Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture: One Shot Laser Pulse Induced Reversible Spin Transition in the Spin-Crossover Complex [Fe(C4H4N2){Pt(CN)4}] at Room Temperature (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 26/2005)
- Page: 3943
- First Published: 17 June 2005
A reversible spin transition …︁ …︁ occurs when a single laser pulse (8 ns) is applied in the hysteresis loop (black curve) of the spin-crossover complex [Fe(pyrazine){Pt(CN)4}] (structure shown). This bi-directional, photoinduced spin switching occurs at room temperature over a wide region of bistability and involves magnetization as well as color changes (low spin: red; high spin: yellow). More details on this phenomenon are given in the Communication by A. Bousseksou and co-workers on page 4069 ff.
A Novel Fluorescent Dye with Strong, Anisotropic Solid-State Fluorescence, Small Stokes Shift, and High Photostability
- Page: 3955
- First Published: 17 June 2005
K. Nakanishi Awarded Gold Nagoya Medal 2005 / M. Suginome Receives Silver Nagoya Medal 2005 / M. Shibasaki Receives Japan Academy Prize
- Page: 3956
- First Published: 17 June 2005
Fritz Haber: Chemist, Nobel Laureate, German, Jew. By Dietrich Stoltzenberg.
- Pages: 3957-3961
- First Published: 17 June 2005
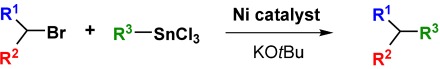
Couplings with Monoorganotin Compounds: A “Radical” Twist from the Original Stille Reaction
- Pages: 3962-3965
- First Published: 17 June 2005
Enzyme Mechanisms for Triterpene Cyclization: New Pieces of the Puzzle†
- Pages: 3966-3971
- First Published: 17 June 2005

Cationic polycyclization cascades: The stereoselective transformations of linear polyolefins to give cyclic triterpenes (see scheme) have fueled half a century of intense research. Structures of triterpene cyclases complexed with the substrate analogue 2-azasqualene and the reaction product lanosterol provide new insights into the elegant mechanisms of these enyzmes.
Efficiency in Nonenzymatic Kinetic Resolution
- Pages: 3974-4001
- First Published: 17 June 2005
Among the numerous synthetic methods for the preparation of chiral products with high enantiomeric excess, kinetic resolution is the oldest. It is unique, as it has been applied to practically every type of chiral substrate, and can be combined with any method of enantioselective synthesis. The scheme shows an example of dynamic kinetic resolution through the enantioselective catalytic hydration of an equilibrated racemic β-ketoester.
Epitaxial Casting of Nanotubular Mesoporous Platinum†
- Pages: 4002-4006
- First Published: 17 June 2005
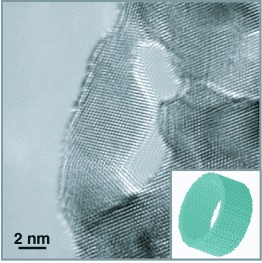
A network of platinum nanotubes with diameters of about 15 nm and walls 1 nm thick that interconnect to form an open, doubly bicontinuous structure (see high-resolution electron micrograph) is formed by coating platinum on a nanoporous gold template then dissolving away the mold. The structure is stable at 125 °C for at least 24 hours, but starts to deform at 150 °C and eventually forms nanoparticles.
A Cationic Zinc Porphyrin as a Chiroptical Probe for Z-DNA†
- Pages: 4006-4009
- First Published: 17 June 2005
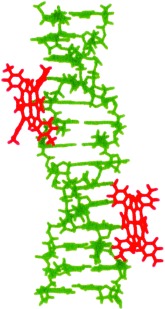
Z for zinc and Z-DNA: As a result of different binding modes, a cationic zinc porphyrin discriminates between B and Z conformations of DNA and holds promise as a probe for Z-DNA. A very intense induced circular dichroism (ICD) effect with a bisignate spectrum is observed upon interaction of the porphyrin with Z-DNA (see graphic; porphyrin red, Z-DNA green), whereas only a weak ICD spectrum results upon its interaction with B-DNA.
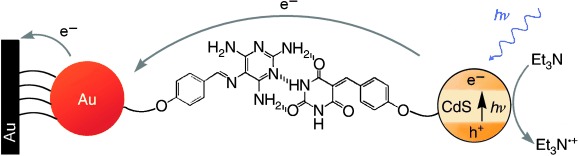
Hydrogen-Bonded CdS Nanoparticle Assemblies on Electrodes for Photoelectrochemical Applications†
- Pages: 4010-4015
- First Published: 17 June 2005
A Rigid Neutral Molecule Involving TTF and TCNQ Moieties with Intrinsic Charge- and Electron-Transfer Properties that Depend on the Polarity of the Solvent†
- Pages: 4015-4018
- First Published: 17 June 2005
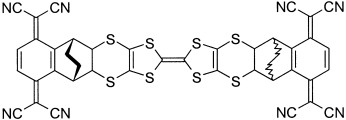
A one-component acceptor-donor-acceptor compound based on a rigid TCNQ-σ-TTF-σ-TCNQ system (see picture) exhibits a unique case of both intramolecular charge and electron transfer through space that is strongly dependent on the polarity of the medium. The strong dependence of the ground-state electronic structure on the solvent polarity provides an unprecedented case of solvatochromism.
An Onion Phase in Salt-Free Zero-Charged Catanionic Surfactant Solutions†
- Pages: 4018-4021
- First Published: 17 June 2005
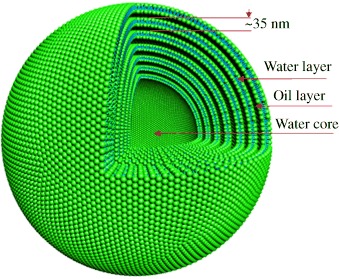
No added salt: Transmission electron microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering studies have shown that uni- and multilamellar vesicles with radii of 25.5 and 366 nm (see schematic diagram; the hydrophilic cation/anion groups are shown as green spheres and the hydrocarbon chains in blue), respectively, are formed from trimethyltetradecylammonium hydroxide and oleic acid in water. The multilamellar phase consists of seven bilayers.
Molecular Tectonics: Porous Cleavable Networks Constructed by Dipole-Directed Stacking of Hydrogen-Bonded Sheets†
- Pages: 4021-4025
- First Published: 17 June 2005
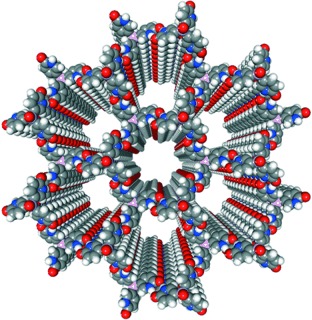
Carefully selected combinations of directional forces can be used to rationally engineer crystals with particular anisotropic features. This approach has led to the generation of cleavable molecular crystals with parallel 15-Å channels by dipole-directed stacking of hydrogen-bonded sheets (see crystal structure). The network remains undeformed when guests included in the channels are exchanged.
[(Ni-Ni-Ni)@(Ge9)2]4−: A Linear Triatomic Nickel Filament Enclosed in a Dimer of Nine-Atom Germanium Clusters†
- Pages: 4026-4028
- First Published: 17 June 2005
The Heme Monooxygenase Cytochrome P450cam Can Be Engineered to Oxidize Ethane to Ethanol†
- Pages: 4029-4032
- First Published: 17 June 2005
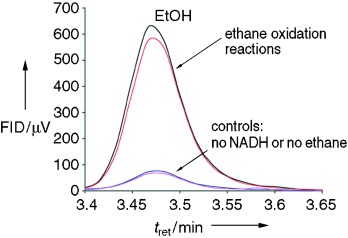
A NADH turnover rate of 741 min−1 in the oxidition of ethane to ethanol is observed with an engineered form of the heme monooxygenase cytochrome P450cam—the first example of such activity for a P450 enzyme (GC analysis shown). Ethanol is formed at 78 min−1 (10.5 % coupling). The mutant is ≈45 % high-spin in the absence of substrate, making it a useful platform for P450 structure–function studies.
Enantioselective Michael Addition to α,β-Unsaturated Imides Catalyzed by a Bifunctional Organocatalyst†
- Pages: 4032-4035
- First Published: 17 June 2005
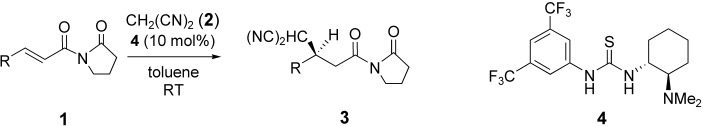
High enantioselectivities (up to 94 % ee) were attained in the Michael addition of a variety of α,β-unsaturated imides 1 and malononitrile (2) catalyzed by bifunctional thiourea 4. The pyrrolidinone moiety of 1 plays a key role in the reaction. The reaction provides access to a variety of Michael adducts 3 (see scheme; R=aryl and alkyl groups).
Total Synthesis of Erythronolide A by MgII-Mediated Cycloadditions of Nitrile Oxides†
- Pages: 4036-4038
- First Published: 17 June 2005
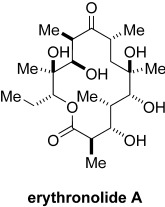
A cycloaddition comes of age: The focal points of a stereoselective total synthesis of erythronolide A (see structure) are two MgII-mediated cycloadditions of nitrile oxides. Of broader significance, the strategy not only facilitates the synthesis of specific polyketide targets (i.e. natural products) but also opens up new possibilities for the preparation of non-natural analogues.
Acetylenic Allenophanes: An Asymmetric Synthesis of a Bis(alleno)-bis(butadiynyl)-meta-cyclophane†
- Pages: 4039-4042
- First Published: 17 June 2005
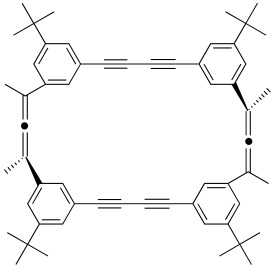
A cyclophane with allene and acetylene bridges has been prepared as a single enantiomer. This acetylenic allenophane (see structure) was synthesized by a series of palladium- and copper-mediated coupling reactions. The allene bridge was derived from the ring opening of a chiral epoxy alkyne, which was prepared by a Sharpless asymmetric epoxidation of an allylic alcohol.
Ru-Catalyzed Anti-Markovnikov Addition of Amides to Alkynes: A Regio- and Stereoselective Synthesis of Enamides†
- Pages: 4042-4045
- First Published: 17 June 2005
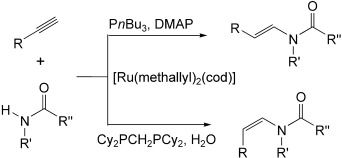
The base-free anti-Markovnikov addition of secondary amides, anilides, lactams, ureas, bislactams, and carbamates to terminal alkynes is accomplished, for the first time, by a ruthenium-catalyzed reaction. Two complementary protocols provide stereoselective synthetic entries to either the E or the Z isomers (see scheme; cod=cycloocta-1,5-diene; DMAP=4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine).
Anilide ortho-Arylation by Using CH Activation Methodology†
- Pages: 4046-4048
- First Published: 17 June 2005
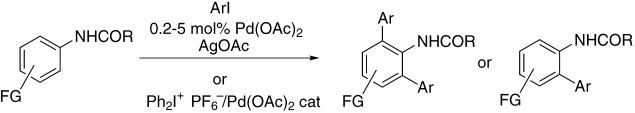
A thousand turnovers in bi- and triaryl formation: Substituted anilides have been ortho-arylated by aryl iodides under palladium catalysis (see scheme). This method is highly tolerant of the presence of additional functional groups (FGs). Even an iodo functionality on the anilide moiety and a bromo functionality on the aryl iodide are compatible with this methodology.
Molecular Recognition of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor by Polyoxometalates†
- Pages: 4048-4052
- First Published: 17 June 2005
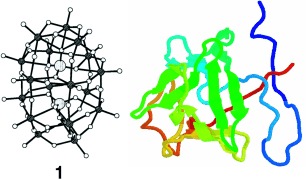
Protein binders: Three representative polyoxometalate (POM) compounds, for example 1, which is of the Wells–Dawson class, were found to interact with the basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF, right). The binding induces dramatic conformational changes in the growth factor. POMs are promising leads for compounds that may represent a new avenue for the development of therapeutic agents against bFGF-induced angiogenesis.
A Benzodipyrrole-Derived Sapphyrin†
- Pages: 4053-4055
- First Published: 17 June 2005
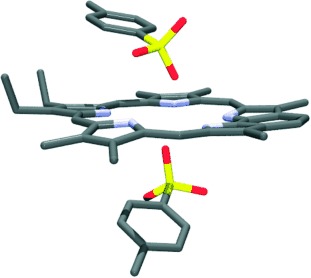
Within the framework: The fused benzodipyrrole unit within the sapphyrin 1 has a significant influence on its structure as compared to those of usual sapphyrins. The fused benzene ring partly inhibits distortion of the macrocycle about the dipyrrole unit (see structure of 1⋅2 H+ 2 (p-CH3C6H4SO3−); C gray, N blue, O red, S yellow) and contributes to the significant red-shift of Q-bands.
2,2′:6′,2′′:6′′,6-Trioxytriphenylamine: Synthesis and Properties of the Radical Cation and Neutral Species†
- Pages: 4056-4058
- First Published: 17 June 2005
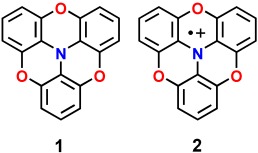
A flat radical: Oxygen-bridged triphenylamine 1 and its radical cation 2 were prepared. The neutral compound has a shallow bowl structure, whereas the radical cation is planar. The properties of the highly stable radical cation were clarified; such compounds have potential applicability in electronic and magnetic materials.
A Labeled Neutral Endopeptidase Inhibitor as a Potential Tool for Tumor Diagnosis and Prognosis†
- Pages: 4058-4061
- First Published: 17 June 2005
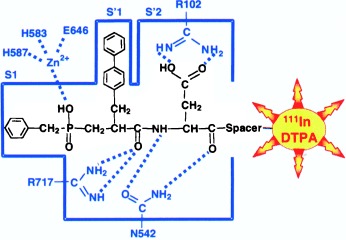
Specific targeting of tumors with radioactive isotopes is the key for high-sensitivity scintigraphy detection. A labeled neutral endopeptidase (NEP) inhibitor is described that accumulates in vivo in tumor cells expressing this enzyme, which makes it a potential tool for noninvasive evaluation of NEP expression. Its structure (black with the label depicted in red, DTPA=diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid) is shown in a model of the NEP active site (blue).
Polymer Therapeutics Designed for a Combination Therapy of Hormone-Dependent Cancer†
- Pages: 4061-4066
- First Published: 17 June 2005
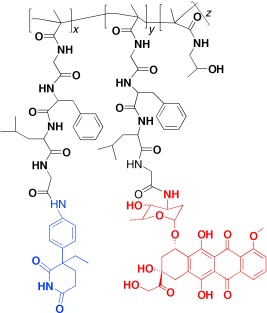
Designer drug: A polymer therapeutic was designed for a combination therapy of breast cancer. N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide was used as the model polymer platform to prepare a unimolecular polymer conjugate (see picture, radius of gyration: 12.8 nm) that combines an endocrine (the aromatase inhibitor aminoglutethimide, blue) and a chemotherapeutic agent (the anthraxcycline antibiotic doxorubicin, red).
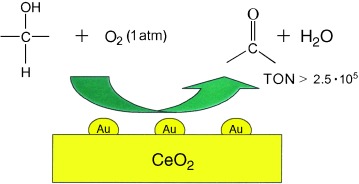
A Collaborative Effect between Gold and a Support Induces the Selective Oxidation of Alcohols†
- Pages: 4066-4069
- First Published: 17 June 2005
One Shot Laser Pulse Induced Reversible Spin Transition in the Spin-Crossover Complex [Fe(C4H4N2){Pt(CN)4}] at Room Temperature†
- Pages: 4069-4073
- First Published: 17 June 2005
![One Shot Laser Pulse Induced Reversible Spin Transition in the Spin-Crossover Complex [Fe(C4H4N2){Pt(CN)4}] at Room Temperature](/cms/asset/e33c9ed5-ace4-4c5b-b0b6-f6fa00391418/mcontent.jpg)
In the loop: A reversible spin transition was observed by Raman spectroscopy on application of a single laser pulse (8 ns) in the hysteresis loop of the spin-crossover complex [Fe(pyrazine){Pt(CN)4}]. This bi-directional, photoinduced spin switching occurs at room temperature over a wide region of bistability and involves magnetization as well as color changes (see picture).
Multistep Electron Transfer in Oligopeptides: Direct Observation of Radical Cation Intermediates†
- Pages: 4073-4075
- First Published: 17 June 2005
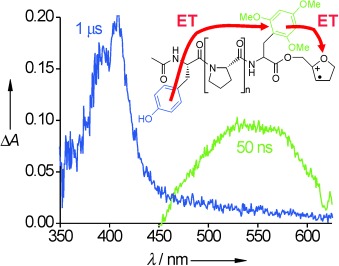
Hopping holes: Oligopeptides with a photosensitive charge-injection system were synthesized and irradiated by a nanosecond laser. A multistep electron-transport process occurred which uses aromatic side chains as hole carriers (see scheme). The rates of this process indicate through-space electron transfer (a hopping mechanism).
Dihydroxyacetone in Amino Acid Catalyzed Mannich-Type Reactions†
- Pages: 4077-4079
- First Published: 17 June 2005

The C3 equivalent dihydroxyacetone was used in its protected form in proline-catalyzed Mannich reactions (see scheme). As little as 5 mol % catalyst is required when using 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol as solvent. The reaction is improved further (reaction time 10 min) under microwave conditions. PMP=p-methoxyphenyl.
Asymmetric Synthesis of Selectively Protected Amino Sugars and Derivatives by a Direct Organocatalytic Mannich Reaction†
- Pages: 4079-4083
- First Published: 17 June 2005
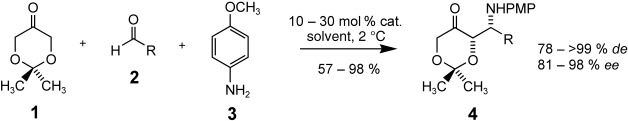
Short and sweet: Starting from the commercially available precursors 1–3, selectively protected amino sugars and derivatives are obtained in one step and with high diastereo- and enantiomeric purity by means of a proline-catalyzed three-component Mannich reaction (see scheme, PMP=para-methoxyphenyl). This efficient organocatalytic procedure can be carried out smoothly on a multigram scale.
Sequential Enzymatic Oxidation of Aminoarenes to Nitroarenes via Hydroxylamines†
- Pages: 4083-4087
- First Published: 17 June 2005
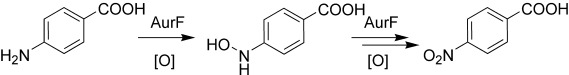
The at-line detection of an amino group oxidation catalyzed by the N-oxygenase AurF provides the first direct evidence for a stepwise enzymatic oxidation of aromatic amines to nitro groups via a hydroxylamine intermediate (see scheme). The sequential nature of this reaction is further supported by biotransformation of the intermediate and the identification of a p-aminobenzoate-derived azoxy side product.
Crystalline, Porous Microspheres Made from Amino Acids by Using Polymer-Induced Liquid Precursor Phases†
- Pages: 4087-4092
- First Published: 17 June 2005

Precipitation of charged amino acids in the presence of oppositely charged polyelectrolytes leads to liquid droplets of the corresponding polymer/amino acid complexes in water. The resulting emulsions are stable against crystallization and Ostwald ripening for several months but can also be used as a starting situation for crystallization of spherical, porous crystal superstructures (see SEM image of L-lysine).
Modified Linear Dextrins (“Acyclodextrins”) as New Chiral Selectors for the Gas-Chromatographic Separation of Enantiomers†
- Pages: 4092-4095
- First Published: 17 June 2005
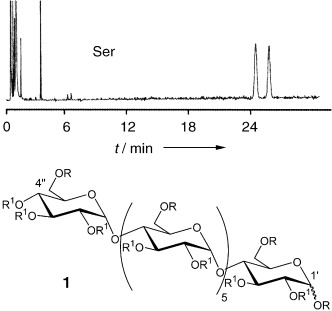
Cyclic or acyclic: Not only modified cyclodextrins but also modified linear dextrins like the silylated (R)and acetylated (R1) maltoheptaose derivatives 1 are suitable selectors for separating racemic N-trifluoroacetyl-O-alkyl esters of α-amino acids by gas chromatography. In the example shown, racemic N-trifluoroacetylserine O-ethyl ester is resolved.
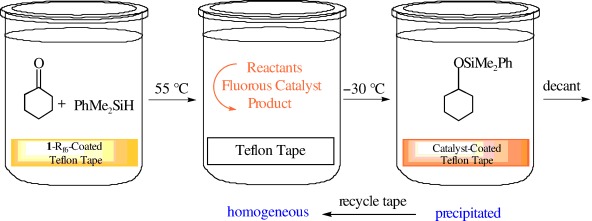
“Catalyst-on-a-Tape”—Teflon: A New Delivery and Recovery Method for Homogeneous Fluorous Catalysts†
- Pages: 4095-4097
- First Published: 17 June 2005




![[(Ni-Ni-Ni)@(Ge9)2]4−: A Linear Triatomic Nickel Filament Enclosed in a Dimer of Nine-Atom Germanium Clusters](/cms/asset/52f762f4-5e08-47fc-9da0-e815c79132f8/mcontent.jpg)