Editor: Jürgen Popp
Journal of Biophotonics, a Wiley physics journal, focuses on the interdisciplinary field of biophotonics, publishing cutting-edge research on interactions between light and biological material.
We cover photonics research in areas such as life sciences, medicine and biomedicine, environmental science, nutrition, biology, physics, and chemistry, ranging from fundamental research to the latest clinical applications.
Journal Metrics
- 4.7CiteScore
- 2.3Journal Impact Factor
- 42%Acceptance rate
- 4 days Submission to first decision
On the Cover
Articles
Algorithms for Intraoperative Neurovascular Inclusion Detection, Diameter and Depth Prediction Based on Frequency Domain Near Infrared Spectroscopy
- 21 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
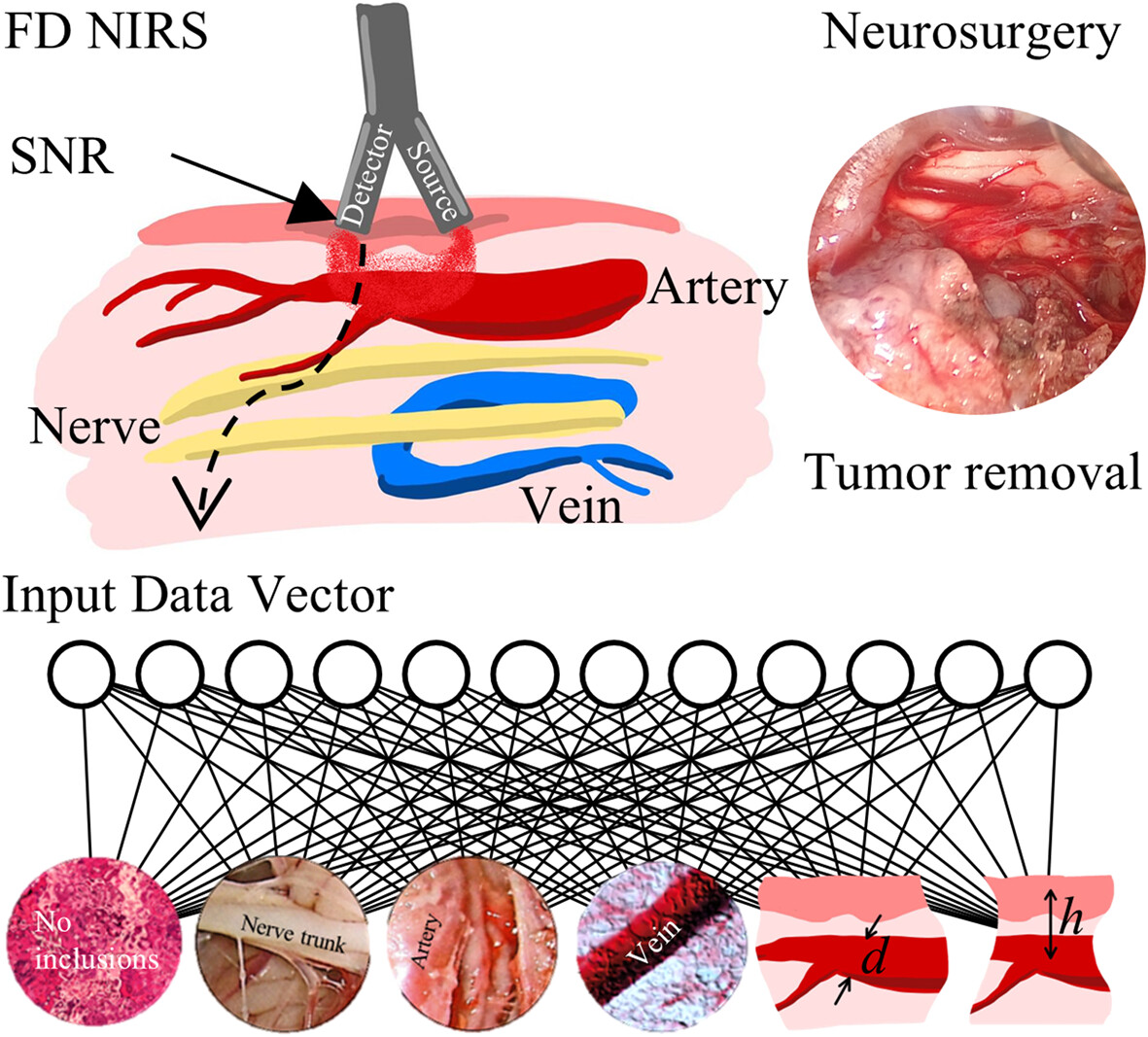
A novel method for detecting neurovascular structures, predicting their diameter and depth using frequency domain near infrared spectroscopy and machine learning was introduced. Key findings include selecting the type of light detector, creating feature vectors, algorithms, and experimental testing of the feasibility of partial training on the simulated data.
Quantitative Assessment of Human Anisotropic Skin Elasticity Using the Dispersion Curve of Surface Acoustic Wave Elastography
- 21 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
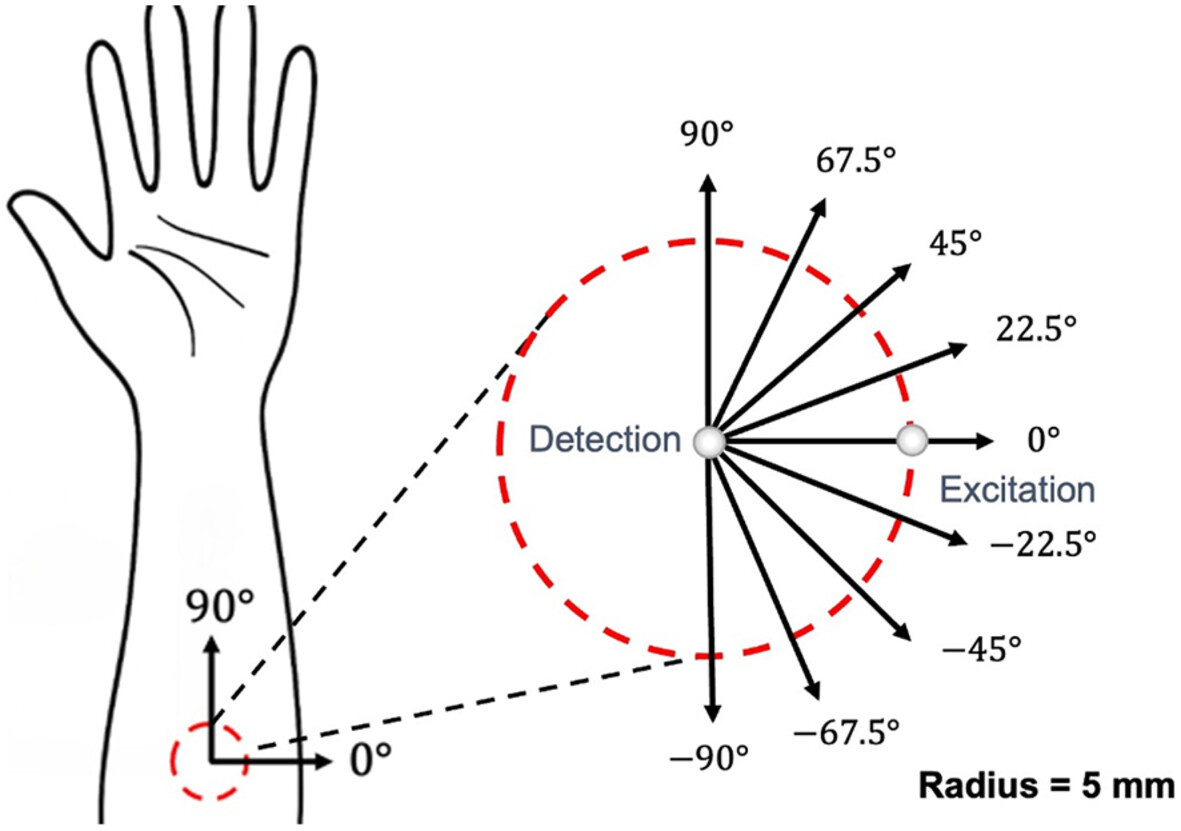
Skin is an anisotropic material, and variations in measurement orientation can significantly affect elasticity estimation. This study investigates the impact of wave propagation direction on the accuracy and robustness of elasticity measurements, using surface acoustic wave optical coherence tomography (SAW-OCT) on both ex vivo chicken thigh samples and in vivo human forearms. The findings offer valuable insights into optimal measurement orientations, providing potential guidance for accurate and reliable skin assessment in clinical applications.
Correlation Between Fingerprint-Guided Sweat Ducts Features From OCT and Diabetic Neuropathy Using Voronoi Diagram
- 19 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
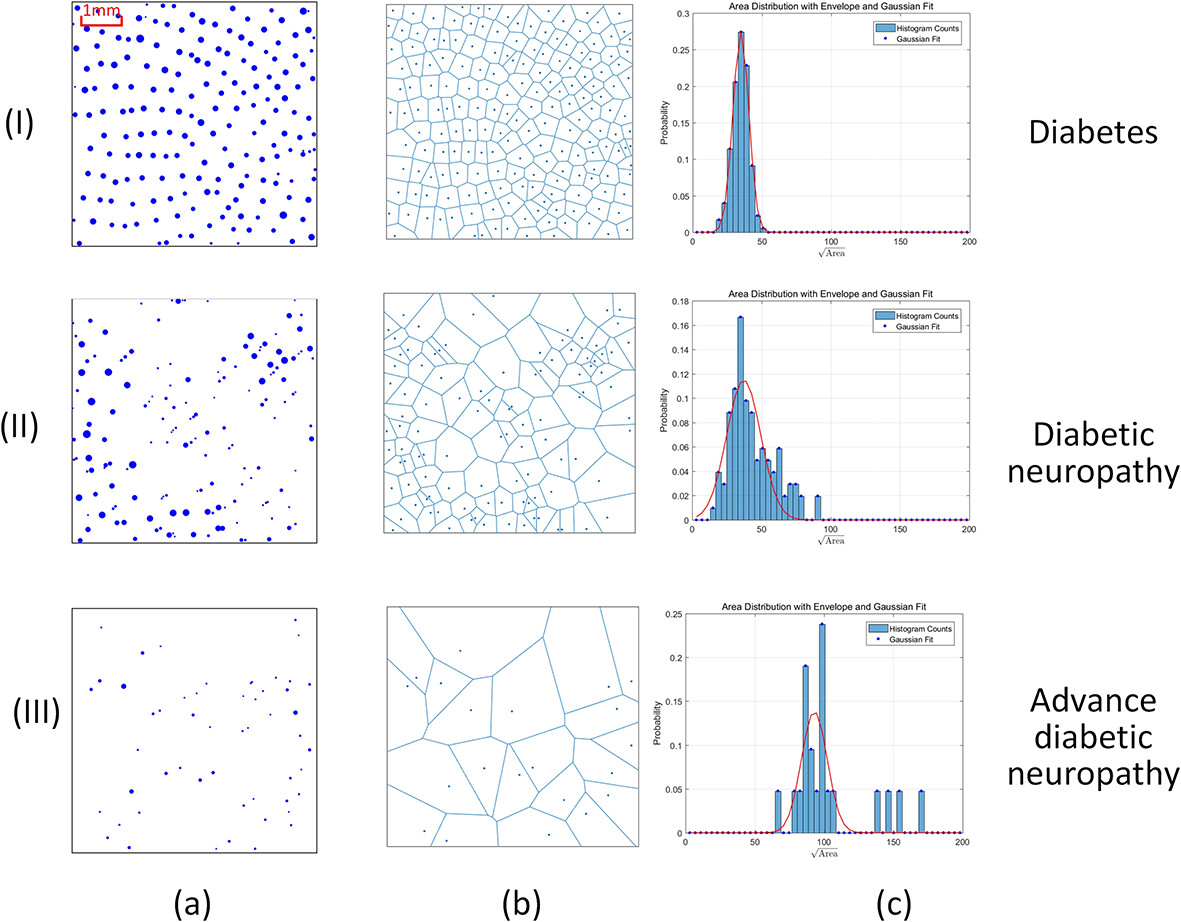
This study aims to investigate the correlation between the characteristics of fingerprint-guided sweat ducts assessed by optical coherence tomography and diabetic neuropathy (DN). The number, volume, and spacing of sweat ducts are correlated with the severity of DN. The Voronoi diagram of the sweat duct distribution demonstrates irregularities in the spatial distribution among patients with DN. These findings suggest that OCT-assessed sweat duct features may serve as non-invasive biomarkers for DN in patients with diabetes.
Brain Activity Within Prefrontal Cortex: A Resting-State fNIRS Comparative Study in High-Functioning Autism Preschoolers and Typically Developed Peers
- 16 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
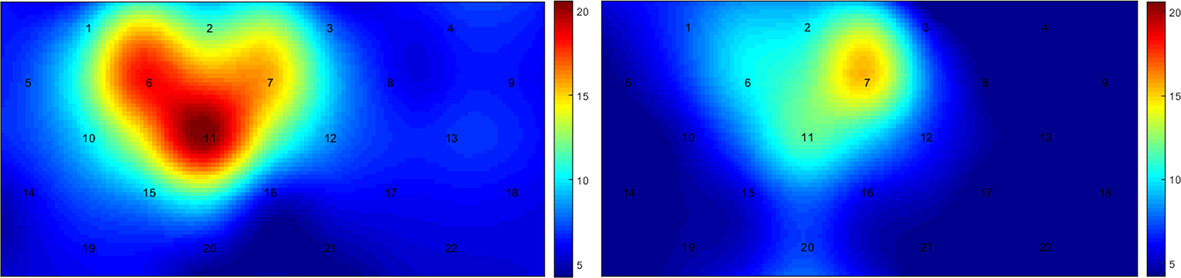
We applied functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) to detect the brain function within the prefrontal cortex in the 23 typically developing (TD) preschool children and 48 children with high-functioning autism (HFA), aiming to observe the differences in brain function within the prefrontal cortex between the two groups. We found that the activation degree of channels 6–7-11 corresponding to the activation area of the right prefrontal lobe in the HFA group is significantly higher than that in the Typical Development TD group. Moreover, the number and intensity of brain functional connectivity in the HFA group are significantly lower than those in the TD group. The active areas of the brain network in the HFA group are not as concentrated as those in the TD group. This demonstrates that fNIRS detection can serve as a potential biomarker for the brain activity within the prefrontal cortex of preschool children with HFA.
Multiparametric Wide‐Field Fluorescence Imaging via Polarization Modulation With Liquid Crystal Rotators
- 15 July 2025
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
The inner clock—Blue light sets the human rhythm
- 21 August 2019
Graphical Abstract
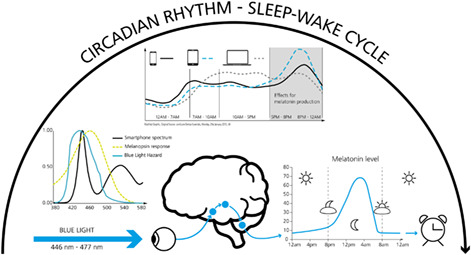
Light is playing an important role beyond vision. The review summarizes the current and most recent knowledge on the role of light around 470 nm and its role in circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm is essential for life. If it is not preserved, serious diseases might develop. Light and its role in synchronization, but also in disruption of the circadian rhythm is discussed.
Mueller polarimetric imaging for surgical and diagnostic applications: a review
- 950-982
- 2 May 2017
Graphical Abstract
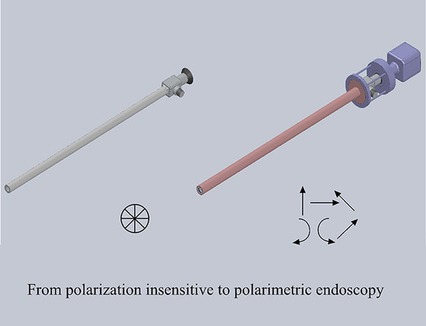
Polarization is a fundamental property of light that is able to provide an interesting and unique insight into tissue. Tissue polarization properties convey morphological, micro-structural and compositional information of tissue with great potential for label free characterization of tissue pathological changes. Recent progress in tissue polarimetric imaging and polarization resolved endoscopy paved the way for translation of polarimetric imaging to surgery and tissue diagnosis.
Surface plasmon resonance based biosensor technique: A review
- 483-501
- 30 March 2012
Optical windows for head tissues in near‐infrared and short‐wave infrared regions: Approaching transcranial light applications
- 11 August 2018
Graphical Abstract
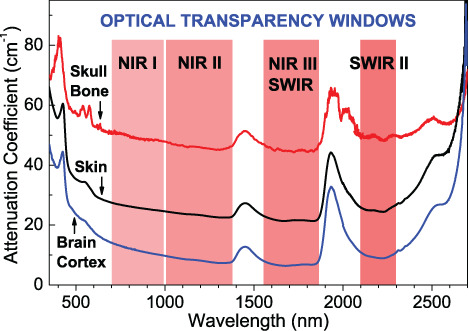
Optical permeability of freshly excised rat head tissues (brain cortex, cranial bone and scalp skin) are studied in the spectral range from 350 to 2800 nm, defining four tissue transparency windows in near-infrared and short-wavelength infrared ranges. The attenuation, scattering and absorption coefficients and attenuation lengths are evaluated for all the windows. The absorption spectra are analyzed in-detail to identify characteristic spectral features of the tissue constituents.
Latest news
Recent issues
- Volume 18, Issue 7July 2025
- Volume 18, Issue 6June 2025
- Volume 18, Issue 5May 2025
- Volume 18, Issue 4April 2025