Quantitative assessment of optical coherence tomography angiography algorithms for neuroimaging
Funding information: Key Research Cultivation Project of Beijing Information Science and Technology University for Promoting University Connotative Development and Improving Research Level, Grant/Award Number: 2019KYNH205; National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Number: 61975019; Research Project of Beijing Municipal Education Commission, Grant/Award Number: KZ202011232050; Start-up Foundation of Beijing Information Science and Technology University, Grant/Award Number: 5029011104
Abstract
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) angiography can noninvasively map microvascular networks and quantify blood flow in a cerebral cortex with a resolution of 1 to 10 μm and a penetration depth of 2 to 3 mm incorporating OCT signals and angiography algorithms. Different angiography algorithms have been developed in recent years; however, the performance of the algorithms has not been assessed quantitatively for neuroimaging applications. In this paper, we developed four metrics including vascular connectivity, contrast-to-noise ratio, signal-to-noise ratio and processing time to quantitatively assess the performance of OCT angiography algorithms in image quality and computation speed. After the imaging of a rat cortex using an OCT system, the cerebral microvascular networks were visualized by seven algorithms, and the performance of the algorithms was quantified and compared. Quantitative performance assessment of the algorithms can provide suggestions for the selection of appropriate OCT angiography algorithms in neuroimaging.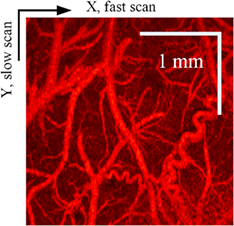
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.




