Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: September 2020

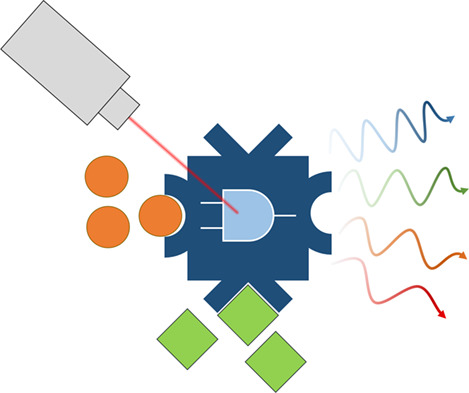
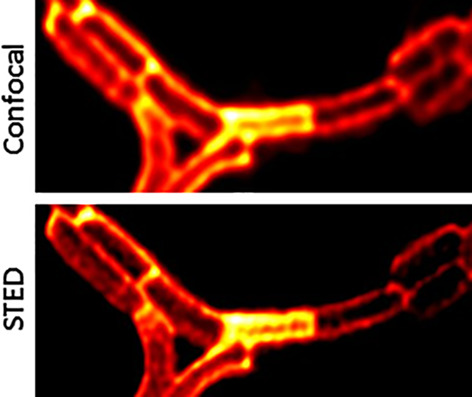
Images of bacterial cells stained with KK114 dye and visualized with STED microscopy. On the monitor: large field of view of B. subtilis cells, the KK114 ball-and-stick model and the schematics of the STED setup. Different space-filling representations of the FtsZ protein are also shown.
Further details can be found in the article by Massimiliano Lucidi, Radu Hristu, Lorenzo Nichele, George A. Stanciu, Denis E. Tranca, Alina Maria Holban, Paolo Visca, Stefan G. Stanciu, and Gabriella Cincotti (e202000097).
Inside Cover
- First Published: September 2020

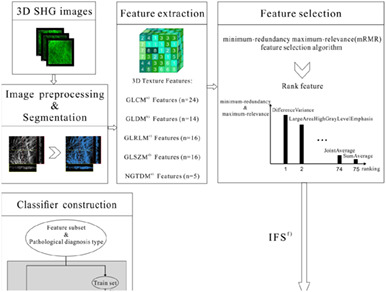
A high-efficiency computer-aided diagnostic model of ovarian cancer was developed, integrating SHG imaging technology for non-invasive imaging of living tissue and machine learning method based on radiomics and TPOT. This model can rapidly, non-destructively, and accurately perform ovarian cancer diagnosis and has great potential in improving diagnostic efficacy and efficiency of medical pathologists.
Further details can be found in the article by Guangxing Wang, Yang Sun, Youting Chen, Qiqi Gao, Dongqing Peng, Hongxin Lin, Zhenlin Zhan, Zhiyi Liu, and Shuangmu Zhuo (e202000050).
Inside Cover
- First Published: September 2020

A cross-scanning optical coherence tomography (CS-OCT) system is newly developed to correct eye motion artifacts in OCT angiography images. The CS-OCT provides two retinal angiograms scanned simultaneously in a perpendicular direction to each other over the same area. Since the eye motion is decomposed into the two retinal angiograms, the motioncorrected retinal angiogram can be obtained by compensating between the two.
Further details can be found in the article by Hyung-Jin Kim, Byeong Joo Song, Youngwoon Choi, and Beop-Min Kim (e202000170).
Inside Cover
- First Published: September 2020

Four metrics including vascular connectivity, contrast-to-noise ratio, signal-to-noise ratio and processing time were developed to quantitatively assess the performance of seven optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) algorithms in image quality and computation speed for neuroimaging. Quantitative assessment of the algorithms provides suggestions for the selection of appropriate OCTA algorithms in the applications of neuroimaging.
Further details can be found in the article by Jianting Liu, Jiang Zhu, Lianqing Zhu, Qiang Yang, Fan Fan, and Fan Zhang (e202000181).
Inside Cover
- First Published: September 2020
Rare earth ions complexes provide numerous highly beneficial optical properties - unusually large Stokes shifts, very narrow line emissions and long-lived excited states being the most prominent of them. Surprisingly few attempts have this far been reported to directly exploit them as direct microbial stains. M. Lezhnina and coworkers here describe basic staining strategies for fluorescence microscopy and outline their eventual potential in fluorescence flow cytometry.
Further details can be found in the article by Marina M. Lezhnina, Weronika Rochowiak, Wolfgang Göhde, Rauni Kuczius, and Ulrich Kynast (e202000068).
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLES
Imaging the invisible—Bioorthogonal Raman probes for imaging of cells and tissues
- First Published: 31 May 2020
This review reports on groundbreaking studies employing linear and non-linear Raman spectroscopic modalities in combination with labeling strategies for the investigation of single cells up to whole tissue samples. Raman spectroscopic imaging in biological and biomedical research is mostly emphasizing its intrinsically label-free nature compared to standard fluorescence microscopy. However, during the past decade more and more pioneering studies present the use of distinct Raman tags for targeting specific biomolecules and investigating their fate on the subcellular level.
FULL ARTICLES
Rapid identification of human ovarian cancer in second harmonic generation images using radiomics feature analyses and tree-based pipeline optimization tool
- First Published: 04 June 2020
Cross-scanning optical coherence tomography angiography for eye motion correction
- First Published: 31 May 2020
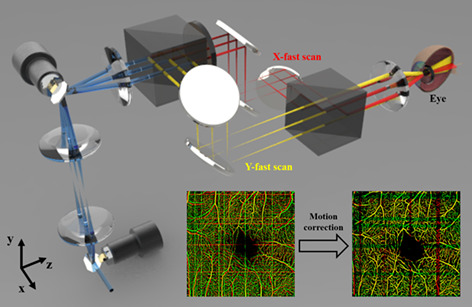
We present a novel method to correct eye motion artifacts in OCT angiography images using a cross-scanning optical coherence tomography (CS-OCT) system. The CS-OCT is a newly developed system that employs a dual illumination configuration with orthogonally polarized two beams, each of which simultaneously performs raster scanning in a perpendicular direction with each other over the same area. Since the cross-scanned two volume data are affected by the same eye motion, we remove motion artifacts using each other and obtain a motion-free angiogram within a single volume scanning time without additional hardware such as eye-tracking devices.
Quantitative assessment of optical coherence tomography angiography algorithms for neuroimaging
- First Published: 15 June 2020
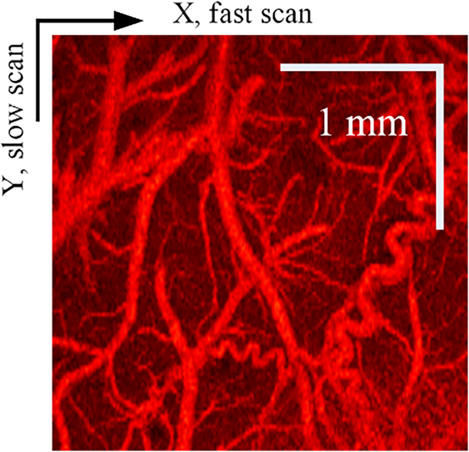
Four metrics including vascular connectivity, contrast-to-noise ratio, signal-to-noise ratio and processing time were developed to quantitatively assess the performance of seven optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) algorithms in image quality and computation speed for neuroimaging. Quantitative assessment of the algorithms can provide suggestions for the selection of appropriate OCTA algorithms for the neuroimaging applications.
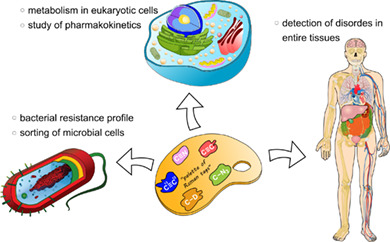
The microbial threat: Can rare earths help?
- First Published: 04 June 2020
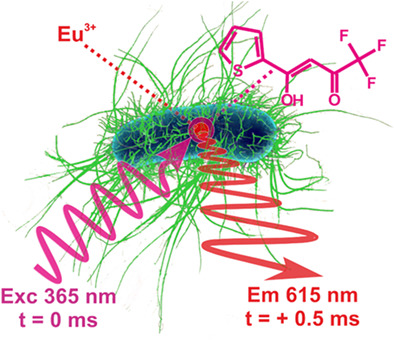
The luminescence of rare earths is hitherto practically unexplored in the microbiological context. Their complexes can be used to readily stain bacteria and characterize them via intracellular or surface luminescence in fluorescence imaging, while luminescence decay times in the millisecond range enable time-delayed spectroscopies. In addition, preliminary experiments on bacteria-like, model polymer particles show the high potential for the enumeration and characterization of microbes by time-gated flow cytometry.
Jones matrix-based speckle-decorrelation angiography using polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography
- First Published: 16 May 2020
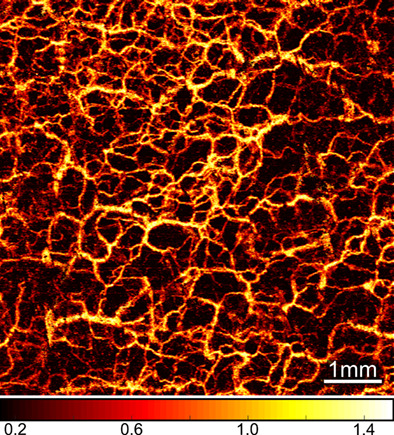
This study investigates Jones matrix-based speckle-decorrelation polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography angiography (PS-OCTA) imaging by assessing the data processing methods and comparing its image quality to conventional OCTA. Imaging of human finger and forearm skin shows the benefits provided by PS-OCTA over conventional OCTA, including improved vessel contrast and imaging depth. This study provides a useful reference point for future preclinical and clinical applications of Jones matrix-based PS-OCTA.
Machine learning of diffraction image patterns for accurate classification of cells modeled with different nuclear sizes
- First Published: 07 June 2020
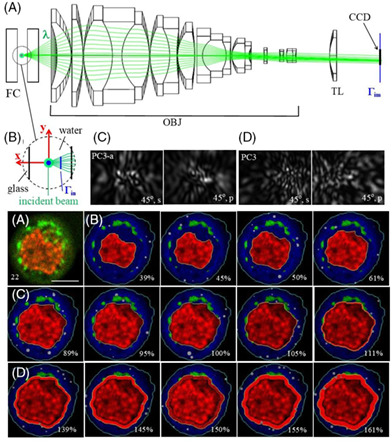
Nuclear size provides an important marker in detecting tumor cells. We obtained 1892 realistic optical cell models from confocal image stacks of human prostate normal and cancer cells to calculate cross-polarized diffraction image (p-DI) pairs in three different nuclear size groups. The support vector machine (SVM) algorithm exhibits robust performance with accuracy above 97% between cells in different nuclear size groups. These results demonstrate significant potential of p-DI data for label-free cell classification by nuclear size.
Hyperspectral imaging and characterization of allergic contact dermatitis in the short-wave infrared
- First Published: 16 May 2020

Hyperspectral imaging in the invisible to human eyes shortwave infrared (SWIR) spectral range was applied to enhance the contrast and reveal underlying mechanistic clues behind ACD—a clinically relevant skin condition caused by a variety of common allergens. Color images generated from the identified three specific wavelengths in SWIR were used to establish a tissue fluid index as a quantitative, proof of concept measure of the skin problem.
The early effects of uninephrectomy on rat kidney metabolic state using optical imaging
- First Published: 21 May 2020
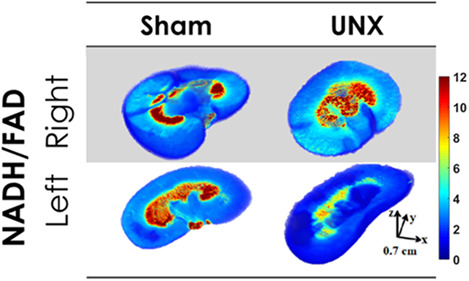
The mechanisms that signal the functional hypertrophic responses of the remaining kidney following partial or total ablation of a kidney are not well understood. This present study provides novel data characterizing the role of mitochondrial metabolism and oxidative stress in the phenomena of compensatory renal hypertrophy of a remnant kidney in the early 3-day period following unilateral nephrectomy (UNX). The data indicate that mitochondria become the dominant source of increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production following UNX and could represent an important hypertrophic signaling mechanism.
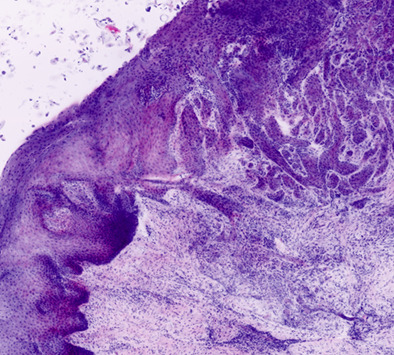
Detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma with ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy: Sensitivity and specificity compared to histopathology
- First Published: 17 May 2020
Vascular changes precede tomographic changes in diabetic eyes without retinopathy and improve artificial intelligence diagnostics
- First Published: 11 May 2020
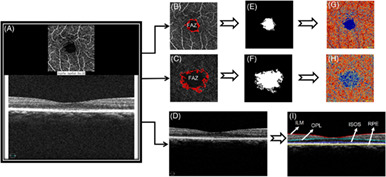
We used artificial intelligence (AI) to link OCT and OCTA features of diabetic changes in the human retina for early diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy (DR). We found that vascular changes preceded the onset of retinopathy and the inclusion of age match normal eyes was vital for the effective training of AI models. Further, imaging features for early diagnosis using combined OCT and OCTA imaging were identified for the first time.
Rapid intraoperative diagnosis of gynecological cancer by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy of fresh tissue biopsy
- First Published: 28 May 2020
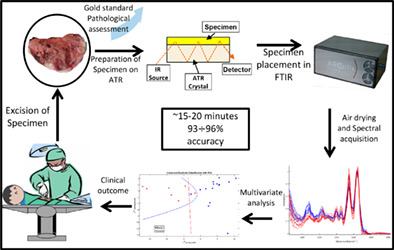
A pseudo real-time intraoperative diagnostic technique based on Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) was developed. Twenty-six fresh tissue samples were collected intraoperatively from patients undergoing gynecological surgeries and examined by Frozen section (FS) histopathology and attenuated total reflection (ATR) FTIR absorption spectra. Two validation schemes were employed: k-fold and “leave one out.” PCA-LDA discrimination model correctly classified the samples into malignant and benign groups with accuracies of 96% and 93% for the k-fold and “leave one out,” respectively.
Cell and nucleus refractive-index mapping by interferometric phase microscopy and rapid confocal fluorescence microscopy
- First Published: 29 May 2020
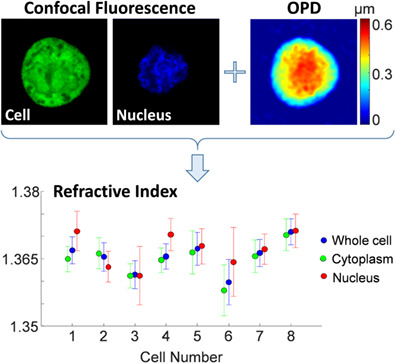
We present a method for measuring the integral refractive index of cell organelles, integrating interferometric phase microscopy (IPM) and rapid confocal fluorescence microscopy. From IPM, we calculate the quantitative cell optical path difference (OPD), which is the product of the cell integral refractive index and physical thickness. From spinning-disk confocal fluorescence microscopy, we calculate the thickness of the entire cell and its nucleus. Finally, we find the integral refractive indices of the whole cell, cytoplasm and nucleus for cancer cells.
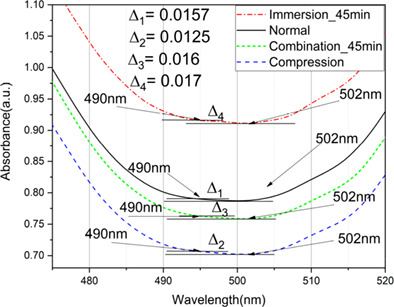
Rapid analysis of disease state in liquid human serum combining infrared spectroscopy and “digital drying”
- First Published: 07 June 2020
Early diagnosis of cancer represents a primary step in increasing survival rates and quality of life in cancer patients. Research on liquid serum samples analysis by ATR-FTIR and QCL-FTIR coupled with “digital drying” shows great classification values when distinguishing brain tumor samples vs healthy control samples. The use of digital drying improves times of acquisition and sample preparation, reducing the barriers through clinical translation.
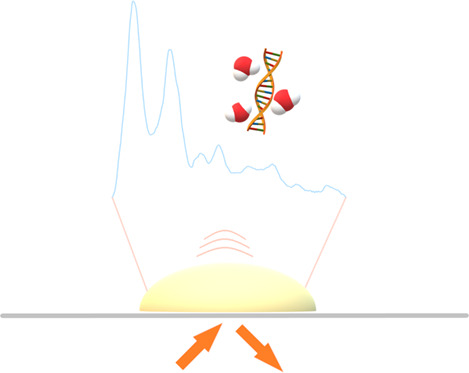
In vivo detection of human cutaneous beta-carotene using computational optical clearing
- First Published: 31 May 2020
The detection of dermal beta-carotene is the main aim of this study using Raman spectroscopy and low-cost diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. We apply computational optical clearing (OC) method to enhance the ability of low-cost diffuse reflection spectroscopy for in vivo detection of dermal beta-carotene in humans. This method can be used as a portable low-cost device to screening the concentration of chromophores such as melanin and carotenoid molecules for oncological studies.
Optically activated and interrogated plasmonic hydrogels for applications in wound healing
- First Published: 15 June 2020
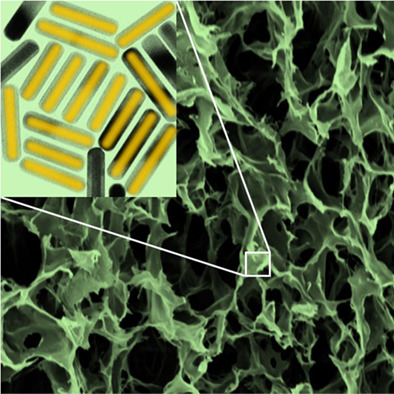
Au/Ag core/shell nanorods are a synergistic bimetallic system for integration in chitosan-based scaffolds that bind to connective tissue upon optical irradiation, change in color according to the environmental level of oxidative stress, hold a reservoir of antimicrobial Ag cations, and retain their compatibility with fabrication processes as electrospinning, which have made this polysaccharide so attractive in tissue engineering.
Photoacoustic and ultrasound (PAUS) dermoscope with high sensitivity and penetration depth by using a bimorph transducer
- First Published: 07 June 2020
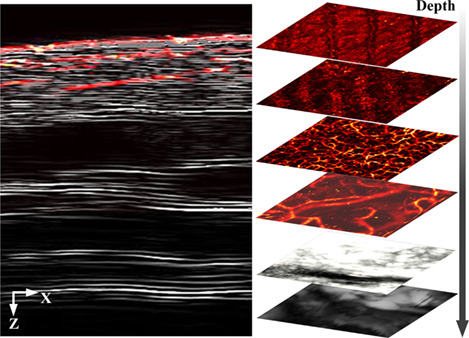
In this study, a bimorph transducer is proposed to improve the detection sensitivity and imaging depth of photoacoustic and ultrasound (PAUS) dermoscope. By applying the bimorph transducer, the imaging depth and sensitivity of PAUS dermoscope were enhanced by simultaneously improving excitation efficiency and reception bandwidth. The integrated design of the imaging head of the dermoscope makes it highly convenient for detecting human skin. The results confirm that the dermoscope with the bimorph transducer is well suited for PA and US dual-modality imaging, which can provide multi-information for skin disease.
CORRIGENDUM
Corrigendum: Photobiomodulation preconditioning prevents cognitive impairment in a neonatal rat model of hypoxia-ischemia
- First Published: 15 July 2020