Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 04 November 2020

We present a 3D printed high-NA catadioptric lens for forward signal collection in laser-scanning microscopy. The lens can replace expensive and bulky high-NA microscope objectives or condensers and is so thin to fit inside top-stage microscope incubators. The lens is particularly beneficial in Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS), where a high-NA beam collection is needed to avoid artefacts due to Cross Phase Modulation.
Further details can be found in the article by Andrea Bertoncini, Sergey P. Laptenok, Luca Genchi, Vijayakumar P. Rajamanickam, and Carlo Liberale (e202000219).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 04 November 2020
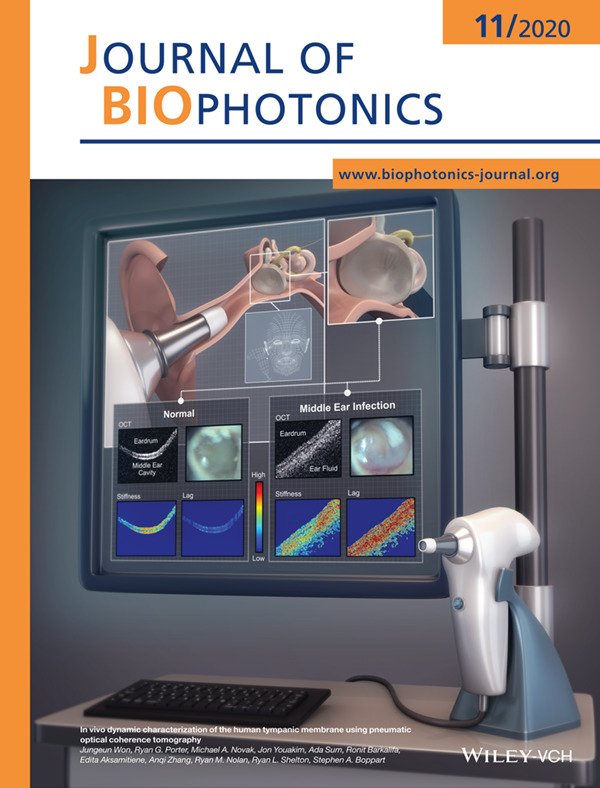
Air pressure-driven movements of the eardrum were captured with a handheld probe-based OCT system. The pneumaticdriven stiffness and time lag were compared between the normal ear and the ear with a middle ear infection.
Further details can be found in the article by Jungeun Won, Ryan G. Porter, Michael A. Novak, Jon Youakim, Ada Sum, Ronit Barkalifa, Edita Aksamitiene, Anqi Zhang, Ryan M. Nolan, Ryan L. Shelton, and Stephen A. Boppart (e202000215).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 04 November 2020

Vascular disrupting agents (VDAs) can be used to damage the tumour vasculature, suppressing oxygen and nutrition supply to the tumour tissue. Photoacoustic imaging was used to assess the structural and functional changes of the tumour vasculature and evaluate the efficacy of the VDAs. Tissues are irradiated with short laser pulses and the photoacoustic waves are analyzed to extract vessel size and hemoglobin composition to evaluate the VDA, hours after administration.
Further details can be found in the article by Muhannad N Fadhel, Sila Appak Baskoy, Yanjie Wang, Eno Hysi, and Michael C. Kolios (e202000209).
ISSUE INFORMATION
FULL ARTICLES
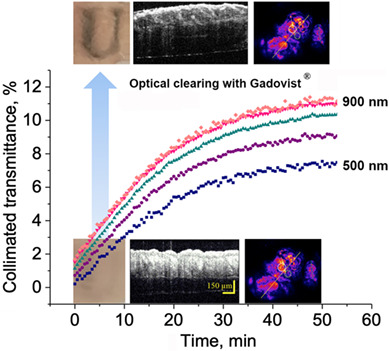
Magnetic resonance contrast agents in optical clearing: Prospects for multimodal tissue imaging
- First Published: 20 July 2020
A pilot study for early detection of oral premalignant diseases using oral cytology and Raman micro-spectroscopy: Assessment of confounding factors
- First Published: 19 July 2020
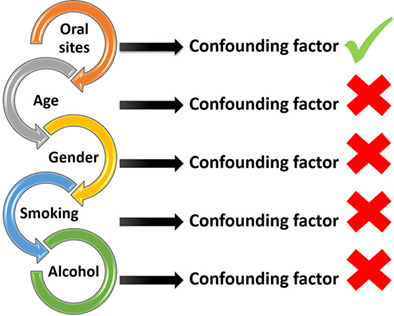
A common drawback of brush biopsy samples for screening oral potentially malignant lesions is that they may not contain morphologically abnormal cells, potentially leading to false-negative results. In this study, it has been demonstrated using Raman micro-spectroscopy that morphologically normal cells are biochemically abnormal. Furthermore, although choice of oral site is a potential confounding factor while developing classification models, age, gender, smoking or alcohol consumption are not.
Multisite cell- and neural-dynamics-resolving deep brain imaging in freely moving mice with implanted reconnectable fiber bundles
- First Published: 27 May 2020
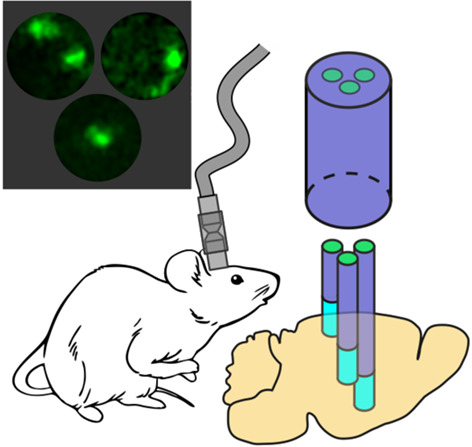
We present a reconnectable implantable ultraslim fiber-optic microendoscope that integrates a branching fiber bundle with GRIN fiber lenses, enabling a simultaneous fluorescence imaging of individual cells in distinctly separate brain regions. We show that time- and cell-resolved traces of calcium signaling can be recorded using this endoscope in parallel with single-cell images, thus enabling multisite correlated circuit-dynamics studies on the brain of freely moving animals.
Guided filter based image enhancement for focal error compensation in low cost automated histopathology microscopic system
- First Published: 15 August 2020
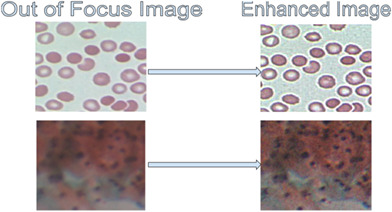
Low-cost automated histopathology microscopy systems usually suffer from optical imperfections, producing images that are slightly Out of Focus (OoF). In this work, a guided filter (GF) based image preprocessing is proposed for compensating focal errors, and its efficacy is demonstrated on images of healthy and malaria infected Red Blood Cells (h-RBCs and i-RBCs), and PAP smears. The images enhanced using GF approach lead to better segmentation accuracy and visual quality compared to six other prominently used methods. Thus, the proposed GF approach is a viable solution for rectifying the OoF microscopy images without the loss of the valuable diagnostic information presented by the color tone.
Breath indeed carries significant information about a disease: Potential biomarkers of cerebral palsy
- First Published: 11 June 2020
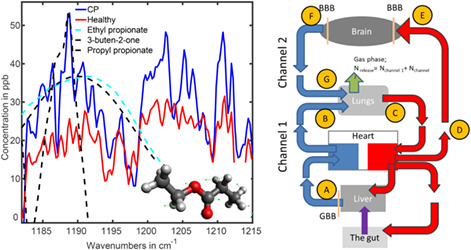
Objective and reliable noninvasive medical diagnostics of a large variety of diseases is still a dream. As a step in the direction of realization, a FTIR spectroscopic breath study of cerebral palsy was performed. Two volatile organic compounds were identified that demonstrate significant deviations in the diseased and healthy groups. A transportation scheme of the compounds in the body was hypothesized that connects the gut, brain and lungs.
Raman mapping coupled to self-modelling MCR-ALS analysis to estimate active cosmetic ingredient penetration profile in skin
- First Published: 17 July 2020
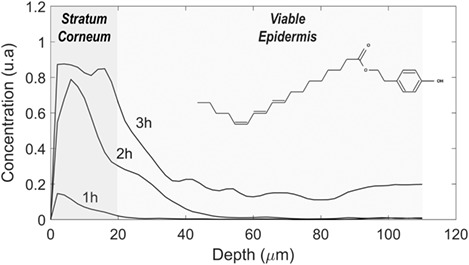
Multivariate curve resolution alternating least squares (MC®-ALS) coupled to confocal Raman mapping to detect and semi-quantitatively describe the diffusion profile of Delipidol in the skin. It is demonstrated that profiling of the kinetics of diffusion into the skin can be established with or without additional spectral equality constraint in the multivariate analysis (ie, no reference spectrum of the active cosmetic ingredient is required).
Practical two-photon-absorption cross sections and spectra of eosin and hematoxylin
- First Published: 26 July 2020
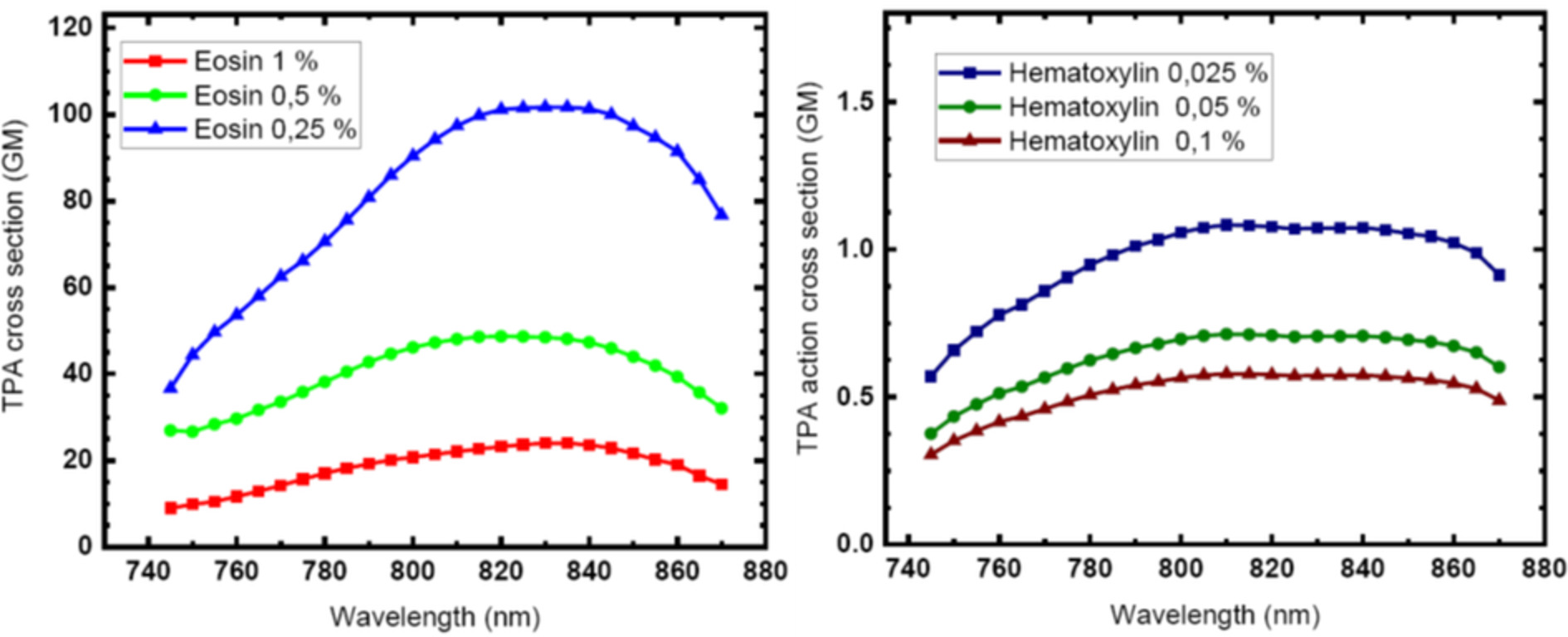
We provide the two-photon absorption cross sections and spectra of eosin and hematoxylin for applicative purposes. The data refer to pure samples of the two dyes in water solution with different concentrations, in the typical range employed in standard staining procedures in the wavelength range from 740 to 880 nm. The obtained data are conceived as a useful tool for researchers in biophotonic, biology and all nonlinear microcopy users.
Understanding Escherichia coli damages after chlorophyllin-based photosensitization
- First Published: 29 July 2020
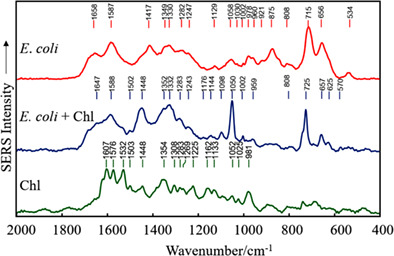
The aim of this research was to examine the mechanism of inactivation of the main food pathogen E. coli by the Chl-based photosensitization and to evaluate the alterations of this bacterium, induced by the treatment. The chemical changes resulting from the inactivation of bacteria by Chl-based photosensitization were investigated by employing the colloidal SERS spectroscopy approach.
Label-free discrimination and selection of cancer cells from blood during flow using holography-induced dielectrophoresis
- First Published: 23 July 2020
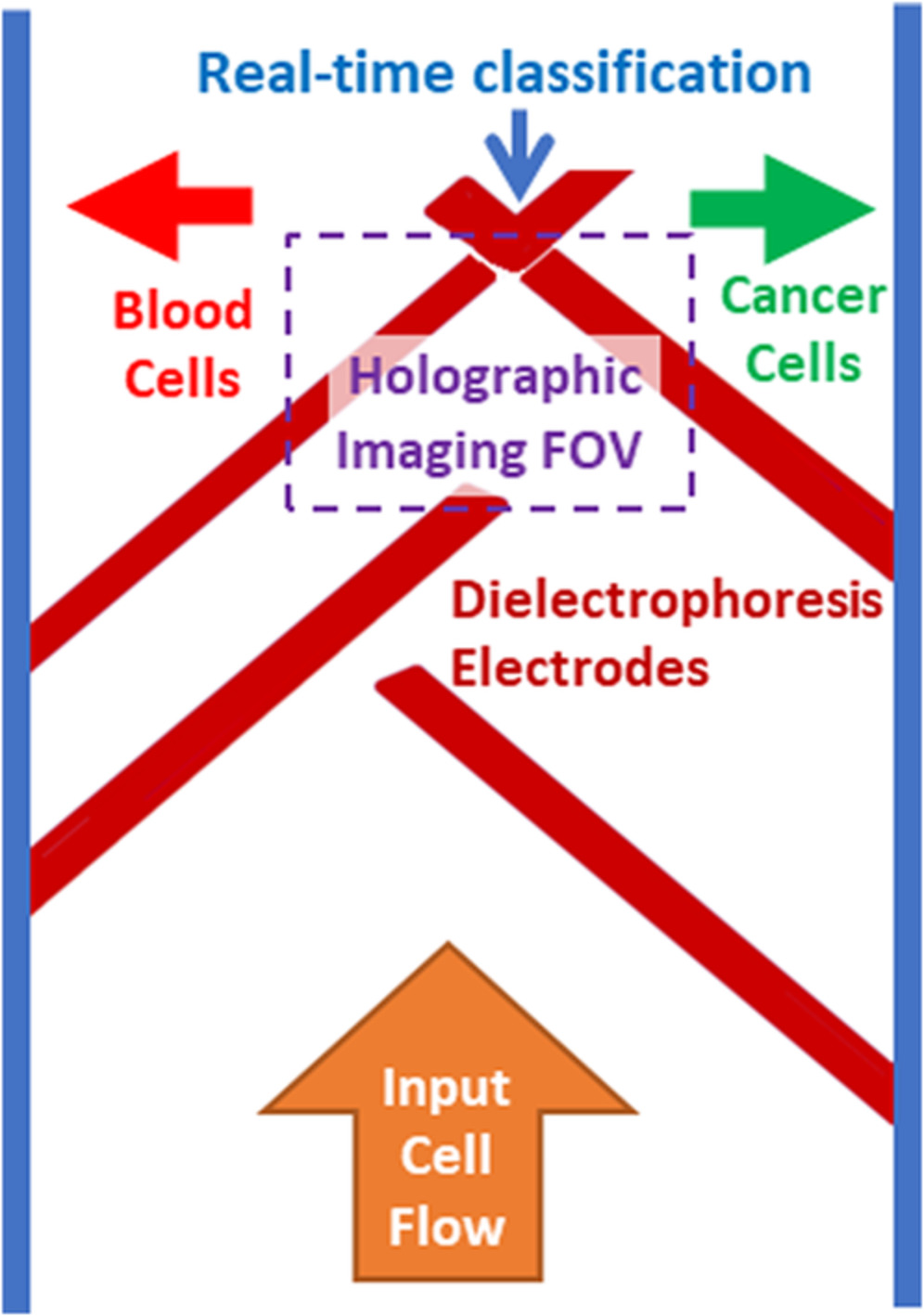
A method for label-free imaging and sorting of cancer cells in blood, based on a dielectrophoretic microfluidic chip and interferometric phase microscopy, is presented. The chip has been embedded with dielectrophoretic electrodes and sorts the cells based on the decisions obtained during the cell flow by the label-free quantitative imaging and real-time machine learning classification.
The near-infrared autofluorescence fingerprint of the brain
- First Published: 21 July 2020
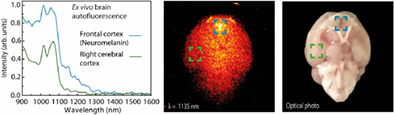
The brain presents a characteristic non-homogeneous autofluorescence signature in the near-infrared that cannot be neglected when using near-infrared fluorophores for brain imaging and sensing. The brain autofluorescence spectrum is related to the content of various chromophores, including brain-specific neuromelanin, which may be altered in some central nervous system diseases, indicating the potential of autofluorescence as an endogenous diagnostic marker.
Characterizing near-infrared spectroscopy signal under hypercapnia
- First Published: 24 July 2020
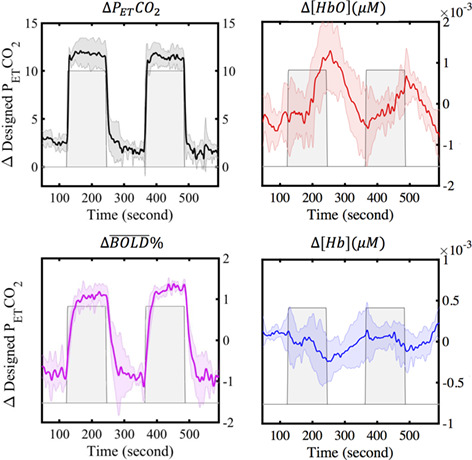
Vasoactive stress tests (i.e. hypercapnia, the elevated partial pressure of arterial CO2 [PaCO2]) are commonly used to induce cerebral blood flow changes and expose hidden perfusion deficits in the brain. In this study, several hypercapnia-induced tests were measured by concurrent functional MRI and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to develop and optimize vasoactive stress tests for NIRS. The results demonstrate that only tests that increase PaCO2 gradually can produce reliable NIRS results.
In vivo and ex vivo confocal microscopy for the evaluation of surgical margins of melanoma
- First Published: 24 July 2020
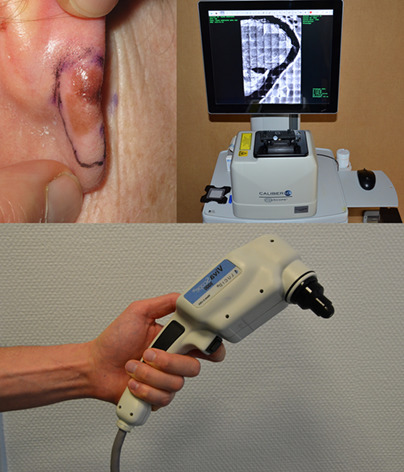
The applications of confocal microscopy are expanding in dermatology. We report the first series of melanomas (MMs) where the surgical margins were evaluated both by in vivo and ex vivo confocal microscopy and we found a good correlation with histopathology. These techniques could help to reduce surgical stages and local recurrences after surgery especially in clinically ill-defined MMs such as lentigo maligna.
Peri-tumoural stroma collagen organization of invasive ductal carcinoma assessed by polarized light microscopy differs between OncotypeDX risk group
- First Published: 25 July 2020
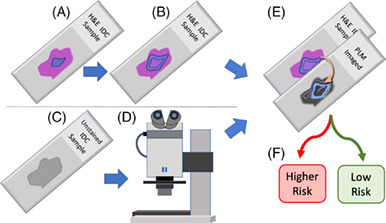
This work provides a first step toward improved stratification of breast cancer patients into appropriate treatment pathways. Using a new flavor of polarized light microscopy, the collagen in breast cancer surgical samples was assessed and a model that could classify a patient's risk was developed. We demonstrate the ability of this model to predict the risk group of a commercially available genomic test OncotypeDX.
A rapid white blood cell classification system based on multimode imaging technology
- First Published: 21 July 2020
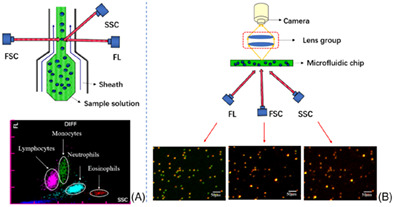
In order to simplify the complexity of the white blood cell classification method in the existing testing equipment, a white blood cell classification and detection system based on microfluidic chip technology and multimode imaging technology was constructed. It can realize the classification and detection of four types of white blood cells, and provides solid technical support for the further development of POCT blood cell detection equipment.
Cortex-wide microcirculation mapping with ultrafast large-field multifocal illumination microscopy
- First Published: 05 August 2020
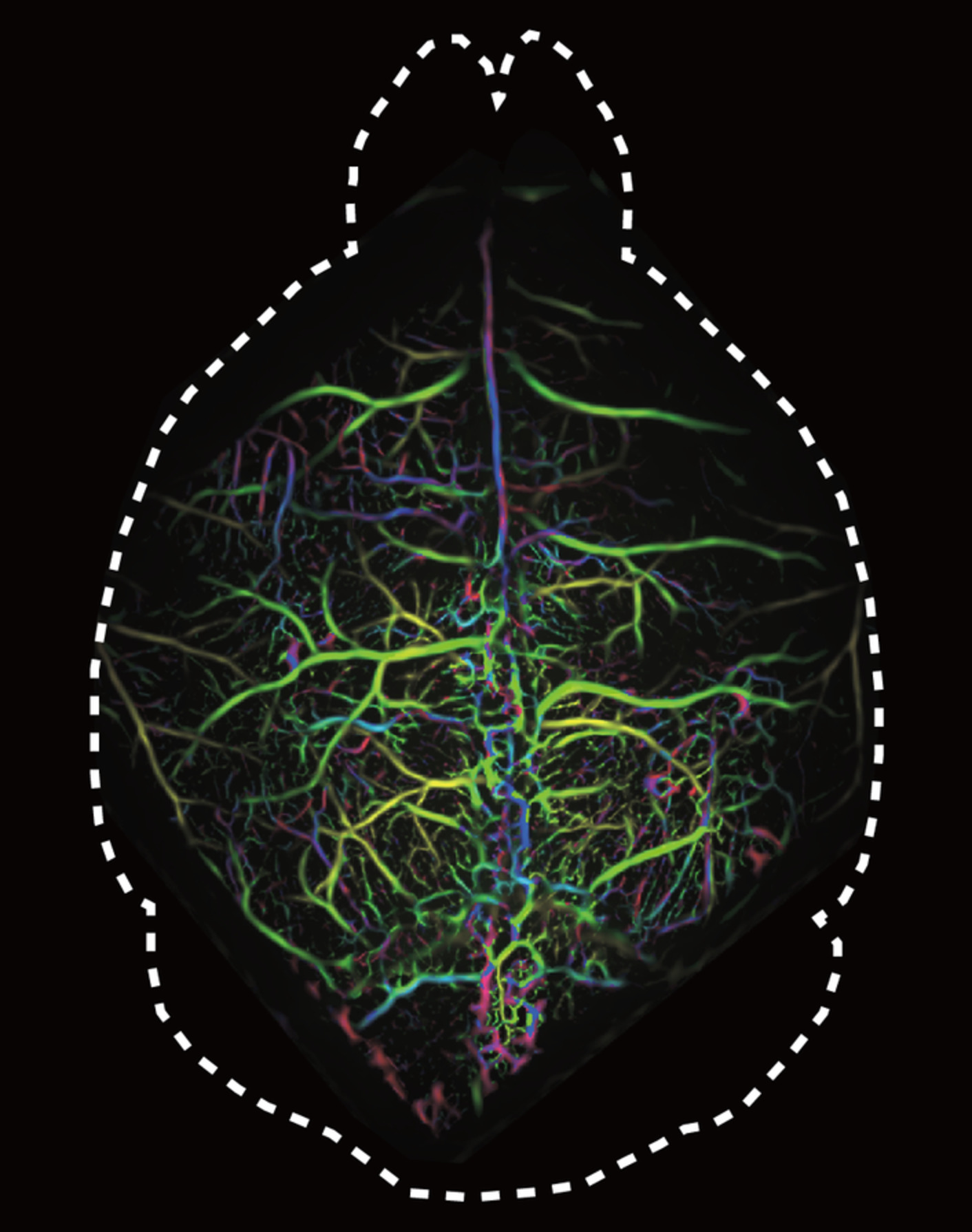
Conventional laser scanning microscopy is subject to hard tradeoffs between resolution, field of view (FOV) and imaging speed. We report on a parallel exposure scheme for large-field multifocal illumination (LMI) fluorescence microscopy. The new technique can visualize centimeter-scale FOVs with capillary level resolution and 200 Hz frame rate, thus opening new venues for studying fast biodynamics, such as cerebral microcirculation, circulating cells or brain signaling.
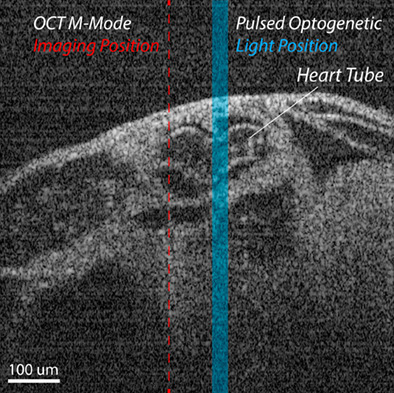
Optogenetic cardiac pacing in cultured mouse embryos under imaging guidance
- First Published: 21 July 2020
Unveiling dose- and time-dependent osteosarcoma cell responses to the γ-secretase inhibitor, DAPT, by confocal Raman microscopy
- First Published: 22 July 2020
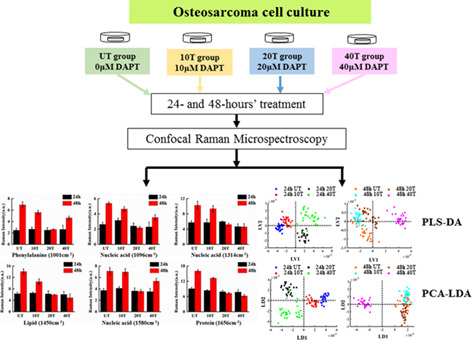
The dose- and time-dependent responses of the γ-secretase inhibitor (DAPT) in osteosarcoma cells were illustrated by Raman microspectroscopy. Main compositional changes (nucleic acids, protein, and lipid) in DAPT treated K7M2 cell line were fully addressed after detailed spectral analyses, testifying inhibitory effects of DAPT on the cell proliferation. Both PLS-DA and PCA-LDA analyses revealed governing compositional variations among investigated groups by distinguishing their spectral characteristics with relatively high accuracies.
Soft-tissue spectral subtraction improves transcutaneous Raman estimates of murine bone strength in vivo
- First Published: 04 August 2020
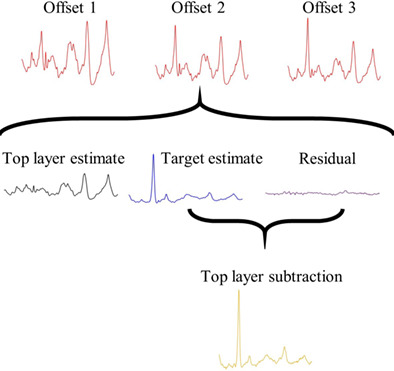
[We adapt a library-based model called SOLD to unmix spatially offset Raman measurements of murine tibiae in vivo to produce a “top layer subtracted” (tls) spectrum. Superior prediction of volumetric bone mineralization density and maximum torque using partial least squares regression on tls spectra rather than the SOLD spectra is reported. Simulations indicate this chemometric approach could have broad applicability when comprehensive spectral libraries are difficult to acquire.]