Cell and nucleus refractive-index mapping by interferometric phase microscopy and rapid confocal fluorescence microscopy
Shir Cohen-Maslaton
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Search for more papers by this authorItay Barnea
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Search for more papers by this authorAlmog Taieb
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Natan T. Shaked
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Correspondence
Natan T. Shaked, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorShir Cohen-Maslaton
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Search for more papers by this authorItay Barnea
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Search for more papers by this authorAlmog Taieb
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Natan T. Shaked
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Correspondence
Natan T. Shaked, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: H2020 European Research Council, Grant/Award Number: 678316
Abstract
We present a multimodal technique for measuring the integral refractive index and the thickness of biological cells and their organelles by integrating interferometric phase microscopy (IPM) and rapid confocal fluorescence microscopy. First, the actual thickness maps of the cellular compartments are reconstructed using the confocal fluorescent sections, and then the optical path difference (OPD) map of the same cell is reconstructed using IPM. Based on the co-registered data, the integral refractive index maps of the cell and its organelles are calculated. This technique enables rapidly measuring refractive index of live, dynamic cells, where IPM provides quantitative imaging capabilities and confocal fluorescence microscopy provides molecular specificity of the cell organelles. We acquire human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells and show that the integral refractive index values are similar for the whole cell, the cytoplasm and the nucleus on the population level, but significantly different on the single cell level.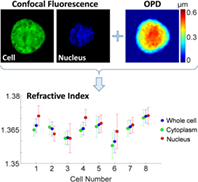
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1N. Lue, W. Choi, G. Popescu, Z. Yaqoob, K. Badizadegan, R. R. Dasari, M. S. Feld, J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 13327.
- 2G. Mazarevica, T. Freivalds, A. Jurka, J. Biomed. Opt. 2002, 7, 244.
- 3K. J. Chalut, A. E. Ekpenyong, W. L. Clegg, I. C. Melhuish, J. Guck, Integr. Biol. 2012, 4, 280.
- 4A. E. Ekpenyong, S. M. Man, S. Achouri, C. E. Bryant, J. Guck, K. J. Chalut, J. Biophotonics 2013, 6(6), 393.
- 5J. Yoon, Y. J. Jo, M. H. Kim, K. Kim, S. Y. Lee, S. J. Kang, Y. K. Park, Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6654.
- 6L. Liu, M. E. Kandel, M. Rubessa, S. Schreiber, M. B. Wheeler, G. Popescu, J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 025003.
- 7P. Wang, R. Bista, R. Bhargava, R. E. Brand, Y. Liu, Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 2840.
- 8R. K. Bista, S. Uttam, P. Wang, K. Staton, S. Choi, C. J. Bakkenist, D. J. Hartman, R. E. Brand, Y. Liu, J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 070503.
- 9P. Girshovitz, N. T. Shaked, Opt. Express 2013, 21, 5701.
- 10P. Girshovitz, N. T. Shaked, Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 1757.
- 11B. Rappaz, P. Marquet, E. Cuche, Y. Emery, C. Depeursinge, P. J. Magistretti, Opt. Express 2005, 13, 9361.
- 12B. Rappaz, A. Barbul, Y. Emery, R. Korenstein, C. Depeursinge, P. J. Magistretti, P. Marquet, Cytom. Part A 2008, 73A, 895.
- 13M. R. Jafarfard, S. Moon, B. Tayebi, D. Y. Kim, Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 2908.
- 14D. Boss, J. Kühn, P. Jourdain, C. Depeursinge, P. J. Magistretti, P. Marquet, J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 036007.
- 15B. Rappaz, F. Charrière, C. Depeursinge, P. J. Magistretti, P. Marquet, Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 744.
- 16B. Kemper, S. Kosmeier, P. Langehanenberg, G. von Bally, I. Bredebusch, W. Domschke, J. Schnekenburger, J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 054009.
- 17S. Kosmeier, B. Kemper, P. Langehanenberg, I. Bredebusch, J. Schnekenburger, A. Bauwens and G. von Bally, in Proc. SPIE 6991, Biophotonics: Photonic Solutions for Better Health Care, Strasbourg, France, 2008, p. 699110.
- 18M. Schürmann, J. Scholze, P. Müller, C. J. Chan, A. E. Ekpenyong, K. J. Chalut, J. Guck, Methods Cell Biol. 2015, 125, 143.
- 19N. Lue, G. Popescu, T. Ikeda, R. R. Dasari, K. Badizadegan, M. S. Feld, Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 2759.
- 20L. Kastl, M. Isbach, D. Dirksen, J. Schnekenburger, B. Kemper, Cytom. Part A 2017, 91, 470.
- 21P. Müller, M. Schürmann, S. Girardo, G. Cojoc, J. Guck, Opt. Express 2018, 26, 10729.
- 22J. Min, B. Yao, V. Trendafilova, S. Ketelhut, L. Kastl, B. Greve, B. Kemper, J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201900085.
- 23G. Dardikman, Y. N. Nygate, I. Barnea, N. A. Turko, G. Singh, B. Javidi, N. T. Shaked, Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 1177.
- 24N. Cardenas, N. Ingle, L. Yu and S. Mohanty, in Proc. SPIE 7904, Three-Dimensional and Multidimensional Microscopy: Image Acquisition and Processing XVIII, San Francisco, California, United States, 2011, p. 790409.
- 25M. Balberg, M. Levi, K. Kalinowski, I. Barnea, S. K. Mirsky, N. T. Shaked, J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 1305.
- 26C. L. Curl, C. J. Bellair, T. Harris, B. E. Allman, P. J. Harris, A. G. Stewart, A. Roberts, K. A. Nugent, L. M. D. Delbridge, Cytom. Part A 2005, 65A, 88.
- 27A. Kus, M. Dudek, B. Kemper, M. Kujawinska, A. Vollmer, J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 046009.
- 28M. Habaza, M. Kirschbaum, C. Guernth-Marschner, G. Dardikman, I. Barnea, R. Korenstein, C. Duschl, N. T. Shaked, Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600205.
- 29S. Chowdhury, W. J. Eldridge, A. Wax, J. Izatt, Optica 2017, 4, 537.
- 30W. Choi, C. Fang-Yen, K. Badizadegan, S. Oh, N. Lue, R. R. Dasari, M. S. Feld, Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 717.
- 31J. W. Su, W. C. Hsu, C. Y. Chou, C. H. Chang, K. Bin Sung, J. Biophotonics 2013, 6(6), 416.
- 32Y. Sung, W. Choi, C. Fang-Yen, K. Badizadegan, R. R. Dasari, M. S. Feld, Opt. Express 2009, 17, 266.
- 33Z. A. Steelman, W. J. Eldridge, J. B. Weintraub, A. Wax, J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 1714.
- 34M. Schürmann, J. Scholze, P. Müller, J. Guck, C. J. Chan, J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 1068.
- 35M. Habaza, B. Gilboa, Y. Roichman, N. T. Shaked, Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1881.
- 36M. Schürmann, G. Cojoc, S. Girardo, E. Ulbricht, J. Guck, P. Müller, J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700145.
- 37A. Nakano, Cell Struct. Funct. 2002, 27, 349.
- 38J. Oreopoulos, R. Berman, M. Browne, Methods Cell Biol. 2014, 123, 153.
- 39S. Shapira, A. Shapira, D. Kazanov, G. Hevroni, S. Kraus, N. Arber, Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38581.
- 40D. Roitshtain, N. A. Turko, B. Javidi, N. T. Shaked, Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2354.
- 41P. Girshovitz, N. T. Shaked, Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 2262.
- 42D. C. Ghiglia, M. D. Pritt, Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping: Theory, Algorithms, and Software, John Wiley and Sons, Inc, New York 1998.
10.1109/IGARSS.1998.702241 Google Scholar
- 43H. Satoh, L. M. D. Delbridge, L. A. Blatter, D. M. Bers, Biophys. J. 1996, 70, 1494.
- 44A. Kaur, L. Kaur, S. Gupta, Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 59, 32.
- 45S. Gupta, L. Kaur, R. C. Chauhan, S. C. Saxena, Digit. Signal Process. 2007, 17, 542.
- 46M. Kumar, X. Quan, Y. Awatsuji, C. Cheng, M. Hasebe, Y. Tamada, O. Matoba, J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 032010.




