestinal homeostasis: molecular and cellular mechanisms and diseases
- First Published: 25 October 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Comprehensive single-cell profiling of monocytes in HLA-B27-positive ankylosing spondylitis with acute anterior uveitis
- First Published: 28 October 2024
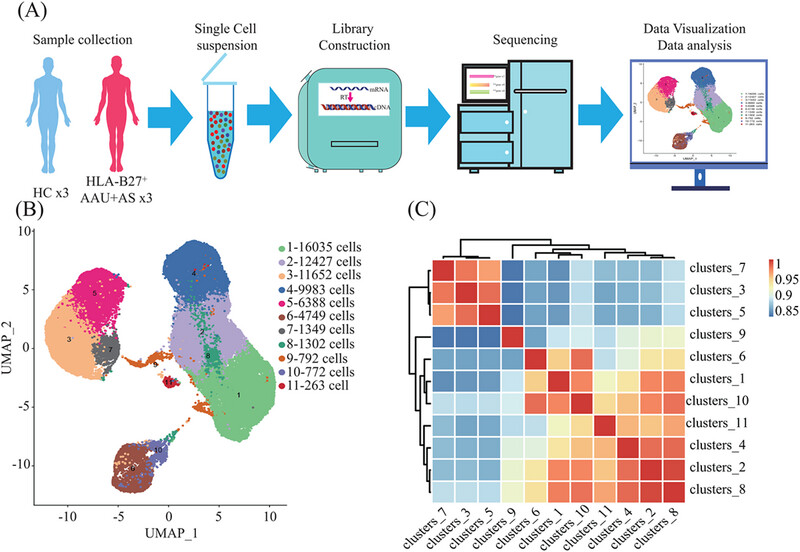
Characterization of the immune system in HL-B27+ AS-associated AAU patients (AAU+AS) and healthy controls (HCs). (A) scRNA-seq procedure. (B) UMAP plot of 65,712 cells (AAU+AS: 34,492; HCs: 31,220), color-coded by sample type (left) and cluster (right). (C) Correlation heatmap of the 11 clusters, with red indicating positive and blue indicating negative correlations.
Reduced intestinal-to-diffuse conversion and immunosuppressive responses underlie superiority of neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy in gastric adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 28 October 2024
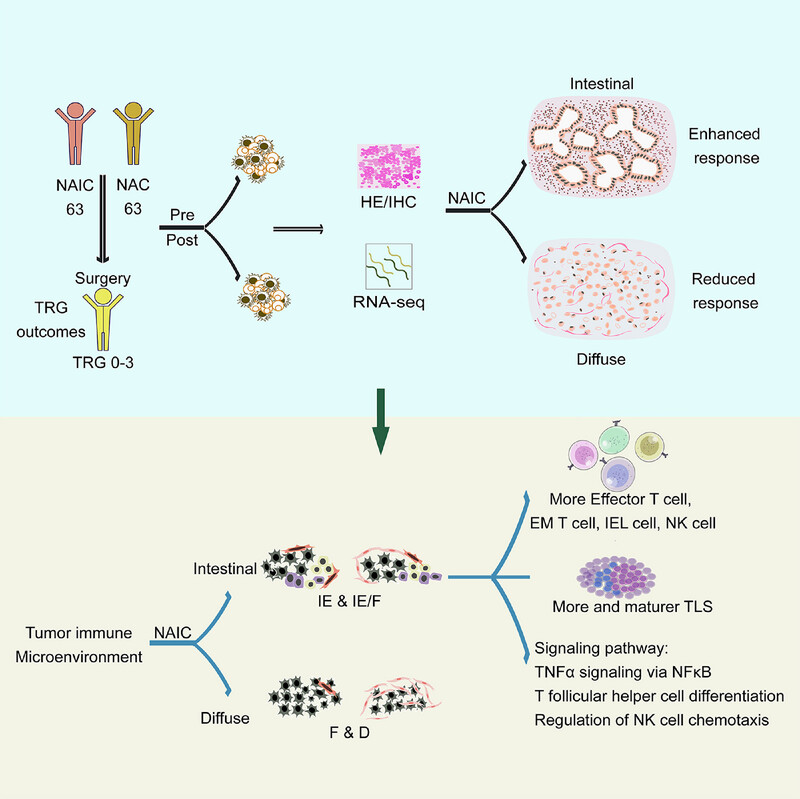
The intestinal subtype of Lauren's classification can improve the efficacy of NAIC by preventing reprogramming to immunosuppressive cells, reducing activated fibroblasts and exhausted CD8+ T cells, inducing the formation and maturation of T-cell-rich inflamed areas, and activating the TNFα signaling pathway through NF-κB.
N6-methyladenosine reader YTHDF3-mediated zinc finger protein 41 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by transcriptional repression of Snail
- First Published: 28 October 2024

In normal liver cells, YTHDF3 shows low expression, leading to a reduction in the m6A modification of ZFP41. This results in increased synthesis of ZFP41 mRNA and an enhanced transcriptional inhibitory effect on Snail. In contrast, in HCC cells, the expression of YTHDF3 is significantly elevated, which enhances the m6A modification of ZFP41. This promotes degradation of ZFP41 mRNA, consequently weakening the transcriptional inhibitory effect on Snail. Ultimately, this facilitates activation of the EMT pathway and promotes proliferation and metastasis of HCC.
REVIEW
Targeting immunosenescence for improved tumor immunotherapy
- First Published: 28 October 2024
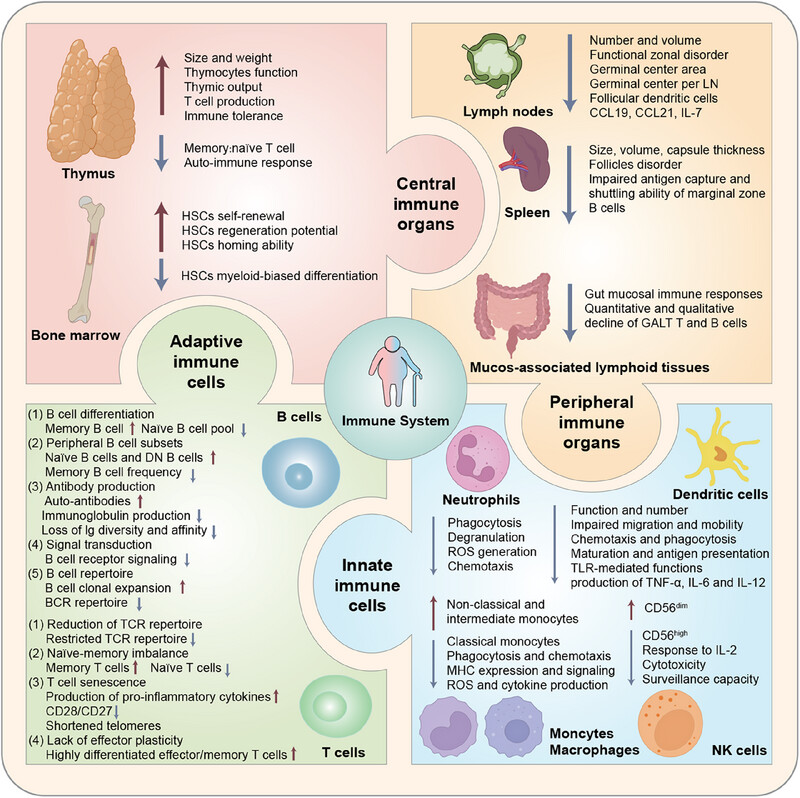
Immune system of human organism has a well-defined structural hierarchy. Over time, human organism undergoes substantial transformation through influence of immunosenescence. Advanced insight into immunosenescence and immunotherapy has facilitated a paradigm shift in treatment of elderly oncology patients. Anti-immunosenescence and anti-tumor strategies are closely interrelated and jointly improve therapeutic patterns and quality of life in oncology for older patients.
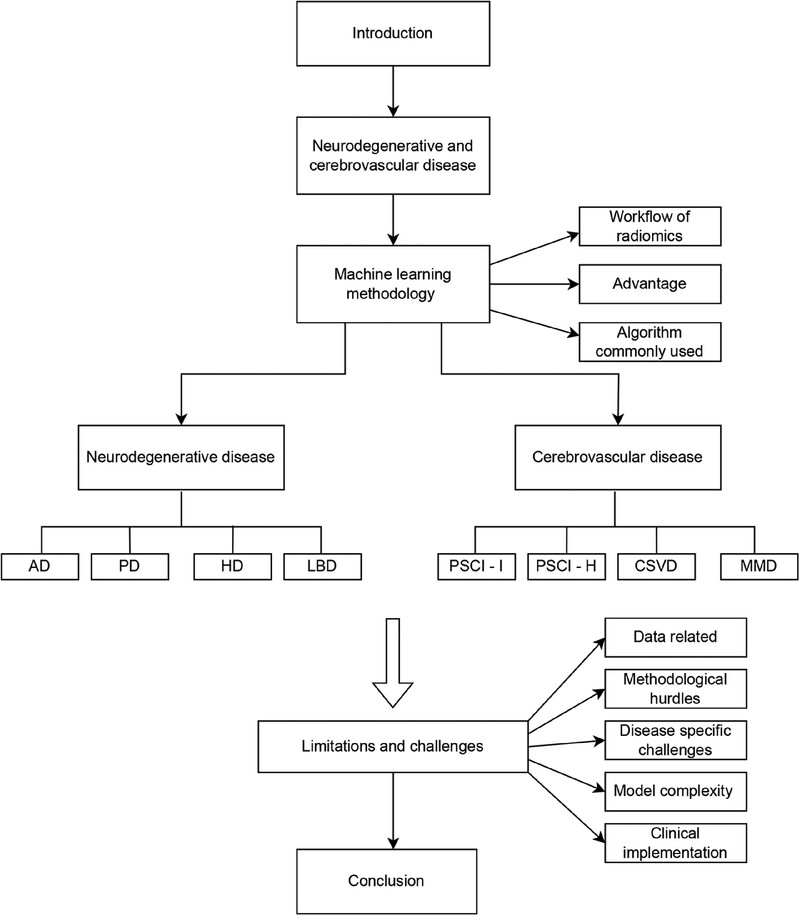
Machine learning-based radiomics in neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular disease
- First Published: 28 October 2024
Neuroscience in peripheral cancers: tumors hijacking nerves and neuroimmune crosstalk
- First Published: 31 October 2024
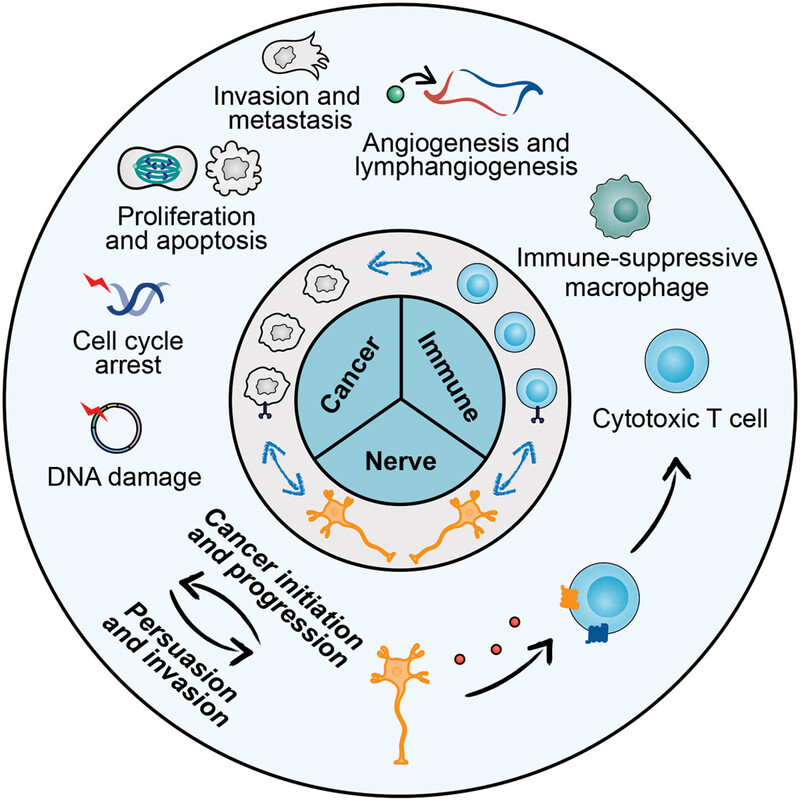
The figure depicts the intricate interactions between cancer cells, the immune system, and nerves within the tumor microenvironment. At the center, the diagram highlights the tripartite relationship among cancer, immune, and nerve cells, illustrating the dynamic and reciprocal influences they exert on one another. Surrounding this core, key biological processes are illustrated, including proliferation and apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and DNA damage, invasion and metastasis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, and immune modulation. The diagram also underscores the feedback loop driving cancer progression, where nerves facilitate cancer initiation and immune evasion, while cancer cells activate neural pathways, further enhancing their invasive potential.
Targeting the DNA damage response in cancer
- First Published: 31 October 2024
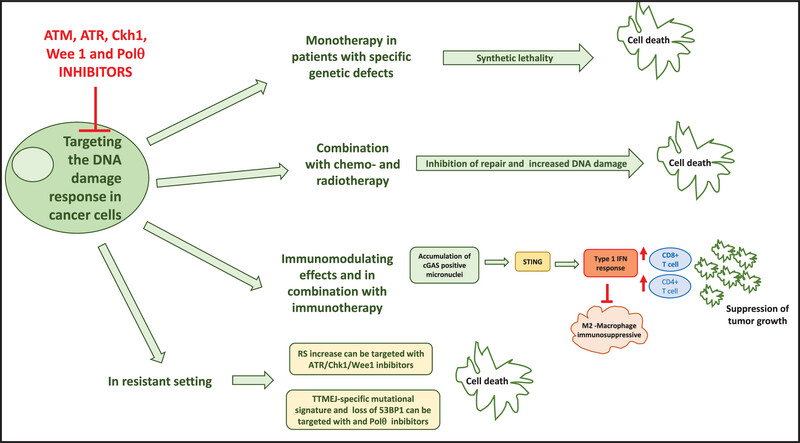
DNA damage response pathway can be effectively targeted with different small molecules inhibitors. They can be used in tumors with specific genetic defects (synthetic lethal approach), in combination with chemotherapy and radiotherapy, in combination with immune checkpoints and in the resistant setting.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Disorganized thalamic subregional functional connectivity in bipolar I disorder
- First Published: 31 October 2024
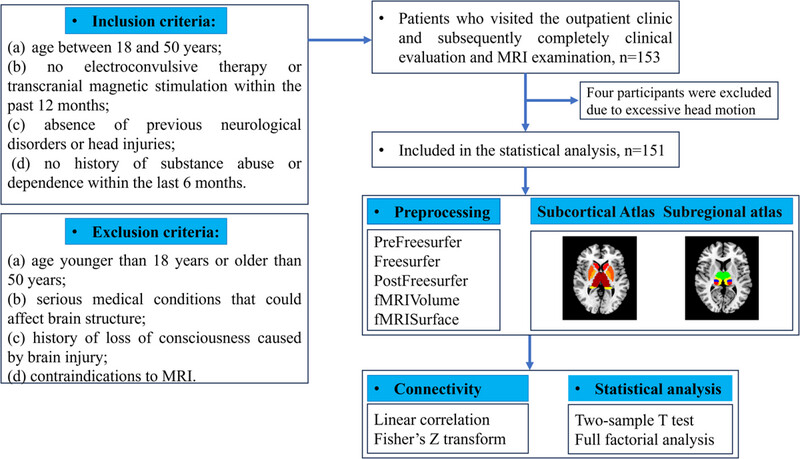
FIGURE 1 Flowchart of inclusion and exclusion criteria, and resting-state functional connectivity (FC) analysis of subcortical regions and thalamic subregions. A total of 151 participants were enrolled. All participants were scanned with high-resolution MRI. After data collection, preprocessing and seed-based FC analysis were then performed. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
Prognostic role of lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk from a perspective on current risk stratification
- First Published: 31 October 2024
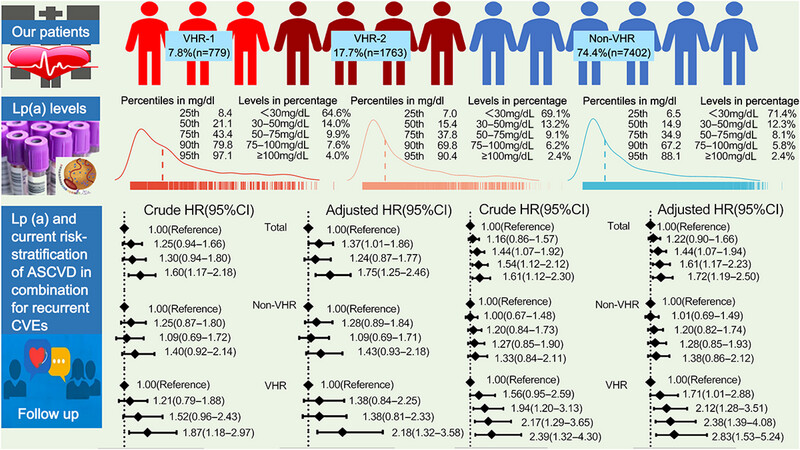
We assessed the relationship of current guideline-stratification of ASCVD with plasma Lp(a). Patients at higher grade of risk stratification showed higher Lp(a) level. Participants with both high grades of Lp(a) and risk stratification were at significantly high risk for recurrent CVEs. The additional value of Lp(a) elevation for CVEs risk prediction was evident in patients at VHR but not those at non-VHR .
Raman spectroscopy on dried blood plasma allows diagnosis and monitoring of colorectal cancer
- First Published: 31 October 2024
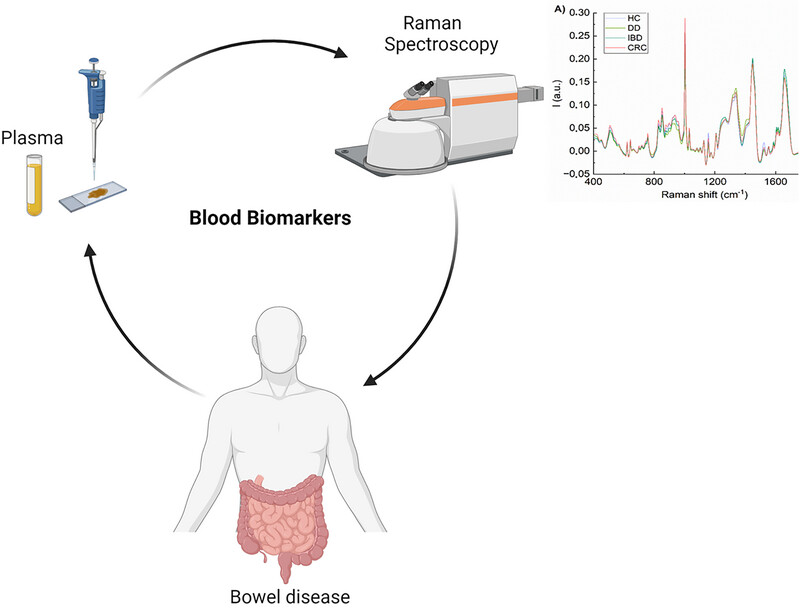
Blood serves as a valuable repository of disease biomarkers, offering insights for diagnosis. Raman spectroscopy (RS) emerges as a promising technique, capable of discerning distinct molecular signatures in biological samples. This study demonstrates RS's efficacy in distinguishing dried plasma samples across various bowel diseases .
Prognostic impact of age on outcomes of hepatic decompensation in patients with compensated cirrhosis (CHESS2102): an international, multicenter cohort study
- First Published: 03 November 2024
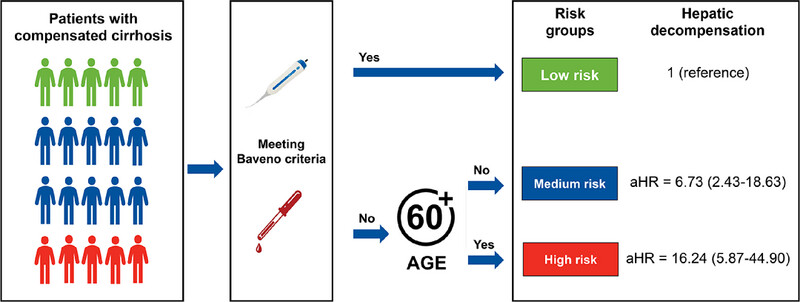
Graphical Abstract: In this international multicenter cohort study, our study showed that integrating age into the Baveno criteria could enhance the assessment of hepatic decompensation. The older patients (age ≥60 years) who do not meet Baveno criteria have the highest risk of decompensation. Here, age should be considered before discharging patients with compensated cirrhosis from the surveillance of hepatic decompensation.
An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts IgA nephropathy severity and progression
- First Published: 03 November 2024
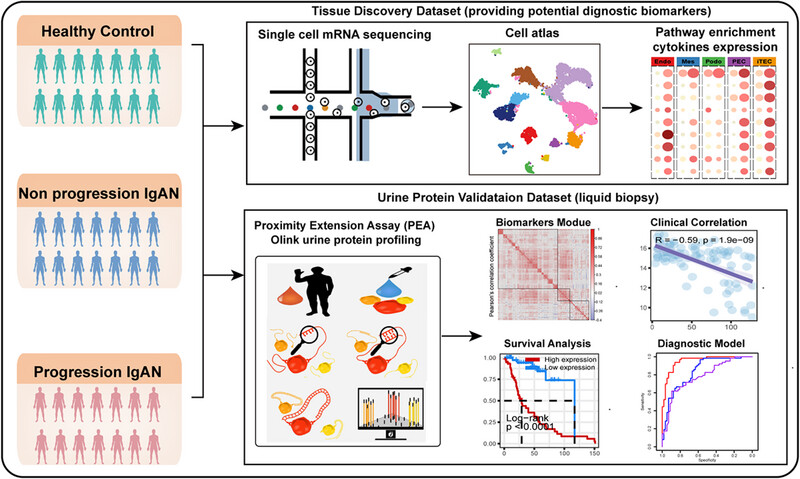
We combined the single-cell mRNA sequencing and proximity extension assay (PEA)-based Olink urine protein profiling method to uncover the inflammation cytokines MCP1 and CXCL12 as potential noninvasive biomarkers to predict the IgAN severity and progression, offering valuable insights for clinical management.
REVIEW
Immunometabolism: signaling pathways, homeostasis, and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 03 November 2024
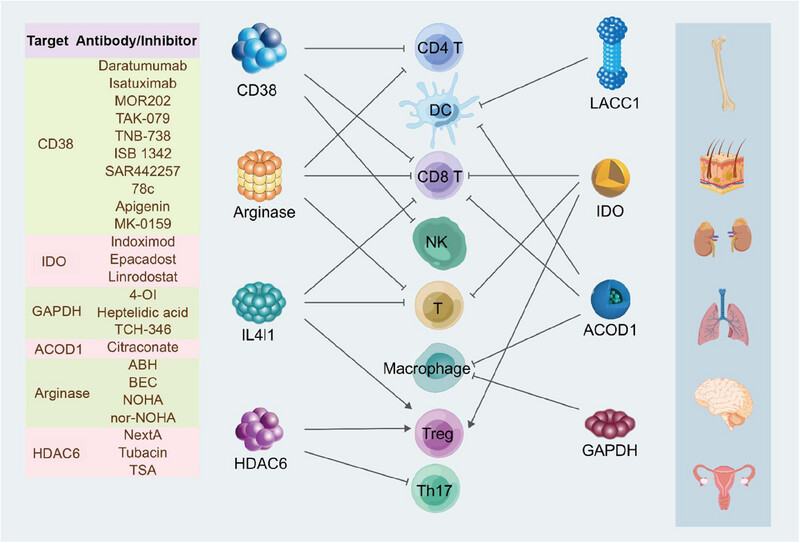
Metabolic enzymes can directly or indirectly impact the differentiation, activation, and proliferation of immune cells through the metabolites generated by their enzymatic activities or nonenzymatic signal interference, thereby modulating the function of immune cells. Currently, a variety of inhibitors or antibodies targeting metabolic enzymes have been developed for the treatment of multiple myeloma, melanoma, glioma, and other diseases .
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals IRF7 regulation of the tumor microenvironment in isocitrate dehydrogenase wild-type glioma
- First Published: 03 November 2024
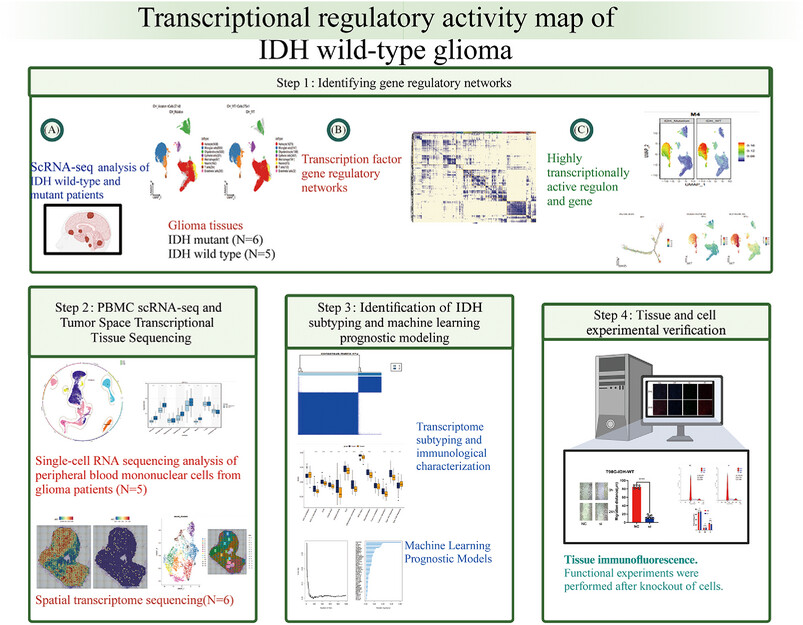
The study presents a transcriptional regulatory activity map for IDH wild-type gliomas, involving single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics to identify gene regulatory networks, machine learning models for IDH subtyping, and experimental validation, highlighting the role of IRF7 in glioma progression.
REVIEW
Synthetic circRNA therapeutics: innovations, strategies, and future horizons
- First Published: 09 November 2024
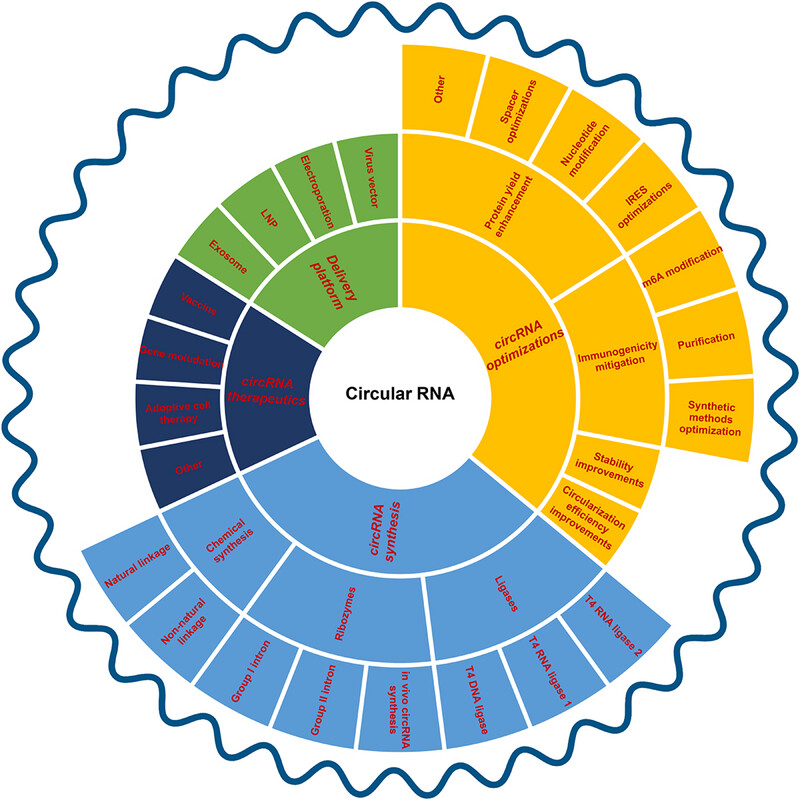
This pie chart visually represents the comprehensive content of this review, categorized into four main sections: circRNA synthesis, circRNA optimizations, delivery platforms, and circRNA therapeutics. Each section is further divided into specific subtopics, facilitating a quick and clear understanding of the key points covered in this review. circRNA, circular RNA
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Full-active pharmaceutical ingredient nanosensitizer for augmented photoimmunotherapy by synergistic mitochondria targeting and immunogenic death inducing
- First Published: 09 November 2024

A nanoscale full-active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) photo-immune stimulator was developed to overcome the limitations of PIT. Along with strengthening the ability to penetrate tumors deeply and inducing precise and potent mitochondria-targeted immunotherapy, this photoimmunotherapy demonstrated potent antitumor efficacy, achieving a remarkable inhibition rate >95% for both established primary tumors and distant abscopal tumors.
REVIEW
Circulating tumor DNA methylation detection as biomarker and its application in tumor liquid biopsy: advances and challenges
- First Published: 09 November 2024
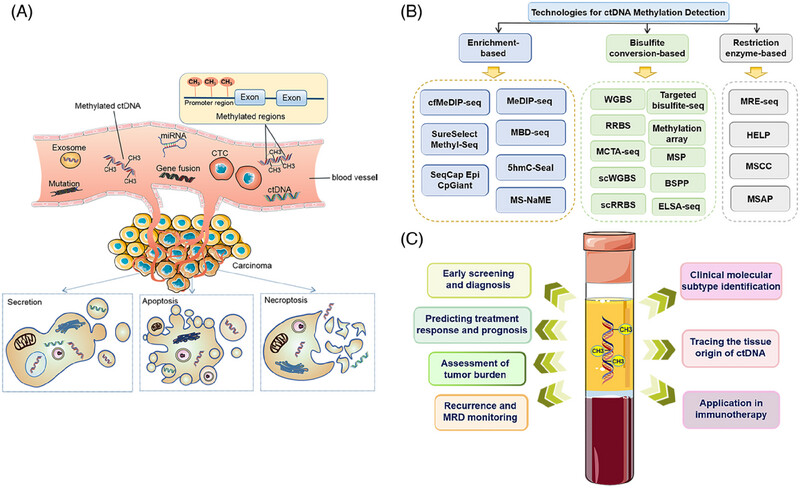
The origin of ctDNA in the bloodstream is derived from CTC, exosomes secreted by tumor cells, apoptotic tumor cells and necrotic tumor cells (A). ctDNA methylation status plays an important role in the occurrence and development of cancer and is a biomarker for tumor liquid biopsy. Therefore, the development and optimization of a variety of ctDNA methylation detection techniques (B) can realize their clinical applications in tumor precision diagnosis and treatment, including early screening and diagnosis of cancer, identification of clinical molecular subtypes, recurrence and minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring, predicting treatment response and prognosis, assessing tumor burden, and tracing tissue source (C).
Multifaceted role of TRIM28 in health and disease
- First Published: 11 November 2024
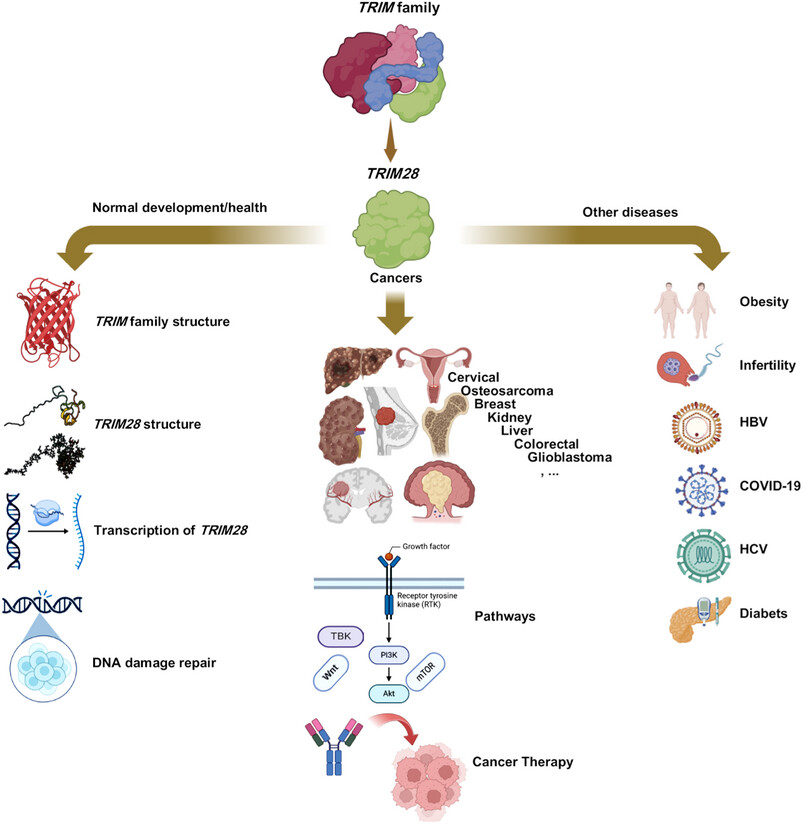
The role of TRIM28 in health and disease. This review demonstrated the role of TRIM28 in health and diseases specially cancers. It explored the vital role of TRIM28 in epigenetics, immune processes, and cancer therapy. This figure was created using BioRender and Microsoft Publisher 2016. HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus.
Metabolomics-driven approaches for identifying therapeutic targets in drug discovery
- First Published: 11 November 2024
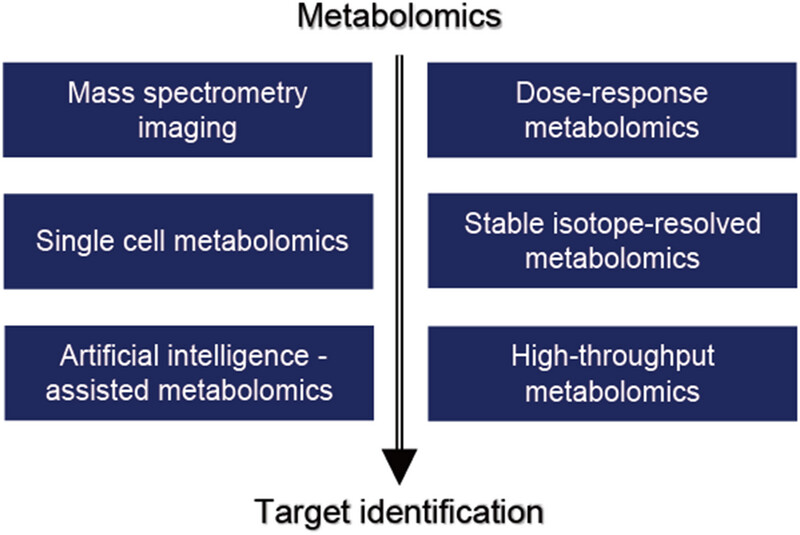
Various metabolomics-based methods were outlined that have been employed for target identification, such as dose–response metabolomics, stable isotope-resolved metabolomics, mass spectrometry imaging metabolomics. Furthermore, the emerging potentials of target identification based on metabolomics, such as artificial intelligence, single-cell metabolomics, and so on, have effectively enhanced the target identification process. Metabolomics has become a powerful tool in drug research and development. .
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
LINC01764 promotes colorectal cancer cells proliferation, metastasis, and 5-fluorouracil resistance by regulating glucose and glutamine metabolism via promoting c-MYC translation
- First Published: 11 November 2024
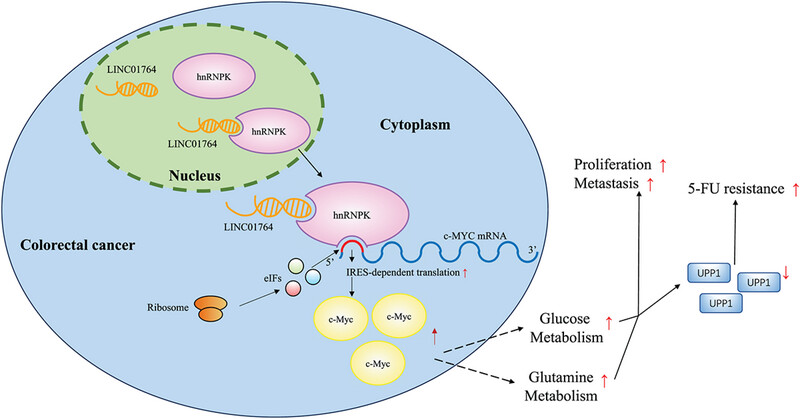
LINC01764 enhanced glycolysis and glutamine metabolism to promote colorectal cells progression and 5-FU resistance. LINC01764 specifically binds to hnRNPK and promotes its binding on c-MYC mRNA, which could promote IRES-dependent translation of c-MYC and thus performs its oncogenic functions. LINC01764 induces 5-FU chemoresistance by promoting the c-MYC, glucose, and glutamine metabolism pathways to downregulate UPP1 mRNA expression, which facilitates the conversion of 5-FU to active ingredient.