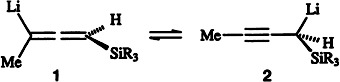Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 20/1996)
- First Published: November 1, 1996
The cover picture shows an everyday application of the combinatorial principle—the door of a safe! The four knobs of the combination lock are analogous to the four different groups R1–R4 attached to a small organic molecule. The illustration underlines the tremendous number of compounds possible by varying relatively few substituents. Combinatorial methods can provide access to every possible combination, and the correct solution provides access to a valuable target.
Graphical Abstract (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 20/1996)
- Pages: 2275-2281
- First Published: November 1, 1996
Reviews
Combinatorial Synthesis of Small Organic Molecules
- Pages: 2288-2337
- First Published: November 1, 1996
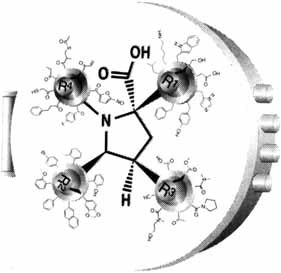
A numbers game or serious science? Many investigators are posing this question about the use of combinatorial chemistry in the search for new pharmaceuticals. It is undisputed, however, that this young and very rapidly developing area has attracted widespread international attention within a very short time. The authors give a comprehensive review and comment on current trends.
Correspondences
Solid-State Chemistry: Restoring the Balance†
- Page: 2338
- First Published: November 1, 1996
A coin with two sides: chemistry has both static and dynamic aspects. Yet in research in solid-state chemistry attention has focused almost exclusively on the former. Thus, the systematic investigation of the dynamic properties of materials such as the mechanisms of solid-state processes can be considered long overdue and essential for the development of strategies for rational synthesis and tailor-made materials.
Highlights
Asymmetric Two-Center Catalysis—Learning from Nature
- Pages: 2339-2342
- First Published: November 1, 1996
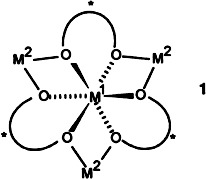
In spite of relatively few examples, two-center catalysis is proving to be a clever and effective means of performing diverse reactions with both high regio- and enantioselectivity. A simple scheme allows classification of the efficient M1–M2–binol complexes 1 as well as the enzymes urease and carbon monoxide dehydrogenase. M1 = La, Al,…; M2 = Li, Na, K,….
Communications
The Oxidation of Gold Powder by Me3El2 (E P, As) under Ambient Conditions; Structures of [AuI3(PMe3)2], [AuI3(AsMe3)], and [(Me3PO)2H][AuI2]†
- Pages: 2344-2346
- First Published: November 1, 1996
![The Oxidation of Gold Powder by Me3El2 (E P, As) under Ambient Conditions; Structures of [AuI3(PMe3)2], [AuI3(AsMe3)], and [(Me3PO)2H][AuI2]](/cms/asset/fed984d0-1406-4251-9037-3e894727dbaa/must001.jpg)
Unactivated gold powder readily reacts with Me3EI2 (E P, As) in diethyl ether to form the planar complex [AuI3(AsMe3)] and, surprisingly, the trigonal-bipyramidal complex [AuI3-(PMe3)2] (structure shown on the right); the latter readily hydrolyzes to form [(Me3PO)2H][AuI2]. The oxidation of this noble metal to Au3+ and the production of complexes of different stoichiometries and structures illustrates the oxidizing power and the subtlety of these Me3EI2 reagents.
The Synthesis of Novel 6-Amido-6-Deoxy-L-Galactose Derivatives as Potent Sialyl Lewisx Mimetics†
- Pages: 2346-2348
- First Published: November 1, 1996
A Practical Method for the Synthesis of N-Acetyl-D-lactosamine Derivatives by the Tandem Use of Galactose Oxidase and β-Galactosidase†
- Pages: 2348-2350
- First Published: November 1, 1996
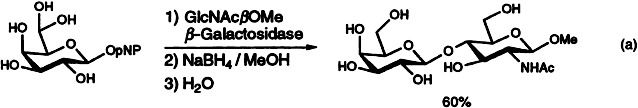
Two enzymes are used for the efficient synthesis of 6′-oxo-N-acetyl-D-lactosamine. GalβOpNP, with the good p-nitrophenyl (pNP) leaving group, is first oxidized to the 6-oxo derivative with galactose oxidase. Subsequent transglycosylation with GlcNAcβOMe, catalyzed by β-galactosidase from Bacillus circulans, leads to the desired disaccharide in good yield [Eq. (a)].
Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of a Sialylated Undecasaccharide–Asparagine Conjugate†‡
- Pages: 2350-2353
- First Published: November 1, 1996
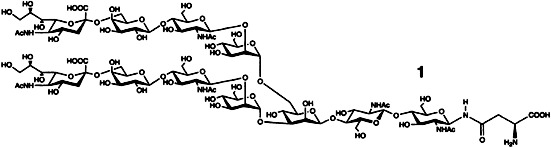
A partial structure of many glycoproteins, the complex undecasaccharide–asparagine conjugate 1 was obtained for the first time by total synthesis. Crucial to the synthesis was a combination of modern chemical and enzymatic methods, which reduced the overall number of steps and allowed efficient deprotonation.
Aromatic Hydroxylation by H2O2 and O2 Catalyzed by a μ-Oxo Diiron(III) Complex
- Pages: 2353-2355
- First Published: November 1, 1996
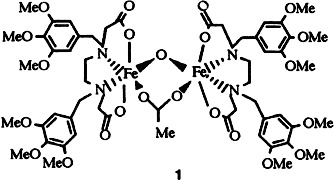
An excellent functionalized enzyme model for the active site of methane monooxygenase and ribonucleotide reductase is represented by the μ-ace-tato- and μ-oxo-bridged diiron complex 1. Reaction with H2O2 or O2 in the presence of ascorbate leads to hydroxylation of one phenyl ring to a phenol. This then coordindates to the metal center with formation of a mononuclear complex.
A New In4 Cluster with Short InIn Bonds in Trigonal-Planar In(InTrip2)3†
- Pages: 2355-2357
- First Published: November 1, 1996
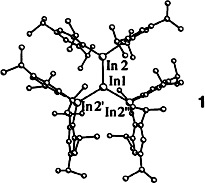
Trigonal-planar coordination is seen for the indium center in In(InTrip2)3 (1) (Trip 2,4,6-iPr3C6H2), the first indane with three unusually short bonds to indium substituents. The compound is obtained by the reduction of the diindane Trip2InInTrip2 with lithium metal. In contrast, reduction of the aluminum and gallium analogs gives the [Trip2M MTrip2]− anions, which have a MM π-bond order of 0.5.
MTrip2]− anions, which have a MM π-bond order of 0.5.
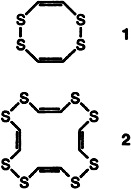
Crystal Structures and Properties of Cyclic Polyenes Possessing Disulfide Units†
- Pages: 2357-2359
- First Published: November 1, 1996
A Route to Pdo from PdII Metallacycles in Animation and Cross-Coupling Chemistry†
- Pages: 2359-2361
- First Published: November 1, 1996
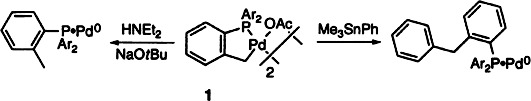
PdII/PdIV or PdII/Pd0? The unusual PdII catalyst 1 was reduced to a Pd0 complex by reaction with an amine and a base. β-Hydrogen elimination and subsequent CH bond-forming reductive elmination generate a coordinated tris(o-tolyl)phosphane. The same palladium(II) metallacycle was reduced to Pd0 in a cross-coupling reaction by CC bond-forming reductive elimination to form coordinated P(oTol)2-(C6H4CH2Ar). Thus, these compounds can react by a PdII/Pd0-containing catalytic cycle.
Homogeneous Catalysts for Claus Chemistry: The Preparation and Structure of cis-[(PPh3)2PtS3O], a Catalytically Active Intermediate†
- Pages: 2362-2363
- First Published: November 1, 1996
Catalytic, Enantioselective Addition of Allylsilanes to Aldehydes: Generation of a Novel, Reactive TiIV Complex from TiF4†
- Pages: 2363-2365
- First Published: November 1, 1996
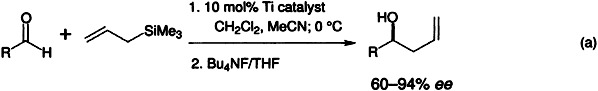
Unique reactivity is shown by the fluorotitanium complex obtained from TiF4 and 1,1′-bi-2-naphthol. It is more reactive than the chloro-, bromo-, and alkoxytitanium complexes previously employed and catalyzes the enantioselective additions of allyltrimethylsilane to aldehydes [Eq. (a)], providing an alternative to known methods involving the corresponding organotin reagents.
Structure of Silyl-Substituted Allenyl/Propargyllithium Reagents in Solution†
- Pages: 2365-2367
- First Published: November 1, 1996
2,7,9-Trimethylenetricyclo[4.3.0.03,8]-non-4-ene†
- Pages: 2368-2369
- First Published: November 1, 1996
![2,7,9-Trimethylenetricyclo[4.3.0.03,8]-non-4-ene](/cms/asset/911697a5-010f-496f-9e32-e942df6669df/must001.jpg)
The first C12H12 hydrocarbon with a central tricyclic skeleton and four double bonds (1) has been synthesized. In the most successful approach 2, obtained from the corresponding ketone by treatment with MeLi, was transformed into the tetraene 1 by elimination of water under mild conditions with (COCl)2/DMSO/NEt3 (the Swern conditions).
Side-Arm Participation in a Four-Component Template Synthesis of a [30]Crown-10 Derivative†
- Pages: 2369-2372
- First Published: November 1, 1996
![Side-Arm Participation in a Four-Component Template Synthesis of a [30]Crown-10 Derivative](/cms/asset/e10d1b30-b8d3-484d-8a87-63fd610d155c/must001.jpg)
Ring closure to the [15]crown-5 derivative is prevented in the reaction of an enediolate with tetraethyleneglycol dimesylate by participation of an acetal side chain (reaction intermediate depicted on the right). The attack of a second enediolate initiates the formation of the corresponding [30]crown-10 derivative in up to 50% yield.
Unusual Enantiomeric Resolution Phenomenon Observed upon Recrystallization of a Racemic Compound†
- Pages: 2372-2374
- First Published: November 1, 1996
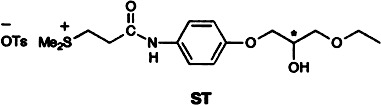
Efficient enantiomeric resolution of the antiallergenic agent (±)-ST, which shows crystalline polymorphism, is accomplished by simple recrystallization. Both stable crystals of the racemic compound and metastable mixed crystals are formed, and the enantiomeric enrichment of the mother liquor virtually reaches 100% ee.
Enantioselective Conjugate Addition of Dialkylzinc Reagents to Cyclic and Acyclic Enones Catalyzed by Chiral Copper Complexes of New Phosphorus Amidites†
- Pages: 2374-2376
- First Published: November 1, 1996
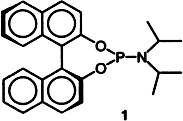
Monodentate phosphorus amidites like 1 and Cu(OTf)2 provide access to the first chiral complexes that catalyze the enantioselective conjugate addition of organozinc reagents to cyclic as well as acyclic enones. The ligand-accelerated process affords β-substituted ketones in excellent yields and with high ee values. Functional groups in the zinc reagent are tolerated.
A Catalyst-Specific, Stereocontrolled Ring-Closing Metathesis†
- Pages: 2376-2378
- First Published: November 1, 1996
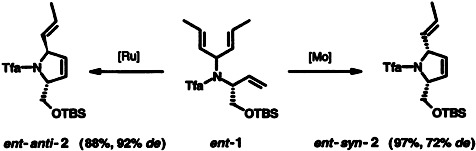
The catalyst decides whether the syn or anti product is formed! In the cyclization of 1, the ring-closing metathesis of two double bonds that are located at a chiral and a prochiral center leads to the α,α′-disubstituted pyrrolidine derivative 2 with viable diastereoselectivity. Tfa = trifluoroacetyl, [Ru] and [Mo] = Ru- and Mo-carbene complexes, respectively.
Reductive Carbon–Sulfur Bond Cleavage: A Simple Pathway to Nonstabilized (Lithiomethyl)amines†
- Pages: 2378-2380
- First Published: November 1, 1996
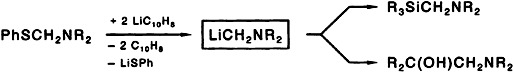
Compounds with the structural element -CH2NR2 are easily accessible from (phenylthiomethyl)amines by reductive CS bond cleavage and subsequent addition or substitution (see below). One advantage of this shorter method than tin–lithium exchange is the ready availability of the starting materials, which need not be purified by chromatography.
The Existence of Stable Tm@C82 Isomers†
- Pages: 2380-2383
- First Published: November 1, 1996
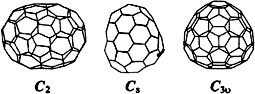
Endohedral fullerene compounds with isomeric carbon frameworks have been identified for the first time. The three stable isomers of Tm2+@C were separated by HPLC, and characterized by cyclic voltammetry and by UV/Vis/NIR and 13C NMR spectroscopy as probably having C2, Cs, and C3v symmetry (see picture).
were separated by HPLC, and characterized by cyclic voltammetry and by UV/Vis/NIR and 13C NMR spectroscopy as probably having C2, Cs, and C3v symmetry (see picture).
Is Kekulene Really Superaromatic?†‡
- Pages: 2383-2386
- First Published: November 1, 1996
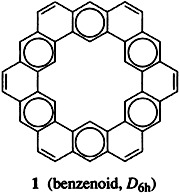
Kekulene is indeed a “normal” aromatic molecule. This conclusion is reached in a theoretical study in which a number of calculated properties of kekulene and reference compounds such as benzene, phenan-threne, and 1,2:7,8-dibenzanthracene were compared. Structure 1 is the most apt description of this molecule, and claims of superaromaticity can finally be laid to rest.
Efficient Recognition of Chiral Carbamoyl-α-Hydroxyacids with a Cleft-Type Receptor†
- Pages: 2386-2388
- First Published: November 1, 1996
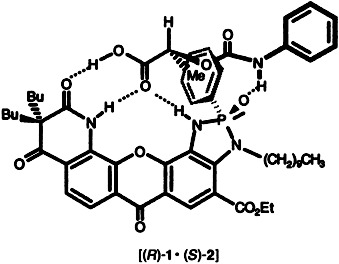
Simple chromatography using SiO2 impregnated with (S)-4-chlorophenyl-carbamoyllactic acid ((S)-2) can be used to separate the enantiomers of receptor 1 (Rf((R)-1/Rf((S)-1) = 0.8/0.1)). The very large association constant of the more stable complex [(R)-1·(S)-2] (5.7 × 105 M−1) was determined in a series of competitive NMR titrations with α-amino acid derivatives, which form less stable complexes with 1.
Enantioselective Synthesis of Vicinal Amino Alcohols by Oxa-Michael Addition of (−)-N-Formylnorephedrine to Nitroalkenes†
- Pages: 2388-2390
- First Published: November 1, 1996
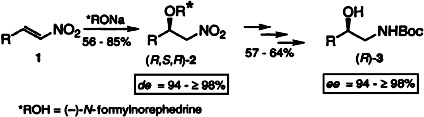
The asymmetric oxa-Michael addition of (-)-N-formylnorephedrine, a chiral oxygen nucleophile with a removable auxiliary, to (E)-nitroalkenes 1 permits the enantioselective synthesis of protected vicinal amino alcohols (R)-3 with high enantiomeric excesses after reduction of the 1,4-adducts 2. This new procedure opens an efficient entry to synthetic building blocks for natural products and drugs.
Thiolate Bridged Nickel–Iron Complexes Containing both Iron(0) and Iron(II) Carbonyls†
- Pages: 2390-2393
- First Published: November 1, 1996
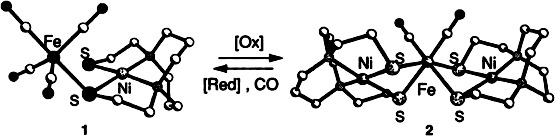
Stable and interconvertible are the NiFe compounds 1 and 2 in which the cis-dithiolato sulfur atoms bind to the Fe0–CO and FeII–CO complex fragments, respectively. Unlike the Ni – S distances, which are essentially independent of the oxidation state of the iron center and the denticity of the metallothiolato ligand, the NiFe distances differ by 0.7 Å.
Low-Temperature Complete Combustion of Methane over Mn-, Co-, and Fe-Stabilized ZrO2†
- Pages: 2393-2395
- First Published: November 1, 1996
Activity comparable to that of noble metal catalysts is shown by the Mn-, Co-, or Fe-stabilized ZrO2 catalysts for the low-temperature combustion of methane. The incorporation of the transition metal into the ZrO2 bulk structure not only stabilizes the cubic (fluorite) modification, but also increases the reactivity of the lattice oxygen atoms drastically.
New Course in the Search for Antitumor Agents: The Use of pH-Dependent Sources of Reactive Radicals†
- Pages: 2395-2396
- First Published: November 1, 1996
Stereoselectivity in Reactions of 1,2-Dioxy-Substituted Radicals under Chelation Control: An Unexpected Result†
- Pages: 2396-2399
- First Published: November 1, 1996
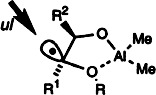
The strong pyramidalization of the radical intermediates (shown on the right) is the reason why anti Cram chelation products are obtained in the reduction of 1,2-dialkyl-1,2-dioxy-substituted radicals, even though a chelate is formed. The main diastereoisomer results from an attack syn to the large substituent R2. R1 CH2CHCHCH2SnBu3, R2 tBu, R para-methoxyphenyl.
An Approach to Epothilones Based on Olefin Metathesis†
- Pages: 2399-2401
- First Published: November 1, 1996
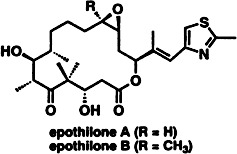
The same mechanism as taxol but a completely different, simpler structure is displayed by the recently described epothilones A and B. These features immediately attracted the attention of synthetic chemists. An approach to the macrocyclic framework of the epothilones has now been devised through use of ring-closing metathesis with the Grubbs catalyst [RuCl2(CHPh){P(C6H11)3}2].
Book Reviews
Book Review: Biotechnology Now–From Theory to Scale-Up: Downstream Processing of Natural Products. A Practical Handbook. Edited by M. S. Verrall
- Pages: 2403-2404
- First Published: November 1, 1996
Book Review: Carbohydrate Building Blocks. By M. Bols
- Page: 2404
- First Published: November 1, 1996
Book Review: Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 59, Protein Purification Protocols. Edited by S. Doonan
- Pages: 2404-2405
- First Published: November 1, 1996
Book Review: Sensors. Vol. 8. Micro- and Nanosensor Technology/Trends in Sensor Markets. Edited by H. Meixner and R. Jones. (Series: Sensors. A Comprehensive Survey). Series editors: W. Göpel, J. Hesse and J. N. Zemel
- Pages: 2405-2406
- First Published: November 1, 1996
Book Review: Metal Complexes in Aqueous Solution. By A. E. Martell and R. D. Hancock. (Series: Modern Inorganic Chemistry. Series editor: J. P. Fackler, Jr.)
- Pages: 2406-2407
- First Published: November 1, 1996
Book Review: Stereochemistry of Coordination Compounds. By A. von Zelewsky
- Page: 2407
- First Published: November 1, 1996





![Homogeneous Catalysts for Claus Chemistry: The Preparation and Structure of cis-[(PPh3)2PtS3O], a Catalytically Active Intermediate](/cms/asset/f33702ca-82de-4195-9e12-edfec8873878/must001.jpg)