Characterizing near-infrared spectroscopy signal under hypercapnia
Ho-Ching (Shawn) Yang
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorZhenhu Liang
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Institute of Electrical Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, China
Search for more papers by this authorNicole L. Vike
Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorTaylor Lee
School of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorJoseph V. Rispoli
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorEric A. Nauman
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
School of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorThomas M. Talavage
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yunjie Tong
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Correspondence
Yunjie Tong, Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorHo-Ching (Shawn) Yang
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorZhenhu Liang
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Institute of Electrical Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, China
Search for more papers by this authorNicole L. Vike
Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorTaylor Lee
School of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorJoseph V. Rispoli
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorEric A. Nauman
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
School of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorThomas M. Talavage
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yunjie Tong
Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA
Correspondence
Yunjie Tong, Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: National Science Foundation, Grant/Award Number: Graduate Research Fellowship (NSF GRFP DGE-1333468); Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute, Grant/Award Number: the Pilot Funding for Research Use of Core Facilit; National Institutes of Health, Grant/Award Number: K25 DA031769 (YT)
Abstract
Vasoactive stress tests (i.e. hypercapnia, elevated partial pressure of arterial CO2 [PaCO2]) are commonly used in functional MRI (fMRI), to induce cerebral blood flow changes and expose hidden perfusion deficits in the brain. Compared with fMRI, near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is an alternative low-cost, real-time, and non-invasive tool, which can be applied in out-of-hospital settings. To develop and optimize vasoactive stress tests for NIRS, several hypercapnia-induced tasks were tested using concurrent-NIRS/fMRI on healthy subjects. The results indicated that the cerebral and extracerebral reactivity to elevated PaCO2 depended on the rate of the CO2 increase. A steep increase resulted in different cerebral and extracerebral reactivities, leading to unpredictable NIRS measurements compared with fMRI. However, a ramped increase, induced by ramped-CO2 inhalation or breath-holding tasks, induced synchronized cerebral, and extracerebral reactivities, resulting in consistent NIRS and fMRI measurements. These results demonstrate that only tasks that increase PaCO2 gradually can produce reliable NIRS results.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio202000173-sup-0001-FiguresS1.docxWord 2007 document , 483 KB | Figure S1 (a) Signal in one NIRS channel with visible heartrate. (b) Signal in one NIRS channel with invisible heartrate. Figure. S2. Under sharp-CI task, averaged MCCCs between ΔPETCO2 and ∆ [HbO] (∆ [Hb]) signals are shown in column 1 (2) from all 10 subjects. Figure. S3. Averaged MCCCs between ΔPETCO2 and ∆ [HbO] (∆ [Hb]) signals are shown in column 1 (2) from 4 subjects. The corresponding tasks are (a) sharp-CI, (b) long-ramped CI, and (c) short-ramped CI tasks. Cross in the channel means the p value is larger than 0.05 under one sample t test. |
| jbio202000173-sup-0002-VideoS1.mp4MPEG-4 video, 6.6 MB | Video S1 Movie of sharp-CI task with high correlations between ΔPETCO2, Δ |
| jbio202000173-sup-0003-VideoS2.mp4MPEG-4 video, 5.6 MB | Video S2 Movie of sharp-CI task with low correlations between ΔPETCO2, Δ |
| jbio202000173-sup-0004-VideoS3.mp4MPEG-4 video, 4.9 MB | Video S3 Movie of breath-holding task. Panel (a) represent dynamic changes of (a1) Δ |
| jbio202000173-sup-0005-VideoS4.mp4MPEG-4 video, 7.8 MB | Video S4 Movie of long-ramped CI task. Panel (a) represent dynamic changes of (a1) ΔPETCO2, (a2) Δ |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1T. L. Davis, K. K. Kwong, R. M. Weisskoff, B. R. Rosen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1998, 95, 1834.
- 2R. D. Hoge, J. Atkinson, B. Gill, G. R. Crelier, S. Marrett, G. B. Pike, Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 849.
10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199911)42:5<849::AID-MRM4>3.0.CO;2-Z CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 3P. A. Chiarelli, D. P. Bulte, D. Gallichan, S. K. Piechnik, R. Wise, P. Jezzard, J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 57, 538.
- 4F. M. Faraci, K. R. Breese, D. D. Heistad, Stroke 1994, 25, 1679.
- 5S. H. Yoon, M. Zuccarello, R. M. Rapoport General, Pharmacol.: The Vasc. Syst. 2000, 35, 333.
- 6N. A. Lassen, Taylor & Francis 1968, 22, 247.
- 7B. Stefanovic, J. M. Warnking, E. Kobayashi, A. P. Bagshaw, C. Hawco, F. Dubeau, J. Gotman, G. B. Pike, Neuroimage 2005, 28, 205.
- 8C. W. Barten, E. S. Wang, Ann. Emerg. Med. 1994, 23, 560.
- 9E. Prisman, M. Slessarev, J. Han, J. Poublanc, A. Mardimae, A. Crawley, J. Fisher, D. Mikulis, J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 27, 185.
10.1002/jmri.21102 Google Scholar
- 10E. Rostrup, H. B. Larsson, P. B. Toft, K. Garde, C. Thomsen, P. Ring, L. Søndergaard, O. Henriksen, NMR Biomed. 1994, 7, 29.
- 11U. S. Yezhuvath, K. Lewis-Amezcua, R. Varghese, G. Xiao, H. Lu, NMR Biomed, 2009, 22, 779.
- 12R. G. Wise, K. T. Pattinson, D. P. Bulte, P. A. Chiarelli, S. D. Mayhew, G. M. Balanos, D. F. O'Connor, T. R. Pragnell, P. A. Robbins, I. Tracey, Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 2007, 27, 1521.
- 13M. Slessarev, J. Han, A. Mardimae, E. Prisman, D. Preiss, G. Volgyesi, C. Ansel, J. Duffin, J. A. Fisher, J. Physiol. 2007, 581, 1207.
- 14A. Kastrup, T.-Q. Li, A. Takahashi, G. H. Glover, M. E. Moseley, Stroke 1998, 29, 2641.
- 15H. Markus, M. Harrison, Stroke 1992, 23, 668.
- 16D. A. Boas, C. E. Elwell, M. Ferrari, G. Taga, Neuroimage 2014, 85, 1.
- 17M. Ferrari, V. Quaresima, Neuroimage 2012, 63, 921.
- 18F. Scholkmann, S. Kleiser, A. J. Metz, R. Zimmermann, J. M. Pavia, U. Wolf, M. Wolf, Neuroimage 2014, 85, 6.
- 19M. Wolf, M. Ferrari, V. Quaresima, J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 062104.
- 20P. Smielewski, P. Kirkpatrick, P. Minhas, J. D. Pickard, M. Czosnyka, Stroke 1995, 26, 2285.
- 21U. Emir, C. Ozturk, A. Akin, Physiol. Meas. 2007, 29, 49.
- 22T. S. Leung, I. Tachtsidis, M. M. Tisdall, C. Pritchard, M. Smith, C. E. Elwell, Physiol. Meas. 2008, 30, 1.
- 23J. Virtanen, T. E. Noponen, P. Meriläinen, J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 054032.
- 24J. J. Selb, D. A. Boas, S.-T. Chan, K. C. Evans, E. M. Buckley, S. A. Carp, Neurophotonics. 2014, 1, 015005.
- 25T. Alderliesten, J. De Vis, P. Lemmers, F. Van Bel, M. Benders, J. Hendrikse, E. Petersen, Neuroimage 2014, 85, 255.
- 26B. J. MacIntosh, L. M. Klassen, R. S. Menon, Neuroimage 2003, 20, 1246.
- 27D. O. Svaldi, C. Joshi, M. E. Robinson, T. E. Shenk, K. Abbas, E. A. Nauman, L. J. Leverenz, T. M. Talavage, Dev. Neuropsychol. 2015, 40, 80.
- 28D. O. Svaldi, E. C. McCuen, C. Joshi, M. E. Robinson, Y. Nho, R. Hannemann, E. A. Nauman, L. J. Leverenz, T. M. Talavage, Brain Imaging Behav. 2017, 11, 98.
- 29D. O. Svaldi, C. Joshi, E. C. McCuen, J. P. Music, R. Hannemann, L. J. Leverenz, E. A. Nauman, T. M. Talavage, Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 14, 164.
- 30A. Riecker, W. Grodd, U. Klose, J. B. Schulz, K. Gröschel, M. Erb, H. Ackermann, A. Kastrup, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2003, 23, 565.
- 31J. F. Schieve, W. P. Wilson, Am. J. Med. 1953, 15, 171.
- 32L. Gagnon, M. A. Yücel, M. Dehaes, R. J. Cooper, K. L. Perdue, J. Selb, T. J. Huppert, R. D. Hoge, D. A. Boas, Neuroimage 2012, 59, 3933.
- 33T. Funane, H. Atsumori, T. Katura, A. N. Obata, H. Sato, Y. Tanikawa, E. Okada, M. Kiguchi, Neuroimage 2014, 85, 150.
- 34D. Harris, F. Cowans, D. Wertheim, In Oxygen Transport to tissue XV, Springer, Boston, MA, 1994, pp. 825.
- 35J. Duffin, O. Sobczyk, A. Crawley, J. Poublanc, L. Venkatraghavan, K. Sam, A. Mutch, D. Mikulis, J. Fisher, Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 5590.
- 36M. G. Bright, K. Murphy, Neuroimage 2013, 83, 559.
- 37J. Peirce, J. R. Gray, S. Simpson, M. MacAskill, R. Höchenberger, H. Sogo, E. Kastman, J. K. Lindeløv, Behav. Res. Methods 2019, 51, 195.
- 38F. B. Tancredi, J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1066.
- 39Y. Xu, H. L. Graber, R. L. Barbour, nirsLAB: acomputing environment for fNIRS neuroimaging data analysis. In: Biomedical Optics, Miami, FL, April, 2014, pp. BM3A.1.
- 40G. Strangman, J. P. Culver, J. H. Thompson, D. A. Boas, Neuroimage 2002, 17, 719.
- 41M. Jenkinson, C. F. Beckmann, T. E. Behrens, M. W. Woolrich, S. M. Smith, Neuroimage 2012, 62, 782.
- 42J. D. Power, A. Mitra, T. O. Laumann, A. Z. Snyder, B. L. Schlaggar, S. E. Petersen, Neuroimage 2014, 84, 320.
- 43X. Shen, F. Tokoglu, X. Papademetris, R. T. Constable, Neuroimage 2013, 82, 403.
- 44R. A. Fisher, Biometrika 1915, 10, 507.
- 45R. A. Fisher, Metron. 1921, 1, 1.
- 46C. R. Genovese, N. A. Lazar, T. Nichols, Neuroimage 2002, 15, 870.
- 47P. W. McCormick, M. Stewart, G. Lewis, M. Dujovny, J. I. Ausman, J. Neurosurg. 1992, 76, 315.
- 48R. B. Saager, A. J. Berger, JOSA A 2005, 22, 1874.
- 49O. Paulson, S. Strandgaard, L. Edvinsson, Cerebrovasc. Brain Metab. Rev. 1990, 2, 161.
- 50K. Sato, T. Sadamoto, A. Hirasawa, A. Oue, A. W. Subudhi, T. Miyazawa, S. Ogoh, J. Phys. I 2012, 590, 3277.
- 51J. S. Vantanajal, J. C. Ashmead, T. J. Anderson, R. T. Hepple, M. J. Poulin, J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 87.
- 52K. Murphy, A. D. Harris, R. G. Wise, Neuroimage 2011, 54, 369.
- 53T. J. Huppert, R. D. Hoge, S. G. Diamond, M. A. Franceschini, D. A. Boas, Neuroimage 2006, 29, 368.
- 54D. A. Boas, T. Gaudette, G. Strangman, X. Cheng, J. J. Marota, J. B. Mandeville, Neuroimage 2001, 13, 76.



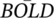 %, and NIRS signals. Panel (a) represent dynamic changes of (a1) ΔPETCO2, (a2) Δ
%, and NIRS signals. Panel (a) represent dynamic changes of (a1) ΔPETCO2, (a2) Δ % from prefrontal region, (a3) Δ[HbO], and (a4) Δ[Hb] signals. The shaded areas indicate the targeted ΔPETCO2 in each task. Panel (b) represent dynamic ΔBOLD% in three axis. Panel (c) represent Δ[HbO] and Δ[Hb] signals in all 17 NIRS channels.
% from prefrontal region, (a3) Δ[HbO], and (a4) Δ[Hb] signals. The shaded areas indicate the targeted ΔPETCO2 in each task. Panel (b) represent dynamic ΔBOLD% in three axis. Panel (c) represent Δ[HbO] and Δ[Hb] signals in all 17 NIRS channels. %, and NIRS signals. Panel (a) represent dynamic changes of (a1) ΔPETCO2, (a2) Δ
%, and NIRS signals. Panel (a) represent dynamic changes of (a1) ΔPETCO2, (a2) Δ % from prefrontal region, (a3) Δ[HbO], and (a4) Δ[Hb] signals. The shaded areas indicate the targeted ΔPETCO2 in each task. Panel (b) represent dynamic ΔBOLD% in three axis. Panel (c) represent Δ[HbO] and Δ[Hb] signals in all 17 NIRS channels.
% from prefrontal region, (a3) Δ[HbO], and (a4) Δ[Hb] signals. The shaded areas indicate the targeted ΔPETCO2 in each task. Panel (b) represent dynamic ΔBOLD% in three axis. Panel (c) represent Δ[HbO] and Δ[Hb] signals in all 17 NIRS channels. % from prefrontal region, (a2) Δ[HbO], and (a3) Δ[Hb] signals. The shaded areas indicate the targeted ΔPETCO2 in each task. Panel (b) represent dynamic ΔBOLD% in three axis. Panel (c) represent Δ[HbO] and Δ[Hb] signals in all 17 NIRS channels.
% from prefrontal region, (a2) Δ[HbO], and (a3) Δ[Hb] signals. The shaded areas indicate the targeted ΔPETCO2 in each task. Panel (b) represent dynamic ΔBOLD% in three axis. Panel (c) represent Δ[HbO] and Δ[Hb] signals in all 17 NIRS channels. % from prefrontal region, (a3) Δ[HbO], and (a4) Δ[Hb] signals. The shaded areas indicate the targeted ΔPETCO2 in each task. Panel (b) represent dynamic ΔBOLD% in three axis. Panel (c) represent Δ[HbO] and Δ[Hb] signals in all 17 NIRS channels.
% from prefrontal region, (a3) Δ[HbO], and (a4) Δ[Hb] signals. The shaded areas indicate the targeted ΔPETCO2 in each task. Panel (b) represent dynamic ΔBOLD% in three axis. Panel (c) represent Δ[HbO] and Δ[Hb] signals in all 17 NIRS channels.
