Correction to: Increased RTN3 phenocopies nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting the AMPK-IDH2 pathway
Hao Huang and Shuai Guo contributed equally to this study.
Correction to: MedComm https://doi.org/10.1002/mco2.226, published online 14 March 2023
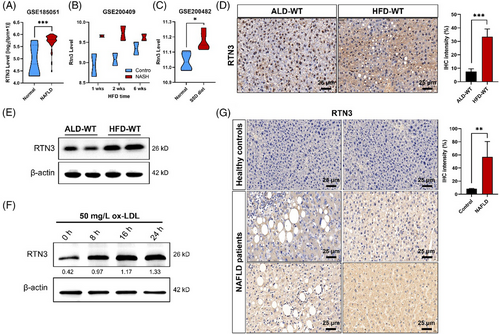
In the process of checking the raw data,1 the authors noticed an inadvertent mistake occurring in Figure 1F that needed to be corrected after the online publication of the article. During the preparation of Figure 1F, the representative image showing the expression of RTN3 was pasted and placed by mistake. The correct result should be as shown below. The authors apologize for these oversights and declare that this correction does not affect the description, interpretation, or conclusions detailed in the original manuscript.