Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTER
Immunotherapy against lung cancer does not need to compromise the outcomes of COVID-19
- First Published: 29 December 2023
REVIEWS
Mycobacterium tuberculosis: immune response, biomarkers, and therapeutic intervention
- First Published: 06 January 2024
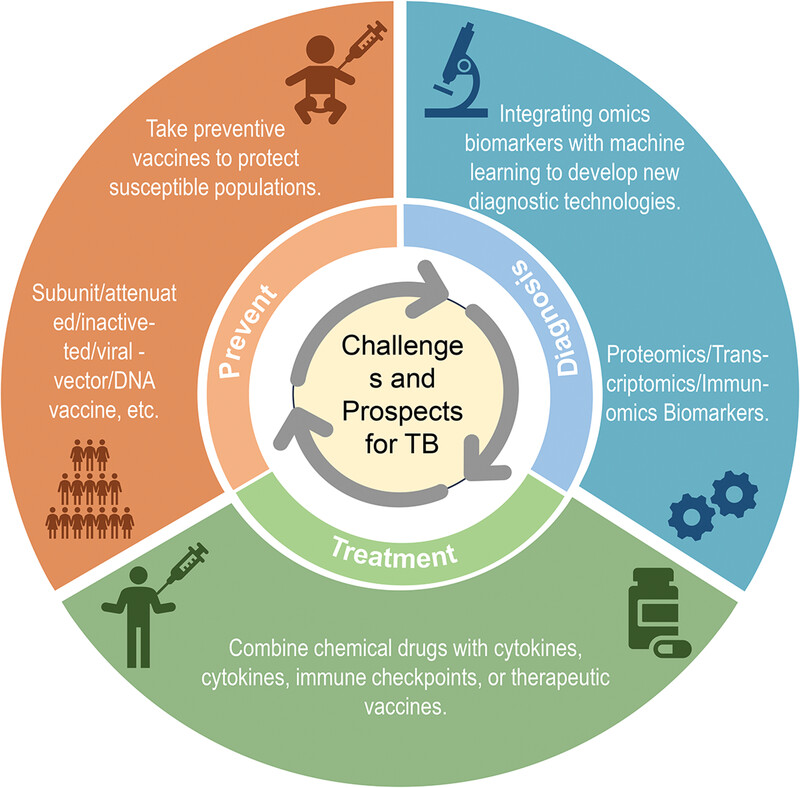
Currently, controlling the source of infection, interrupting transmission pathways, and protecting susceptible populations are key measures in tackling MTB infection. However, preventative, diagnostic, and therapeutic interventions for TB are also important in reducing the burden of the disease. First, in terms of preventing MTB infection, the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine, the only known vaccine with some protective effects, has limited efficacy and duration of protection in adults. Therefore, the development of multiple vaccines with preventative efficacy may offer new strategies for susceptible populations. Second, in the diagnosis of MTB infection, current diagnostic technologies lack high specificity and sensitivity, and cannot differentiate LTBI from ATB. Therefore, the identification of biomarkers related to immune mechanisms for diagnostic purposes may be an important goal in improving tuberculosis diagnosis efficiency. Last, in the treatment of MTB infection, challenges arise from the effectiveness of conventional chemotherapy drugs and the emergence of MDR-TB. Thus, the use of immunomodulatory cytokines, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and therapeutic vaccines in combination with anti-TB chemotherapy drugs may represent effective approaches for TB treatment.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Duchenne muscular dystrophy treatment with lentiviral vector containing mini-dystrophin gene in vivo
- First Published: 06 January 2024
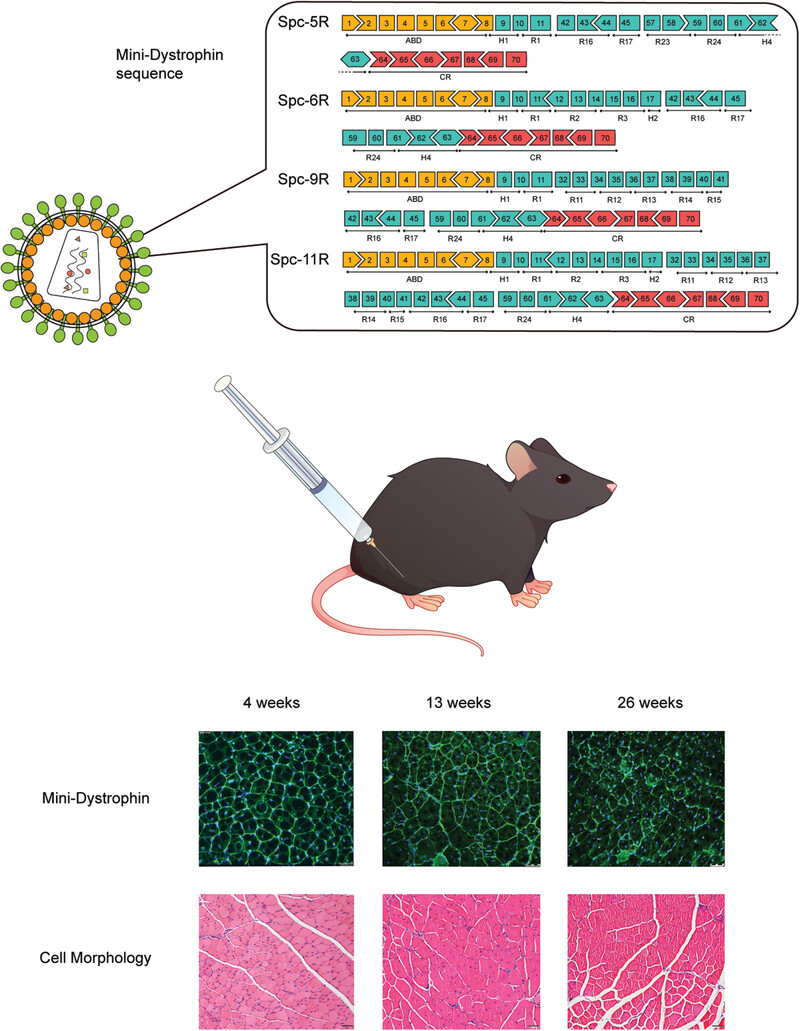
We constructed four lentiviral vectors that could restore mini-dystrophin expression, dystrophin distribution, and pull force in vivo. Also they reduced the number of mononuclear cells in the treated mice. This study preliminarily demonstrated the feasibility and safety of lentiviral vectors with mini-dystrophin for DMD gene therapy.
Inhibition of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase protects neurons from ferroptosis in ischemic stroke
- First Published: 07 January 2024
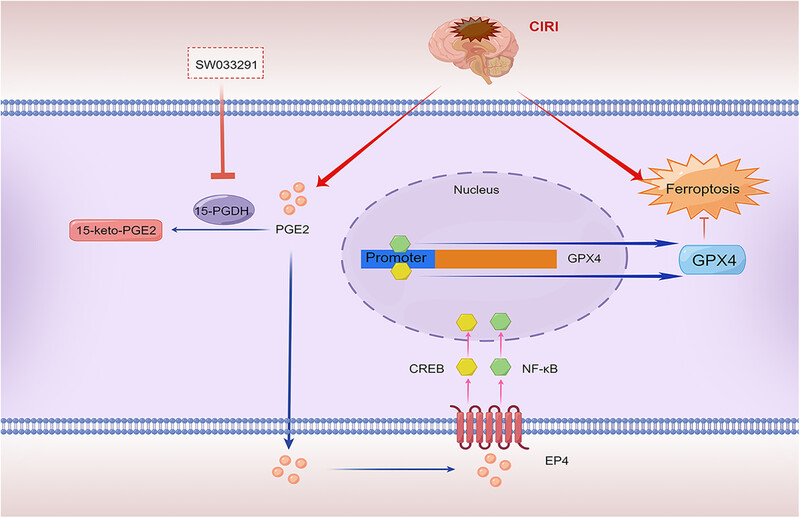
Ischemic stroke simultaneously induces the massive release of PGE2 and ferroptosis of neurons. While the PGE2 degrading enzyme 15-PGDH degrades PGE2 and subsequently reduces the level of EP4, a receptor of PGE2, which can transcriptionally reduce GPX4 level to promote ferroptosis through CREB and NF-κB, finally exacerbates ischemic stroke .
Silibinin, a potential fasting mimetic, inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by triggering extrinsic apoptosis
- First Published: 11 January 2024
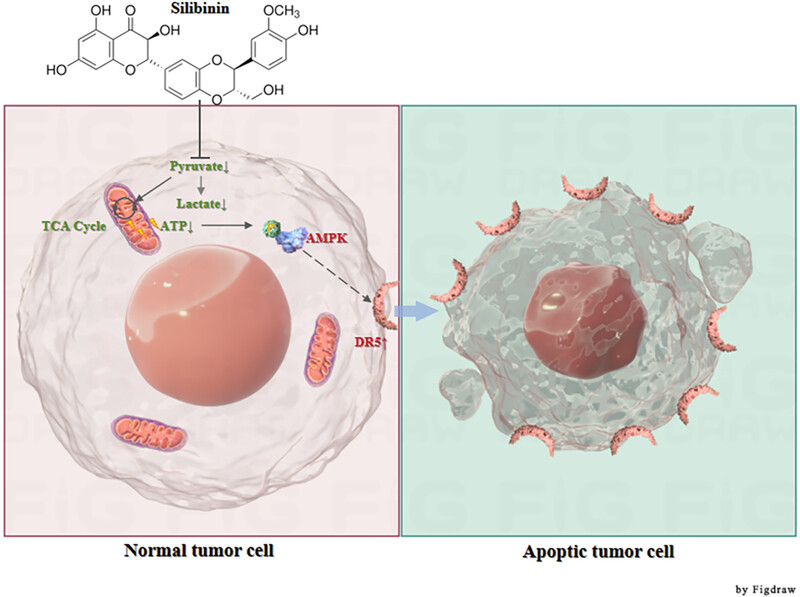
This study highlights the hepatoprotective drug silibinin triggers AMPK pathway, and inhibits intracellular ATP levels and glycolysis, which served as a fasting mimetic to induce extrinsic apoptosis and inhibit HCC growth. Silibinin achieves this effect partially by activating the AMPK–DR5 pathway. These findings suggest silibinin holds promise as a therapeutic agent to improve outcomes for HCC patients.
Unveiling the impact of tertiary lymphoid structures on immunotherapeutic responses of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- First Published: 12 January 2024
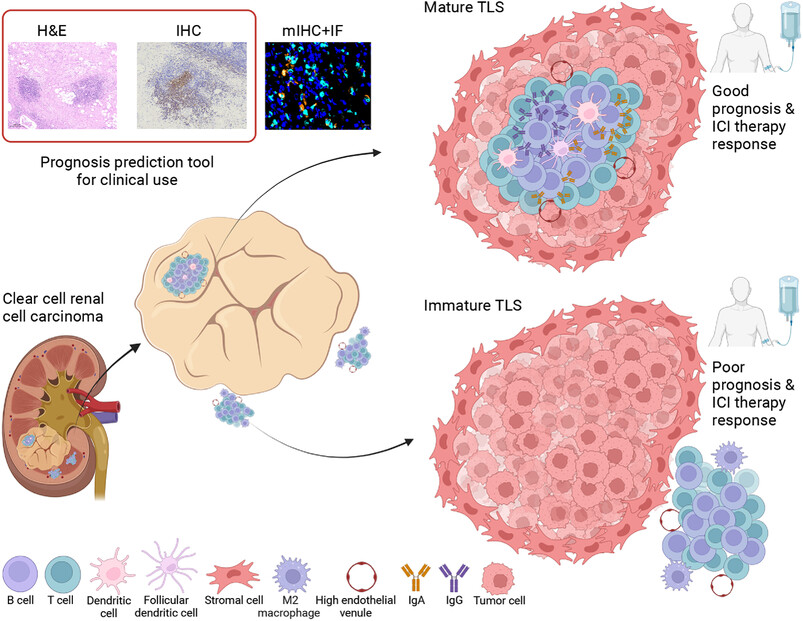
H&E, IHC, mIHC, and spatial transcriptomics were implemented to analyze spatial and maturation heterogeneity of tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS) in ccRCC. Mature TLS within tumors participate in antitumor immunity and might serve as the locale for the generation of IgA and IgG plasma cell, predicting favorable prognosis and effectiveness of immunotherapy, whereas peritumoral immature TLS show opposite effects for ccRCC patients subjected to immunotherapy.
HIGHLIGHTS
An emerging and promising anticancer strategy: colonization of engineered Staphylococcus epidermidis
- First Published: 12 January 2024
Human peri-gastruloids: a significant advancement in embryology research
- First Published: 30 December 2023

The peri-gastruloids comprise both embryonic (epiblast) and extraembryonic (hypoblast) tissues, faithfully mirroring crucial developmental events spanning from the immediate post-implantation phase to early organogenesis, encompassing the emergence of amniotic and yolk sac cavities, as well as the progression from bilaminar to trilaminar embryonic discs.
The presence of Y chromosome leads to the difference of cancer in patients with different sexes
- First Published: 12 January 2024
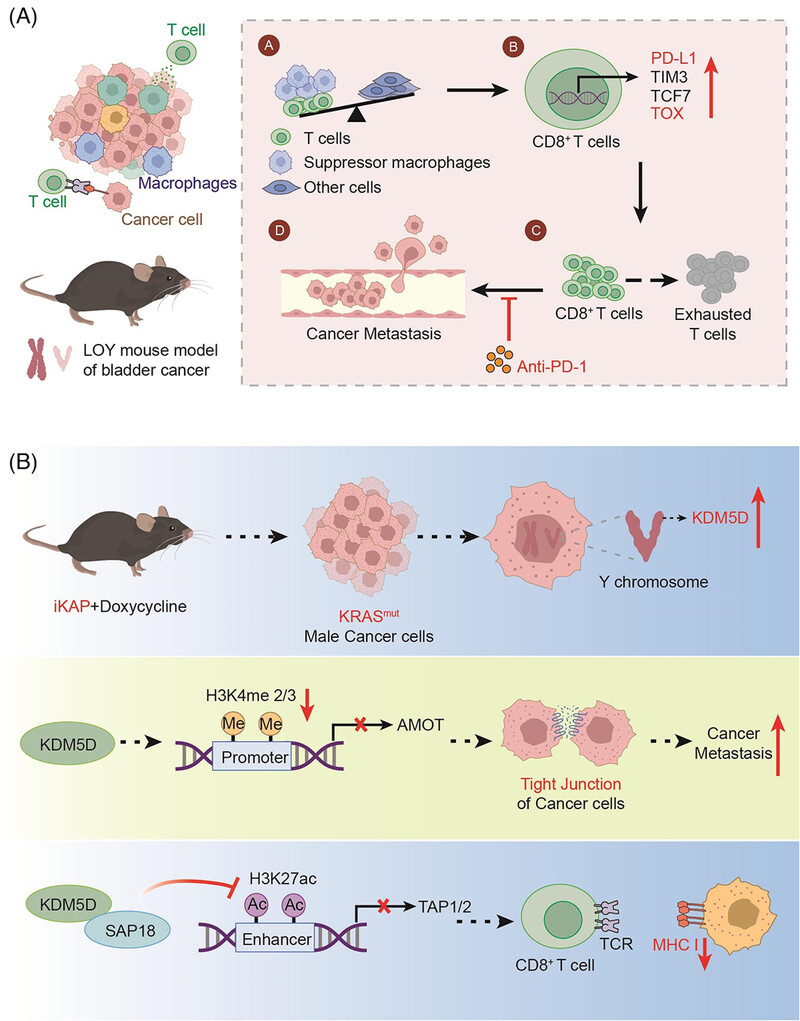
(A) In the case of LOY, the proportion of T cells and suppressor macrophages rises and T cells enhance the expression of TOX, eventually leading to the metastasis of the tumor. (B) KRASmut enhances the gene expression of KDM5D, leading to a decreased expression of the AMOT and TAP1/2 downstream of KDM5D. Thereby, the cell−cell junction and antigen presentation are affected. All elements in Figure 1 are original .















