Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
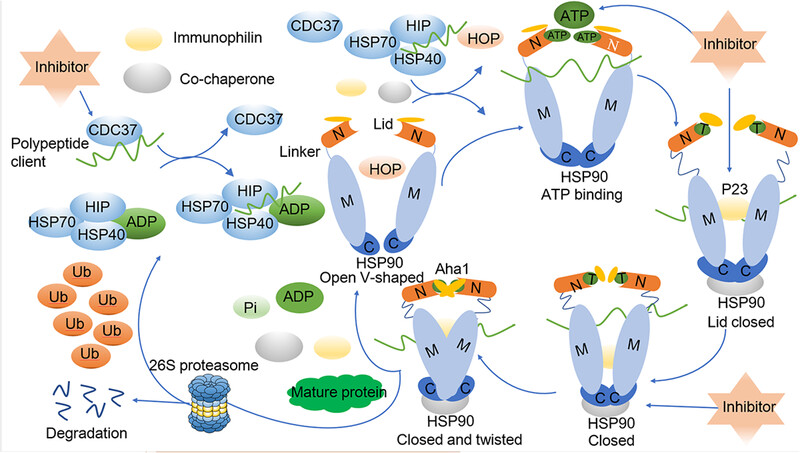
Heat shock protein 90: biological functions, diseases, and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 25 January 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase suppresses insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor expression to inhibit cell adhesion and proliferation in gastric cancer
- First Published: 30 January 2024
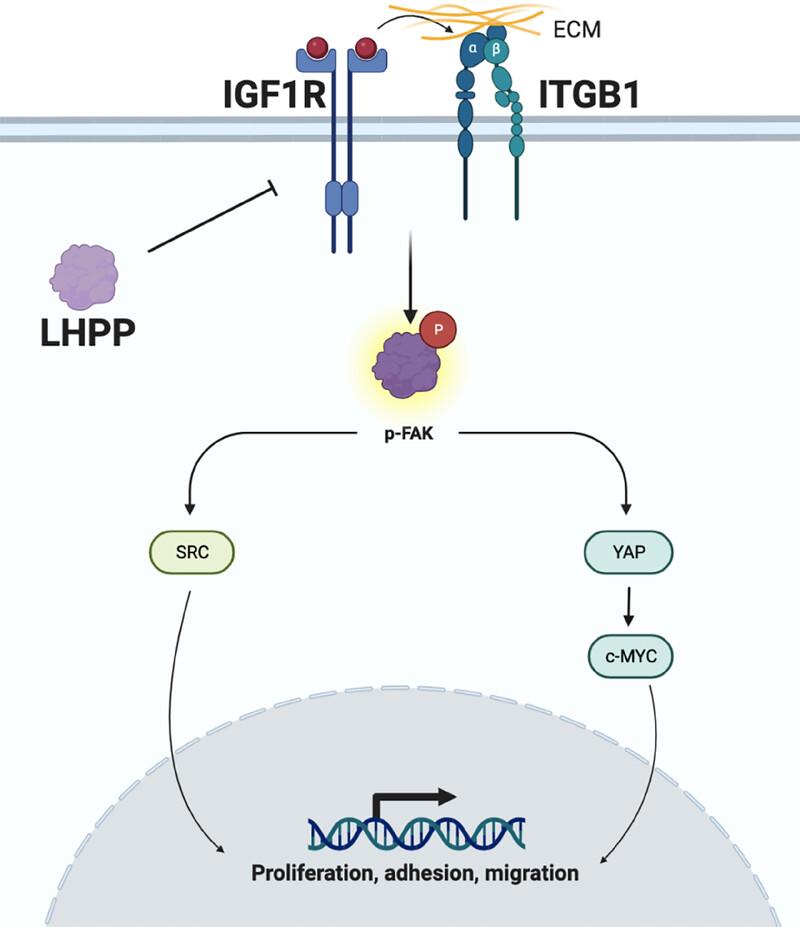
LHPP, downregulated in gastric cancer, can be used as an independent risk factor for gastric cancer patients, and its expression level is positively correlated with the prognosis of patients. LHPP inhibits gastric cancer cells' proliferation, migration, invasion, and adhesion. The dysregulation of LHPP expression leads to the upregulation of IGF1R, thereby activating the downstream ITGB1–FAK–SRC/YAP–c-MYC signaling pathway, resulting in the development and progression of gastric cancer.
Repurposing iron chelators for accurate positron emission tomography imaging tracking of radiometal-labeled cell transplants
- First Published: 30 January 2024
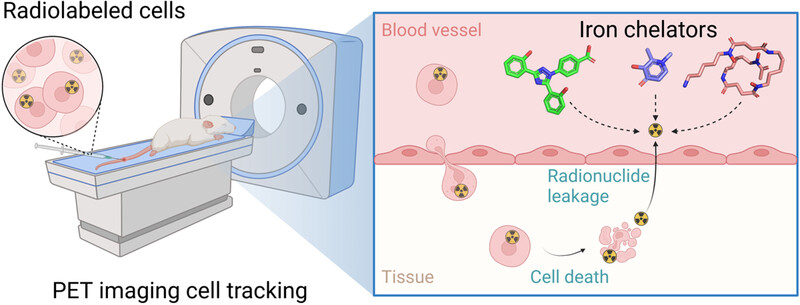
PET imaging tracks radiolabeled cell therapies, but dead cells release free radionuclides, confounding live cell signals. Iron chelators deferoxamine and deferiprone cleared radionuclides 89Zr and 68Ga in vivo, enabling accurate radionuclides-mesenchymal stem cell tracking and reduced radiation. Chelation avoided radionuclide bone accumulation, enabling precise cell homing observation. This clinically translatable method promises widespread utility for cell tracking studies.
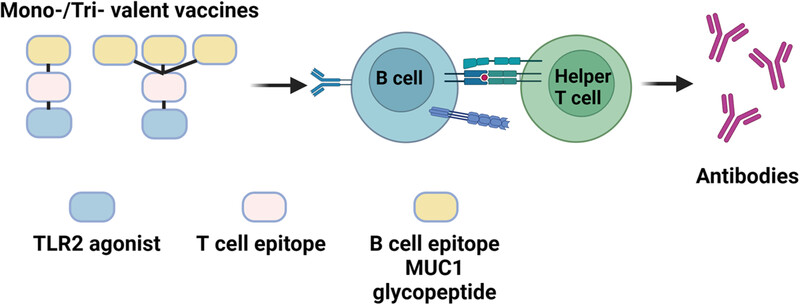
Synthetic self-adjuvanted multivalent Mucin 1 (MUC1) glycopeptide vaccines with improved in vivo antitumor efficacy
- First Published: 09 February 2024
Stromal interaction molecule 1/microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3B complex induces metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting autophagy
- First Published: 09 February 2024
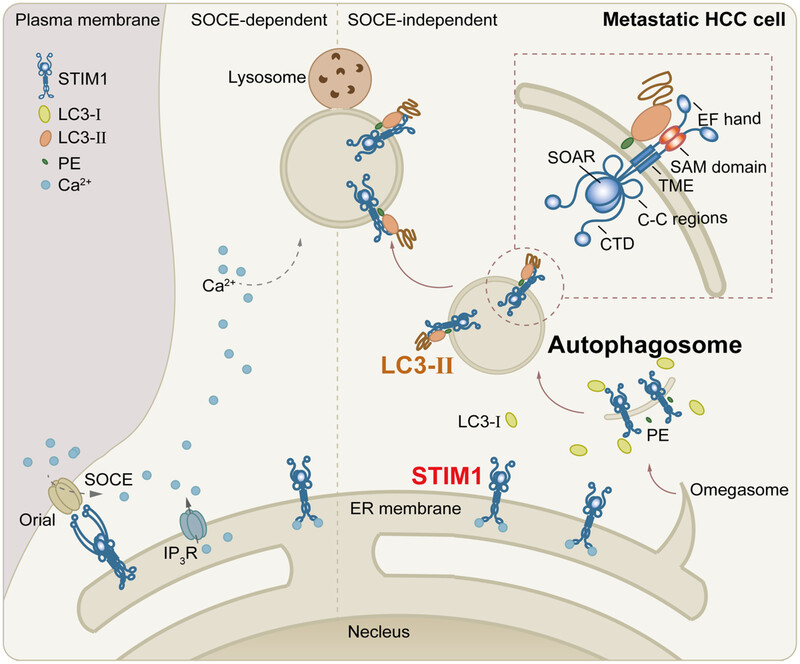
The role of STIM1 in regulating autophagy during HCC metastasis remains unclear. In this study, the authors demonstrate that STIM1 enhances autophagy flux by directly binding with LC3B, independently of SOCE. Mechanistically, STIM1 interacts with LC3B through the SAM domain, promoting the formation of autophagosomes. These findings suggest a potential therapeutic approach for preventing HCC metastasis.
Reticulon 3 regulates sphingosine-1-phosphate synthesis in endothelial cells to control blood pressure
- First Published: 13 February 2024
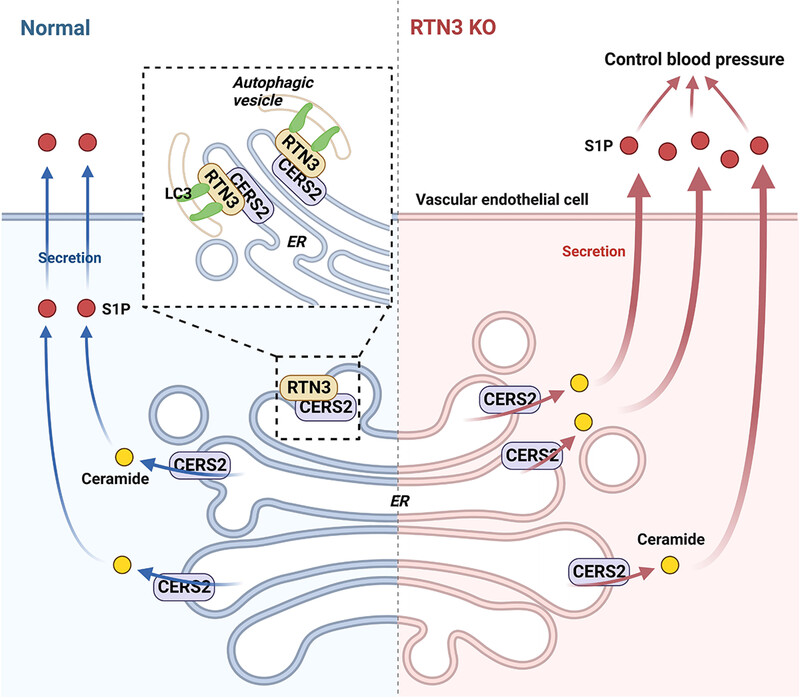
We first linked RTN3 with blood pressure regulation in humans and mice and reported the first RTN3 variant in a hypertension patient. RTN3 controlled blood pressure partly through binding to CERS2 to induce its selective autophagy and negatively regulate S1P metabolism in endothelial cells. Our data preliminarily elucidated the importance of RTN3 in S1P synthesis and blood pressure regulation.
mRNA PROTACs: engineering PROTACs for high-efficiency targeted protein degradation
- First Published: 19 February 2024
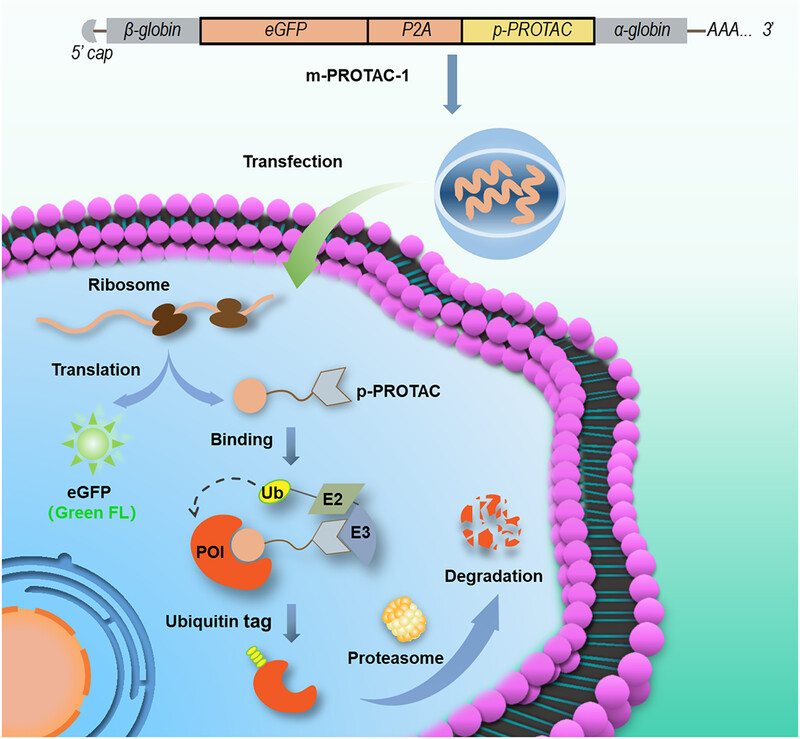
We developed mRNA proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs), a novel type of PROTACs, which incorporate mRNAs encoding E3 ligase recruiting peptide ligand and protein of interest (POI)-binding peptide ligand to promote cellular POI degradation. For the first time, we demonstrated that the encoding peptide PROTACs could degrade POIs and inhibit cell proliferation more effectively than the traditional peptide PROTACs, indicating their tremendous potential for targeted protein degradation therapy.
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 3-mediated lipid droplets accumulation confers chemoresistance of colorectal cancer
- First Published: 09 February 2024
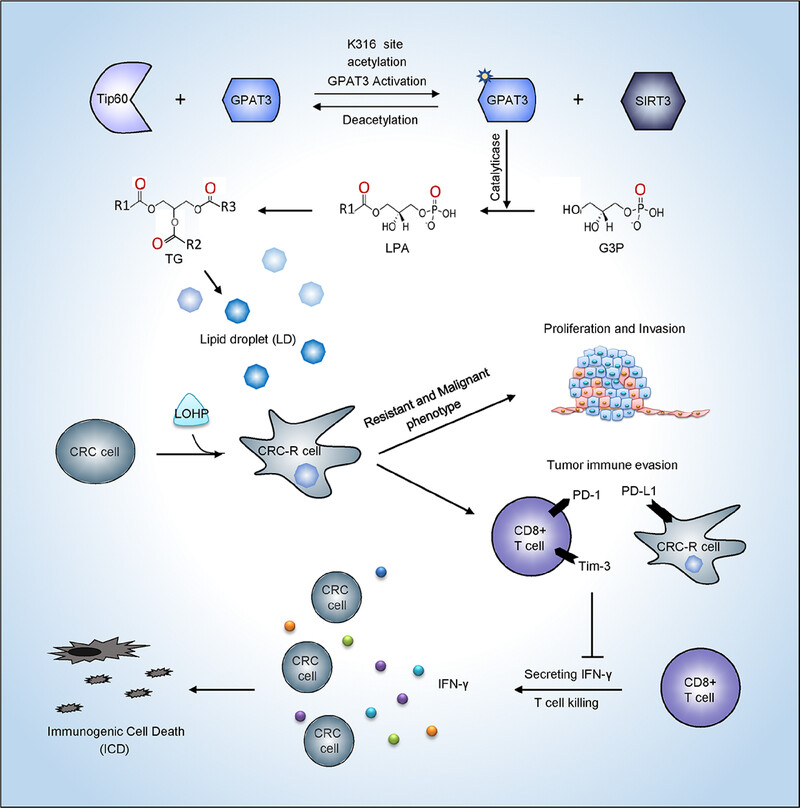
GPAT3 is responsible for G3P converting to LPA. It is the first step in TG synthesis and LD production. Oxa induces GPAT3 overexpression and LDs accumulation, which confers chemoresistance to CRC cells. Chemoresistant cells present a more malignant phenotype and suppress the cell killing effect of CD8+T cells, resulting in immune evasion and tumor recurrence
HIGHLIGHTS
Booster vaccination: host preparation against Omicron challenge by innate immunity training
- First Published: 30 January 2024
REVIEWS
Hepatocellular carcinoma: signaling pathways, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy
- First Published: 04 February 2024
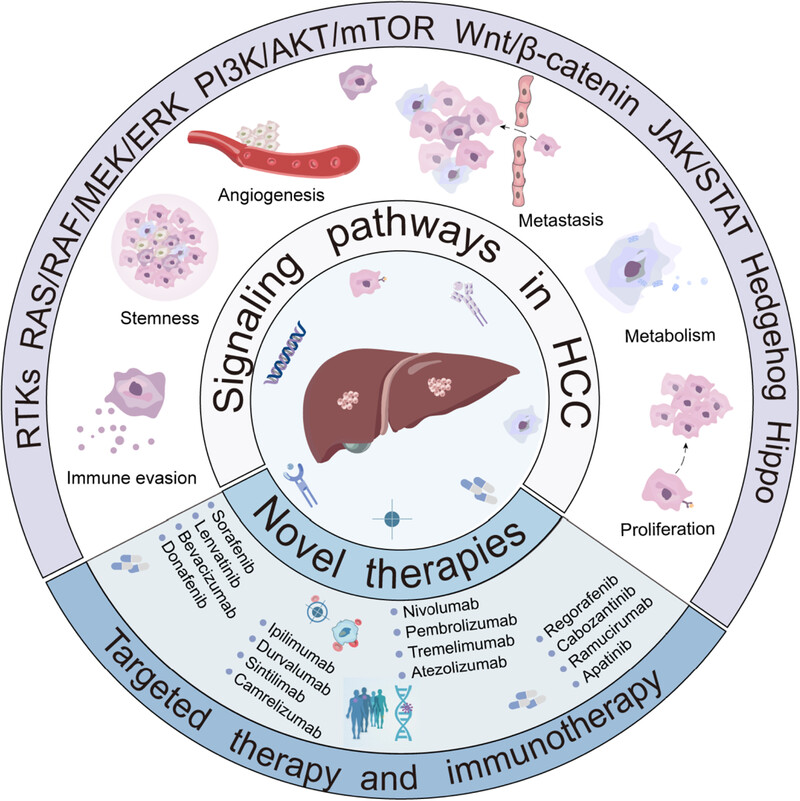
This review describes the signaling pathways and the clinical targeted therapies and immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Abnormal activation of signaling pathways in HCC can lead to a series of physiological activities such as cell proliferation, metabolism, metastasis, angiogenesis, activated stemness and immune evasion. Therefore, corresponding targeted drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors in HCC have been developed and put into clinical use.
Drug development advances in human genetics-based targets
- First Published: 09 February 2024
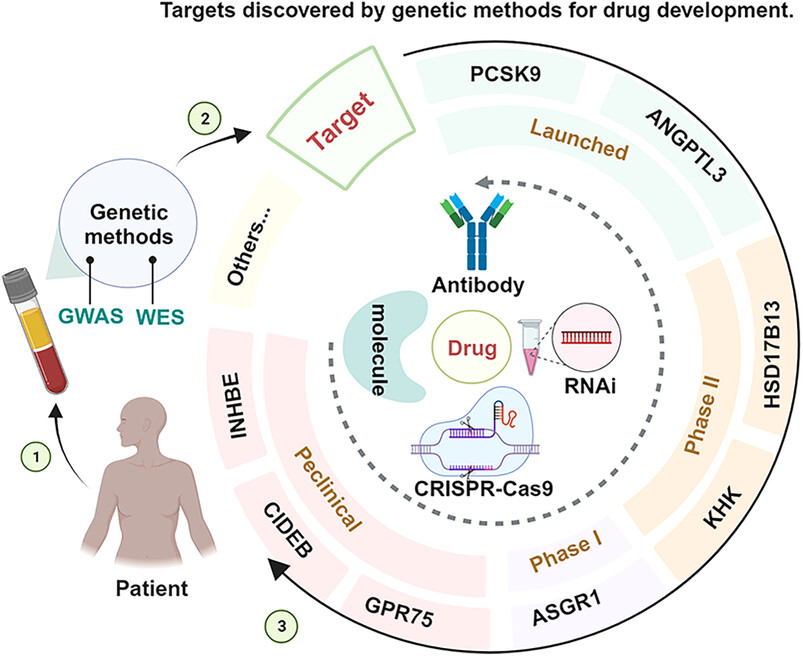
Progress in drug discovery based on targets with favorable LOF variants identified by WES, WGS, and GWAS. Targets primarily include PCSK9, ANGPTL3, HSD17B13, KHK, ASGR1, GPR75, CIDEB, and INHBE. Drug types primarily include small molecules, monoclonal antibodies, RNAi, and CRISPR gene editing therapies. The timeline is determined by the status of the target's current investigational drugs.
Epigenetic regulation in cancer
- First Published: 19 February 2024
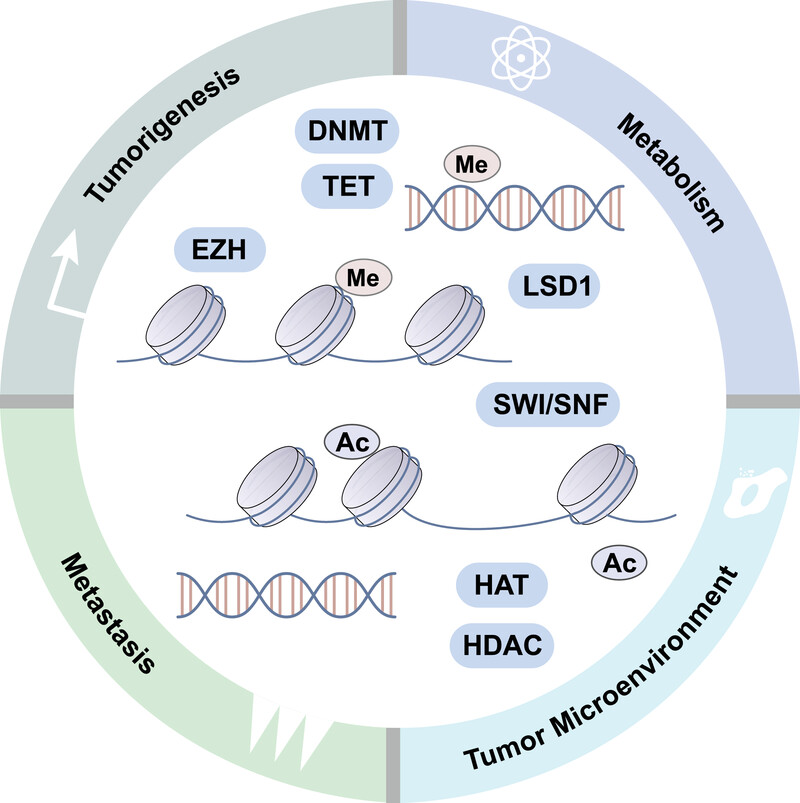
Epigenetic alterations can contribute to the acquisition of hallmark capabilities during tumor development and malignant progression. Central to these changes are aberrant DNA methylation patterns, which can silence tumor suppressor genes and activate oncogenes. Histone modifications also influence chromatin structure and gene expression. Furthermore, chromatin remodeling alters the transcriptional regulation of genes, while changes in higher-order chromatin structure may modify the spatial interactions between genes and their regulatory elements. We focus on how these mechanisms impact tumorigenesis, metastasis, metabolic reprogramming, and the tumor microenvironment.
Lung regeneration: diverse cell types and the therapeutic potential
- First Published: 23 February 2024
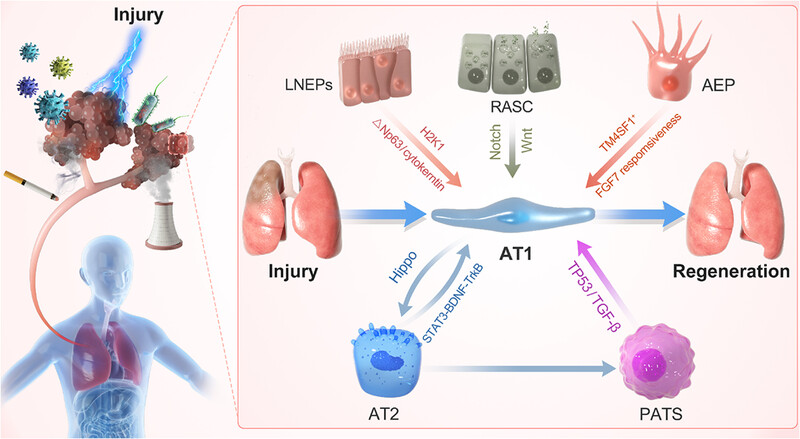
Sources of type I alveolar epithelial cells during lung regeneration. Type I alveolar epithelial cells are the specific units of lung tissue that perform the function of gas exchange. After injury, to rapidly restore lung function, in addition to type II alveolar epithelial precursor cells, other cell types of the respiratory system (such as bronchioalveolar stem cells and respiratory airway secretory cells) also rapidly transdifferentiate to supplement the number of AT1 cells. AEP, Wnt-responsive alveolar epithelial progenitor; AT2, type 2 alveolar epithelial cell; H2-K1, MHC class I marker; LNEPs, lineage negative epithelial progenitors; PATS, prealveolar type-1 transitional cell state; RASC, respiratory airway secretory cells; TM4SF1, transmembrane 4 L six family 1.
Cholesterol metabolism: physiological regulation and diseases
- First Published: 24 February 2024
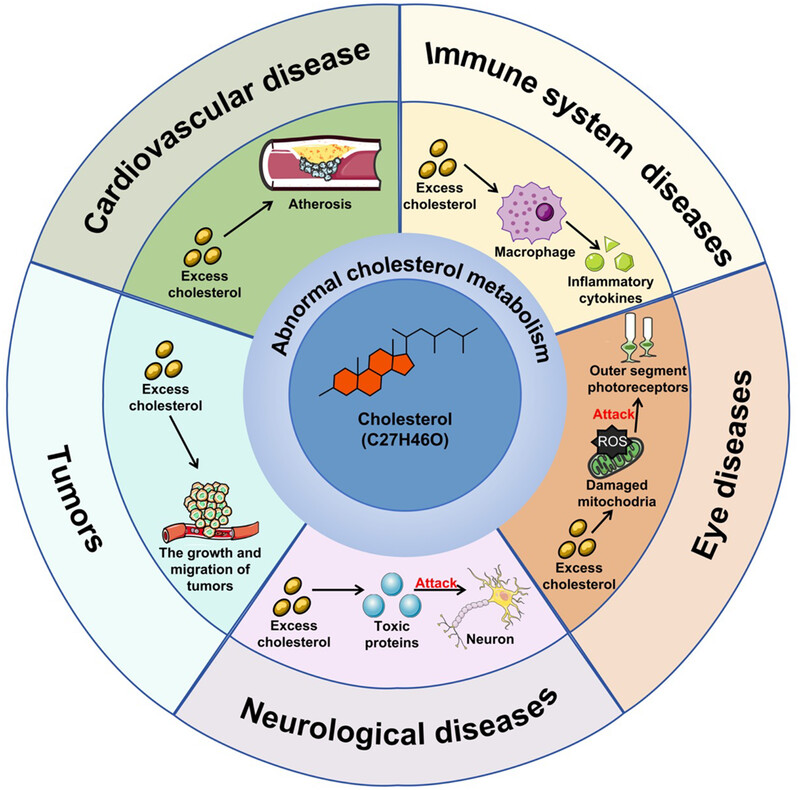
At present, increasing evidence suggests that abnormal cholesterol metabolism is closely related to various systemic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, tumors, neurological conditions immune system disorders, and eye diseases. Cholesterol overload caused by abnormal cholesterol metabolism can induce elevated oxidative stress, heightened inflammatory responses, reduced autophagy, and increased apoptosis in cells through various signaling pathways, ultimately accelerating the development of diseases. Therefore, this review will summarize the relationship between cholesterol metabolism and common diseases and aim to provide new perspectives for the pathogenesis of diseases.
Epigenetic modifications in obesity-associated diseases
- First Published: 24 February 2024
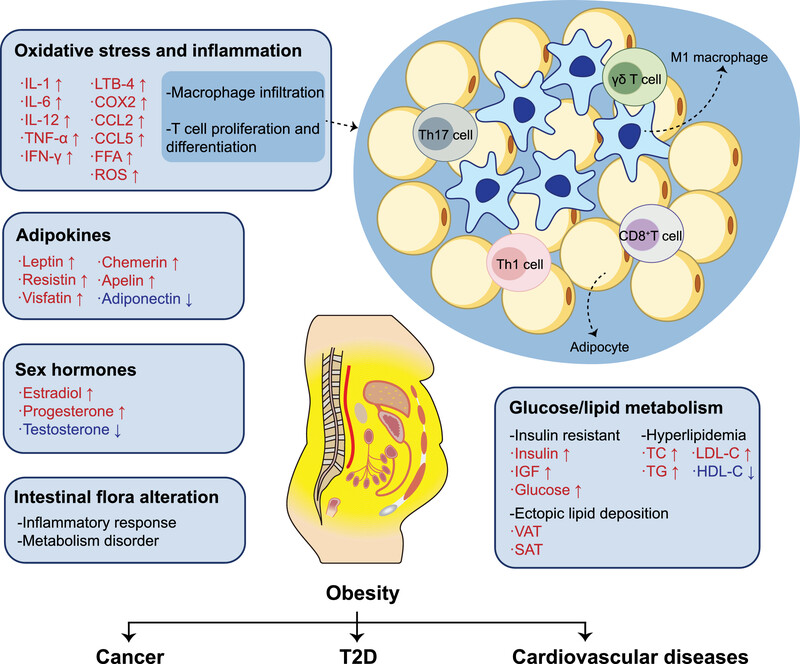
Obesity is implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancers through multiple pathways, encompassing disturbances in glucose and lipid metabolism, dysregulation of sex hormones and adipokines, as well as the progression of inflammatory processes and alterations in gut microbiota. In this review, we elucidate the epigenetic modifications involved in these pathogenic mechanisms.
ERRATUM
Correction to: Increased RTN3 phenocopies nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting the AMPK-IDH2 pathway
- First Published: 04 February 2024