Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 9/2018
- Page: 1691
- First Published: 23 August 2018

A sugar mill factory creating smoke in front of a blue sky. Christian Kobierski@Shutterstock
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 9/2018
- Pages: 1692-1693
- First Published: 23 August 2018
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 9/2018
- Page: 1693
- First Published: 23 August 2018
Highlights
Erratum
Experimental Assessment and Modeling of the Solubility of Malonic Acid in Different Solvents
- Page: 1696
- First Published: 23 August 2018
Research Articles
ONIOM Study for Selectivity of Extractants for Extraction of Rare-Earth Metals
- Pages: 1697-1705
- First Published: 13 June 2018
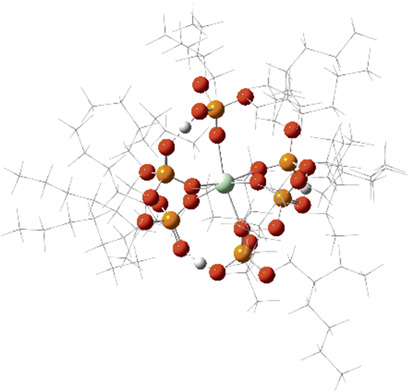
Solvent extraction is the most efficient technique used to obtain high-purity rare-earth metals commercially. A theoretical study to screen solvent extractants prior to carrying out experiments is described herein. This hybrid method, known as “our own N-layered integrated molecular orbital and molecular mechanics” (ONIOM) method, improves understanding of the metal extraction process with reduced cost.
Assessment of a Thermally Modified Cellulose Acetate Forward-Osmosis Membrane Using Response Surface Methodology
- Pages: 1706-1715
- First Published: 19 June 2018
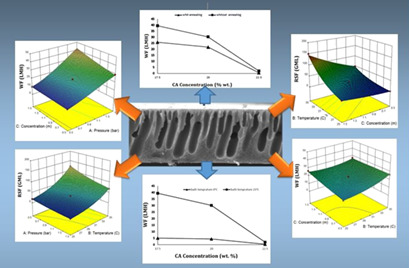
Forward osmosis (FO) has become an emerging desalination technology but the fabrication of high-performance and low-price membranes for FO is still a concern. Cellulose acetate was investigated as starting material for production of flat sheet FO membranes. The performance of such membranes was evaluated for different operational conditions. Two validated models were elaborated.
Influence of Longitudinal Vortex Generator Configuration on the Hydrodynamics in a Novel Spouted Bed
- Pages: 1716-1726
- First Published: 22 June 2018
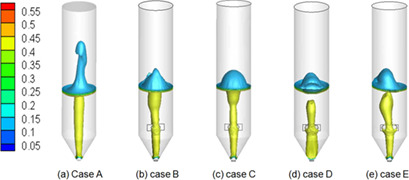
Spouted beds are considered as efficient fluid-particle contactors in industrial processes. The 3D gas-solid two-phase flow characteristics in a novel spouted bed structure under longitudinal vortex effects was numerically studied by a two-fluid model. The influence of the radius of the sphere installed on longitudinal vortex generators on gas-solid two-phase flow in spouted beds is discussed.
Minimization of the Theoretical Error of Input Parameters for a Vapor Permeation Apparatus
- Pages: 1727-1736
- First Published: 22 June 2018
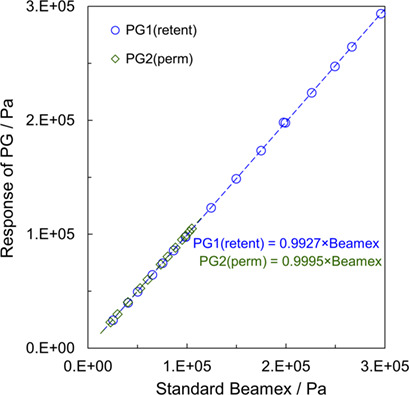
Only few discussions of experimental errors in permeation measurements are found in the literature. A detailed analysis of such errors is carried out for a representative binary system of hexane and nitrogen. Selecting an optimal operational range for input parameters could eliminate at least 2/3 of the theoretical relative error for subsequent evaluation of the permeability of individual species.
Thermochemical Processing of Miscanthus through Fluidized-Bed Fast Pyrolysis: A Parametric Study
- Pages: 1737-1745
- First Published: 22 June 2018
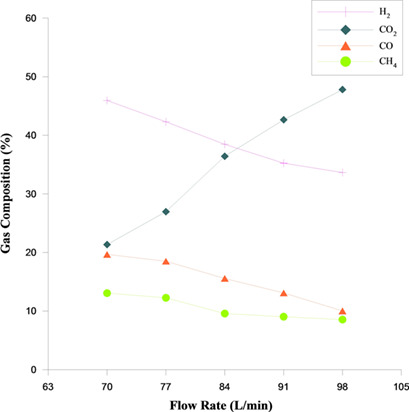
Fluidized-bed fast pyrolysis was used to convert Miscanthus, one of the largest agriculture wastes in Taiwan, into bio-oil, bio-char, and pyrolytic gases. The product distributions were studied depending on various parameters and the properties of the bio-oil were tested via standard methods. Bio-oil derived from Miscanthus is still unfavorable for application in combustion engines.
Enhanced BTX Production in Refineries with Sulfur Dioxide Oxidation by Thermal Integrated Model
- Pages: 1746-1758
- First Published: 25 June 2018
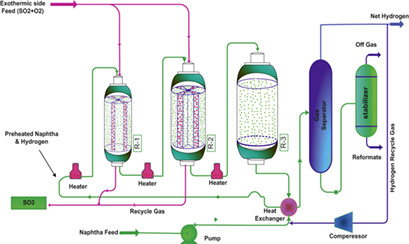
Multifunctional autothermal reactors as a novel strategy in process integration technology have been introduced to supply innovative energy to industries. A novel thermal integrated model with the combination of SO2 oxidization and catalytic reforming process iss proposed. Reduction of energy consumption in the oil refineries is achieved and the production rate in naphtha reforming is improved.
Effects of Temperature on the Filtration Characteristics of a Dual-Layer Granular Bed Filter
- Pages: 1759-1766
- First Published: 25 June 2018
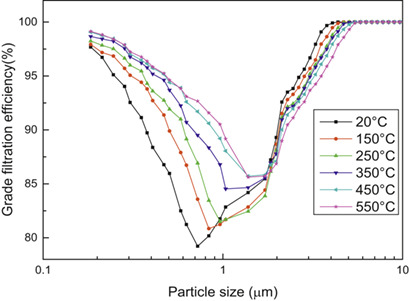
The impact of temperature on the filtration efficiency and pressure drop of a dual-layer granular bed filter in a hot dual-layer granular bed filter with experimental dust was evaluated. Higher filtration temperatures improved the filtration efficiency and the removal efficiency of ultrafine dust. The dual-layer granular bed has excellent potential for application to low-temperature coal pyrolysis.
Synthesis of High-Performance Pebax®-1074/DD3R Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation
- Pages: 1767-1775
- First Published: 27 June 2018

Before natural gas can be transported and used, it is essential to remove impurities such as CO2. In this work, polymer/zeolite (Pebax®-1074/DD3R) mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs) were fabricated for gas-separation applications. The performances of the MMMs were studied at different operating conditions and DD3R loadings. The separation performance of Pebax®-1074 was improved by using DD3R as a filler.
Spectrophotometric Determination of Molybdenum-Containing Compounds in Aqueous Glucose Solutions
- Pages: 1776-1782
- First Published: 28 June 2018
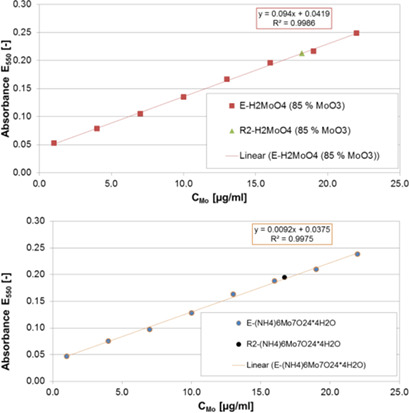
Molybdenum very rapidly forms a violet complex with pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid (chelating agent) and stannous chloride (reducing agent). The absorption of this complex can be utilized for the photometric determination of small amounts of molybdenum-containing compounds in aqueous glucose solutions. The process is fast, sensitive, and reproducible.
Short-Circuit Flow in Hydrocyclones with Arc-Shaped Vortex Finders
- Pages: 1783-1792
- First Published: 05 July 2018
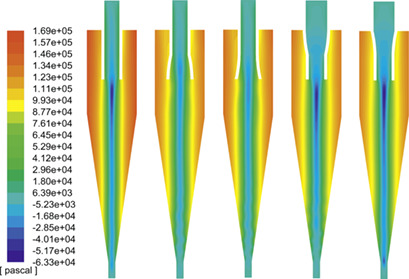
The existence of short-circuit flow greatly affects the separation performance of hydrocyclones during operation. Possibilities to reduce the circuit flow from the angle of the geometric structure of vortex finders are evaluated. Several new arc-shaped vortex finder structures are presented and their effects on the flow field are compared by particle image velocimetry test and numerical simulation.
Characteristics of Nitric Acid-Modified Carbon Nanotubes and Desalination Performance in Capacitive Deionization
- Pages: 1793-1799
- First Published: 05 July 2018
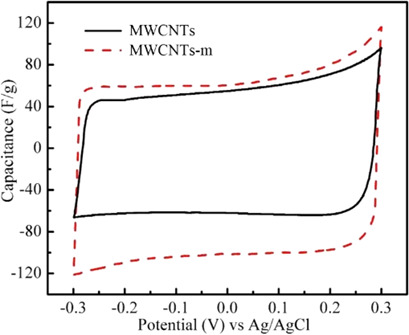
Capacitive deionization is an emerging charge-based water desalination technology. In order to improve the electrochemical properties of the electrodes, multiwalled carbon nanotubes were treated with nitric acid to evaluate the effect of modification on their properties and desalination performance in capacitive deionization. The desalination efficiency could be largely improved by this treatment.
Microreactor Technology as a Tool for the Synthesis of a Glitazone Drug Intermediate
- Pages: 1800-1807
- First Published: 06 July 2018
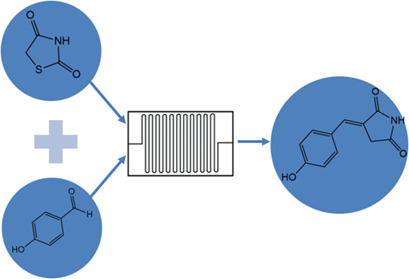
Microreactor technology is applied to the synthesis of a glitazone drug intermediate. The flow in the microreactor is laminar and plug-like owing to the Dean flow caused by curves. The production is larger than that in the batch process thanks to the possibility of working safely and simply in the liquid state at temperatures well above the solvent boiling point.
Coproduction of Ethyl Acetate and n-Butyl Acetate by Using a Reactive Dividing-Wall Column
- Pages: 1808-1817
- First Published: 06 July 2018
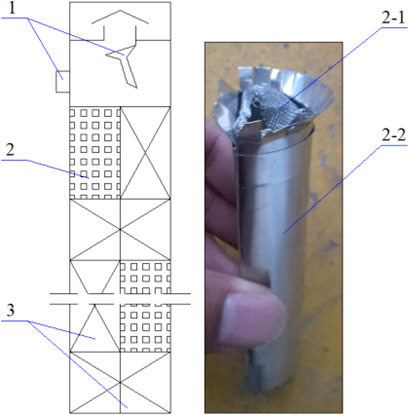
Reactive distillation (RD) is a sustainable and energy- and cost-efficient process for the coproduction of ethyl acetate and butyl acetate. The benefits of combining RD with a dividing-wall column are revealed by studying a variety of factors experimentally and through simulations. Complete conversion of ethanol and easy product separation show great industrial application potential.
Separation of Methane and Carbon Dioxide Gas Mixtures Using Activated Carbon Modified with 2-Methylimidazole
- Pages: 1818-1825
- First Published: 06 July 2018
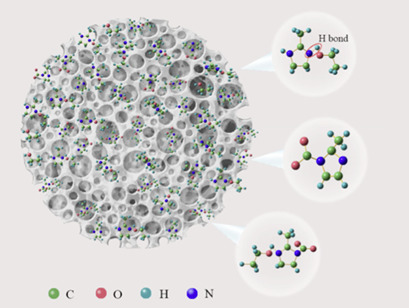
2-Methylimidazole, ethanol, and glycol are proposed for the modification of activated carbon for use in the separation of CH4+CO2 gas mixtures. The selectivity coefficient of the modified activated carbon was about five times higher than that of the fresh activated carbon. The CO2 capture mechanism of 2-methylimidazole and glycol is outlined.
Opportunities for Low-Cost Particulate Matter Sensors in Filter Emission Measurements
- Pages: 1826-1832
- First Published: 06 July 2018

An innovative approach utilizing low-cost particulate matter sensors for emission control is introduced. Applicability and new limitations are tested in a laboratory setting, measuring particulate emissions of surface filters and comparing results with conventional measuring devices. The suitability and limitations of a low-cost sensor are evaluated in comparison to a professional sensor.
Interfacial Friction Factor Prediction in Vertical Annular Flow Based on the Interface Roughness
- Pages: 1833-1841
- First Published: 06 July 2018
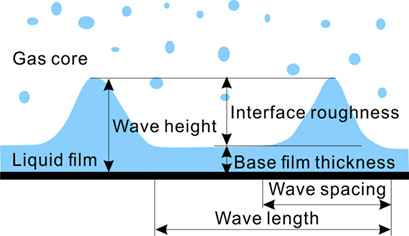
Interface roughness plays a decisive role in the momentum exchange between the gas core and the liquid film in vertical annular flow. Correlations for the interface roughness were suggested for conditions without or with disturbance waves and compared with an experimental database. The proposed correlations significantly reduce the prediction error of the interfacial friction factor.
Effect of Isomerization on the Reversible Reaction of Hydrogenation-Dehydrogenation of ortho-Terphenyl on a Pt/C Catalyst
- Pages: 1842-1846
- First Published: 11 July 2018
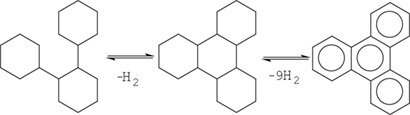
The role of isomerization processes in hydrogen storage based on aromatic substrates is evaluated. In particular, the effect of isomerization on the reversible reaction of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation was analyzed using one of the most efficient substrates, o-terphenyl, with a commercial Pt/C catalyst applied successfully in both hydrogenation and dehydrogenation processes.
Hydrodynamics and Mass Transfer in a Lab-Scale Stirred-Pulsed Extraction Column
- Pages: 1847-1856
- First Published: 11 July 2018

In a miniaturized extraction column, stirring provides small droplets with a narrow size distribution, while pulsation helps to ensure stable and efficient countercurrent flow. This stirred-pulsed apparatus offers high extraction performance at low flow rates for process development purposes or small-scale production. Its hydrodynamics and mass transfer are characterized in detail.
Response Surface Optimization of Dysprosium Extraction Using an Emulsion Liquid Membrane Integrated with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
- Pages: 1857-1870
- First Published: 22 May 2018
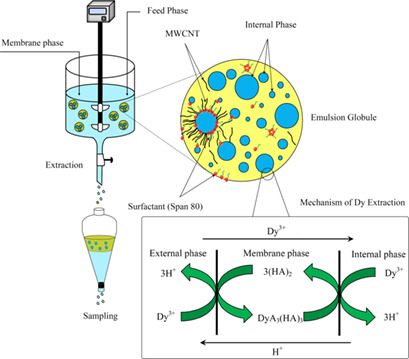
An innovative emulsion liquid membrane was prepared by integrating multi-walled carbon nanotubes for extraction of a rare earth element. The parameters were optimized by response surface methodology and a regression model was developed. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes in conjunction with surfactants stabilize the emulsion and the extraction efficiency can be promoted due to the enhanced stability.
Spatially Resolved Characterization of the Gas Propagator in Monolithic Structured Catalysts Using NMR Diffusiometry
- Pages: 1871-1880
- First Published: 18 July 2018
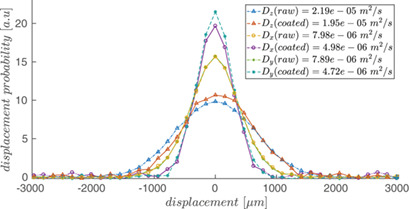
The propagator of thermally polarized methane gas was measured locally within commercial monolithic catalyst supports using an optimized pulsed-field gradient nuclear magnetic resonance method. A clear effect of the monolith type and its pore size and coating on the effective gas diffusion coefficient and tortuosity was found.
The Reaction Kinetics of Gaseous Alkali Capture by Kaolin in Syngas Atmosphere
- Pages: 1881-1888
- First Published: 18 July 2018
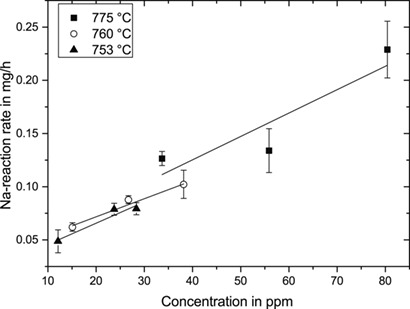
Kaolin is a promising sorbent for the control of alkali species in gasification systems. A thermogravimetric analyzer was used to obtain kinetic data for the sorption reaction. The influence of temperature and alkali partial pressure was investigated, and a kinetic model was found to describe the sorption mathematically.










