Towards quantitative assessment of burn based on photoacoustic and optical coherence tomography
Funding information: National High Technology Research and Development Program of China, Grant/Award Number: 2015AA020901; Ph.D. Start-up Fund of Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, Grant/Award Number: 2017A030310363; Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China, Grant/Award Numbers: 2014B020215003, 2015B020233016; National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Numbers: 61627827, 61705068, 81630046, 91539127
Abstract
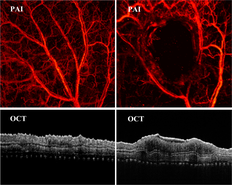
Accurate and timely assessment of the severity of burn is essential for the treatment of burns. Currently, although most first-degree and third-degree burns are easily diagnosed through visual inspection or auxiliary diagnostic methods, the second-degree burn is still difficult to distinguish due to the ambiguity boundaries of second-degree with first-degree and third-degree burns. In this study, we proposed a non-invasive technique by combing photoacoustic imaging (PAI) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to multi-parameter quantitatively assess the burns. The feasibility and capacity of the dual-mode PAT/OCT for assessing the burns was first testified by tissue-mimicking phantom and burn wounds in mouse pinna in vivo. The further experiments conducted on the back of rats showed that the changes in skin scattering structure, vascular morphology and blood flow provided by the dual-mode PAI/OCT system can determine distinct boundaries and depth of the burns. The experimental results prove that combined PAI/OCT as a novel method can be used to assess the severity of burn, which has the potential to diagnose the burns in clinic.