Visible-near infrared-II skull optical clearing window for in vivo cortical vasculature imaging and targeted manipulation
Dong-Yu Li
Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentations, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Zheng
Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Branch of Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Tissue Restoration and Reconstruction Division of Life Science, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience, Institute for Advanced Study, Institute of Molecular Functional Materials, Division of Biomedical Engineering, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Search for more papers by this authorTing-Ting Yu
Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Search for more papers by this authorBen-Zhong Tang
Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Branch of Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Tissue Restoration and Reconstruction Division of Life Science, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience, Institute for Advanced Study, Institute of Molecular Functional Materials, Division of Biomedical Engineering, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Search for more papers by this authorPeng Fei
School of Optical and Electronic Information-Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jun Qian
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentations, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Correspondence
Dan Zhu, Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China.
Email: [email protected]
Jun Qian, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dan Zhu
Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Correspondence
Dan Zhu, Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China.
Email: [email protected]
Jun Qian, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDong-Yu Li
Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentations, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Zheng
Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Branch of Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Tissue Restoration and Reconstruction Division of Life Science, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience, Institute for Advanced Study, Institute of Molecular Functional Materials, Division of Biomedical Engineering, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Search for more papers by this authorTing-Ting Yu
Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Search for more papers by this authorBen-Zhong Tang
Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Branch of Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Tissue Restoration and Reconstruction Division of Life Science, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience, Institute for Advanced Study, Institute of Molecular Functional Materials, Division of Biomedical Engineering, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Search for more papers by this authorPeng Fei
School of Optical and Electronic Information-Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jun Qian
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentations, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Correspondence
Dan Zhu, Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China.
Email: [email protected]
Jun Qian, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dan Zhu
Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Correspondence
Dan Zhu, Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China.
Email: [email protected]
Jun Qian, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorFunding information: National Key Research and Development Program of China, Grant/Award Number: 2017YFA0700501; National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Numbers: 61721092, 61735016, 61860206009, 81870934; China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project, Grant/Award Numbers: BX20190131, 2019M662633; Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Number: LR17F050001
Abstract
Skull optical clearing window permits us to perform in vivo cortical imaging without craniotomy, but mainly limits to visible (vis)-near infrared (NIR)-I light imaging. If the skull optical clearing window is available for NIR-II, the imaging depth will be further enhanced. Herein, we developed a vis-NIR-II skull optical clearing agents with deuterium oxide instead of water, which could make the skull transparent in the range of visible to NIR-II. Using a NIR-II excited third harmonic generation microscope, the cortical vasculature of mice could be clearly distinguished even at the depth of 650 μm through the vis-NIR-II skull clearing window. The imaging depth after clearing is close to that without skull, and increases by three times through turbid skull. Furthermore, the new skull optical clearing window promises to realize NIR-II laser-induced targeted injury of cortical single vessel. This work enhances the ability of NIR-II excited nonlinear imaging techniques for accessing to cortical neurovasculature in deep tissue.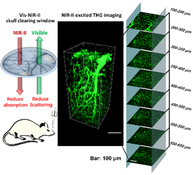
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data can be requested from the authors.
REFERENCES
- 1B. I. Choi, D. Park, S. H. Lee, D. K. Bae, G. Yang, Y. H. Yang, T. K. Kim, E. K. Choi, H. J. Lee, K. C. Choi, S. S. Nahm, Y. B. Kim, Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 33, 60.
- 2D. Cachia, J. Swearer, W. Ferguson, M. Moonis, Arch. Med. Sci. 2011, 7, 168.
- 3S. T. Carmichael, NeuroRx 2005, 2, 396.
- 4K. H. Wang, A. Majewska, J. Schummers, B. Farley, C. C. Hu, M. Sur, S. Tonegawa, Cell 2006, 126, 389.
- 5N. Wagner, N. Norlin, J. Gierten, G. de Medeiros, B. Balazs, J. Wittbrodt, L. Hufnagel, R. Prevedel, Nat Methods 2019, 16, 497.
- 6R. Prevedel, A. J. Verhoef, A. J. Pernia-Andrade, S. Weisenburger, B. S. Huang, T. Nobauer, A. Fernandez, J. E. Delcour, P. Golshani, A. Baltuska, A. Vaziri, Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 1021.
- 7M. Kneipp, J. Turner, H. Estrada, J. Rebling, S. Shoham, D. Razansky, J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 117.
- 8X. F. Fan, W. T. Zheng, D. J. Singh, Light-Sci. Appl. Ther. 2014, 3, e179.
- 9N. G. Horton, K. Wang, D. Kobat, C. G. Clark, F. W. Wise, C. B. Schaffer, C. Xu, Nat Photon. 2013, 7, 205.
- 10J. T. Robinson, K. Welsher, S. M. Tabakman, S. P. Sherlock, H. L. Wang, R. Luong, H. J. Dai, Nano Res. 2010, 3, 779.
- 11Z. Feng, X. Yu, M. Jiang, L. Zhu, Y. Zhang, W. Wang, W. Xi, G. Li, J. Qian, Theranostics 2019, 9, 5706.
- 12K. Welsher, S. P. Sherlock, H. J. Dai, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2011, 108, 8943.
- 13H. Wan, J. Y. Yue, S. J. Zhu, T. Uno, X. D. Zhang, Q. L. Yang, K. Yu, G. S. Hong, J. Y. Wang, L. L. Li, Z. R. Ma, H. P. Gao, Y. T. Zhong, J. Su, A. L. Antaris, Y. Xia, J. Luo, Y. Y. Liang, H. J. Dai, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1171.
- 14M. X. Zhang, J. Y. Yue, R. Cui, Z. R. Ma, H. Wan, F. F. Wang, S. J. Zhu, Y. Zhou, Y. Kuang, Y. T. Zhong, D. W. Pang, H. J. Dai, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2018, 115, 6590.
- 15W. Yu, B. Guo, H. Zhang, J. Zhou, X. Yu, L. Zhu, D. Xue, W. Liu, X. Sun, J. Qian, Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 410.
- 16J. Qi, C. Sun, A. Zebibula, H. Zhang, R. T. K. Kwok, X. Zhao, W. Xi, J. W. Y. Lam, J. Qian, B. Z. Tang, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706856.
- 17Y. Shen, H. Dana, A. S. Abdelfattah, R. Patel, J. Shea, R. S. Molina, B. Rawal, V. Rancic, Y. F. Chang, L. Wu, Y. Chen, Y. Qian, M. D. Wiens, N. Hambleton, K. Ballanyi, T. E. Hughes, M. Drobizhev, D. S. Kim, M. Koyama, E. R. Schreiter, R. E. Campbell, BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 9.
- 18J. Qian, B. Z. Tang, Chem 2017, 3, 56.
- 19O. S. Oliinyk, A. A. Shemetov, S. Pletnev, D. M. Shcherbakova, V. V. Verkhusha, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 279.
- 20M. Abbaci, A. Conversano, F. De Leeuw, C. Laplace-Builhe, C. Mazouni, Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 1778.
- 21S. Wang, W. Xi, F. Cai, X. Zhao, Z. Xu, J. Qian, S. He, Theranostics 2015, 5, 251.
- 22H. Zhang, N. Alifu, T. Jiang, Z. Zhu, Y. Wang, J. Hua, J. Qian, J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2757.
- 23Y. Wang, X. Han, W. Xi, J. Li, A. W. Roe, P. Lu, J. Qian, Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700685.
- 24M. A. Busche, G. Eichhoff, H. Adelsberger, D. Abramowski, K. H. Wiederhold, C. Haass, M. Staufenbiel, A. Konnerth, O. Garaschuk, Science 2008, 321, 1686.
- 25J. Kain, C. Stokes, Q. Gaudry, X. Z. Song, J. Foley, R. Wilson, B. de Bivort, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1910.
- 26C. Xu, W. Zipfel, J. B. Shear, R. M. Williams, W. W. Webb, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996, 93, 10763.
- 27J. Qian, Z. F. Zhu, A. J. Qin, W. Qin, L. L. Chu, F. H. Cai, H. Q. Zhang, Q. Wu, R. R. Hu, B. Z. Tang, S. L. He, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2332.
- 28Y. L. Wang, M. Chen, N. Alifu, S. W. Li, W. Qin, A. J. Qin, B. Z. Tang, J. Qian, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10452.
- 29S. W. Wang, J. Liu, G. X. Feng, L. G. Ng, B. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808365.
- 30T. Wang, D. G. Ouzounov, C. Wu, N. G. Horton, B. Zhang, C. H. Wu, Y. Zhang, M. J. Schnitzer, C. Xu, Nat Methods 2018, 15, 789.
- 31A. Holtmaat, T. Bonhoeffer, D. K. Chow, J. Chuckowree, V. De Paola, S. B. Hofer, M. Hubener, T. Keck, G. Knott, W. C. A. Lee, R. Mostany, T. D. Mrsic-Flogel, E. Nedivi, C. Portera-Cailliau, K. Svoboda, J. T. Trachtenberg, L. Wilbrecht, Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1128.
- 32G. Yang, F. Pan, C. N. Parkhurst, J. Grutzendler, W. B. Gan, Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 201.
- 33R. D. Dorand, D. S. Barkauskas, T. A. Evans, A. Petrosiute, A. Y. Huang, Dermatol. Int. 2014, 3, e21978.
- 34Y. J. Zhao, T. T. Yu, C. Zhang, Z. Li, Q. M. Luo, T. H. Xu, D. Zhu, Light-Sci. Appl. Ther. 2018, 7, 17153.
- 35C. Zhang, W. Feng, Y. J. Zhao, T. T. Yu, P. C. Li, T. H. Xu, Q. M. Luo, D. Zhu, Theranostics 2018, 8, 2696.
- 36C. Zhang, W. Feng, E. Vodovozova, D. Tretiakova, I. Boldyrevd, Y. S. Li, J. Kurths, T. T. Yu, O. Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, D. Zhu, Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 4850.
- 37C. Zhang, W. Feng, Y. Li, J. Kürths, T. Yu, O. Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, D. Zhu, Lasers Surg. Med. 2019, 51, 625.
- 38W. Feng, S. Liu, C. Zhang, Q. Xia, T. Yu, Z. Dan, Theranostics 2019, 9, 5854.
- 39C. C. Petty, J. A. Curcio, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1951, 41, 302.
- 40Z. Zheng, D. Li, Z. Liu, H.-Q. Peng, H. H. Y. Sung, R. T. K. Kwok, I. D. Williams, J. W. Y. Lam, J. Qian, B. Z. Tang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904799.
- 41E. A. Genina, A. N. Bashkatov, V. V. Tuchin, Adv. Opt. Technol. 2008, 2008, 267867.
10.1155/2008/267867 Google Scholar
- 42J. M. Hirshburg, K. M. Ravikumar, W. Hwang, A. T. Yeh, J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 055002.
- 43L. Chen, G. Li, Y. Li, Y. Li, H. Zhu, L. Tang, P. French, J. Mcginty, S. Ruan, Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12218.
- 44K. Tainaka, A. Kuno, S. I. Kubota, T. Murakami, H. R. Ueda, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 32, 713.
- 45H. Hama, H. Kurokawa, H. Kawano, R. Ando, T. Shimogori, H. Noda, K. Fukami, A. Sakaue-Sawano, A. Miyawaki, Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1481.
- 46B. Yang, J. B. Treweek, R. P. Kulkarni, B. E. Deverman, C. K. Chen, E. Lubeck, S. Shah, L. Cai, V. Gradinaru, Cell 2014, 158, 945.
- 47H. Liu, X. Deng, S. Tong, C. He, H. Cheng, Z. Zhuang, M. Gan, J. Li, W. Xie, P. Qiu, K. Wang, Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 5260.
- 48D. G. Ouzounov, T. Wang, M. Wang, D. D. Feng, N. G. Horton, J. C. Cruz-Hernandez, Y. T. Cheng, J. Reimer, A. S. Tolias, N. Nishimura, C. Xu, Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 388.
- 49B. Chen, X. Huang, D. Gou, J. Zeng, G. Chen, M. Pang, Y. Hu, Z. Zhao, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhou, H. Wu, H. Cheng, Z. Zhang, C. Xu, Y. Li, L. Chen, A. Wang, Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 1992.
- 50X. H. Wang, Z. P. Li, Y. D. Ding, K. X. Wang, Z. K. Xing, X. Sun, W. Q. Guo, X. Hong, X. J. Zhu, Y. C. Liu, Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122693.
- 51B. Gu, W. B. Wu, G. X. Xu, G. X. Feng, F. Yin, P. H. J. Chong, J. L. Qu, K. T. Yong, B. Liu, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 170106.
- 52D. Y. Li, H. Q. Zhang, L. L. Chu, X. Y. Zhao, J. Qian, Opt. Quant. Electron. 2015, 47, 3081.
- 53S. Hososhima, H. Yuasa, T. Ishizuka, M. R. Hoque, T. Yamashita, A. Yamanaka, E. Sugano, H. Tomita, H. Yawo, Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1.
- 54T. Kinjo, K. Terai, S. Horita, N. Nomura, K. Sumiyama, K. Togashi, S. Iwata, M. Matsuda, Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1029.
- 55M. Dal Maschio, J. C. Donovan, T. O. Helmbrecht, H. Baier, Neuron 2017, 94, 774.