Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture: Phosphorus Nanorods—Two Allotropic Modifications of a Long-Known Element (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 32/2004)
- Page: 4111
- First Published: 09 August 2004
Alternatives to the structure of Hittorf phosphorus were predicted a few years ago, and these have now been confirmed experimentally as phosphorus nanorods. A. Pfitzner, H. Eckert, and co-workers report on page 4228 ff. that these new allotropic forms of phosphorus can be isolated from the adduct compounds (CuI)8P12 and (CuI)3P12 by extraction with an aqueous cyanide solution. The nanorods have been characterized by high-resolution TEM and 31P magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy.
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 32/2004
- Pages: 4114-4121
- First Published: 09 August 2004
Orville L. Chapman (1932–2004): Organic Chemistry and Education
- Page: 4122
- First Published: 09 August 2004
Experimental Design for Combinatorial and High Throughput Materials Development. Edited by James N. Cawse.
- Page: 4123
- First Published: 09 August 2004
Organosilanes in Radical Chemistry. Principles, Methods and Applications. By Chryssostomos Chatgilialoglu.
- Page: 4124
- First Published: 09 August 2004
Oxidative Synthesis of α-Amino Nitriles from Tertiary Amines
- Pages: 4126-4128
- First Published: 09 August 2004
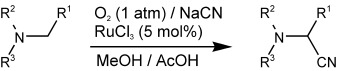
A catalytic option: Tertiary amines are converted into the corresponding α-amino nitriles in the presence of hydrated ruthenium trichloride (5 mol %), sodium cyanide (1.2 equiv), and molecular oxygen (see scheme). This is a valuable alternative to the Strecker synthesis of α-amino nitriles and can be used to prepare N-aryl glycine derivatives and unsymmetrical 1,2-diamines.
Semiconductor Quantum Dots as Biological Imaging Agents†
- Pages: 4129-4131
- First Published: 09 August 2004
N2O Reduction by the μ4-Sulfide-Bridged Tetranuclear CuZ Cluster Active Site†
- Pages: 4132-4140
- First Published: 09 August 2004
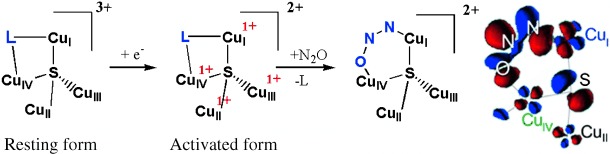
A spectrum of unusual features: N2O reduction is accomplished in biology by an active site consisting of a μ4-sulfide-bridged tetranuclear copper cluster (the CuZ center), which has many unusual spectroscopic features. Recent studies have led to electronic-structure descriptions of resting CuZ, its catalytically relevant form, and elucidated the role of CuZ in N2O activation and reduction (see scheme).
Functional Models for Rhodium-Mediated Olefin-Oxygenation Catalysis
- Pages: 4142-4157
- First Published: 09 August 2004
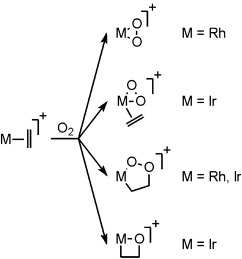
A rational improvement of rhodium/iridium-catalyzed olefin oxygenation by dioxygen or hydrogen peroxide requires more detailed insight into underlying mechanisms and ligand effects (see scheme). In this Review, results from model studies are related to known catalytic systems, and differences between rhodium/iridium- and palladium-catalyzed olefin oxidation are discussed.
[(CF3)3BCP]− and [(CF3)3BCAs]−: Thermally Stable Phosphaethynyl and Arsaethynyl Complexes†
- Pages: 4160-4163
- First Published: 09 August 2004
![[(CF3)3BCP]− and [(CF3)3BCAs]−: Thermally Stable Phosphaethynyl and Arsaethynyl Complexes](/cms/asset/865f467c-7dd9-4e20-807a-d61c6dde4ca7/mcontent.jpg)
Make mine a triple: The tetraphenyl phosphonium salts of [(CF3)3BCX]− (X=P, As) are stable even well above room temperature. The synthesis of these first phospha- and arsaethynyl complexes of boron from (CF3)3BCO is carried out in two steps (see scheme). The complex [(CF3)3BCAs]− is the first stable anionic arsaalkyne.
Unusual Biosynthesis of Leupyrrins in the Myxobacterium Sorangium cellulosum†
- Pages: 4163-4167
- First Published: 09 August 2004
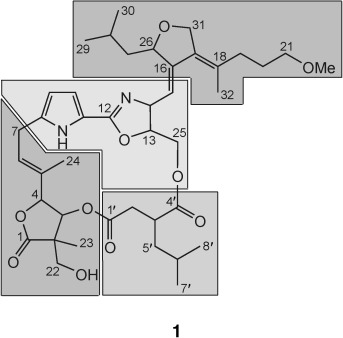
Classical feeding experiments indicate involvement of nonribosomal peptide, polyketide, and isoprenoid biosynthesis in the formation of the myxobacterial antibiotic leupyrrin (1). The resulting structural elements are modified further (e.g. by a semipinacol-like rearrangement and oxidative formation of a methylene bridge) to yield the unique leupyrrin framework.
The Cluster Ion [Pt12O8(SO4)12]4−†
- Pages: 4168-4170
- First Published: 09 August 2004
![The Cluster Ion [Pt12O8(SO4)12]4−](/cms/asset/ec3330f2-0777-4397-9dc5-fdbabae0d20e/mcontent.jpg)
Platinum dumbbells: The reaction of platinum nitrate with concentrated sulfuric acid at 350 °C leads to the deep red oxide–sulfate (NH4)Pt3O2(SO4)3, in which six [Pt2]6+ dumbbells are linked by oxide ions and sulfate groups to the novel cluster anion [Pt12O8(SO4)12]4− (see picture). The structure of the core of this anion matches exactly the recent prediction for dodecanuclear complexes built from six metal dumbbells.
An SECM Detection Scheme with Improved Sensitivity and Lateral Resolution: Detection of Galactosidase Activity with Signal Amplification by Glucose Dehydrogenase†
- Pages: 4170-4172
- First Published: 09 August 2004
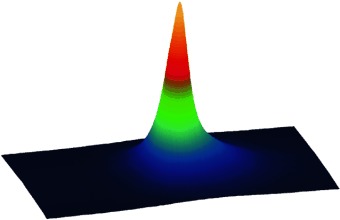
An enzymatic amplification cycle is used in a novel detection scheme for scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM). An immobilized enzyme system comprising galactosidase and PQQ-dependent glucose dehydrogenase was imaged by SECM with high sensitivity and high lateral resolution. PQQ=pyrroloquinolinequinone.
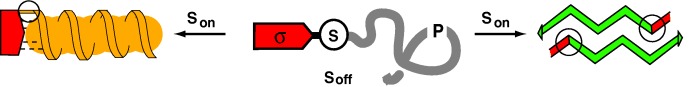
Switch Peptides In Statu Nascendi: Induction of Conformational Transitions Relevant to Degenerative Diseases†
- Pages: 4172-4178
- First Published: 09 August 2004
The Photochemical cis–trans Isomerization of Free Stilbene Molecules Follows a Hula-Twist Pathway†
- Pages: 4178-4182
- First Published: 09 August 2004
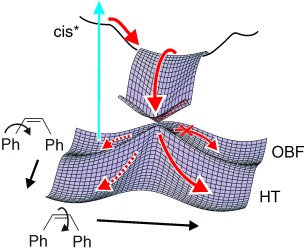
A motion breaking with tradition: The cis–trans isomerization of nonpolar conjugated π systems does not proceed simply by the 180° twist of a CC bond (“one-bond flip”, OBF), but by the rotation of a central CH group out of the plane (“hula twist”, HT). The hula-twist motion does not require any external constraint but is driven by an internal force: the slope on the way through a conical intersection.
Partitioning of Solvent Effects and Intrinsic Interactions in Biological Recognition†
- Pages: 4183-4186
- First Published: 09 August 2004
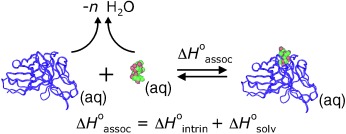
Divide and conquer: A novel approach was used to separate solvent effects from the intrinsic interactions involved in the association of biological complexes (see figure). The enthalpy of solvent reorganization for the formation of an intermolecular hydrogen bond in a biomolecular complex was determined by comparing the solution and gas-phase stabilities of structurally related complexes.
Towards Electrochemical Artificial Muscles: A Supramolecular Machine Based on a One-Dimensional Copper-Containing Organophosphonate System†
- Pages: 4186-4189
- First Published: 09 August 2004
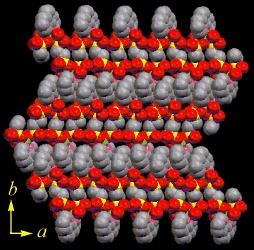
Robo copper: A mechanically robust corrugated sheet, 1 DOP-Cu, is composed of mats of individual chain-bundles joined by π–π interactive forces (see structure). Upon electrochemical charge injection into 1 DOP-Cu, the variations of the cell parameters of the Li-inserted phase were observed by X-ray diffraction. The mechanical deformation of the whole sheet is produced by a CuII/CuI redox process.
Forced Peptide Synthesis in Nanoscale Confinement under Elastomeric Stamps†
- Pages: 4190-4193
- First Published: 09 August 2004
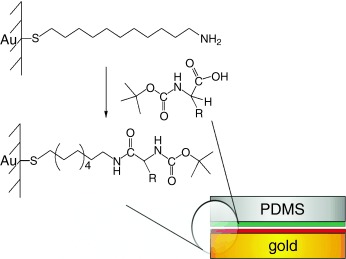
Pressing a rubber stamp inked with carboxylic acids onto an amine-terminated surface leads to the formation of amide bonds at room temperature (see scheme). Oligopeptides were created on the surface in this way from a monolayer. This rapid and uncatalyzed formation of amide bonds is attributed to the nanoscale confinement of the molecules between the stamp and the preorganized monolayer substrate. PDMS=poly(dimethylsiloxane).
Design and Synthesis of Endoperoxide Antimalarial Prodrug Models†
- Pages: 4193-4197
- First Published: 09 August 2004
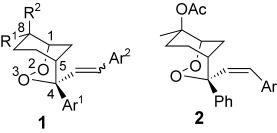
A masked combination chemotherapy which relies on the embedding of a number of active components, in a latent form, within a single endoperoxidic chemical entity is the aim of the research presented. The approach is illustrated by means of purposely designed bicyclic endoperoxide prodrug prototypes 1 and subsequently validated through the study of model compounds 2 (Ar=Ph, p-FC6H4, p-ClC6H4).
Reversible Thermochromism in Hydrogen-Bonded Polymers Containing Polydiacetylenes†
- Pages: 4197-4200
- First Published: 09 August 2004
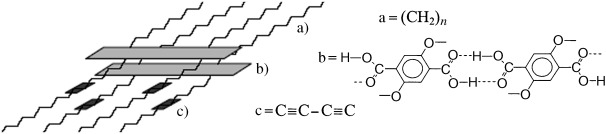
Out of the blue: A reversible temperature-dependent change in the absorption characteristics of spin-coated terephthalic acid/diacetylene polymers is observed. The polymer is prepared by topochemical photopolymerization of the diacetylene side chains of the stacked terephthalic acid units (see picture). The absorption bands of the polymeric product move reversibly from 640 nm (blue form of the polymer) to 580 nm (red form) during heating–cooling cycles.
Aromaticity: The Alternating CC Bond Length Structures of [14]-, [18]-, and [22]Annulene†
- Pages: 4200-4206
- First Published: 09 August 2004
![Aromaticity: The Alternating C<span class='icomoon'></span>C Bond Length Structures of [14]-, [18]-, and [22]Annulene](/cms/asset/412a6343-7ab6-44fc-a384-95a7c9911fae/mcontent.jpg)
First among unequals: Equal CC bond lengths, as found in benzene, are not necessary for aromaticity. [18]Annulene is the next Hückel monocycle where D6h symmetry is possible topologically (see picture). However, this widely accepted structure of [18]annulene is not correct. The 1H NMR chemical shifts and energy computations show that [18]annulene prefers CC bond-length alternation and C2 symmetry.
Total Synthesis of (+)-Scyphostatin, a Potent and Specific Inhibitor of Neutral Sphingomyelinase†
- Pages: 4207-4209
- First Published: 09 August 2004
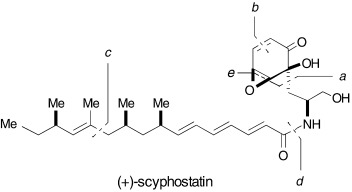
The five crucial steps in the first total synthesis of (+)-scyphostatin from D-arabinose involve (see picture): a) stereoselective aldol coupling to form a quaternary stereocenter, b) ring-closing metathesis (RCM) to construct the cyclohexene ring, c) Negishi coupling for the preparation of the fatty acid side chain, d) amide formation to connect the cyclohexene and fatty acid segments, e) stereospecific epoxide-ring formation.
A Silver-Catalyzed Intramolecular Amidation of Saturated CH Bonds†
- Pages: 4210-4212
- First Published: 09 August 2004
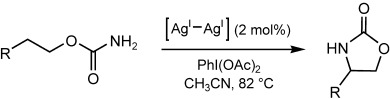
Opportunities with silver: A dinuclear silver(I) compound was found to efficiently catalyze the intramolecular amidation of saturated CH bonds of carbamates and sulfamates (see scheme). This highly regioselective, stereospecific reaction offers a practical method for the construction of cyclic nitrogen-containing organic molecules.
Ni(OH)2 Tubes with Mesoscale Dimensions as Positive-Electrode Materials of Alkaline Rechargeable Batteries†
- Pages: 4212-4216
- First Published: 09 August 2004
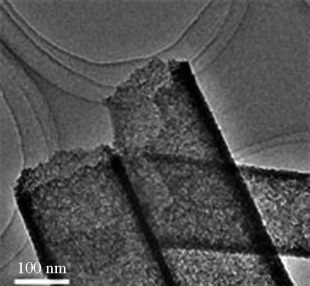
Higher capacity rechargeable batteries can be constructed by using mesoscale nickel hydroxide tubes as the positive-electrode material. The tubes were prepared by deposition of nickel ions and aqueous ammonia in an anodic alumina membrane as the template. The picture shows a high-resolution TEM image of the tubes.
Donor–Donor Energy-Migration Measurements of Dimeric DsbC Labeled at Its N-Terminal Amines with Fluorescent Probes: A Study of Protein Unfolding†
- Pages: 4216-4219
- First Published: 09 August 2004
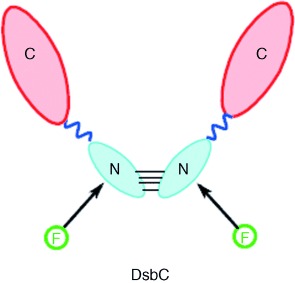
The folding/unfolding of a protein structure has been studied through measuring the donor–donor energy migration between two fluorescent probes (F) coupled selectively to the N termini of the homodimeric DsbC protein (see picture). The fluorometric strategy provides a convenient and reliable method to investigate conformational changes in dimeric proteins.
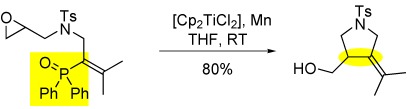
Titanium-Mediated Domino Radical Cyclization/β Elimination of Phosphine Oxides†
- Pages: 4220-4222
- First Published: 09 August 2004
Total Synthesis of Lepadins B, D, E, and H; Determination of the Configuration of the Latter Three Alkaloids†
- Pages: 4222-4225
- First Published: 09 August 2004
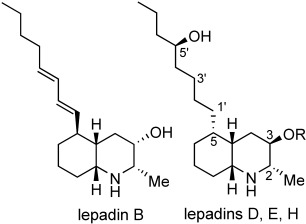
A common bicyclic intermediate was used in an efficient strategy towards lepadins B, D, E, and H shown. These alkaloids are members of a family of natural products with diverse biological activity. The described total syntheses of lepadins D, E, and H enabled the full elucidation of their configuration.
Highly Enantioselective Iron-Catalyzed Sulfide Oxidation with Aqueous Hydrogen Peroxide under Simple Reaction Conditions†
- Pages: 4225-4228
- First Published: 09 August 2004
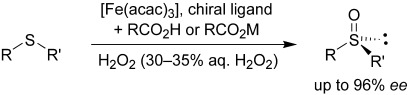
An attractive alternative to the currently existing methods for the metal-catalyzed oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides is asymmetric iron-catalyzed oxidation with hydrogen peroxide as the terminal oxidant (see scheme). In the presence of a benzoic acid derivative, this simple process provides sulfoxides with up to 96 % ee in moderate to good yields (up to 78 %).
Phosphorus Nanorods—Two Allotropic Modifications of a Long-Known Element
- Pages: 4228-4231
- First Published: 09 August 2004
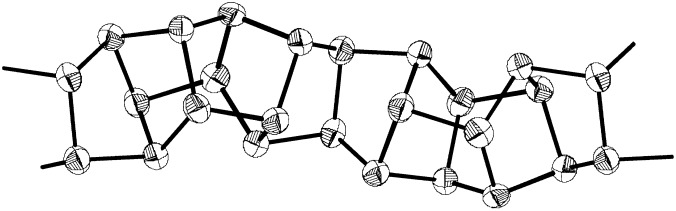
Extracting the P: Two novel amorphous allotropes of elemental phosphorus that consist of polymeric chains (see example depicted) were obtained in a pure form by extraction from their copper iodide adducts with an aqueous solution of potassium cyanide. 31P NMR spectra and high-resolution TEM images suggest that the structure of these phosphorus nanorods is unchanged after extraction.
Zirconium Triflate Catalyzed Direct Coupling Reaction of Lactams with Heterocyclic Arenes under Atmospheric Oxygen
- Pages: 4231-4233
- First Published: 09 August 2004
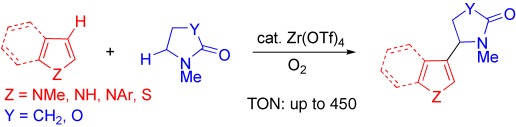
Exclusive coupling: High turnover numbers were attained in the dehydrogenative coupling reaction between C(sp2) and C(sp3) atoms. A zirconium catalyst mediates the coupling reactions of heterocyclic arenes and lactams exclusively at the carbon atom adjacent to the nitrogen atom of the latter under an oxygen atmosphere (see scheme).