Machine learning of diffraction image patterns for accurate classification of cells modeled with different nuclear sizes
Jing Liu
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Information Science and Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYaohui Xu
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Information Science and Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Search for more papers by this authorWenjin Wang
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Physics & Electronic Science, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYuhua Wen
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Physics & Electronic Science, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHeng Hong
Department of Pathology and Comparative Medicine, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, USA
Search for more papers by this authorJun Q. Lu
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Department of Physics, East Carolina University, Greenville, North Carolina, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Peng Tian
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Physics & Electronic Science, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Correspondence
Xin-Hua Hu, Department of Physics, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC 27858.
Email: [email protected]
Peng Tian, Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan 414006, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xin-Hua Hu
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Department of Physics, East Carolina University, Greenville, North Carolina, USA
Correspondence
Xin-Hua Hu, Department of Physics, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC 27858.
Email: [email protected]
Peng Tian, Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan 414006, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJing Liu
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Information Science and Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYaohui Xu
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Information Science and Engineering, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Search for more papers by this authorWenjin Wang
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Physics & Electronic Science, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Search for more papers by this authorYuhua Wen
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Physics & Electronic Science, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Search for more papers by this authorHeng Hong
Department of Pathology and Comparative Medicine, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, USA
Search for more papers by this authorJun Q. Lu
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Department of Physics, East Carolina University, Greenville, North Carolina, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Peng Tian
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
School of Physics & Electronic Science, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Correspondence
Xin-Hua Hu, Department of Physics, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC 27858.
Email: [email protected]
Peng Tian, Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan 414006, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xin-Hua Hu
Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan, China
Department of Physics, East Carolina University, Greenville, North Carolina, USA
Correspondence
Xin-Hua Hu, Department of Physics, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC 27858.
Email: [email protected]
Peng Tian, Institute for Advanced Optics, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, Hunan 414006, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJing Liu and Yaohui Xu contributed equally to this study.
Funding information: Education Department of Hunan Province, Grant/Award Number: 18B348; Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department, Grant/Award Number: 19A198
Abstract
Measurement of nuclear-to-cytoplasm (N:C) ratios plays an important role in detection of atypical and tumor cells. Yet, current clinical methods rely heavily on immunofluroescent staining and manual reading. To achieve the goal of rapid and label-free cell classification, realistic optical cell models (OCMs) have been developed for simulation of diffraction imaging by single cells. A total of 1892 OCMs were obtained with varied nuclear volumes and orientations to calculate cross-polarized diffraction image (p-DI) pairs divided into three nuclear size groups of OCMS, OCMO and OCML based on three prostate cell structures. Binary classifications were conducted among the three groups with image parameters extracted by the algorithm of gray-level co-occurrence matrix. The averaged accuracy of support vector machine (SVM) classifier on test dataset of p-DI was found to be 98.8% and 97.5% respectively for binary classifications of OCMS vs OCMO and OCMO vs OCML for the prostate cancer cell structure. The values remain about the same at 98.9% and 97.8% for the smaller prostate normal cell structures. The robust performance of SVM over clustering classifiers suggests that the high-order correlations of diffraction patterns are potentially useful for label-free detection of single cells with large N:C ratios.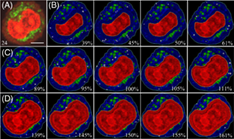
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio202000036-sup-0001-TableS1.docWord document, 103 KB | Table S1 Definition of GLCM Parameters |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1D. Zink, A. H. Fischer, J. A. Nickerson, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 677.
- 2L. J. Vaickus, R. H. Tambouret, Cancer Cytopathol. 2015, 123, 524.
- 3T. Takaki, M. Montagner, M. P. Serres, M. Le Berre, M. Russell, L. Collinson, K. Szuhai, M. Howell, S. J. Boulton, E. Sahai, M. Petronczki, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16013.
- 4N. Agarwal, A. M. Biancardi, F. W. Patten, A. P. Reeves, E. J. Seibel, J. Med. Imaging (Bellingham) 2014, 1, 017501.
- 5P. J. McIntire, J. T. Snow, S. S. Elsoukkary, L. Soong, J. Sweeney, B. D. Robinson, M. T. Siddiqui, Cancer Cytopathol. 2019, 127, 120.
- 6N. Lue, W. Choi, G. Popescu, K. Badizadegan, R. R. Dasari, M. S. Feld, Opt. Express 2008, 16, 16240.
- 7O. C. Marina, C. K. Sanders, J. R. Mourant, Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 296.
- 8T. Kim, R. Zhou, M. Mir, S. D. Babacan, P. S. Carney, L. L. Goddard, G. Popescu, Nat. Photon. 2014, 8, 256.
- 9M. Schürmann, J. Scholze, P. Müller, J. Guck, C. J. Chan, J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 1068.
- 10Z. A. Steelman, W. J. Eldridge, J. B. Weintraub, A. Wax, J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 1714.
- 11M. Habaza, M. Kirschbaum, C. Guernth-Marschner, G. Dardikman, I. Barnea, R. Korenstein, C. Duschl, N. T. Shaked, Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600205.
- 12M. M. Villone, P. Memmolo, F. Merola, M. Mugnano, L. Miccio, P. L. Maffettone, P. Ferraro, Lab Chip 2017, 18, 126.
- 13S. Wang, J. Liu, J. Q. Lu, W. Wang, S. A. Al-Qaysi, Y. Xu, W. Jiang, X. H. Hu, J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800287.
- 14M. A. Yurkin, J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201800033.
- 15K. M. Jacobs, J. Q. Lu, X. H. Hu, Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 2985.
- 16K. M. Jacobs, L. V. Yang, J. Ding, A. E. Ekpenyong, R. Castellone, J. Q. Lu, X. H. Hu, J. Biophotonics 2009, 2, 521.
- 17Y. Sa, Y. Feng, K. M. Jacobs, J. Yang, R. Pan, I. Gkigkitzis, J. Q. Lu, X. H. Hu, Cytometry A 2013, 83, 1027.
- 18Y. Feng, N. Zhang, K. M. Jacobs, W. Jiang, L. V. Yang, Z. Li, J. Zhang, J. Q. Lu, X. H. Hu, Cytometry A 2014, 85, 817.
- 19H. Wang, Y. Feng, Y. Sa, Y. Ma, R. Pan, J. Q. Lu, X. H. Hu, Appl. Optics 2015, 54, 5223.
- 20K. Dong, Y. Feng, K. M. Jacobs, J. Q. Lu, R. S. Brock, L. V. Yang, F. E. Bertrand, M. A. Farwell, X. H. Hu, Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 1717.
- 21X. Yang, Y. Feng, Y. Liu, N. Zhang, W. Lin, Y. Sa, X. H. Hu, Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 2172.
- 22W. Jiang, J. Q. Lu, L. V. Yang, Y. Sa, Y. Feng, J. Ding, X. H. Hu, J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 071102.
- 23H. Wang, Y. Feng, Y. Sa, J. Q. Lu, J. Ding, J. Zhang, X.-H. Hu, Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 234.
- 24W. Wang, J. Liu, J. Q. Lu, J. Ding, X. H. Hu, Opt. Express 2017, 25, 9628.
- 25J. Jin, J. Q. Lu, Y. Wen, P. Tian, X. H. Hu, J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, e201900242.
- 26R. Pan, Y. Feng, Y. Sa, J. Q. Lu, K. M. Jacobs, X. H. Hu, Opt. Express 2014, 22, 31568.
- 27J. Zhang, Y. Feng, W. Jiang, J. Q. Lu, Y. Sa, J. Ding, X. H. Hu, Opt. Express 2016, 24, 366.
- 28R. S. Brock, X. H. Hu, D. A. Weidner, J. R. Mourant, J. Q. Lu, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 2006, 102, 25.
- 29Y. Zhang, Y. Feng, C. R. Justus, W. Jiang, Z. Li, J. Q. Lu, R. S. Brock, M. K. McPeek, D. A. Weidner, L. V. Yang, X. H. Hu, Integr. Biol. 2012, 4, 1428.
- 30Y. Wen, Z. Chen, J. Lu, E. Ables, J. L. Scemama, L. V. Yang, J. Q. Lu, X. H. Hu, PLoS One 2017, 12, e0184726.
- 31H. Shahin, M. Gupta, A. Janowska-Wieczorek, W. Rozmus, Y. Y. Tsui, Opt. Express 2016, 24, 28877.
- 32J. Stark, T. Rothe, S. Kiess, S. Simon, A. Kienle, Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 2749.
- 33X. Lin, N. Wan, L. Weng, Y. Zhou, Appl. Optics 2017, 56, 3608.
- 34R. M. Haralick, Proc. IEEE 1979, 67, 786.
- 35M. Kalashnikov, W. Choi, C.-C. Yu, Y. Sung, R. R. Dasari, K. Badizadegan, M. S. Feld, Opt. Express 2009, 17, 19674.
- 36M. A. Yurkin, A. G. Hoekstra, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 2011, 112, 2234.
- 37W. Wang, Y. Wen, J. Q. Lu, L. Zhao, S. A. Al-Qaysi, X.-H. Hu, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 224, 453.
- 38P. Willett, Inf. Process. Manag. 1988, 24, 577.
- 39H. Permuter, J. Francos, I. Jermyn, Pattern Recognit. 2006, 39, 695.
- 40N. Shental, A. Bar-Hillel, T. Hertz, D. Weinshall, Proc. Neural Inf. Process. Sys. 2003, 16, 465.
- 41Y. Tan, Y. Xia, J. Wang, in Proc. IEEE-INNS-ENNS Int. Joint Conf. Neural Netw. (IJCNN), IEEE, Como, Italy 2000), pp. 411–416.




