Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 22 December 2020

Poly-L-lysine-coated, highly microporous silicon nanoparticles are herein characterized and successfully used as longer-lived luminescent probes for in vivo time-gated imaging using Hydra vulgaris as model organism. The uptake in living polyp is promoted by the positive surface charge of the nanocomposite. The outcomes show that time gating allows to get rid of nonspecific tissue autofluorescence and leads to a contrast enhancement by a factor > 1 order of magnitude.
Further details can be found in the article by Chiara Schiattarella, Rosalba Moretta, Thomas Defforge, Gaël Gautier, et al. (e202000272).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 22 December 2020

Physical and chemical cellular stimulation combined in a unique home-use device provides an effective and long-lasting skin care regime for extrinsic skin aging prevention. The innovative principle relies on potentiating the effect of active ingredients contained in a topical serum with visible and near infrared photons to prevent extrinsic skin aging.
Further details can be found in the article by Cyprien Guermonprez, Lieve Declercq, Géraldine Decaux, and Jean-Alexis Grimaud (e202000230).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 22 December 2020
Vascular disrupting agents (VDAs) can be used to damage the tumour vasculature, suppressing oxygen and nutrition supply to the tumour tissue. Photoacoustic imaging was used to assess the structural and functional changes of the tumour vasculature and evaluate the efficacy of the VDAs. Tissues are irradiated with short laser pulses and the photoacoustic waves are analyzed to extract vessel size and hemoglobin composition to evaluate the VDA, hours after administration.
Further details can be found in the article by Muhannad N Fadhel, Sila Appak Baskoy, Yanjie Wang, Eno Hysi, and Michael C. Kolios (e202000209).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 22 December 2020
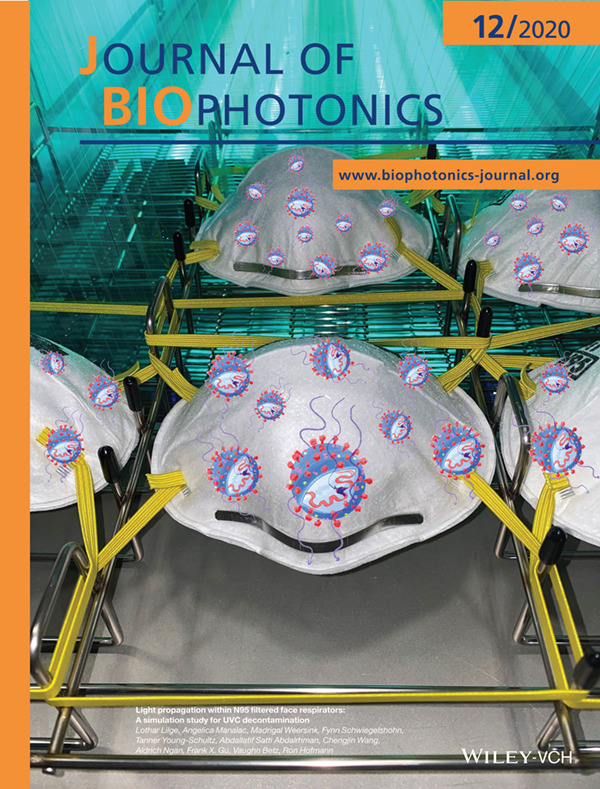

Access to sterile personal protective equipment, in particular for filtered face respirators is critical in the current pandemic for front line healthcare workers. Extended use may be required during supply shortages or due to economic considerations. UVC sterilization can be a cost-effective technique capable of high throughput. The suitability of various N95 respirator designs for UV mediated reuse were evaluated based on the materials utilized. (Background image: with permission from Prescientx. Virus image: Sophia Lilge.
Further details can be found in the article by Lothar Lilge, Angelica Manalac, Madrigal Weersink, Fynn Schwiegelshohn, Tanner Young-Schultz, Abdallatif Satti Abdalrhman, Chengjin Wang, Aldrich Ngan, Frank X. Gu, Vaughn Betz, Ron Hofmann (e202000232).
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLES
Autofocusing technologies for whole slide imaging and automated microscopy
- First Published: 25 August 2020
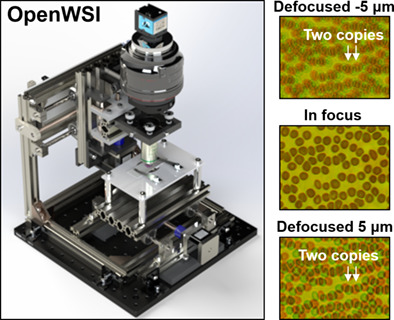
A fundamental challenge with automated microscopy and high-throughput imaging has been the ability to acquire high-quality, in-focus images at high speed. This review article discusses different autofocusing approaches for automated microscopy and whole slide imaging (WSI). The technical concepts, merits and limitations of these methods are explained and compared to those of a traditional WSI system.
Photoacoustic endoscopy: A progress review
- First Published: 16 September 2020
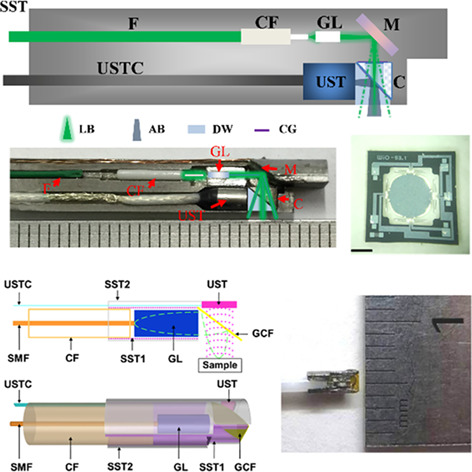
Photoacoustic endoscopy (PAE) has been developed for more than one decade since the first report. Unfortunately, there is no mature device recognized in clinic due to various limitations. To address this concern, recent advances have significantly promoted the progress of PAE. We comprehensively review the recent progresses in single- and multimodality PAE to achieve practical devices for potential applicable scenarios, and propose challenges and prospects for future PAEs.
FULL ARTICLES
Time-gated luminescence imaging of positively charged poly-l-lysine-coated highly microporous silicon nanoparticles in living Hydra polyp
- First Published: 21 August 2020
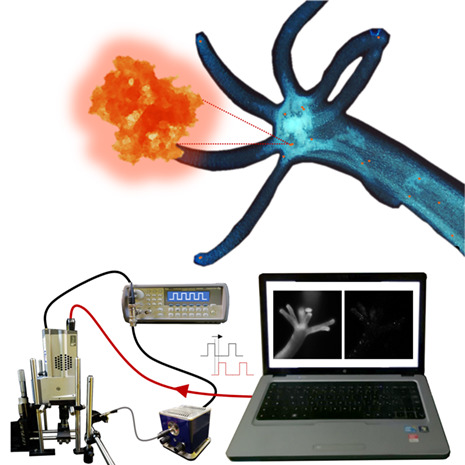
Poly-l-lysine-coated, luminescent highly microporous silicon nanoparticles are herein characterized and successfully used as label-free longer-lived probes for in vivo time-gated luminescence imaging using Hydra vulgaris as target. The uptake in living organism is promoted by the positive surface charge of the nanocomposite. The outcomes show that time gating allows to get rid of nonspecific tissue autofluorescence and leads to a ~ 20-fold enhancement in the image signal-to-noise ratio.
Safety and efficacy of a novel home-use device for light-potentiated (LED) skin treatment
- First Published: 19 September 2020
Optimizing skin health through an effective and long-lasting skin care regime requires a global approach, encompassing various mechanisms to stimulate this interplay beyond the action scope of a classical topical solution. This study evaluates the impact of a novel home-use device combining a topical serum, light-emitting diodes and massage on the clinical signs of extrinsic skin aging. The innovative principle relies on potentiating the effect of active ingredients contained in the topical serum with visible and near infra-red photons to prevent extracellular matrix degradation and promote its reconstruction.
Novel input polarisation independent endoscopic cross-polarised optical coherence tomography probe
- First Published: 01 August 2020
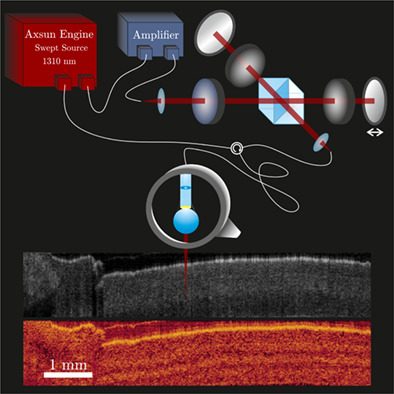
Cross-polarised optical coherence tomography is a promising technique to reveal certain pathologic conditions in tissue like for example tumorous areas. However, endoscopic devices with flexible small probes to detect the diseased areas intraoperatively barely exist. The approach presented here is an extension of a commercially available swept-source OCT system, which impresses by its simplicity. Applying a common-path probe, polarisation of reference and sample arm does not need to be further balanced. A depolariser makes the system independent of the polarisation state of the source.
Light propagation within N95 filtered face respirators: A simulation study for UVC decontamination
- First Published: 05 September 2020
Access to sterile personal protective equipment, in particular for filtered face respirators is critical in the current pandemic for front line healthcare workers. Extended use may be required during supply shortages or due to economic considerations. UVC sterilization can be a cost-effective technique capable of high throughput. Here we evaluated the suitability of various N95 respirator designs for UV mediated reuse based on the materials utilized. The work determines the respirator fabric's light absorption and scattering coefficients and models the UVC light distributions inside the respirators.
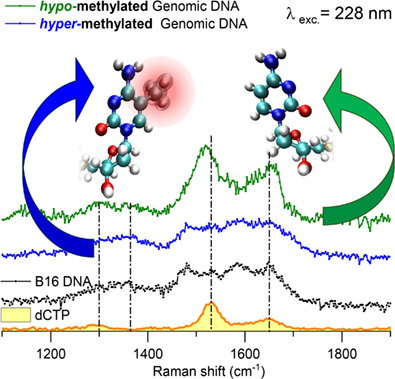
Investigation of genomic DNA methylation by ultraviolet resonant Raman spectroscopy
- First Published: 29 July 2020
Reliability assessment on intravascular photoacoustic imaging of lipid: ex vivo animal and human sample validation
- First Published: 13 September 2020
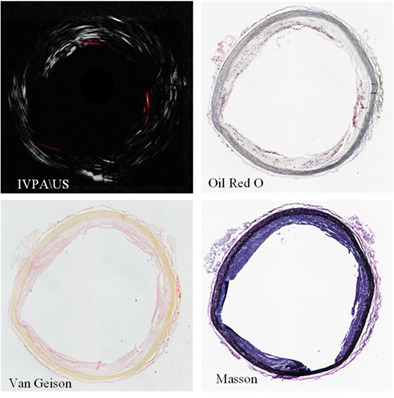
IVPA imaging has been proven to characteristically detect the lipids. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy assessment on IVPA imaging of lipids were verified by comparing the IVPA images with the Oil Red O staining results from rabbit aorta and human carotid plaque samples. And the results demonstrated the reliability of IVPA imaging on distinguishing the lesions vessel with lipid-rich plaque, which provided the foundation for IVPA translation to clinical application.
UnaG as a reporter in adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer for biomedical imaging
- First Published: 07 September 2020
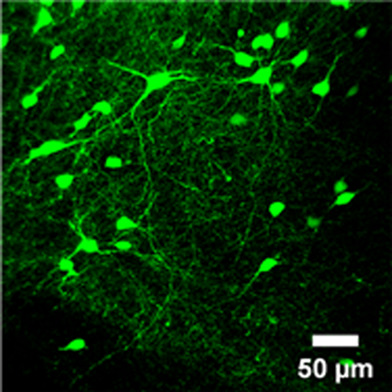
UnaG, a bilirubin-inducible extrinsically fluorescent tag from vertebrates, can act as a small intrinsically fluorescent reporter in the mouse brain without an additional ligand. It can label the neurons morphology as well as EGFP. It shows better performance in SeeDB tissue clearing than EGFP. In sum, UnaG provides an alternative over EGFP for AAV mediated neurons labeling in mammals for biomedical imaging.
Deep convolutional neural network recovers pure absorbance spectra from highly scatter-distorted spectra of cells
- First Published: 25 August 2020

A Deep Learning-based approach for near-real-time Mie-scatter correction of FT-IR hyperspectral images is proposed. A Descattering Autoencoder is presented and trained on a subset of measured spectra corrected with the state-of-the-art Mie Extinction EMSC algorithm. This method is shown to perform the task of Mie-scatter correction three orders of magnitude faster than the conventional algorithm, as well as being more robust and yielding informative hyperspectral maps.
Effects of cold atmospheric pressure plasma and disinfecting agents on Candida albicans in root canals of extracted human teeth
- First Published: 15 September 2020
Automated vessel diameter quantification and vessel tracing for OCT angiography
- First Published: 28 August 2020
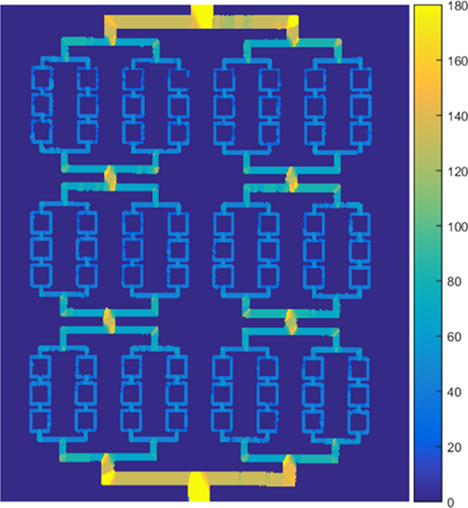
We present a method for automated mapping of vessel diameter down to individual capillaries and incorporated a modified A* path searching algorithm to trace vessel branches and to calculate the diameter, tortuosity and bifurcation angle of vessel branches from the OCTA images. Our techniques provide a platform for the automated evaluation of the vasculature and may aid in diagnosis of vascular diseases, especially those resulting in regional early-stage morphological changes. The image shows vessel diameter map of microfluidic channels mimicking healthy vasculature (color bar in μm). Quantitative OCTA maps of microfluidic channels mimicking healthy vasculature.
Physicochemical damage and early-stage biological response to X-ray radiation studied in prostate cancer cells by Raman spectroscopy
- First Published: 25 August 2020
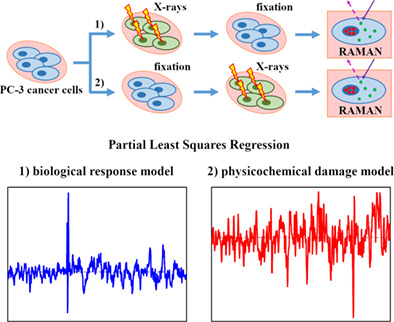
Raman studies of radiation effects have been shown to be sensitive enough to discriminate between the initial damage and the response of the cell. The physicochemical damage has been found to be a more subtle effect than the early-stage biological response of the cells. Both exposure effects have been associated with different biochemical changes and the early-stage biological response of the cells cannot be confused with the physicochemical damage caused by X-ray irradiation.
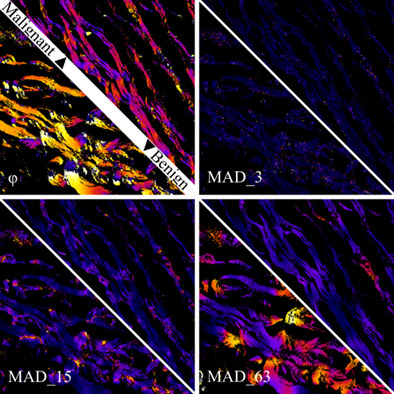
Pixel-level angular quantification of capsular collagen in second harmonic generation microscopy images of encapsulated thyroid nodules
- First Published: 05 September 2020
Multimodal vibrational studies of drug uptake in vitro: Is the whole greater than the sum of their parts?
- First Published: 05 September 2020
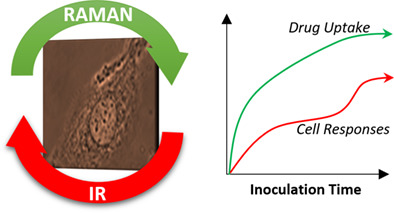
The use of multimodal vibrational spectroscopy is evaluated for the investigation of doxorubicin uptake and cell responses. Infrared (IR) and Raman spectra were acquired at different incubation times, and the information obtained from individual and joint analysis of both techniques was compared. Different methods to study combined spectral data are investigated, including MCR-ALS and 2D-correlation, exploring the added value of combining information from different spectroscopic modalities.
Tracking heavy-water-incorporated confocal Raman spectroscopy for evaluating the effects of PEGylated emulsifiers on skin barrier
- First Published: 24 September 2020
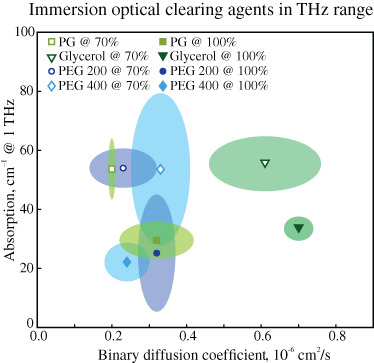
Optimal hyperosmotic agents for tissue immersion optical clearing in terahertz biophotonics
- First Published: 02 September 2020
Measurement of two-photon properties of indocyanine green in water and human plasma excited at the 1700-nm window
- First Published: 07 October 2020

Indocyanine green (ICG) is a human compatible dye and is ideal for deep-tissue two-photon fluorescence microscopy excited at the 1700-nm window in vivo. Here we demonstrate measurement of the two-photon excitation and emission properties of ICG in both water and human plasma, using home-built two-photon action cross-sectional measurement and two-photon emission spectrum measurement systems. Our results will provide key two-photon parameters for the clinical use of ICG.
Calcium oxalate kidney stones, where is the organic matter?: A synchrotron based infrared microspectroscopy study
- First Published: 06 September 2020
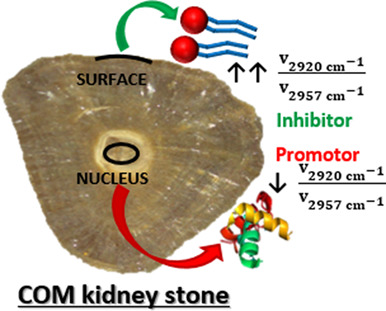
This is a novel study regarding the in situ distribution of the organic matter in oxalocalcic kidney stones, using a synchrotron-based infrared microspectrometer. These components location could give important information about their role during on the nephroliths formation, participating as promotors or inhibitors.
3-photon microscopy of myelin in mouse digital skin excited at the 1700-nm window
- First Published: 24 September 2020
Immunofluorescence and histopathological assessment using ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy in lichen planus
- First Published: 06 October 2020
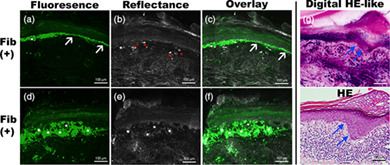
In this study, we assessed the performance of ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) in identifying histomorphological and immunofluorescence features of lichen planus (LP). Ex vivo CLSM showed a perfect agreement with conventional histopathology in identifying key features of LP namely interface dermatitis, vacuolar degeneration and band-like infiltration. Ex vivo CLSM could detect fibrinogen deposition in 62.5% of the sections; whereas, conventional DIF detected fibrinogen deposition in 93.8% of the sections.
Fluorescence lifetime metabolic mapping of hypoxia-induced damage in pancreatic pseudo-islets
- First Published: 07 October 2020
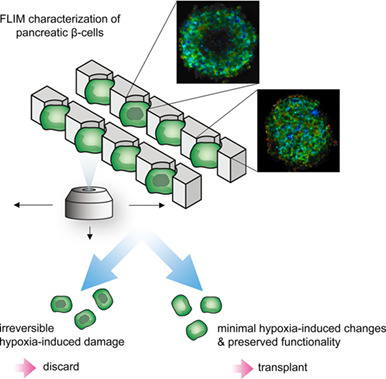
Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) is a powerful technique for the screening of pancreatic β-cell-composed islets prior transplantation. In our study, FLIM-based metabolic profiles utilizing the endogenous fluorescence of the coenzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide enabled the detection of early hypoxia-induced damages. Glucose-response was detected noninvasively in β-cells. The use of FLIM has the potential to improve the outcome of β-cell islet transplantation to treat type 1 diabetes mellitus.