Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 02 October 2020
Infrared spectroscopy enables insight into light-activated riboflavin-induced collagen cross-linking for future intervertebral disc treatment and repair.
Further details can be found in the article by Ioannis Vasilikos, Julian Haas, Graciosa Q. Teixeira, Julia Nothelfer, Cornelia Neidlinger-Wilke, Hans-Joachim Wilke, Andreas Seitz, Demetrios G. Vavvas, Josef Zentner, Jürgen Beck, Ulrich Hubbe, and Boris Mizaikoff (e202000110).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 02 October 2020
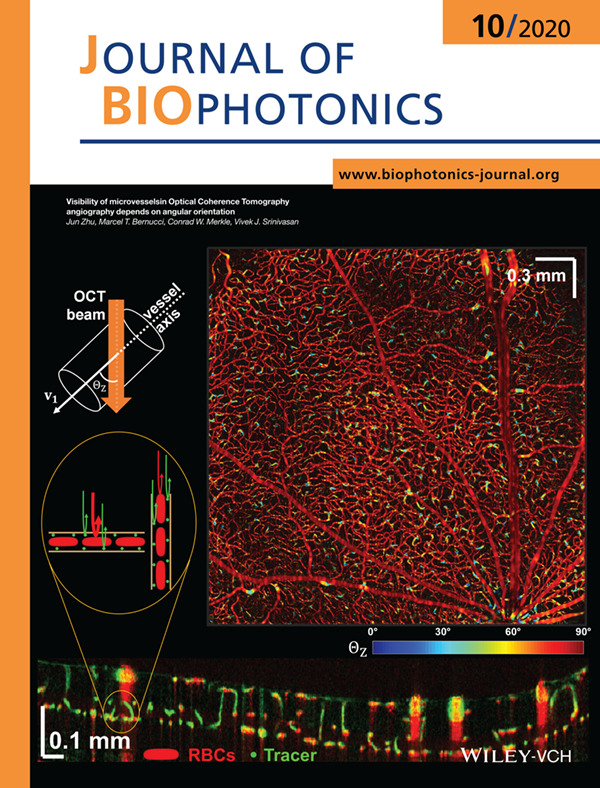
Optical Coherence Tomography angiography (OCTA) is widely used to image chorioretinal vasculature, with contrast that derives from scattering and motion of red blood cells (RBCs). In the rat eye, a scattering tracer highlights vertical vessels which are not visualized by intrinsic RBC scattering alone. The dependence of microvessel OCTA on angular orientation, explored in this work, represents a potential artifact that should be considered in the clinical interpretation of OCTA.
Further details can be found in the article by Jun Zhu, Marcel T. Bernucci, Conrad W. Merkle, and Vivek J. Srinivasan (e202000090).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 02 October 2020
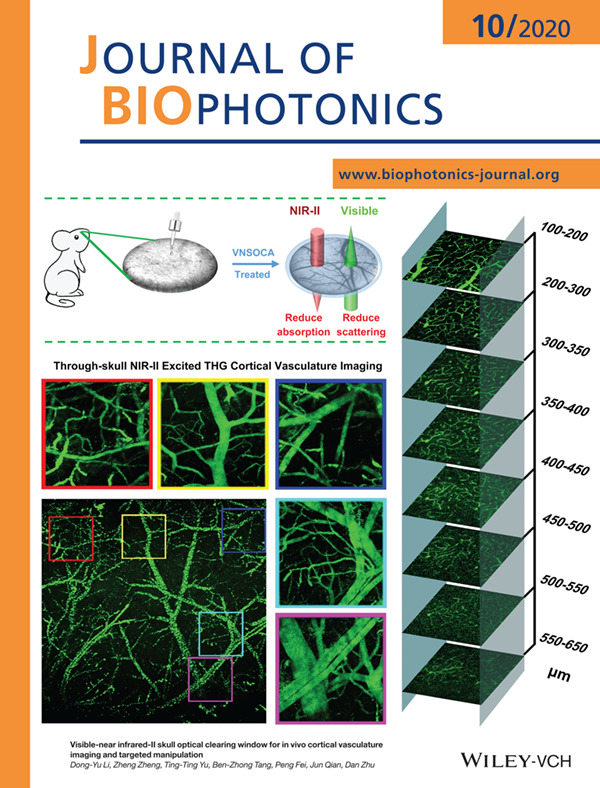
Optical clearing skull window is a novel technique compared to the traditional surgery based cranial window, which could reduce the scattering of skull and make it transparent to visible light. Here, the NIR-II optimized skull clearing window was established. In the application of NIR-II excited THG microscopy, the imaging depth was more than 3 times as it without optical clearing, and close to it with the open-skull window. In addition, the established skull optical clearing window promises to realize NIR-II laser induced targeted injury of cortical singlevessel.
Further details can be found in the article by Dong-Yu Li, Zheng Zheng, Ting-Ting Yu, Ben-Zhong Tang, Peng Fei, Jun Qian, Dan Zhu (e202000142).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 02 October 2020
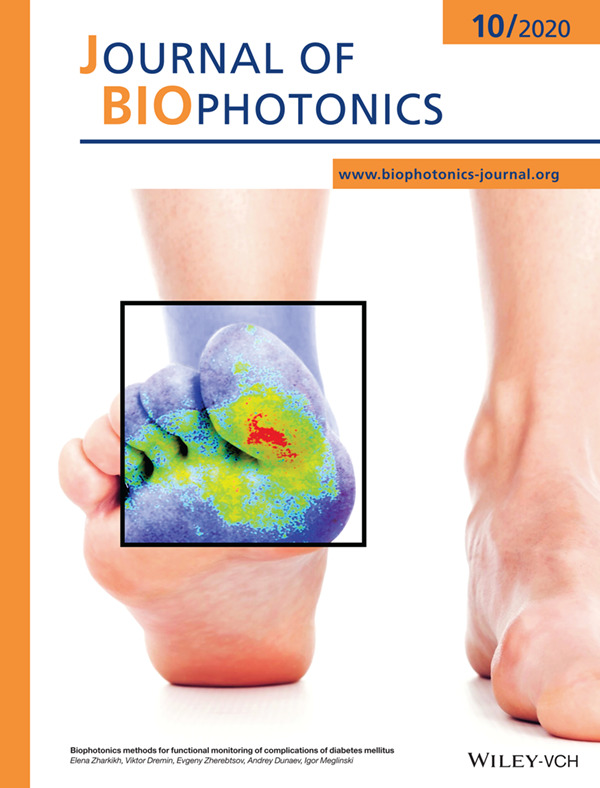
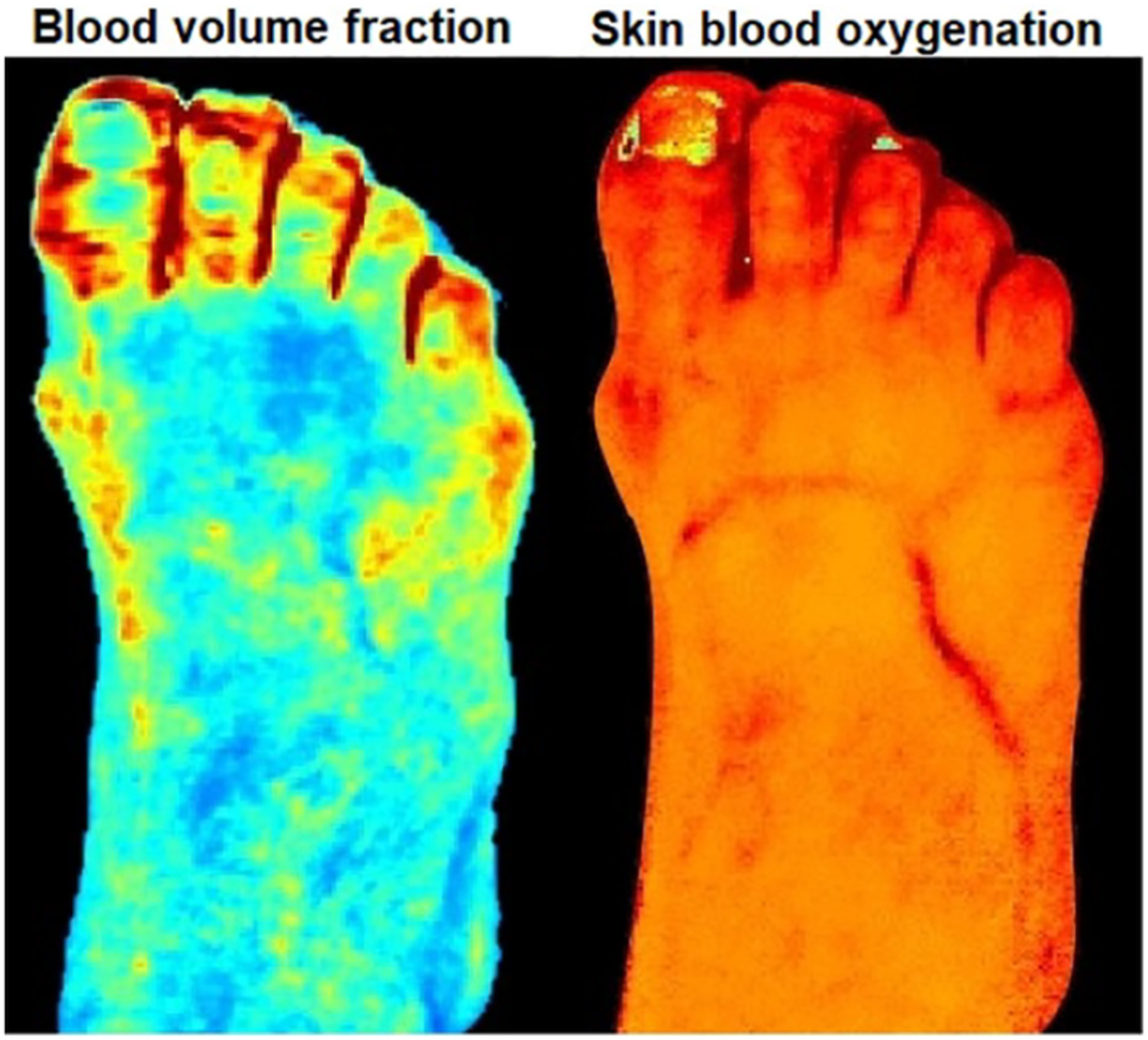
Biophotonics technologies allow obtaining clinically important diagnostic information about pathological changes that occur in diabetes mellitus, including impaired tissue perfusion and oxygen saturation, structural and functional changes. A review presents the current state-of-the-art in biophotonics technologies and their transfer to clinical use to identify the complications of diabetes mellitus, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, and cardiovascular disease as well as the methods used in the evaluation of foot ulceration and wound healing processes. Further details can be found in the article by Elena Zharkikh, Viktor Dremin, Evgeny Zherebtsov, Andrey Dunaev, and Igor Meglinski (e202000203).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 02 October 2020

Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) has been proposed as a noninvasive modality for detecting complications in patients undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and it can simultaneously reveal the global circulatory status of thesepatients. We monitor the real-time changes of oxygenation in peripheral tissues to demonstrate the feasibility of NIRS for optimizing ECMO therapy.
Further details can be found in the article by Hsiao-Huang Chang, Yi-Chih Chen, Chun-Jung Huang, Chia-Cheng Kuo, Yi-Min Wang, and Chia-Wei Sun (e202000116).
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLES
Biophotonics methods for functional monitoring of complications of diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 12 July 2020
Comparative study on the inactivation of MS2 and M13 bacteriophages using energetic femtosecond lasers
- First Published: 17 June 2020

We study and compare the mJ femtosecond laser inactivation of MS2 and M13, two bacteriophages with considerably different structures and genome compositions. We show that the inactivation mechanisms for these two are radically different. For MS2, inactivation is mainly due to the protein aggregation of the viral capsid. On the other hand, the inactivation mechanism of M13 is related to the deterioration of their viral capsid.
LETTERS
Raman spectroscopy-based detection of RNA viruses in saliva: A preliminary report
- First Published: 01 July 2020

Non-invasive low-cost diagnostic tests capable of detecting pathogens at the point of care could play a significant role in early diagnosis. We present a proof of concept using Raman spectroscopy to detect a distinct RNA viral signature in human saliva, with potential for application to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Deep learning protocol for improved photoacoustic brain imaging
- First Published: 21 July 2020
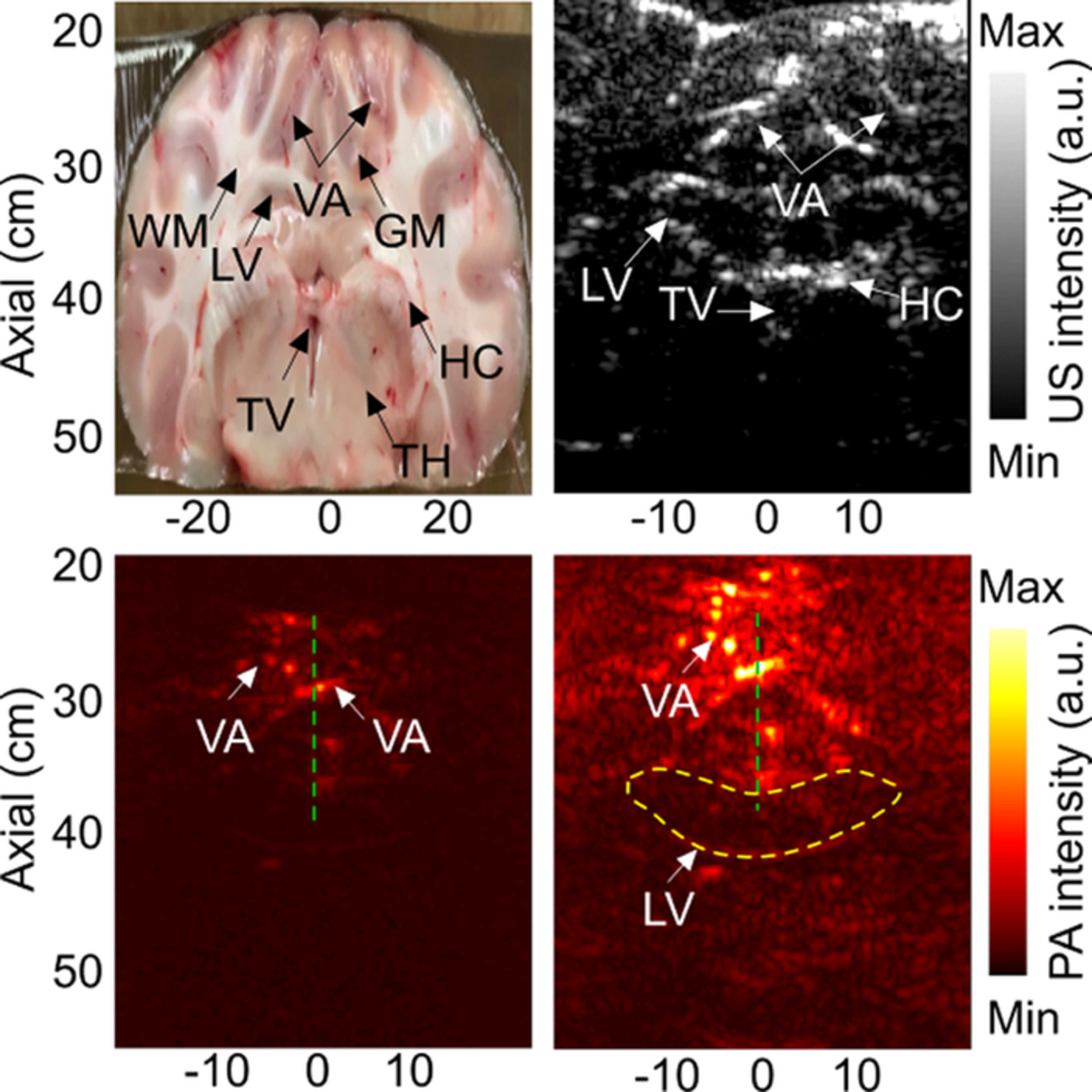
One of the key limitations for the clinical translation of photoacoustic imaging is penetration depth that is linked to the tissue maximum permissible exposures (MPE) recommended by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Here, we propose a method based on deep learning in order to enhance the deep structures in the image of the brain. The proposed method is evaluated in an in vivo sheep brain imaging experiment.
FULL ARTICLES
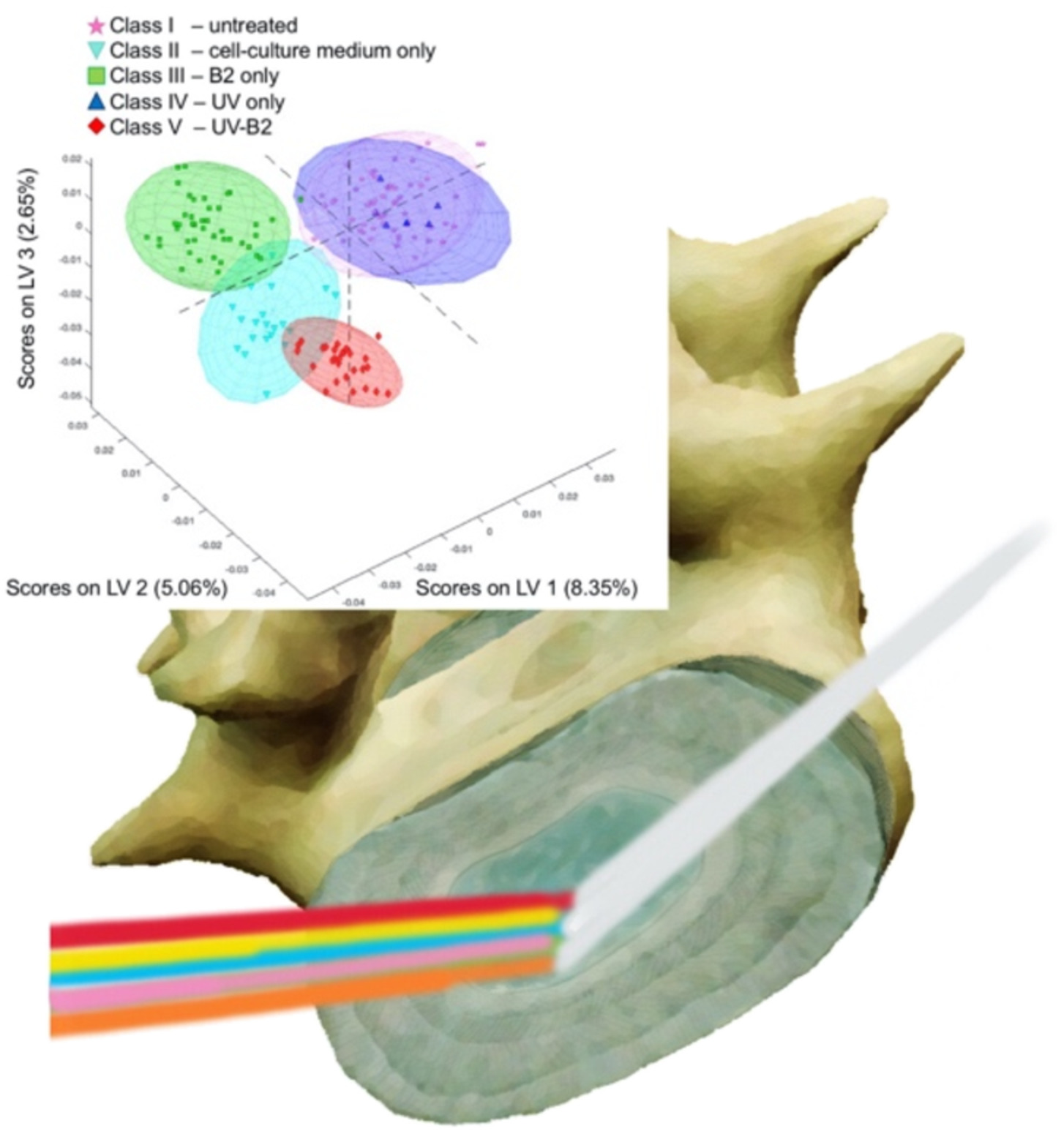
Infrared attenuated total reflection spectroscopic surface analysis of bovine-tail intervertebral discs after UV-light-activated riboflavin-induced collagen cross-linking
- First Published: 26 June 2020
Visibility of microvessels in Optical Coherence Tomography angiography depends on angular orientation
- First Published: 29 May 2020
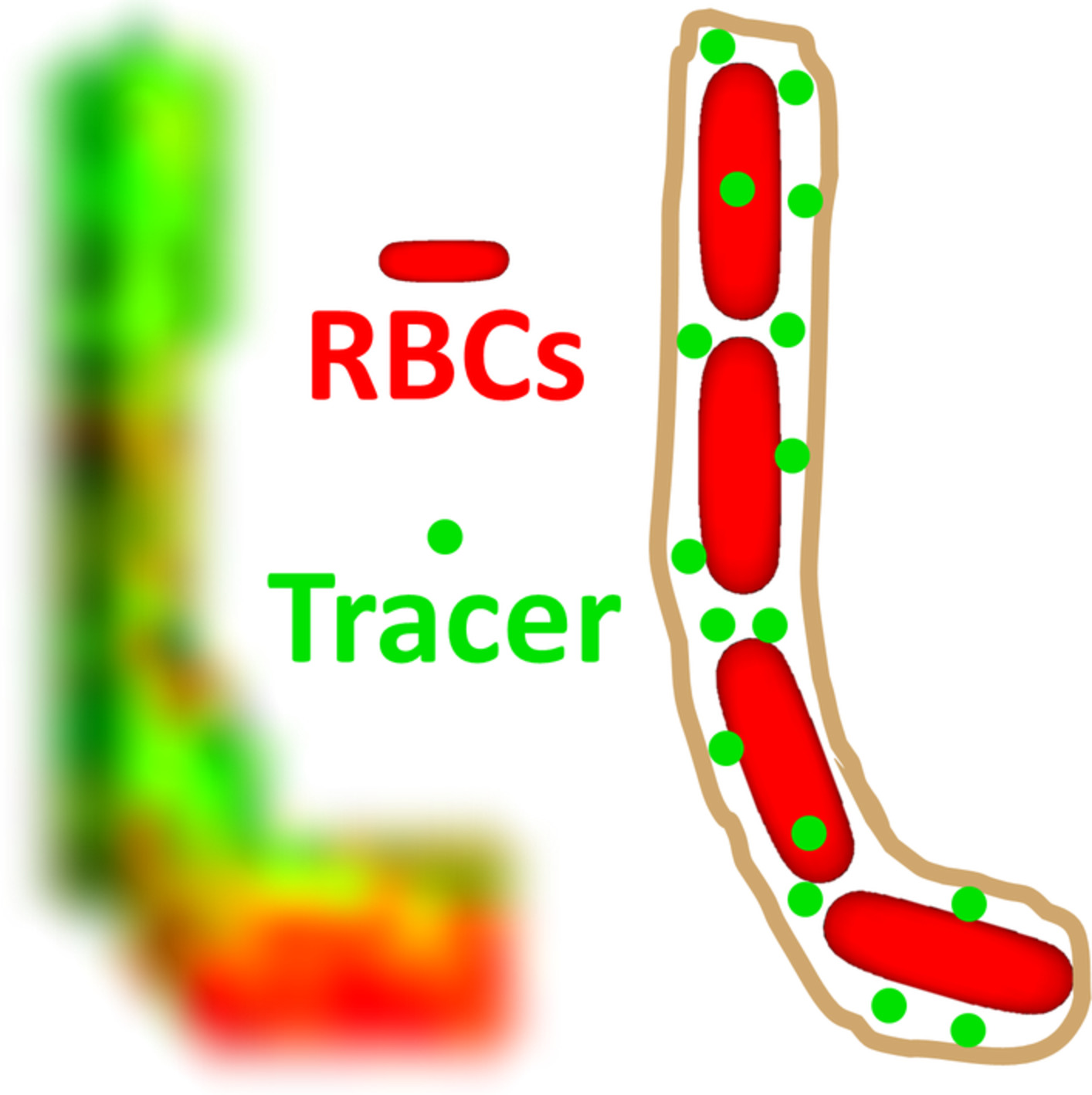
Optical Coherence Tomography angiography (OCTA) visualizes microvessels without an exogenous contrast agent and enjoys widespread clinical use. Angiography is based on intrinsic backscattering from moving red blood cells, but it is not known how well angiography can detect and visualize red blood cells in microvessels of differing orientations. Here, using an intravascular tracer as a reference, we show that intrinsic angiography often misses vertical retinal vessels, parallel to the incident light.
Visible-near infrared-II skull optical clearing window for in vivo cortical vasculature imaging and targeted manipulation
- First Published: 26 June 2020
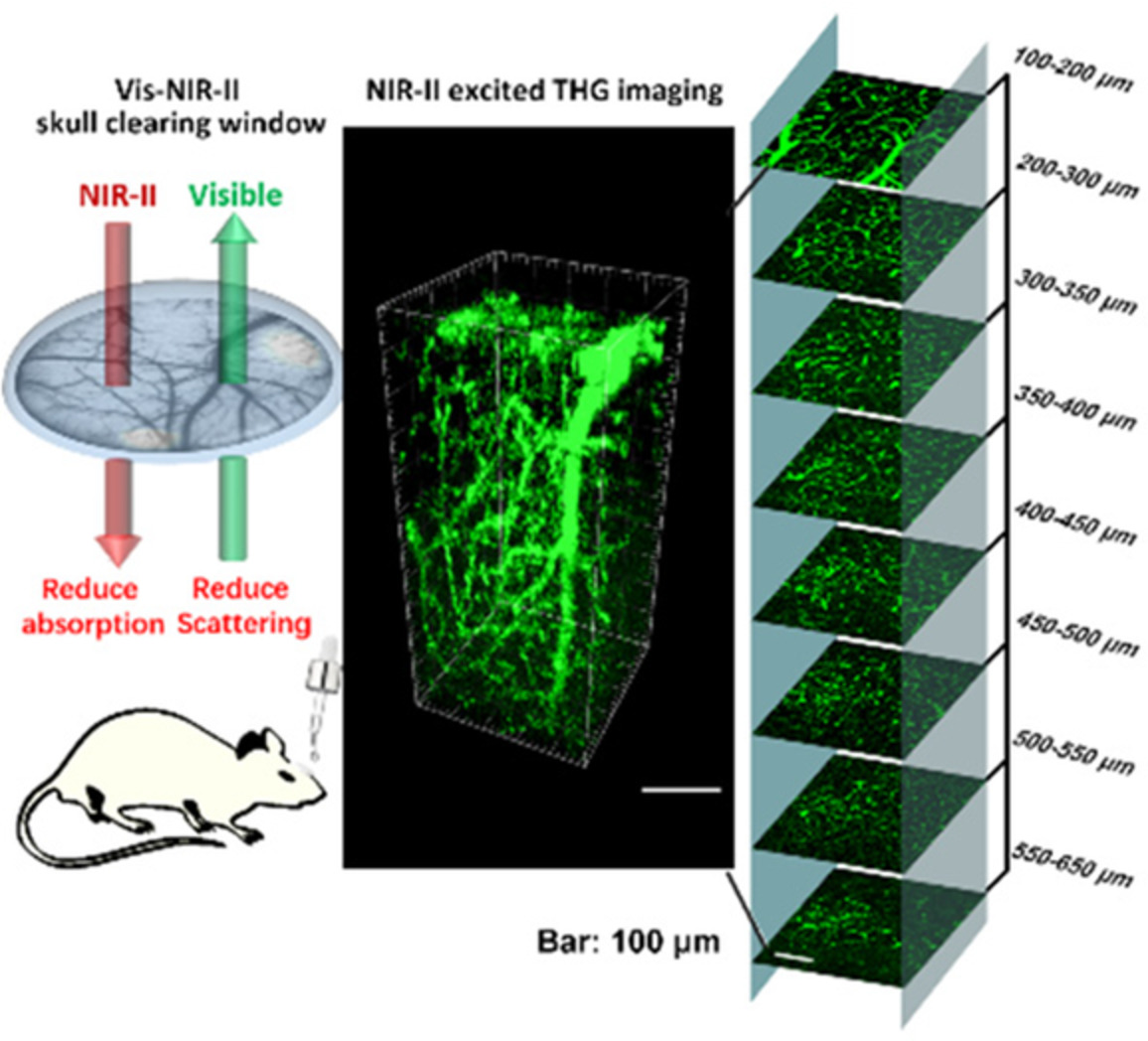
Optical clearing skull window is a novel technique compared to the traditional surgery based cranial window, which could reduce the scattering of skull and make it transparent to visible light. Here, the near infrared (NIR)-II optimized skull clearing window was established. Comparing with turbid skull, the transparent skull window promised the NIR-II excited third harmonic generation imaging depth to exceed three times.
Optimization of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy using near-infrared spectroscopy to assess changes in peripheral circulation: A pilot study
- First Published: 10 July 2020
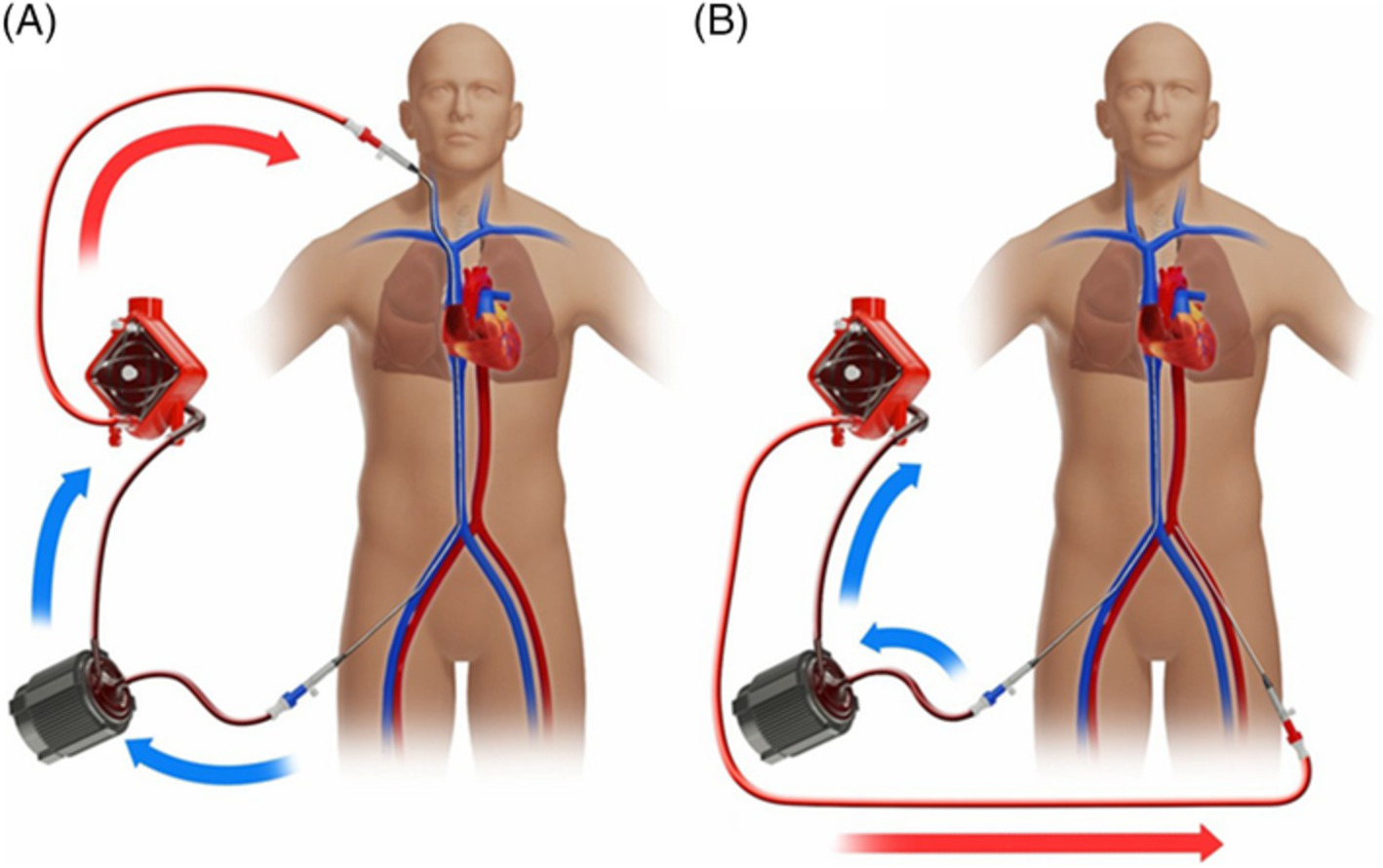
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) has been proposed as a noninvasive modality for detecting complications in patients undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and it can simultaneously reveal the global circulatory status of these patients. We optimized ECMO therapy on the basis of real-time peripheral NIRS probing. It was found that NIRS for optimizing ECMO therapy may enable the reliable monitoring of global circulatory status.
Quantitative assessment of distant recurrence risk in early stage breast cancer using a nonlinear combination of pathological, clinical and imaging variables
- First Published: 23 June 2020
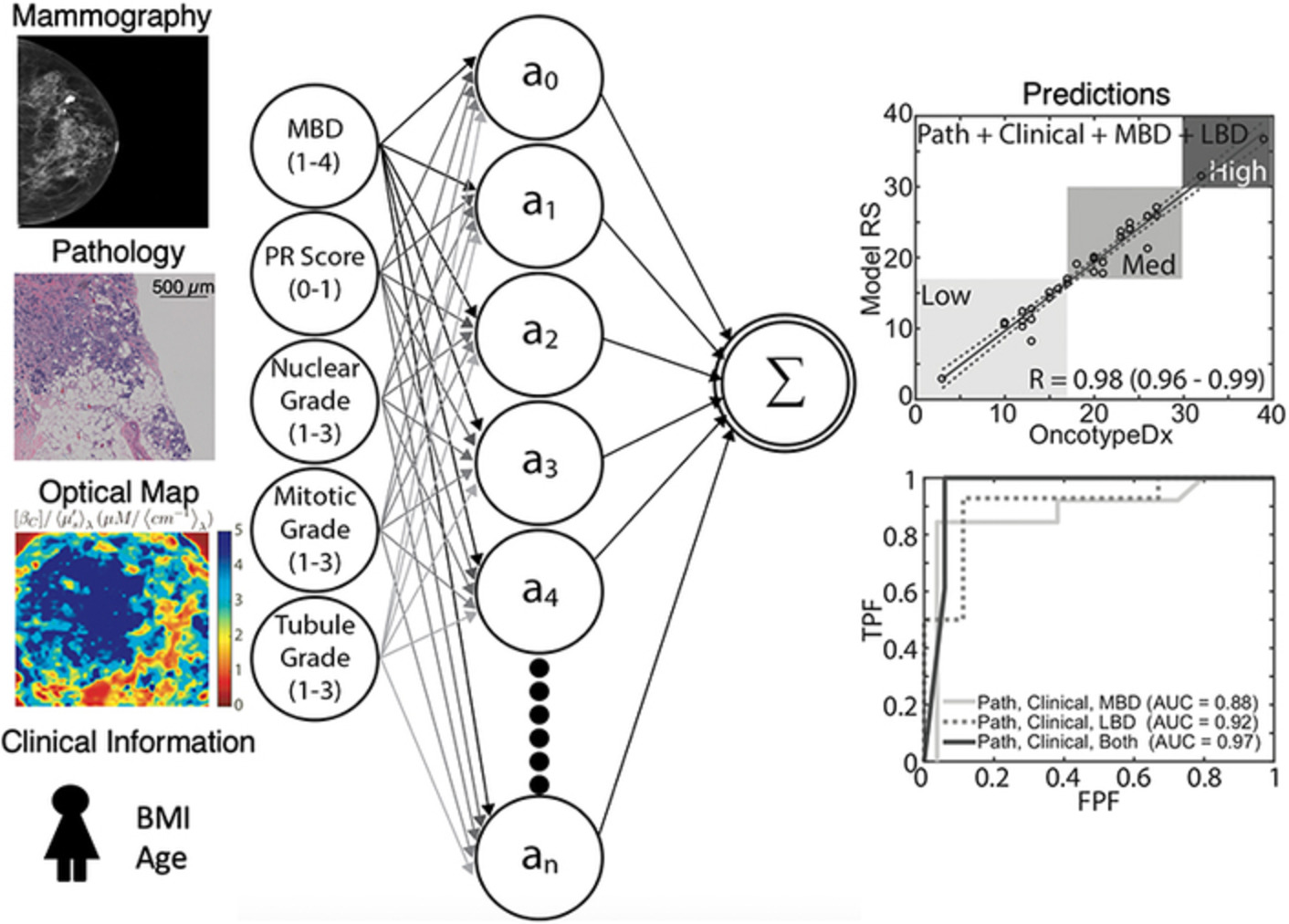
The inclusion of global breast density (obtained via mammography) as well as the inclusion of local variations in breast density (obtained via optical spectral imaging) improve OncotypeDx prediction when combined with clinicopathological variables. The relationship between these input variables is inherently nonlinear, thus the use of artificial neural networks improves OncotypeDx prediction compared wth linear methods.
Lipids status and copper in a single astrocyte of the rat model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Correlative synchrotron-based X-ray and infrared imaging
- First Published: 28 May 2020
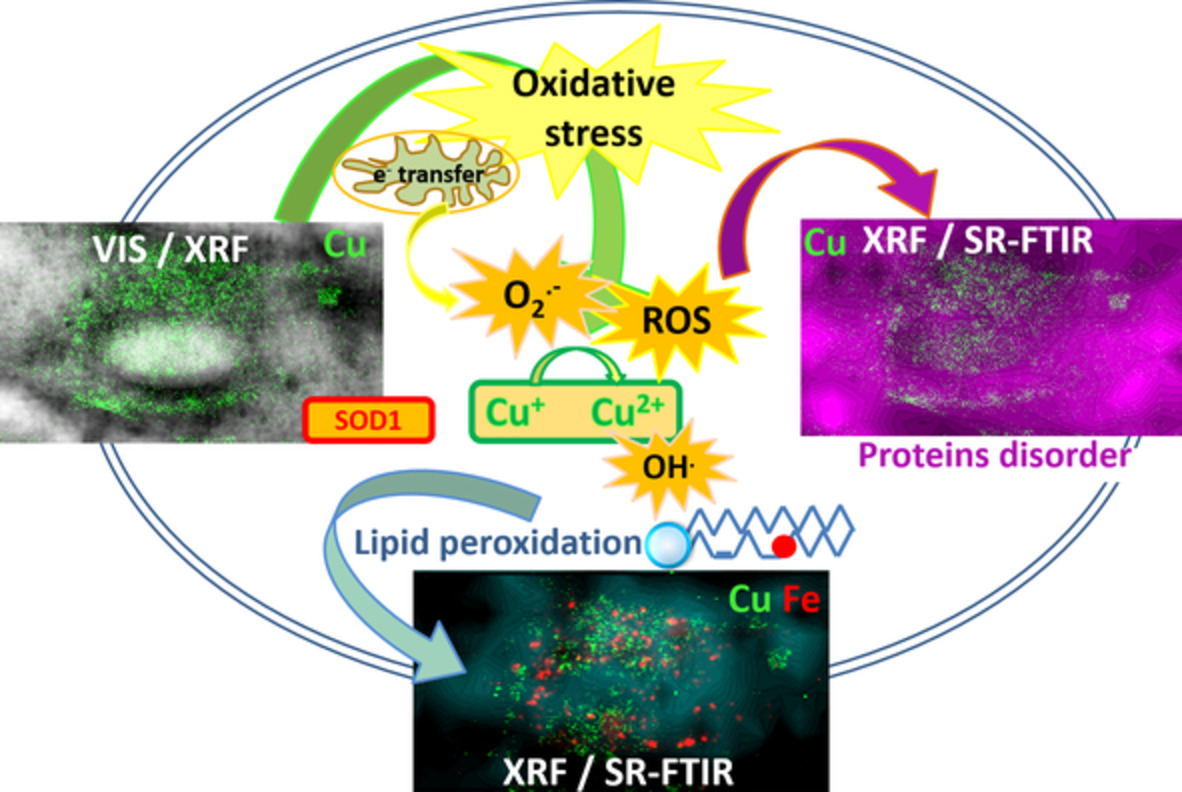
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease, causing death of motor neurons controlling voluntary muscles. In this study we followed the bio-macromolecular organic composition and compartmentalization together with trace metal distribution in situ in single astrocytes from the ALS rat model and compared them to the control astrocytes from non-transgenic littermates by simultaneous use of two synchrotron radiation- based methods: Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy (SR-FTIR)and hard X-ray fluorescence microscopy (XRF).
Diffuse optical assessment of cerebral-autoregulation in older adults stratified by cerebrovascular risk
- First Published: 13 June 2020
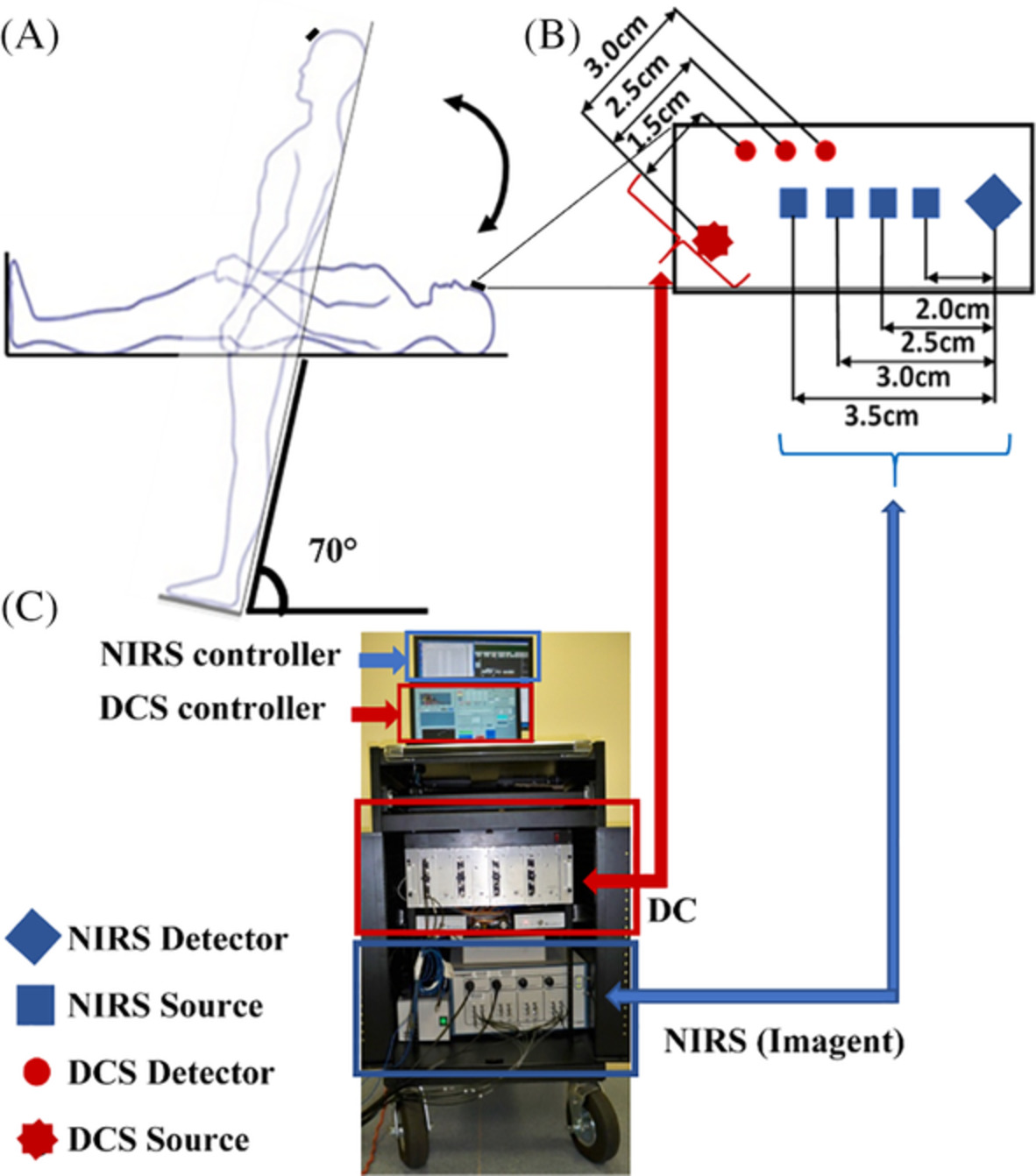
A hybrid diffuse optical instrument was used to simultaneously detect lowfrequency oscillation (LFO) signals of cerebral blood flow and oxygenation in older adults at low-risk or high-risk for developing cerebrovascular disease (CVD). Compared to the low-risk group, the high-risk group demonstrated higher LFO gains at resting baseline but smaller gain reductions during head-up-tilting. LFO gain, correlating inversely with cerebral autoregulation capability, is a potential biomarker for early detection of CVD.
A deep-learning-based approach for noise reduction in high-speed optical coherence Doppler tomography
- First Published: 10 July 2020
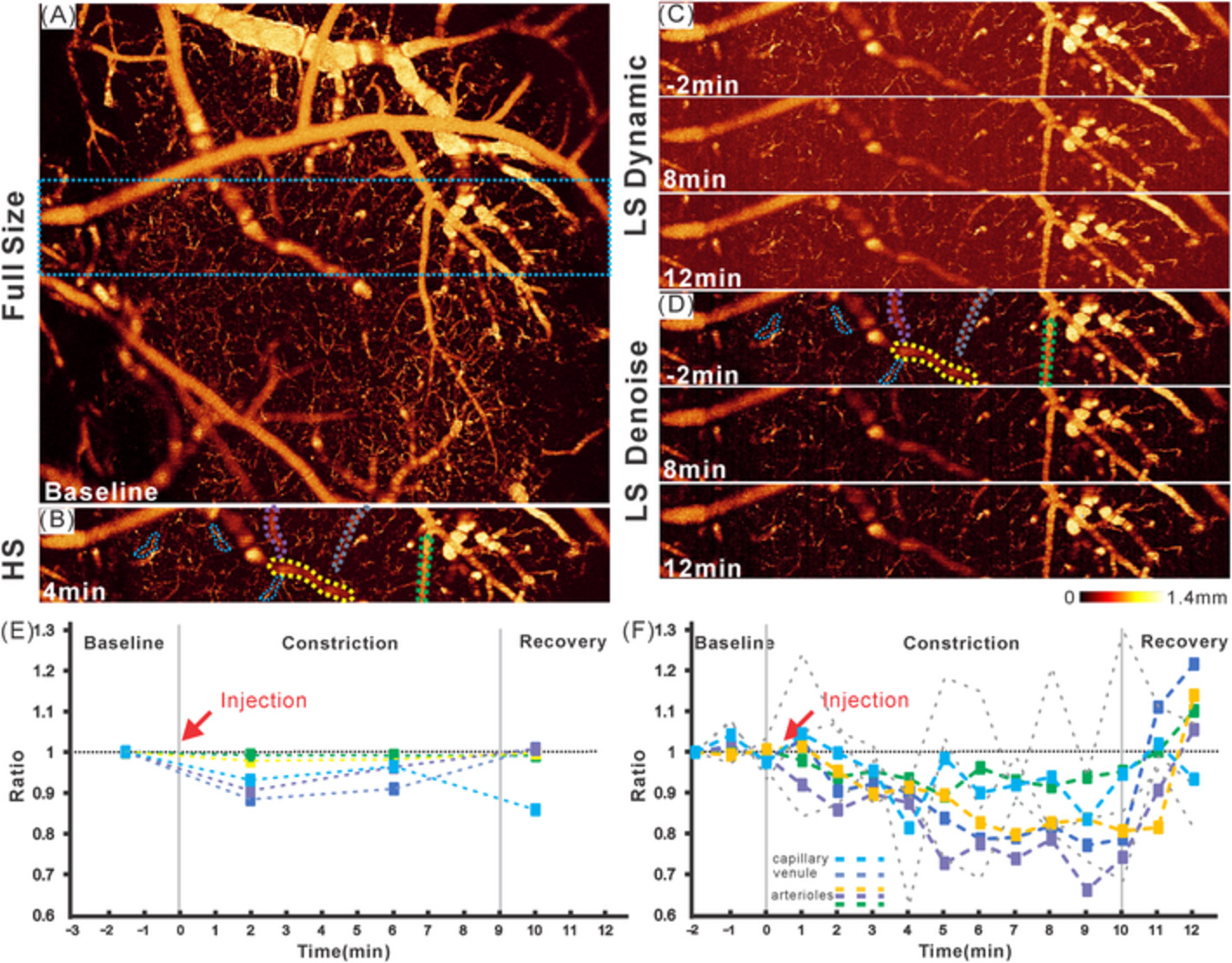
In this study, we report a deep-learning-based image denoise method to substantially enhance the signal-to-noise ratio of optical coherence Doppler tomography (ODT) for 3D imaging of microcirculatory blood flow networks. As the flow detection sensitivity of ODT is a trade-off between imaging rate and phase noise, the results demonstrate the potential of this method to effectively improve ODT acquisition speed and thus track dynamic events occurring during the brain functional activations.
Hyperspectral characterization of re-epithelialization in an in vitro wound model
- First Published: 17 June 2020
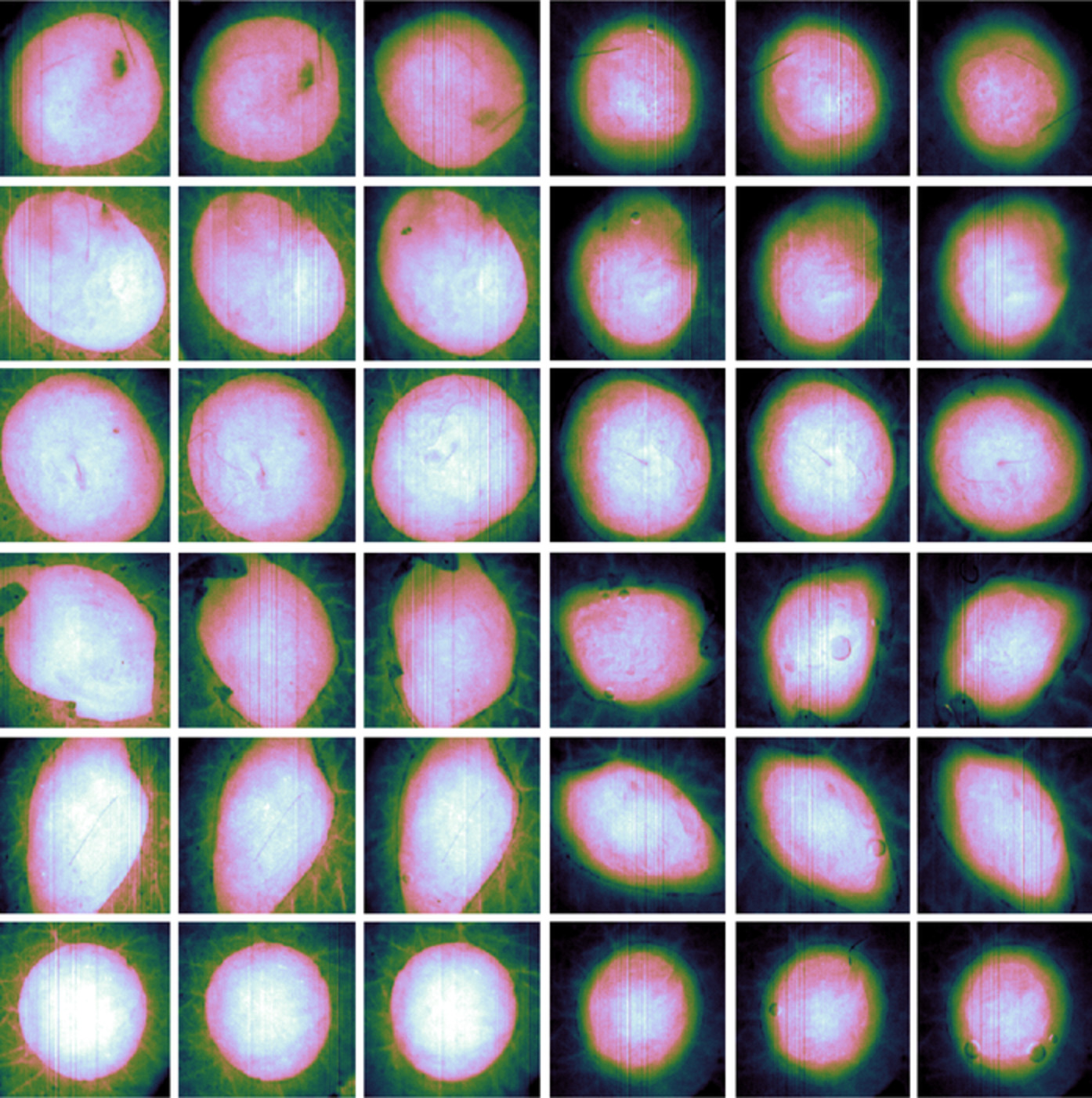
Hyperspectral imaging is a promising technique for applications like detection of wound re-epithelialization. The technique is in this paper applied to an in vitro wound model. Wounded tissue is separated from healing and intact tissue, and their spectral characteristics are summarized. Photon transport through healing tissue is found to be representable using wound tissue properties with an epidermis-like layer on top. The findings set a clear route for further development of detection algorithms, enabling non-destructive characterization of in vitro wound models.
Determination and correction of aberrations in full field optical coherence tomography using phase gradient autofocus by maximizing the likelihood function
- First Published: 08 July 2020
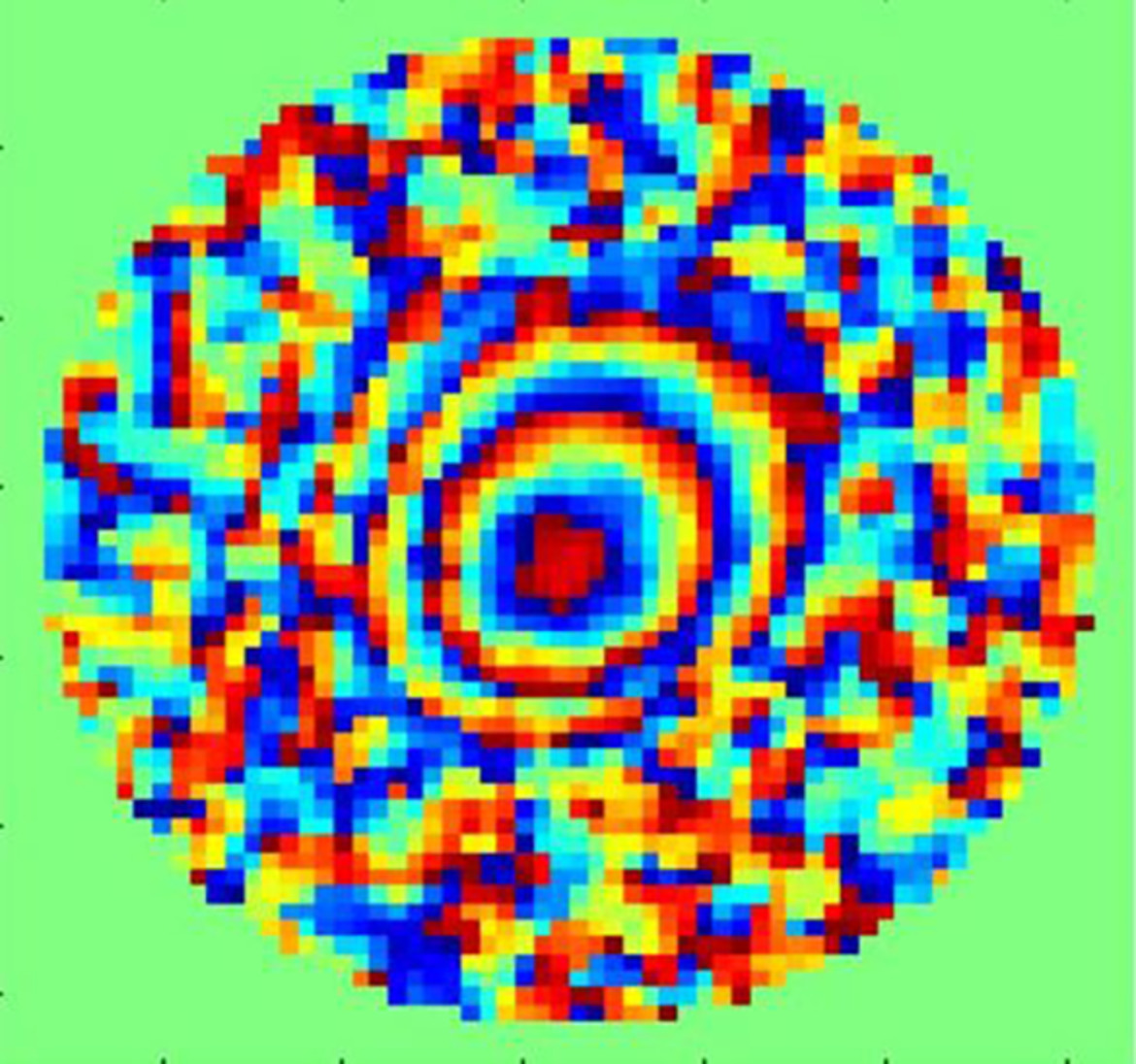
This work is dedicated to the development of a method for numerical estimation and correction of aberrations of the eye in fundus imaging with OCT. Aberration evaluation is performed statistically by using the estimate based on likelihood function maximization. The efficiency of the proposed method has been demonstrated in OCT fundus imaging with 6λ aberrations. It has been shown that spatial high-frequency wave front distortions can be determined.
Towards quantitative assessment of burn based on photoacoustic and optical coherence tomography
- First Published: 01 July 2020
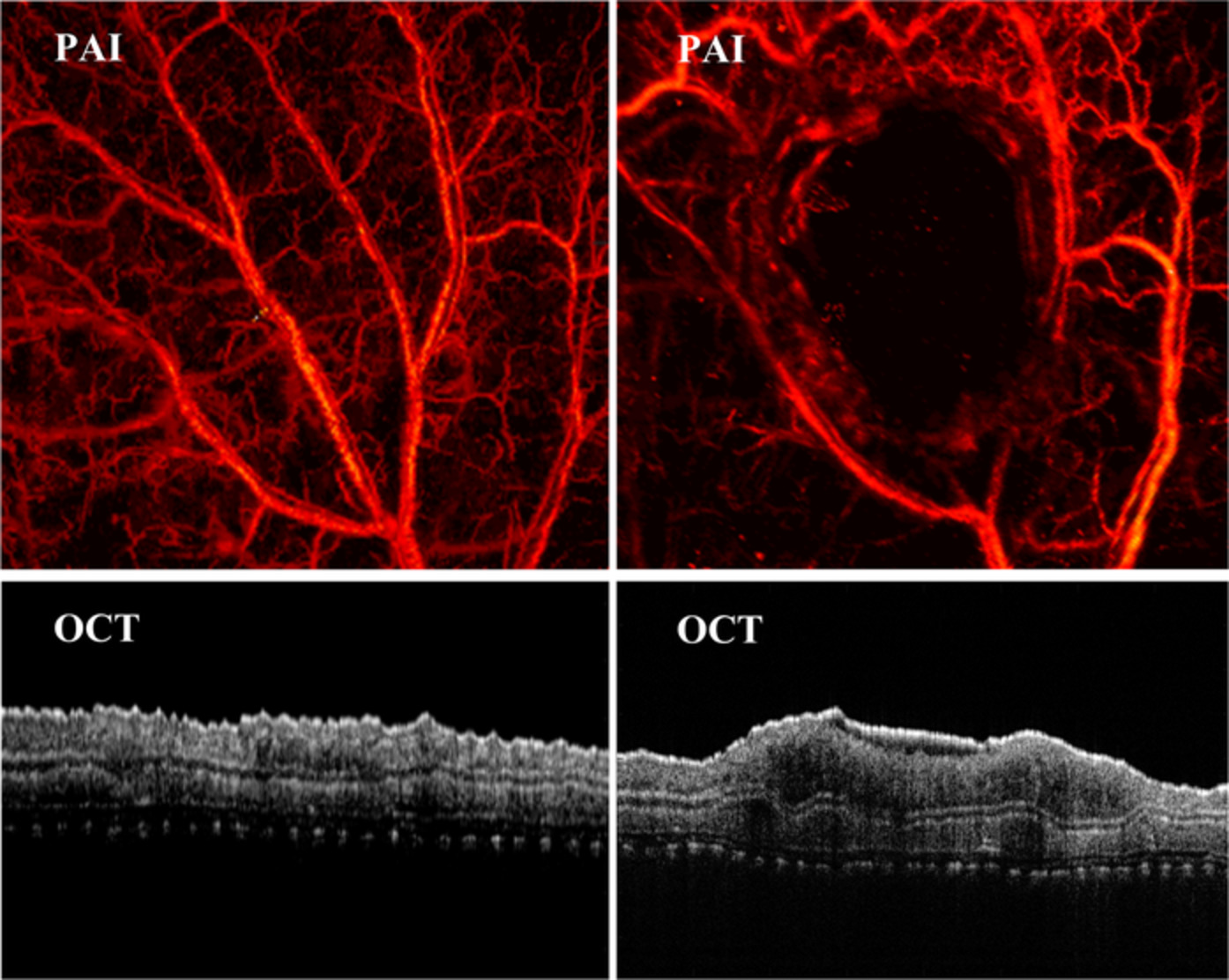
A non-invasive technique by combing photoacoustic imaging (PAI) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to multi-parameter quantitatively assess the burns was report. The experimental results prove that combined PAI/OCT as a novel method can be used to assess the severity of burn, which has the potential to diagnose the burns in clinic.
Raman microspectroscopic study for the detection of oral field cancerisation using brush biopsy samples
- First Published: 29 June 2020
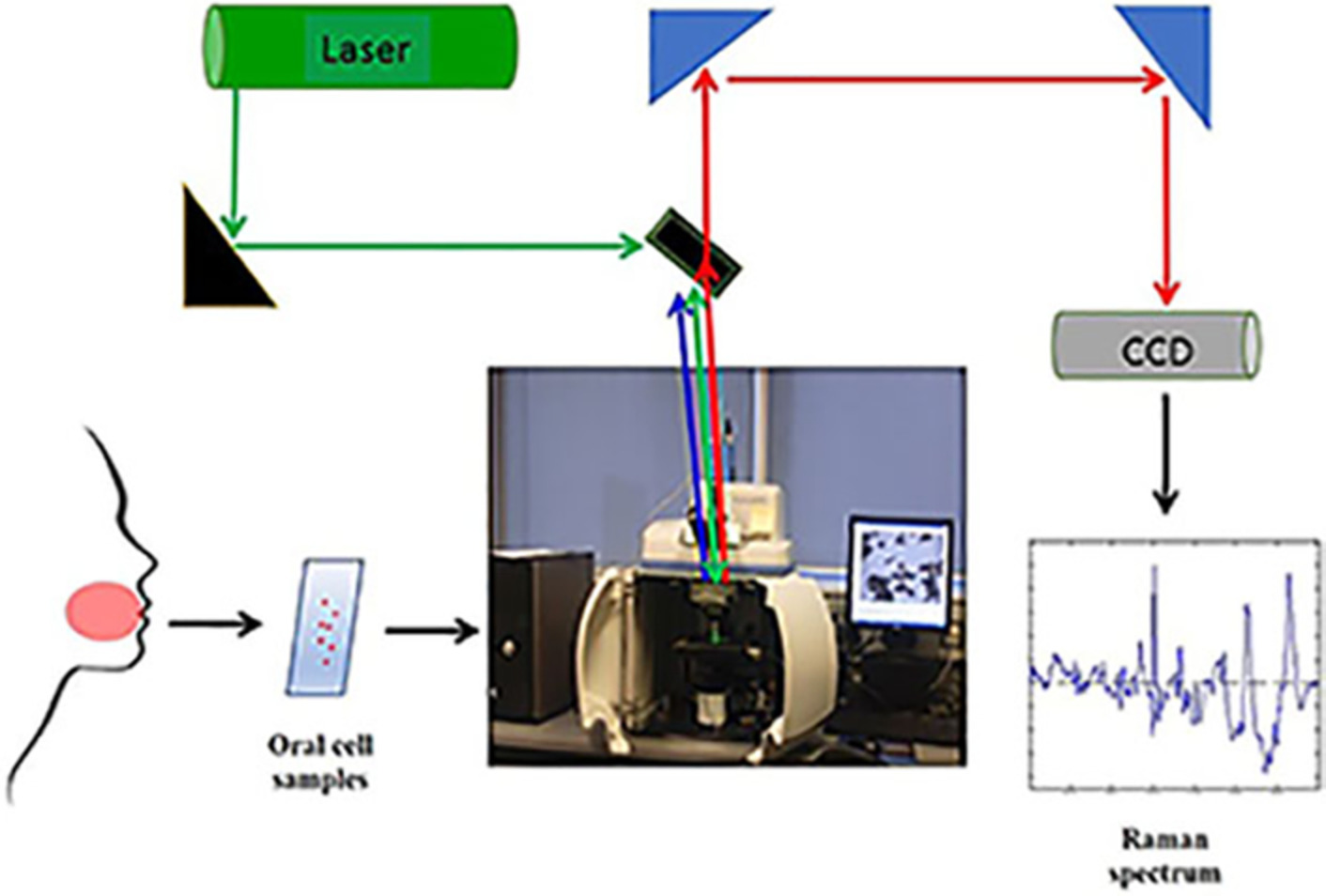
The prognosis of oral cancer can be influenced by the potential of malignant transformation of tissues surrounding an original lesion- field cancerisation. It is demonstrated that Raman microspectroscopy of oral brush biopsy samples can identify this phenomenon with high accuracy, supporting its potential role in screening protocols for potentially malignant lesions.
Evaluation of corneal structures in myopic eyes more than twenty-two years after photorefractive keratectomy
- First Published: 15 July 2020
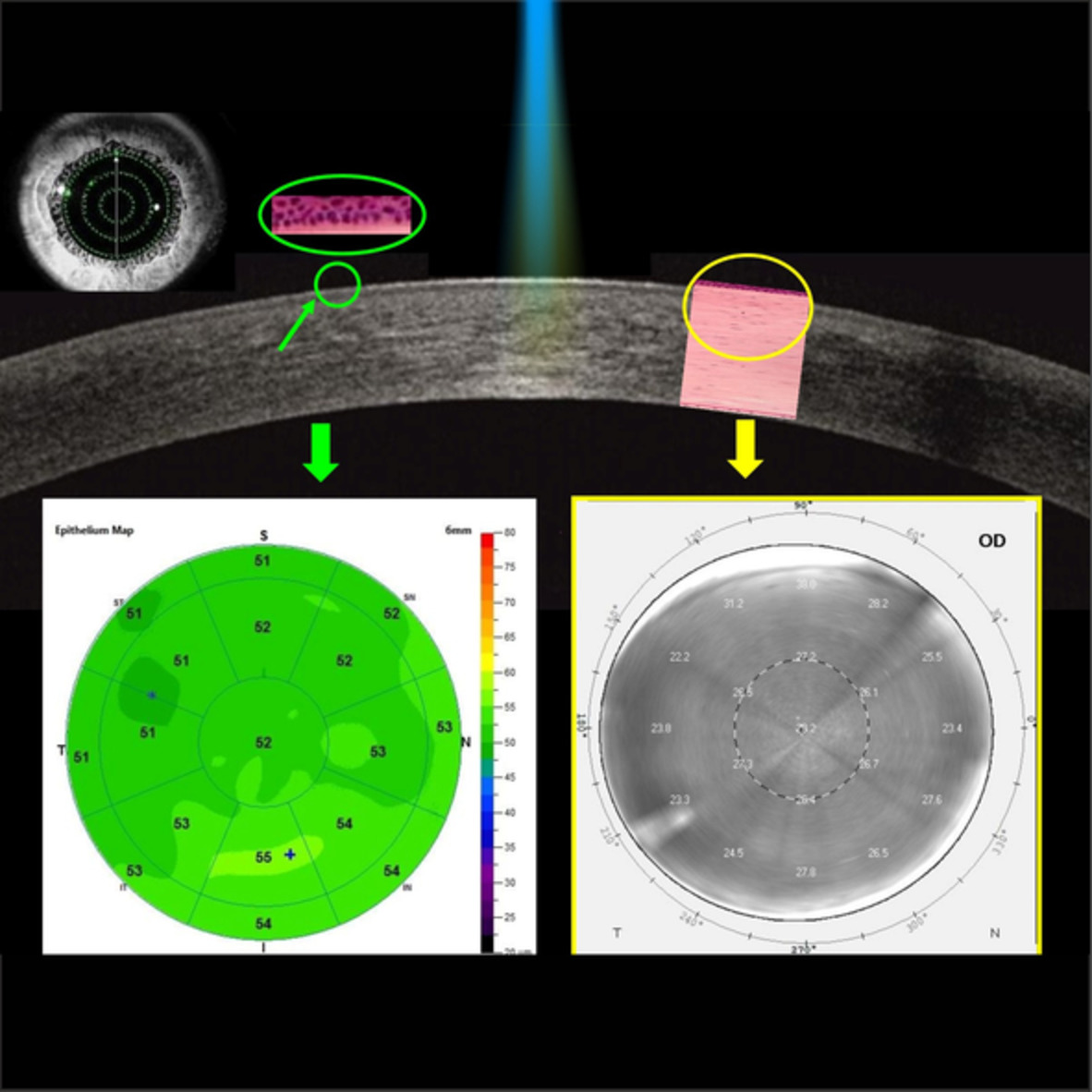
The aim of this study is to evaluate corneal epithelial thickness (CET), corneal densitometry (CD) in myopic eyes more than 22 years after photorefractive keratectomy, using anterior segment-optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) and Scheimpflug imaging system. These noninvasive imaging techniques allow to better understand the corneal remodeling process after photoablation and to monitor the patients over time.
Quantification of diabetic macular ischemia using novel three-dimensional optical coherence tomography angiography metrics
- First Published: 11 June 2020
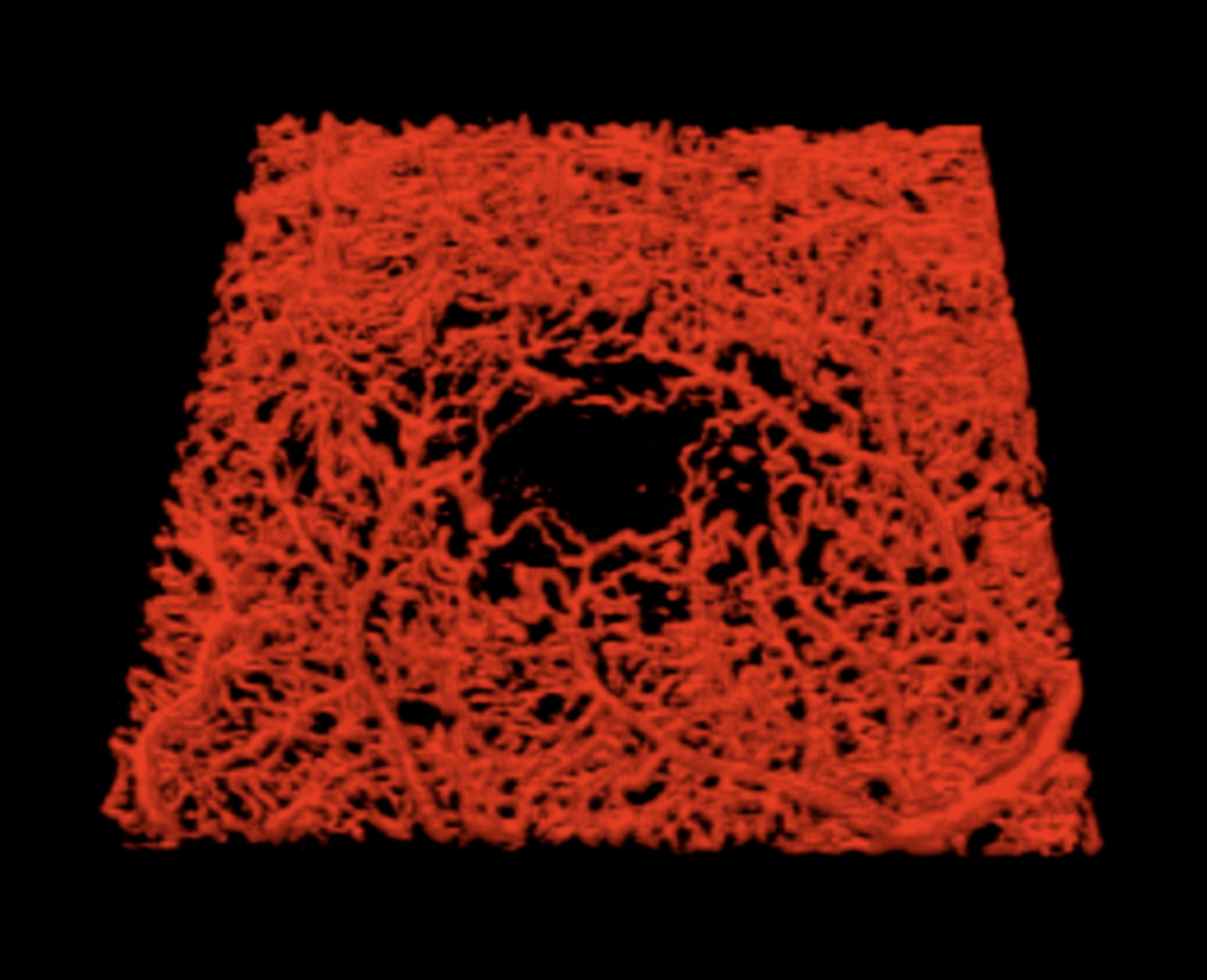
Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) is an emerging and noninvasive imaging modality to visualize the retinal and choroidal microvasculature in the eye. Assessing macular ischemia may be important in eyes with diabetic retinopathy (DR) as these findings may predict visual outcomes. In this paper, we used novel three-dimensional OCTA metrics to assess macular ischemia in eyes with DR. Our results suggest that these metrics may be effective in the evaluation of diabetic macular ischemia.
Unique corneal tomography features of allergic eye disease identified by OCT imaging and artificial intelligence
- First Published: 10 July 2020
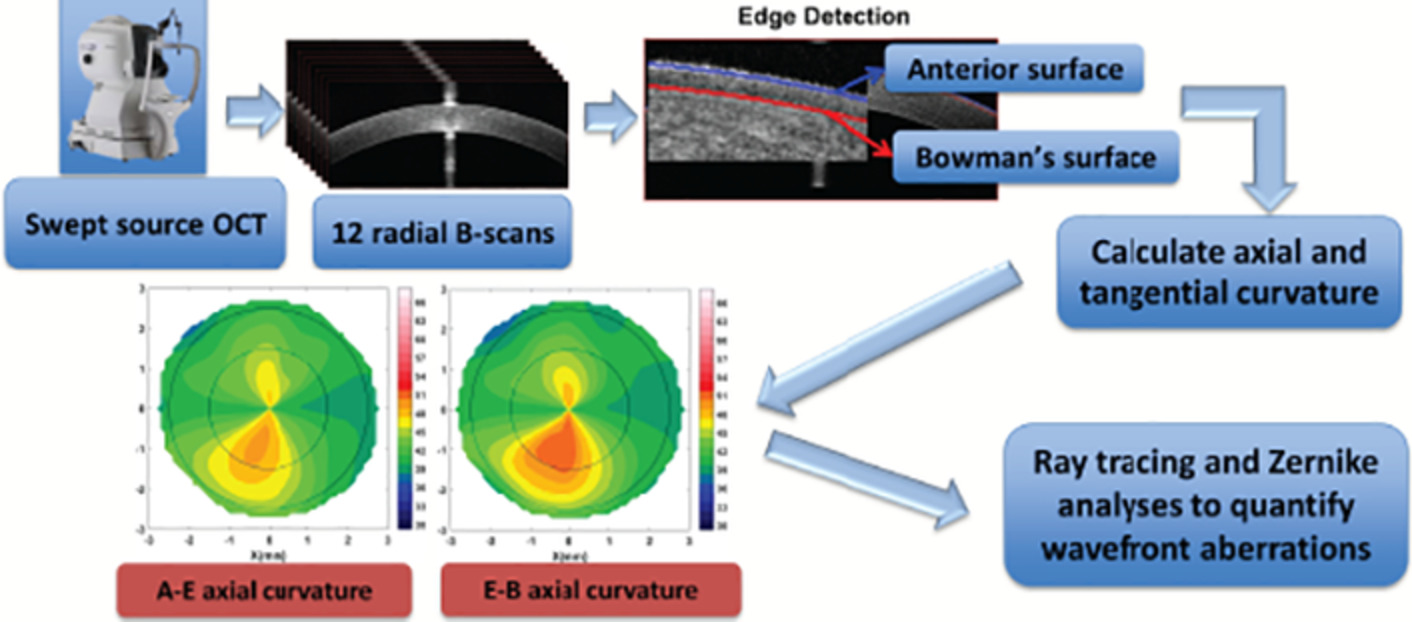
Subtle changes in corneal tomography may occur in allergic eye disease (AED). With OCT imaging of the cornea and use of artificial intelligence, these changes relative to healthy eyes were identified and observed as unique indicators of AED compared to early degenerative disease such as forme fruste keratoconus (KC). Further, few AED eyes had changes similar to KC eyes and may be early indicators of future progression of cornea to KC state.
Microfocusing sapphire capillary needle for laser surgery and therapy: Fabrication and characterization
- First Published: 18 July 2020
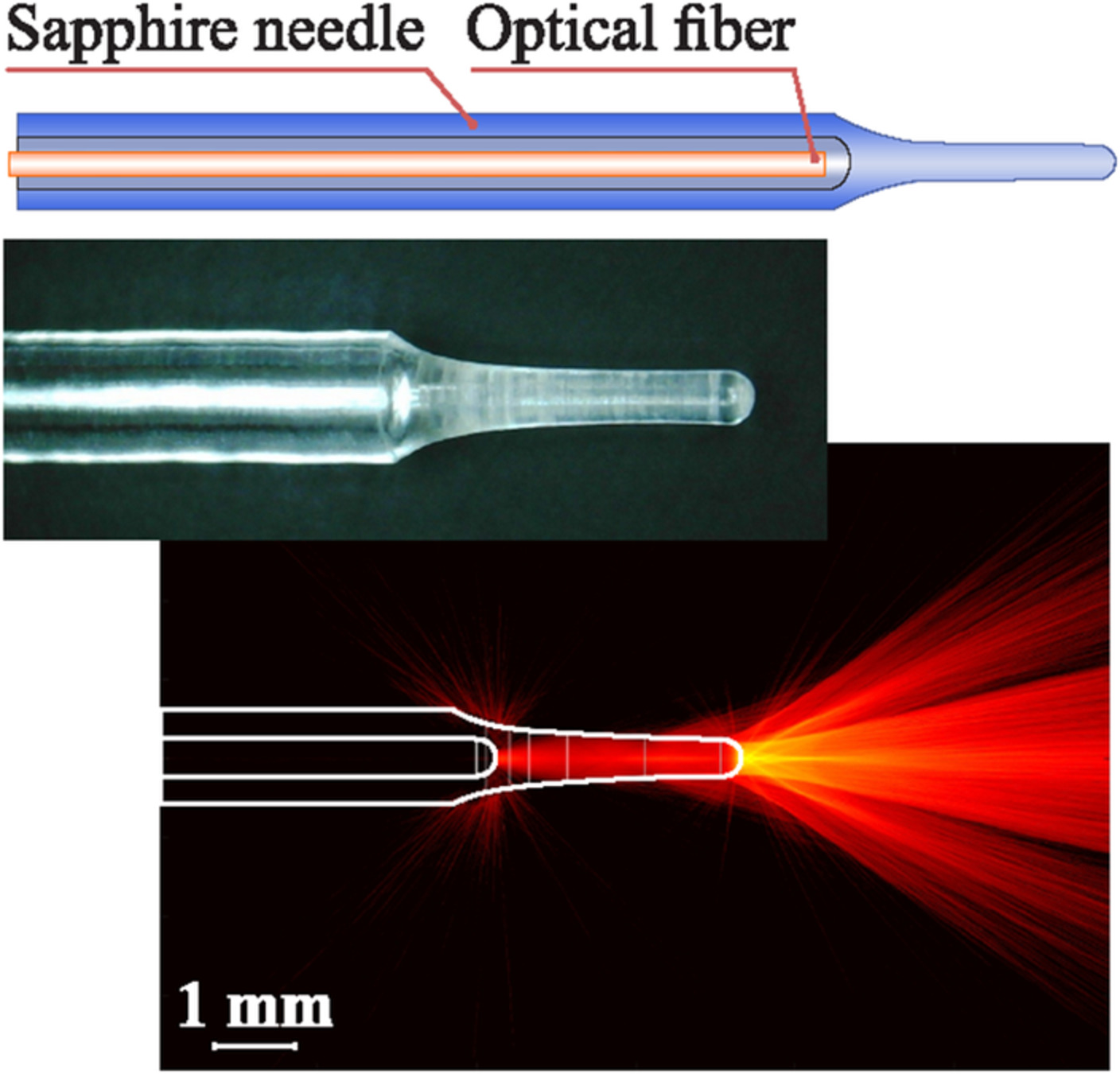
A sapphire microfocusing needle produced by means of the edge-defined film-fed growth technique can be applied for precise and intensive laser therapy and surgery. It is compatible with various types of optical fibers, protecting them from the direct contact with tissue and from overheating. Changing the needle geometry directly during the growth process, it is possible to adjust it for different tissues and types of therapy.
Safety and delivery efficiency of a photodynamic treatment of the lungs using indocyanine green and extracorporeal near infrared illumination
- First Published: 15 July 2020
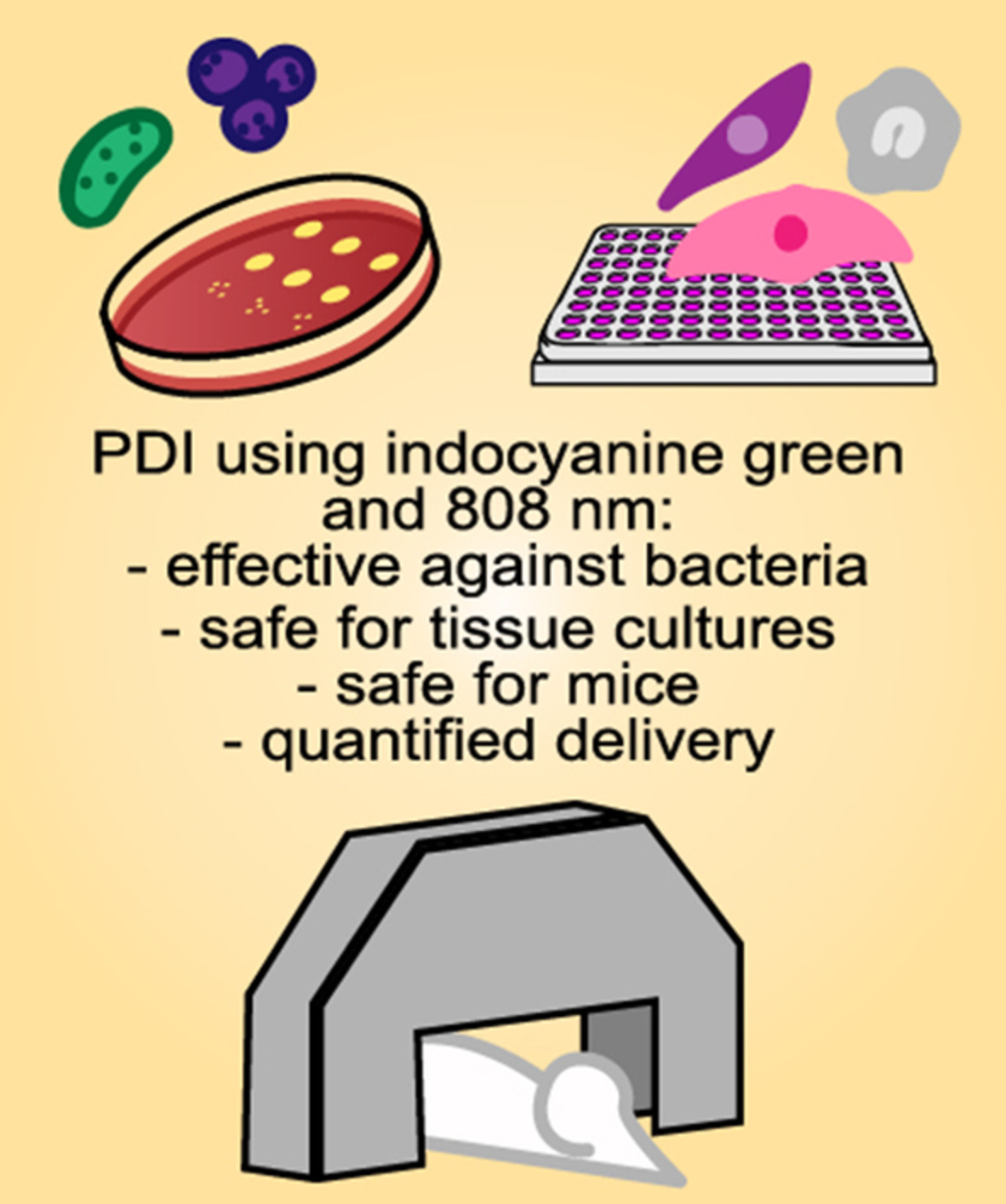
Photodynamic inactivation (PDI) using extracorporeal light and indocyanine green is a promising alternative treatment for bacterial pneumonias. The results here presented show that PDI can efficiently kill Staphylococcus aureus with no toxicity on host cells. The pulmonary delivery of the photosensitizer and light, and the safety of the protocol are shown in mice. The selective delivery and low toxicity of this PDI protocol support its potential to treat pneumonias caused by S. aureus and other important pathogens.
Polarization-dependent second-harmonic generation for collagen-based differentiation of breast cancer samples
- First Published: 09 July 2020
The development of label free non invasive techniques to be used as novel diagnostic tools in cancer research is of great importance for improving the quality of life for millions of patients. Information concerning the structure and directionality of collagen fibers in thin breast tissue sections was collected using polarization-dependent SHG imaging measurements. This approach enables to quantitatively differentiate benign from cancerous breast biopsy samples thus PSHG could be a unique tool helping to improve cancer detection rates.
Investigating the feasibility of spatially offset Raman spectroscopy for in-vivo monitoring of bone healing in rat calvarial defect models
- First Published: 13 July 2020
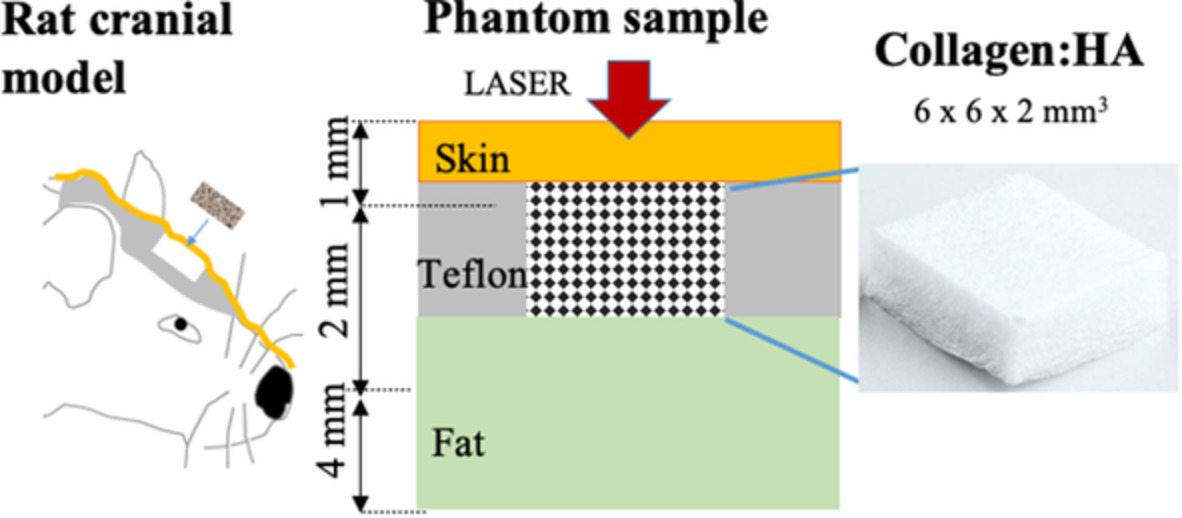
A wide range of biomaterials and tissue-engineered scaffolds are being investigated to support and stimulate bone healing in animal models. Using phantoms and rat cadavers, we investigated the feasibility of using spatially offset Raman spectroscopy to monitor changes in collagen concentration at levels similar to those expected to occur in vivo during bone regeneration. A partial least squares regression model was developed to quantify collagen concentration in plugs consisting of mixtures or collagen and hydroxyapatite.
Optical coherence tomography angiography for mapping cerebral microvasculature based on normalized differentiation analysis
- First Published: 08 July 2020
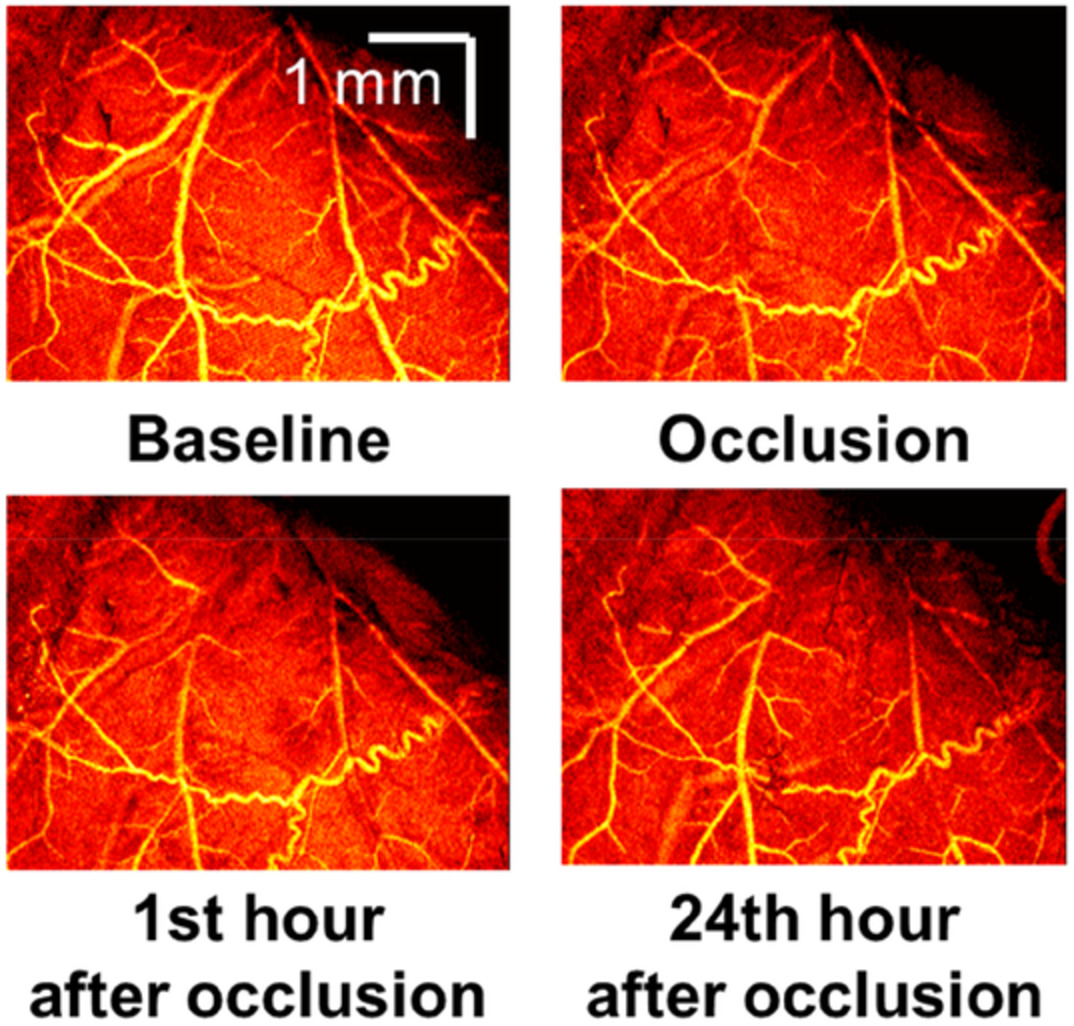
A normalized differentiation method was developed for mapping cerebral microvasculature. The measurements in a rat cerebral cortex show that the OCTA based on the normalized differentiation analysis can generate microvascular images with high quality and monitor spatiotemporal dynamics of blood flow with simple computation and fast processing before and after localized ischemia.