Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Molybdenum Dichalcogenide Cathodes for Aluminum-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 05 June 2020

Molybdenum dichalcogenides are interesting 2D-layered materials that have the capacity to intercalate molecules, atoms, and ions. The ability of different types of these dichalcogenides to act as hosts for tetrachloroaluminate, the charge carrier in aluminium-ion batteries, is studied. The cover picture shows an artistic interpretation of tetrachloroaluminates intercalating and deintercalating during charging and discharging of the battery. More details can be found in article number 2000038 by Thomas Nann and co-workers.
Inside Front Cover
An Energy Harvester for Low-Frequency Electrical Signals
- First Published: 05 June 2020

A technology to harvest energy from low frequency sources is designed, eliminating the need for up-conversion techniques. This is accomplished by modeling and tuning the resonant frequency of an energy harvesting system, which comprises a step-up transformer and a boost converter on a miniaturized printed circuit board prototype. More details can be found in article number 2000114 by Paulo R. F. Rocha and co-workers.
Inside Back Cover
A Potential Cathode Material for Rechargeable Potassium-Ion Batteries Inducing Manganese Cation and Oxygen Anion Redox Chemistry: Potassium-Deficient K0.4Fe0.5Mn0.5O2
- First Published: 05 June 2020

A layered oxide cathode is identified in the K2O–Fe2O3–MnO2 ternary phase system that shows facile and reversible K-ion mobility via a cumulative participation of cationic and anionic redox reaction, paving the way for the further development of high-energy-density cathode materials for K-ion batteries that effectively rely on both cation and anion multi-redox chemistry. More details can be found in article number 2000039 by Titus Masese, Zhen-Dong Huang, Yuki Orikasa, and co-workers.
Back Cover
Micronano Porous Mo2C@C Nanorods Composites as Robust Anodes for Li-ion Battery
- First Published: 05 June 2020

Micronano porous Mo2C@C nanorods composite anodes are successfully synthesized using abundant sodium chloride microparticle templates, and impressively deliver favorable electrochemical stability when applied in lithium-ion batteries. More details can be found in article number 202000189 by Chuang Yue, Fang Hu, and co-workers.
Masthead
Reviews
Molybdenum Disulphide Heterointerfaces as Potential Materials for Solar Cells, Energy Storage, and Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 16 January 2020
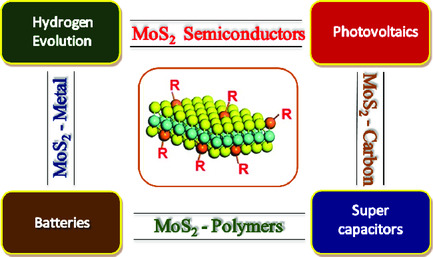
Molybdenum disulphide is an interesting, layered semiconductor which can be peeled down to a single unit cell (monolayer) and thus exhibits many interesting tunable optoelectronic properties. It is predicted that MoS2 and its interfaces will be significantly important materials for energy applications. This Review aims to cover many of these aspects.
Challenges and Perspectives of Metal-Based Proton Exchange Membrane's Bipolar Plates: Exploring Durability and Longevity
- First Published: 06 March 2020

Bipolar plates (BPs) have several important roles during proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) operation, and there are many challenges when it comes to finding suitable metal- and alloy-based BP materials such as their sustainability, durability, and longevity. In this Review, different metal and alloy types (copper, nickel, titanium, and aluminum and stainless-steel alloys) are discussed.
Advances and Future Challenges of Wax Removal in Pipeline Pigging Operations on Crude Oil Transportation Systems
- First Published: 13 March 2020

Mechanical pigging is the most widely used wax remediation technique for crude oil pipelines. This review seeks to clarify the current picture of wax removal in crude oil pipeline pigging. Relevant wax layer properties and wax removal mechanisms are discussed. Development of wax breaking force and wax removal efficiency models is analyzed. Key concerns for future endeavors are also highlighted.
Communications
An In-Plane Sliding Triboelectric Nanogenerator with a Multielectrode Array for Self-Powered Dynamic Addressing and Trajectory Tracking
- First Published: 17 April 2020
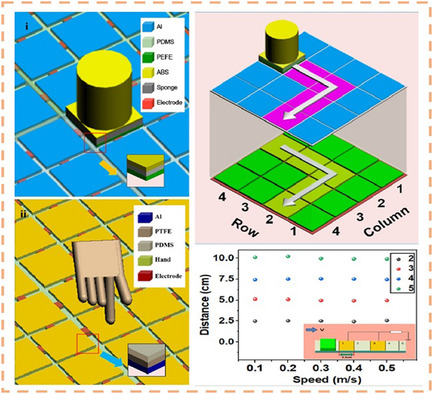
A subtle in-plane sliding triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) composed of a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) plate and an adjustable Al electrode array is reported. An array of Al electrodes linearly aligned along the sliding direction enables dynamic addressing. By integrating TENG units into a sensor matrix, two matrices show accurate mapping capability for stylus or finger movements, realizing real-time self-powered trajectory tracking.
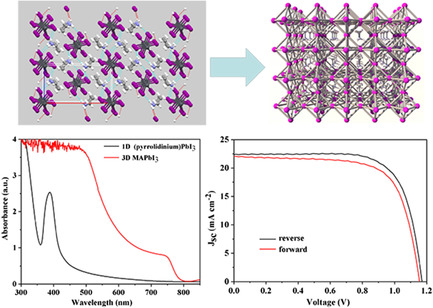
From 1D to 3D: Fabrication of CH3NH3PbI3 Perovskite Solar Cell Thin Films from (Pyrrolidinium)PbI3 via Organic Cation Exchange Approach
- First Published: 03 April 2020
Full Papers
Molybdenum Dichalcogenide Cathodes for Aluminum-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 10 April 2020
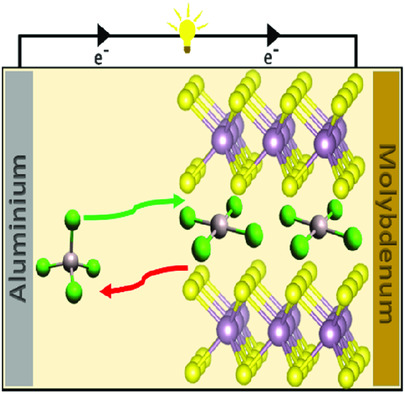
Molybdenum dichalcogenides (MoX2, where X = S, Se) are used as active cathode materials for nonaqueous aluminum-ion batteries. The batteries show clear discharge voltage plateaus in the ranges 1.6–1.4 V for MoS2 and MoSe2, and 0.6–0.5 V for MoSSe. Despite having similar structures, MoSe2 performs better than MoS2.
An Energy Harvester for Low-Frequency Electrical Signals
- First Published: 01 April 2020
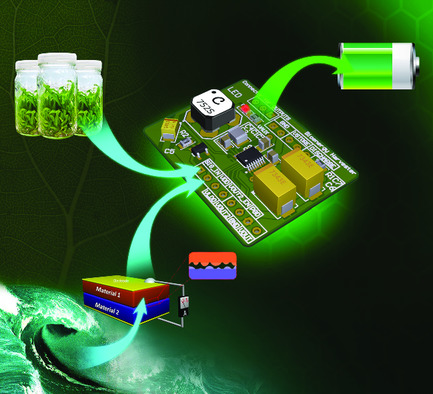
A technology to harvest energy from low-frequency sources is devised, eliminating the need for up-conversion techniques. This is accomplished by modeling and tuning the resonant frequency of an energy-harvesting system, which comprises a step-up transformer and a boost converter on a miniaturized printed circuit board prototype.
A Potential Cathode Material for Rechargeable Potassium-Ion Batteries Inducing Manganese Cation and Oxygen Anion Redox Chemistry: Potassium-Deficient K0.4Fe0.5Mn0.5O2
- First Published: 31 March 2020
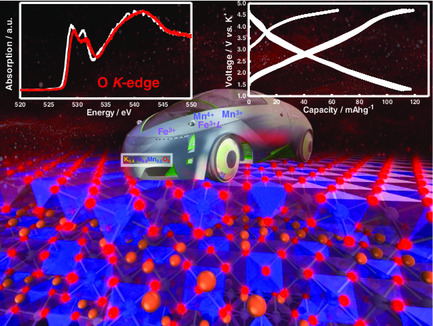
A potassium-deficient layered K0.4Fe0.5Mn0.5O2 cathode is identified in the K2O–Fe2O3–MnO2 ternary phase system that shows reversible potassium-ion (K-ion) reinsertion via a cumulative participation of cationic and anionic redox reactions, paving the way for the further development of high-energy-density cathode materials for K-ion batteries that effectively rely on both cation and anion multi-redox chemistry.
Micronano Porous Mo2C@C Nanorods Composites as Robust Anodes for Li-ion Battery
- First Published: 18 April 2020

Unique micronano porous Mo2C@C nanorod (NR) composite anodes are successfully synthesized using the raw materials of MoO3 NRs, polyacrylonitrile (PAN) polymer, and abundant sodium chloride (NaCl) microparticle templates. The obtained robust Mo2C@C NRs composite anodes deliver favorable electrochemical stability when applied in lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium Metal Battery Pouch Cell Assembly and Prototype Demonstration Using Tailored Polypropylene Separator
- First Published: 06 March 2020
Solar Reactor Demonstration of Efficient and Selective Syngas Production via Chemical-Looping Dry Reforming of Methane over Ceria
- First Published: 26 February 2020
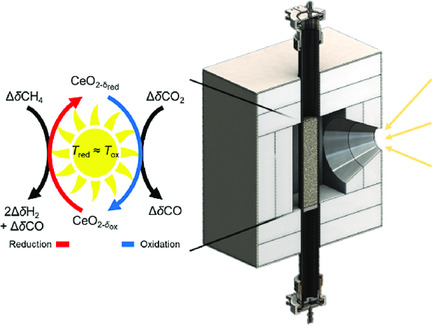
Efficient and selective production of liquid fuel precursors, H2 and CO, via solar thermochemical conversion of greenhouse gases, CH4 and CO2, is demonstrated in a prototype reactor, thus providing motivation for future implementation of solar energy in the sustainable production of long-chain hydrocarbons such as diesel or kerosene.
All-Carbon Hybrid Mobile Ion Capacitors Enabled by 3D Laser-Scribed Graphene
- First Published: 12 March 2020
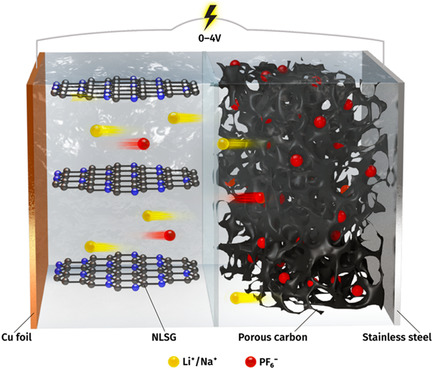
Laser-scribed nitrogen-doped 3D graphene (NLSG) is demonstrated as a binder-free, conductive, and additive-free anode for hybrid Li-ion capacitors (HLICs). The hybrid capacitors are assembled by combining 3D graphene anodes with porous carbon (PC) cathodes. The NLSG//PC HLICs show an energy density (including the total weight of two electrodes) of 186 Wh kg−1 at 200 W kg−1.
Facile Synthesis of Sheet Stacking Structure NiCo2S4@PPy with Enhanced Rate Capability and Cycling Performance for Aqueous Supercapacitors
- First Published: 03 March 2020
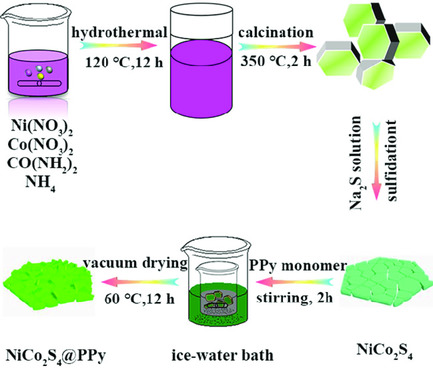
A NiCo2S4@PPy series with a sheet stacking structure and suitable pore size distribution is synthesized through a one-step vulcanization process and polymerization process, which delivers good electrochemical properties and remarkable cycling stability even at 20 A g−1. The significance for the general and low-cost route design of high-performance electrode materials in supercapacitor applications is explained.
Influence of Surface Modifier Molecular Structures on the Photovoltaic Performance of Sb2S3-Sensitized TiO2 Nanorod Array Solar Cells
- First Published: 12 March 2020
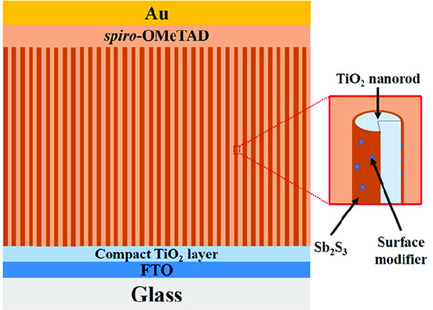
Surface modifiers with different functional groups and carbon numbers, including C10H21PO3H2, C12H25SO3Na, C3H7COOH, C5H11COOH, C7H15COOH, C11H23COOH, C13H27COOH, C15H31COOH, and C17H35COOH, are applied to modify Sb2S3-sensitized TiO2 nanorod arrays. These surface modifiers can penetrate into the pinholes, further absorb on the bare TiO2 surface, and prevent direct contact between TiO2 and spiro-OMeTAD.
Investigation into Properties of Carbohydrate Polymers Formed from Acid-Catalyzed Conversion of Sugar Monomers/Oligomers over Brønsted Acid Catalysts
- First Published: 13 March 2020
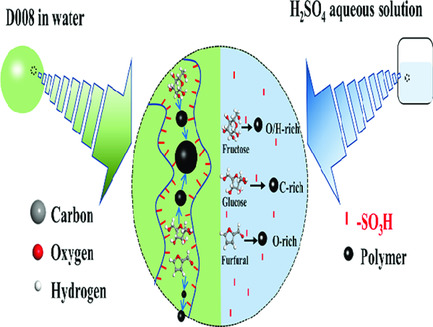
Influence of steric hindrance due to D008 on sugars is greater than that of furfural, as chain form of sugar monomers/oligomers is much bigger than that of furfural and sugars structures determine their polymers’ properties. Thermal stability of polymers derived from sugar oligomers is lower than that from sugar monomers due to more aliphatic structures in the resulting coke.
Porphyrin-Based Conducting Polymer Hydrogel for Supercapacitor Application
- First Published: 06 April 2020
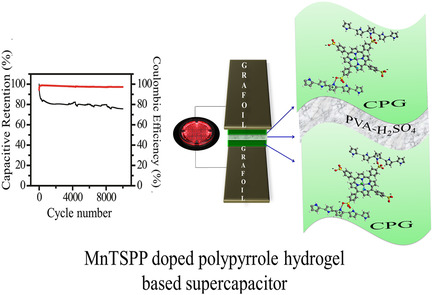
A novel 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-sulfonatophenyl)-21H,23H-porphine manganese (III) chloride (MnTSPP) doped polypyrrole hydrogel is prepared to construct an all solid state supercapacitor (ASSP) device. For the demonstration of the ASSP, a 2.4 V red light-emitting diode is powered by connecting three such solid supercapacitors in series to provide the required voltage.
Nanodiamond-Based Separators for Supercapacitors Realized on Paper Substrates
- First Published: 03 March 2020
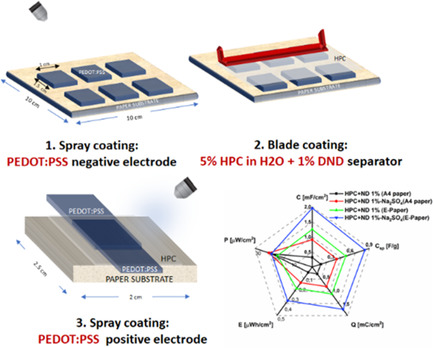
A scalable, low-cost, and easy-to-process approach for the preparation of symmetric paper-based supercapacitors using spray and blade coating techniques is reported. Following a green strategy, all components are formulated in water-based dispersions. The novelty of this work is the use of hydroxypropyl cellulose charged with detonation nanodiamonds and sodium sulfate to realize the separator and electrolyte.
Oxygen-Carrier Development of Calcium Manganite–Based Materials with Perovskite Structure for Chemical-Looping Combustion of Methane
- First Published: 28 February 2020
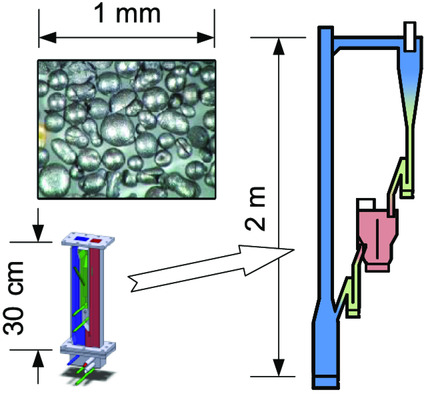
Production and testing of calcium manganite–based oxygen-carrier materials are upscaled. Part of the process is substitution of pure chemicals with inexpensive raw materials. Results are presented from chemical-looping combustor units of 300 W and 10 kW, and material characterization. The composition of the oxygen-carrier materials seems robust and flexible with respect to the precursors used in its manufacturing.
High Capacity and Reversibility of Oxygen-Vacancy-Controlled MoO3 on Cu in Li-Ion Batteries: Unveiling Storage Mechanism in Binder-Free MoO3−x Anodes
- First Published: 02 April 2020
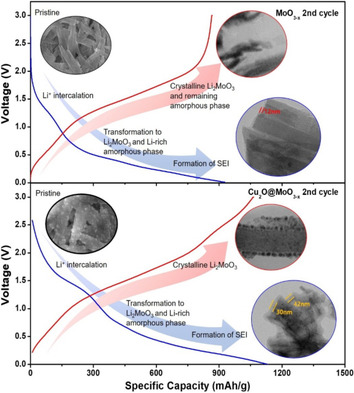
The Li-storage mechanism of MoO3−x demonstrates a chain reaction; an irreversible reaction from MoO3−x to crystalline Li2MoO3 and a reversible reaction between crystalline Li2MoO3 and amorphous LixMoOy. Furthermore, improvements of the mechanism are shown by conjugating the MoO3−x with Cu2O. Cu2O leads to cycling stability due to higher reversibility of MoO3−x and thicker solid-electrolyte interphase formation, functioning as an effective catalyst.
Piezoelectric Nanogenerators Based on Helical Carbon Materials and Polyvinyledenedifluoride–Trifluoroethylene Hybrids with Enhanced Energy-Harvesting Performance
- First Published: 24 March 2020
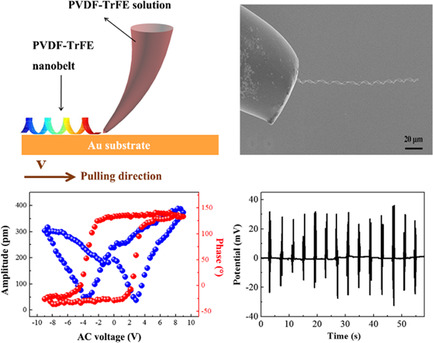
Helical piezoelectric nanogenerators based on poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene) (PVDF–TrFE) and their hybrid nanobelts are prepared by a direct-write technique. The increase in the piezoelectric coefficient (d33) indicates a high crystalline degree of helical. The significant improvement of output potentials is observed for piezoelectric nanogenerators based on graphene/PVDF–TrFE hybrid nanobelts.
A High-Efficiency, Portable, Solar-Powered Cooling System Based on a Foldable-Flower Mechanism and Wireless Power Transfer Technology for Vehicle Cabins
- First Published: 25 March 2020
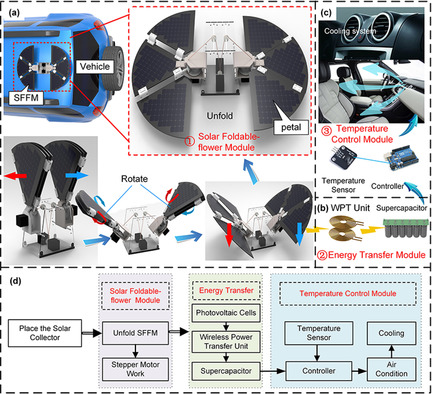
A portable solar-powered cooling system (SPCS) is proposed to cool cabins of vehicles parked under the scorching sun. A novel foldable-flower mechanism is designed to collet solar energy. Meanwhile, wireless power transfer technology is applied to cooling systems of vehicles. Experiment and simulation results indicate that the SPCS has a considerable effect on cooling the vehicle cabin.
Waste-Derived Heteroatom-Doped Activated Carbon/Manganese Dioxide Trio-Composite for Supercapacitor Applications
- First Published: 06 April 2020
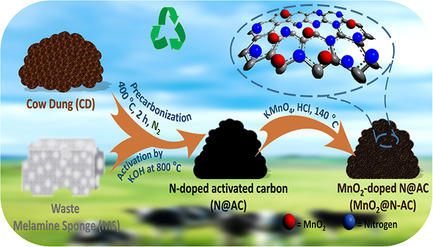
The consumption of biological-waste materials to produce heteroatom-doped activated carbon (AC) and subsequent metal oxide doping for high-performance supercapacitors is defined. Herein, easily available and cheap biowastes, i.e., cow dung, and low priced, nontoxic waste melamine sponge are consumed to produce nitrogen-functionalized AC, subsequently the economically inexpensive manganese dioxide (MnO2) is doped to provide efficient energy-storage materials.
Impact of Highly Stable Catalyst Support Materials on Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Performance
- First Published: 27 February 2020
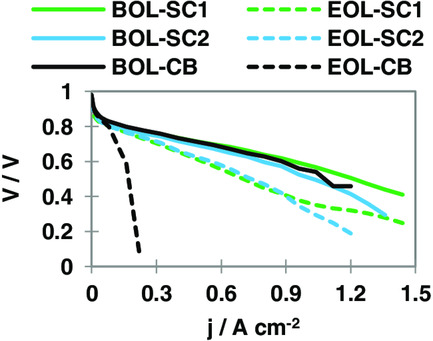
Highly stabilized noble metal support materials for a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) cathode is presented. The sensitivity of ionomer amounts on the catalyst layers for several supported catalysts is investigated. Catalysts prepared with stabilized carbon supports are found with higher stability as well as identical performance as traditional carbon black supports while applying to the cathode for PEMFC.
Catalytic Toluene Reforming with In Situ CO2 Capture via an Iron–Calcium Hybrid Absorbent for Promoted Hydrogen Production
- First Published: 04 April 2020
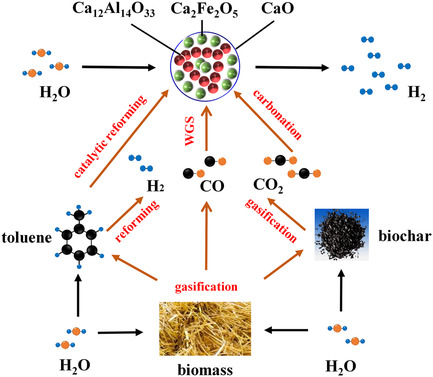
A CaO-based iron–calcium hybrid absorbent is synthesized by a modified sol–gel method for biomass calcium looping gasification. Due to synergetic effects of mayenite and brownmillerite, this absorbent presents stable cyclic carbonation reactivity, high mechanical strength as well as maximum toluene conversion and hydrogen yield due to improved absorbent structure, catalytic tar reforming, and enhanced water gas shift reaction.
Li2S–Li3PS4 (LPS) Composite Synthesized by Liquid-Phase Shaking for All-Solid-State Lithium–Sulfur Batteries with High Performance
- First Published: 15 April 2020
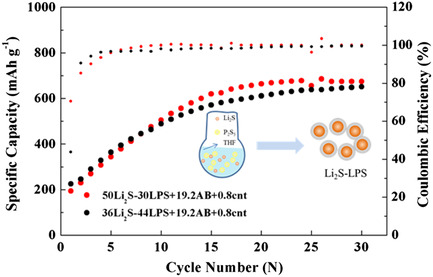
Li2S–Li3PS4 (LPS) composite materials are prepared by in situ growth of LPS on the surface of Li2S through the method of liquid-phase shaking. The composite cathode with high active material Li2S, whose content is up to 50%, delivers a discharge specific capacity of 674.3 mAh g−1 after 30 cycles at a current density of 0.2 mA cm−2.
Production Research as Key Factor for Successful Establishment of Battery Production on the Example of Large-Scale Automotive Cells Containing Nickel-Rich LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 Electrodes
- First Published: 02 April 2020
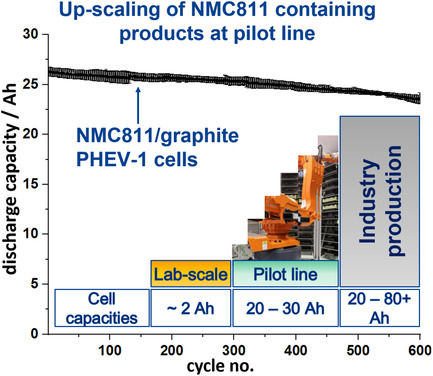
The adoption of lab-formulations in automotive lithium-ion battery (LIB) mass production is not a straightforward one-to-one transfer. Pilot lines serve as a bridge between laboratory and industry and allow for mass production research. Automotive NMC811/graphite PHEV-1 cells are successfully produced under close-to-mass production conditions and show excellent electrochemical performance with a capacity retention of 96.6% after 300 cycles.
Core–Shell Structure and X-Doped (X = Li, Zr) Comodified O3-NaNi0.5Mn0.5O2: Excellent Electrochemical Performance as Cathode Materials of Sodium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 15 April 2020
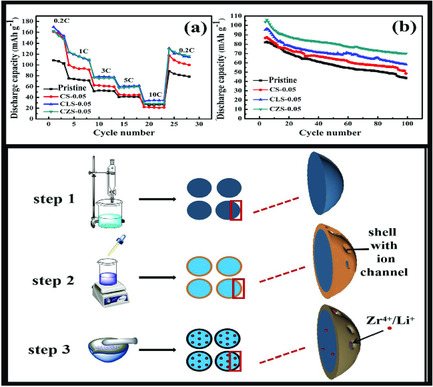
Cathode materials O3-Na0.98X0.02Ni0.5Mn0.5O2@5%Na–Mn–O (X = Li, Zr) are synthesized through an uncomplicated synthesis method. The utilization of an optimal ratio of high-nickel core and high concentration ultrathin Mn4+ shell ensures that the cycle stability is improved by ≈1.2 times, where Mn4+ is nonelectrochemically active. The incorporation of Li and Zr further improves the rate performance and initial capacity.
Three-Dimensional Porous Fe–N–C Derived from Iron-Citrate-Functionalized Melamine Foam as a Highly Active Oxygen Reduction Catalyst for Zn–Air Batteries
- First Published: 04 April 2020
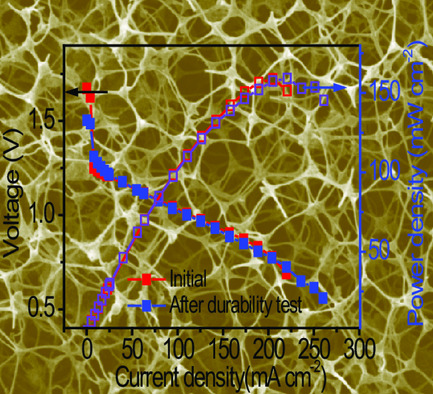
A new 3D porous Fe–N–C composite is constructed, where melamine foam is used as the self-scarified template, and citric acid (CA) and iron salts are used as the precursors. The Zn–air battery fabricated with CA-Fe/MF-N900 as the cathode catalyst displays outstanding discharging performance with peak power density of 158 mW cm−2 and long-term stability.
In Situ Template-Sacrificing Approach to a Highly Conductive 3D Hybrid Interlayer of an Advanced Lithium–Sulfur Battery Separator
- First Published: 07 April 2020
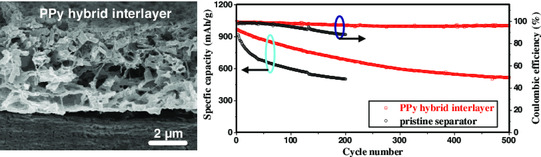
An in situ template-sacrificing approach is developed to produce a polypyrrole (PPy) hybrid interlayer with a 3D network on a commercial separator. The combination of high conductivity and strong absorption makes the PPy hybrid interlayer effective to suppress the shuttle effect, thus contributing to superior Li–S battery performance.
Polarization Analysis of Gas Diffusion Electrode with Different Fabrication Parameters in Metal–Air Batteries
- First Published: 08 April 2020
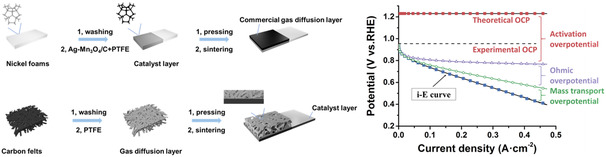
Herein, a polarization separation method from total polarization curve to single polarization of gas diffusion electrode (GDE) in metal–air batteries is first proposed, which is applied in the investigation of detailed polarization behaviors of the GDE by changing the fabrication parameters. Through this analysis, the structure–performance relationship of GDE can be achieved, to improve the electrode performance.
WOx-Modified Ni Catalyst Supported on Mesoporous Silica with Extra-Large Mesopores for CO Methanation
- First Published: 04 April 2020
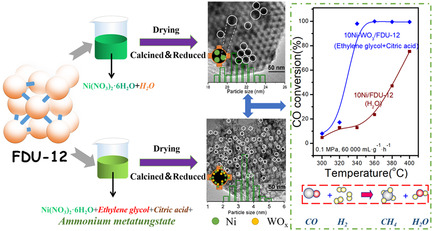
Herein, a group of Ni–WOx/FDU-12 (x < 3) catalysts is prepared for CO methanation. The various characterization results show that the utilization of ethylene glycol and citric acid significantly reduces the size of Ni, and the addition of WOx promoter further improves both Ni dispersion and distinctly the performance of the catalysts.
Organic Solar Cells' Efficiency Enhanced by Perylene Monoimide Phosphorus Salt Cathode Interfacial Layer
- First Published: 04 April 2020
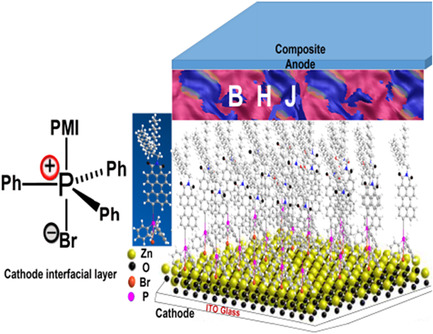
Organic phosphorus and perylene-imide derivatives (PDI or PMI) as electron transfer buffer layers to construct composite cathodes are arousing great interest and have achieved an impressively high power conversion efficiency. Herein, two perylene monoimide phosphorus salts are used as cathode interfacial layers. One of the two salts has an obviously positive effect on organic solar cell devices.
Flexible Textile-Based Self-Driven Sensor Used for Human Motion Monitoring
- First Published: 09 April 2020
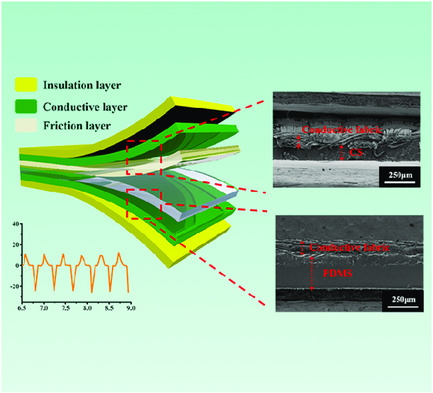
Herein, a self-driven sensor, whose application is the effective recognition of human motion through triggered electrical signals, is proposed, featuring the simple integrated structure, ease of manufacturing, and relatively low cost, as wearable flexible textile-based material. It can effectively perform motion monitoring without any external power sources. What's more, it shows rapid response performance and outstanding durability in practical applications.
MoOx-Doped Ordered Mesoporous Ni/Al2O3 Catalyst for CO Methanation
- First Published: 14 April 2020
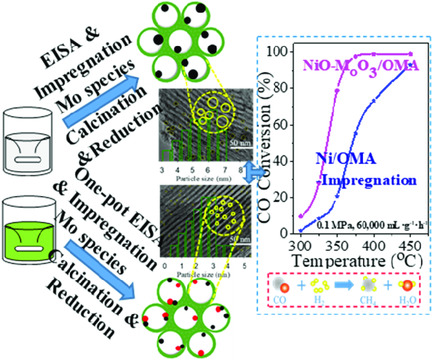
MoOx-doped (x < 3) ordered mesoporous Ni/Al2O3 catalysts are prepared by two different methods, including the impregnation method and evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) method. The results show that the synthesized mesoporous catalysts possess the desired textural properties and exhibit high low-temperature catalytic activity and long-lived stability.
Triboelectric Harvesting by a Dual-Tip Peak Power Multiplier under Airtight Condition
- First Published: 14 April 2020
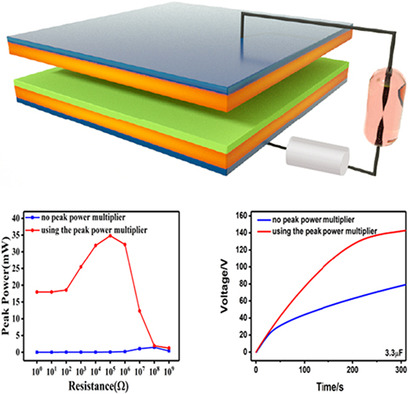
A dual-tip-assisted triboelectric nanogenerator is demonstrated that uses a peak power multiplier. The gas in the dual-tip structure ionizes to form a conductive path, which increases the peak power from the triboelectric nanogenerator. The influence of the peak power multiplier's design parameters on the output voltage is investigated to provide guidance for optimization.
In Situ Incorporation of Super-Small Metallic High Capacity Nanoparticles and Mesoporous Structures for High-Performance TiO2/SnO2/Sn/Carbon Nanohybrid Lithium-Ion Battery Anodes
- First Published: 10 April 2020
Incorporation of super-small sized metallic high capacity tin-based component and creation of mesoporous structures within TiO2/C nanohybrids using difunctional methacrylate monomers as solvent and carbon source achieves high reversible capacities, excellent rate capability, and good capacity retention simultaneously.
On the Use of Carbon Nanotubes in Prototyping the High Energy Density Li-ion Batteries
- First Published: 10 April 2020

The main aspects of LiFePO4-based high areal capacity electrode fabrication using carbon nanotubes as a conductive additive are considered. Prototyping the pouch cell with obtained high areal capacity cathodes and specific energy density of 150 Wh kg (cell)−1/295 Wh L (cell)−1 confirms practical applicability of the presented results.
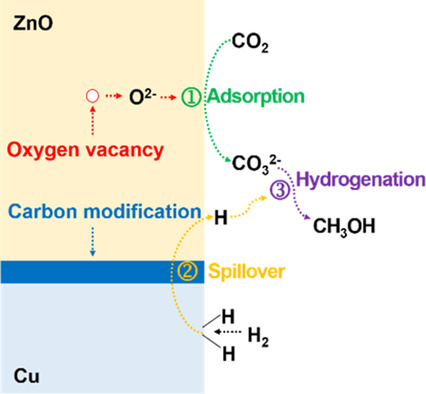
Carbon-Modified CuO/ZnO Catalyst with High Oxygen Vacancy for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol
- First Published: 10 April 2020
Effect of Calcination and Reduction Temperatures on the Catalytic Activity of Ru/La0.5Ce0.5O1.75 for Ammonia Synthesis under Mild Conditions
- First Published: 10 April 2020
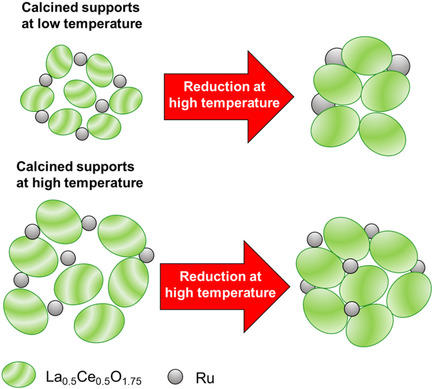
The effect of high-temperature calcination of the La0.5Ce0.5O1.75 support is examined. Calcination at high temperature prevents sintering of the support and agglomeration of Ru particles during reduction of Ru/La0.5Ce0.5O1.75 catalyst at high temperature. The obtained catalysts are electron rich, have a high number of active sites, and have high NH3-synthesis activity.
Heat Treatment–Controlled Morphology Modification of Electrospun Titanium Oxynitride Nanowires for Capacitive Energy Storage and Electrocatalytic Reactions
- First Published: 23 April 2020
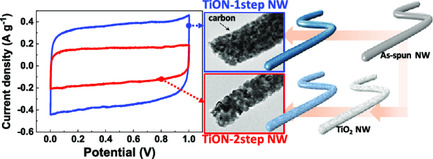
Electrospun titanium oxynitride nanowires (TiON NWs) with different morphologies are fabricated by post-annealing processes (roughly categorized as 1step [nitridation] and 2step [oxidation followed by nitridation]) of as-spun nanowires, and corresponding changes of physicochemical/electrochemical characteristics are observed in supercapacitor and oxygen reduction reactions. Owing to advantageous morphological features, directly nitridated TiON NW shows superior electrochemical performance.
Secondary Reactions and the Heat of Pyrolysis of Wood
- First Published: 04 April 2020
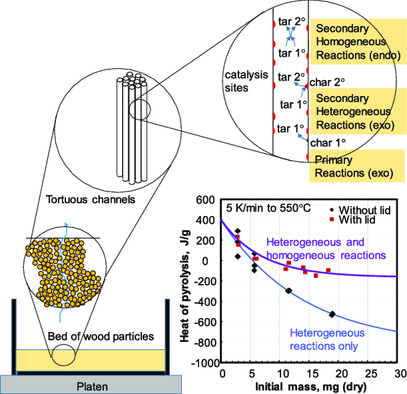
Slow pyrolysis of wood is explained by a parallel reaction scheme, where dedicated fractions of the primary reactive volatiles undergo heterogeneous and homogeneous secondary reactions. The model is able to predict the char yield and heat of pyrolysis as a function of the sample mass, system pressure, and heating rate.
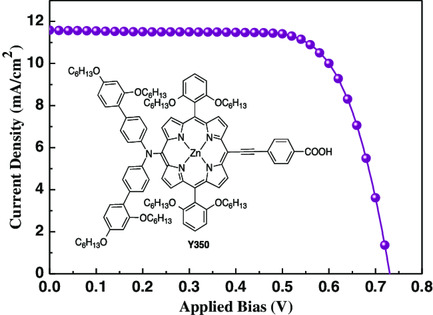
Photovoltaic Performance of Porphyrin-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells with Binary Ionic Liquid Electrolytes
- First Published: 15 April 2020
Enabling Dual-Ion Batteries via the Reversible Storage of Pyr14+ Cations into Coronene Crystal
- First Published: 18 April 2020
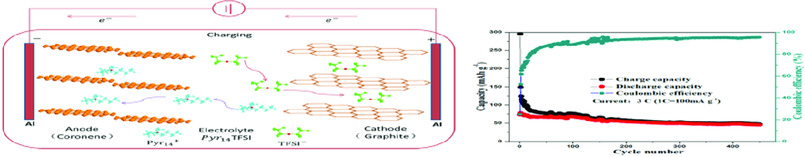
An organic/graphite dual-ion battery with ionic liquid electrolyte is fabricated using coronene as the anode material, and with graphite as counter electrode. The battery shows excellent cycling performance, and obtains a high initial discharge specific capacity of ≈73.3 mA h g−1 at 3 C (1 C = 100 mA g−1), outperforming most of the dual-graphite batteries using ionic liquid as electrolyte.