Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURES
Front Cover: Spectrally encoded coherence tomography and reflectometry: Simultaneous en face and cross-sectional imaging at 2 gigapixels per second (J. Biophotonics 4/2018)
- First Published: 17 April 2018
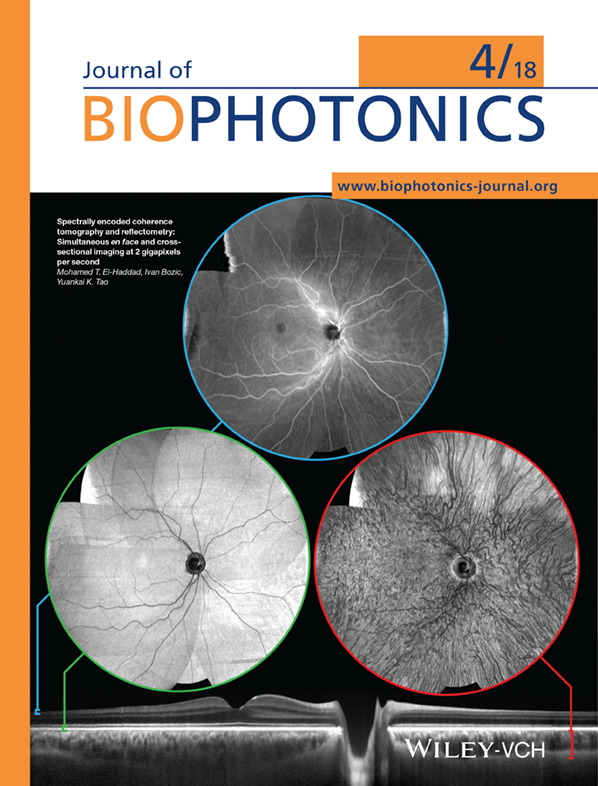
SECTR is a novel multimodal imaging platform for combined volumetric optical coherence tomography (OCT) and en face spectrally encoded reflectometry (SER). The authors demonstrate three-dimensional motion-tracking with millisecond temporal and micron spatial resolution using complementary data from OCT and SER, and preliminary algorithms and results showing real-time image aiming and multi-volumetric mosaicking for reconstruction of wide-field composites. The image shows a noninvasively imaged nine-field mosaic of in vivo human retina and depth-resolved visualization of tissue microstructures.
Further details can be found in the article by Mohamed T. El-Haddad, Ivan Bozic, and Yuankai K. Tao (e201700268)
Inside Cover: Internalization kinetics and cytoplasmic localization of functionalized diatomite nanoparticles in cancer cells by Raman imaging (J. Biophotonics 4/2018)
- First Published: 17 April 2018
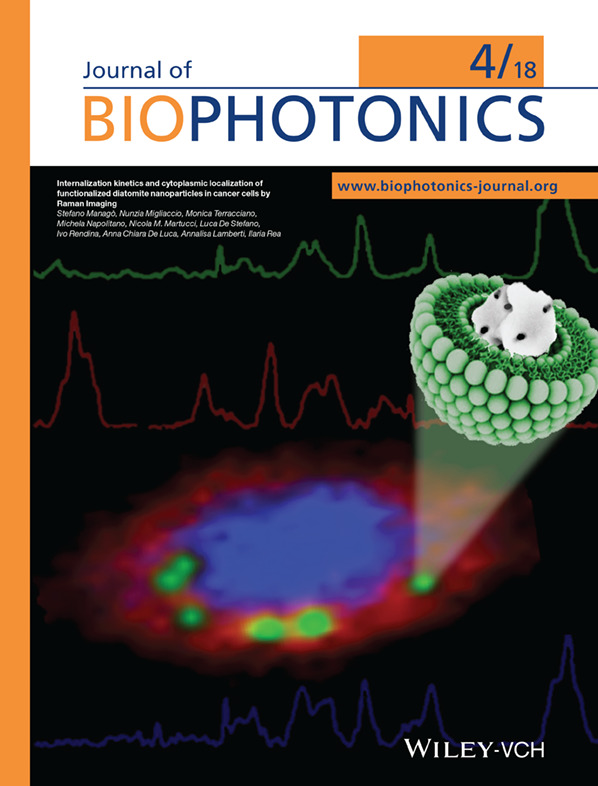
The internalization kinetics and intracellular spatial distribution of functionalized diatomite nanoparticles in human lung epidermoid carcinoma cell line have been investigated by confocal fluorescence and Raman microscopy. In this context, Raman imaging due to its non-destructive, chemically selective and label-free working principle provides evidence that the nanovectors are internalized and co-localize with lipid environments, suggesting an endocytic internalisation route. Nanoparticle uptakes and intracellular persistence are observed up to 72 hours, without damage to cell viability or morphology.
Further details can be found in the article by Stefano Managò et al. (e201700207)
Inside Cover: Polarimetric imaging of biological tissues based on the indices of polarimetric purity (J. Biophotonics 4/2018)
- First Published: 17 April 2018

The cover shows the image enhancement of biological tissues provided by the Indices of Polarimetric Purity (IPPs). By measuring the Mueller matrix of a biological sample, using an imaging polarimeter, the IPPs are calculated. They are polarimetric indicators providing further synthetization of depolarizing samples and leading to enhanced image contrast for some biological structures. Once the IPPs are calculated, a pseudo-colouring technique is applied for higher visualization.
Further details can be found in the article by Albert Van Eeckhout et al. (e201700189)
Inside Cover: Noninvasive, high-speed, near-infrared imaging of the biomolecular distribution and molecular mechanism of embryonic development in fertilized fish eggs (J. Biophotonics 4/2018)
- First Published: 17 April 2018

The biomaterial distribution and its molecular mechanism of embryonic development in Japanese medaka fish were visualized without staining using high-speed near-infrared imaging. It was a remarkable achievement to visualize the structures of eyes, lipid bilayer membranes, micelles, and water structural variations at the interface of different substances. Furthermore, insights on lipid metabolism and membrane functions were obtained from the biased distribution of lipoproteins and the presence of unsaturated fatty acids in the egg membrane.
Further details can be found in the article by Mika Ishigaki (e201700115)
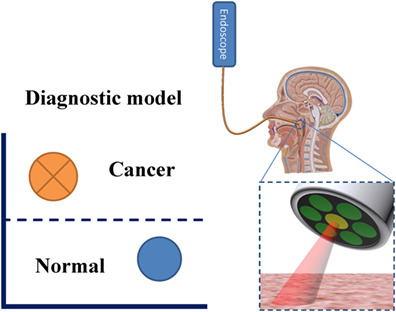
Back Cover: Autofluorescence and white light imaging-guided endoscopic Raman and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for in vivo nasopharyngeal cancer detection (J. Biophotonics 4/2018)
- First Published: 17 April 2018

An integrated 4-modality endoscopy system combining white light imaging, autofluorescence imaging, diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy technologies was developed for in vivo endoscopic nasopharyngeal cancer detection. Both high diagnostic sensitivity (98.6%) and high specificity (95.1%) for differentiating cancer from normal tissue sites were achieved using this system combined with multivariate diagnostic algorithm, demonstrating great potential for improving real-time, in vivo diagnosis of cancer at endoscopy.
Further details can be found in the article by Duo Lin et al. (e201700251)
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Biofluid spectroscopic disease diagnostics: A review on the processes and spectral impact of drying
- First Published: 26 January 2018
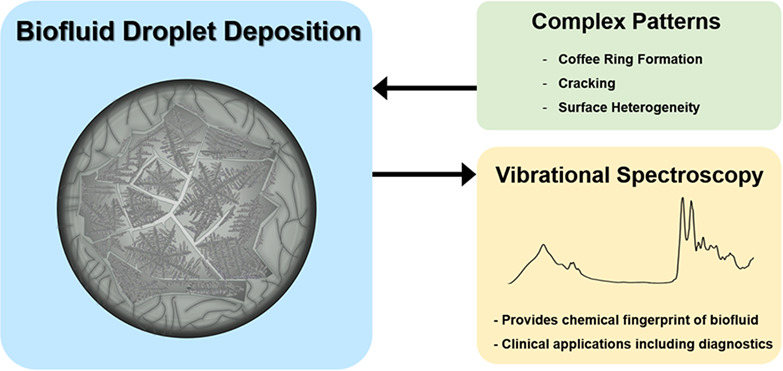
Over the past 2 decades, researchers have examined the processes involved in evaporating liquid drops, however, the phenomenon is still not completely understood. Homogeneous drop deposition is key in many applications, but complex patterns observed from dried biofluid drops currently inhibits clinical translation of various techniques, namely spectroscopic disease diagnostics. A better understanding of the fundamental processes involved in a drying droplet could enhance the development of reliable cancer diagnostics.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: Single layer molybdenum disulfide as an optical nanoprobe for 2 photon luminescence and second harmonic generation cell imaging
- First Published: 09 January 2018
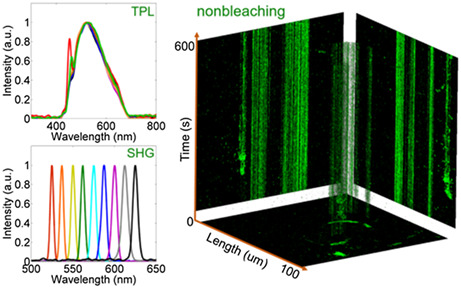
In this work, for the first time, the strong two photon luminescence (TPL) and strong second harmonic generation (SHG) from single layer small chitosan decorated MoS2 (CS-MoS2) nanosheets were demonstrated to be nonbleaching and nonblinking. As highly photostable and biocompatibility optical nanoprobes, CS-MoS2 nanosheets were carried out to TPL and SHG high-contrast imaging and cellular three-dimensional optical sectioning under low-power laser excitation. And this work will have bright prospects in future molybdenum disulfide applications.
FULL ARTICLES
Spectrally encoded coherence tomography and reflectometry: Simultaneous en face and cross-sectional imaging at 2 gigapixels per second
- First Published: 17 November 2017
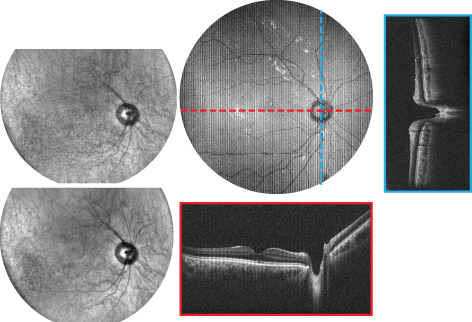
A novel system design for a multimodal imaging system is presented. The system is designed for combined wide-field topographic and tomographic imaging at multi-gigapixel throughput, with potential applications in research and clinical settings. System performance is demonstrated through in vivo human imaging of the anterior chamber and the posterior retina. A preliminary algorithm is outlined that takes advantage of the three-dimensional motion information to perform multivolumetric mosaicking of ultrawide-field retinal composites.
Internalization kinetics and cytoplasmic localization of functionalized diatomite nanoparticles in cancer cells by Raman imaging
- First Published: 16 November 2017
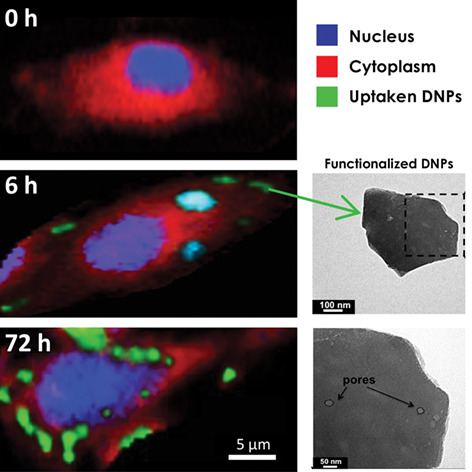
The kinetics of cellular uptake and spatial distribution of functionalized diatomite nanoparticles (siRNA-DNPs) in human lung epidermoid carcinoma cell line (H1355) are investigated by label-free Raman imaging with subcellular resolution. The co-localization in the Raman data of DNP bands with lipid environments (lipid-coated DNPs) proves their cellular uptake. A considerable DNPs uptake is observed within 6 hours and, the DNPs are still inside the cells after 72 hours, without damage of the cell viability and morphology.
Polarimetric imaging of biological tissues based on the indices of polarimetric purity
- First Published: 05 October 2017
In this work, we highlight the interest of using the indices of polarimetric purity (IPPs), a new mathematical method to synthetize and characterize depolarizing content of samples, in the framework of biological applications. The potential of the method is validated by performing different ex-vivo experiments, and we provide how the IPP-based methods significantly enhance image contrast of samples when compared with current polarimetric methods.
Noninvasive, high-speed, near-infrared imaging of the biomolecular distribution and molecular mechanism of embryonic development in fertilized fish eggs
- First Published: 22 November 2017
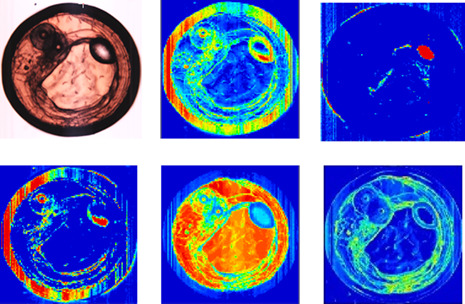
The biomaterial distribution and its molecular mechanism of embryonic development in Japanese medaka fish were visualized without staining using high-speed near-infrared (NIR) imaging. It was a remarkable achievement to visualize the structures of eyes, lipid bilayer membranes, micelles and water-structure differences at the interface of different substances constituting different structures on the egg. Furthermore, insights on the metabolic mechanisms of lipids and membrane functions were drawn from the biased distribution of lipoproteins and the presence of unsaturated fatty acids in the egg membrane.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Autofluorescence and white light imaging-guided endoscopic Raman and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for in vivo nasopharyngeal cancer detection
- First Published: 14 December 2017
FULL ARTICLES
Dual-wavelength reflectance spectroscopy of the superior vena cava: A method for placing central venous catheters at the cavoatrial junction
- First Published: 03 August 2017
Spectra of vena cava and atrial tissues were measured. Using these and literature data, wavelengths were selected for use in an optical system to differentiate between these tissues. It was hypothesized that identification of this juncture in vivo would provide for accurate peripherally inserted central catheter placement at the cavoatrial junction. The system was developed and then validated in a porcine model against fluoroscopy and electrocardiogram.
TiO2-coated fluoride nanoparticles for dental multimodal optical imaging
- First Published: 13 July 2017
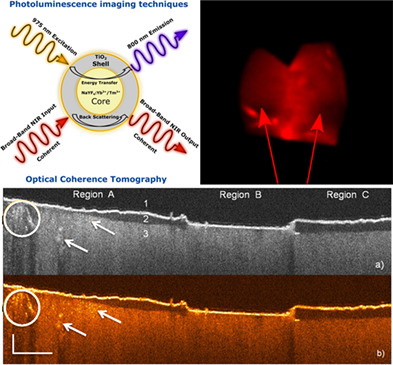
A novel core-shell nanostructure design as a contrast agent for dental adhesion evaluation by multimodal imaging was introduced. This nanostructure consists of a rare-earth-doped (NaYF4:Yb 60%,Tm 0.5%)/NaYF4 core and a highly refractive TiO2 shell. The TiO2 shell provides enhanced contrast for optical coherence tomography, while the rare-earth-doped core upconverts excitation light from 975 nm to an emission peaked at 800 nm for photoluminescence imaging.
A hybrid clustering algorithm for multiple-source resolving in bioluminescence tomography
- First Published: 12 July 2017
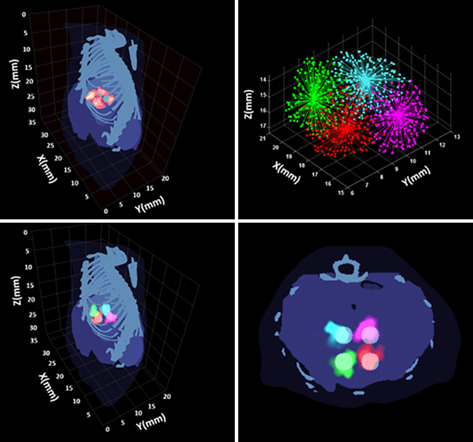
Resolving multiple targets in the reconstruction result of bioluminescence tomography is still a challenging issue. In this study, it is treated as an unsupervised pattern recognition problem, and a novel hybrid clustering algorithm combining the advantages of affinity propagation (AP) and K-means is incorporated into a general multiple-source reconstruction framework. This technique can provide stable reconstruction and accurate resolving result without providing the number of targets.
Pixel classification method in optical coherence tomography for tumor segmentation and its complementary usage with OCT microangiography
- First Published: 29 August 2017
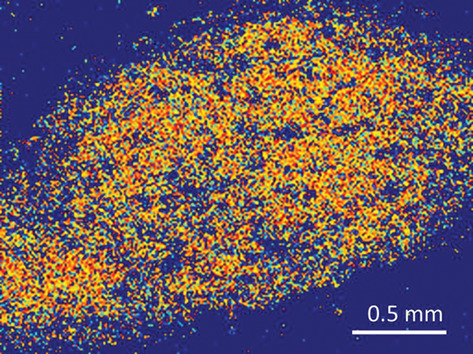
En face projection of the mouse colon carcinoma CT-26 tumor on mouse ear delineated with proposed algorithm. A novel machine-learning framework to distinguish between tumor and normal tissue in optical coherence tomography (OCT) has been developed. Prospects of complementary usage of tissue classification and OCT angiography have been demonstrated and applications to radiomics-based multimodal OCT analysis have been envisioned.
Assessment of tissue polarimetric properties using Stokes polarimetric imaging with circularly polarized illumination
- First Published: 13 November 2017
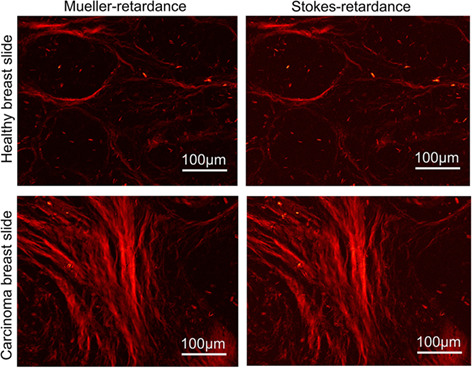
This study suggests that where short acquisition times, instant polarimetric image analysis or low optical system complexity are priorities, Stokes polarimetry could become a useful method to assess circular-depolarization and to approximate linear-retardance for many anisotropic tissues with weak diattenuation.
Endomicroscopic optical coherence tomography for cellular resolution imaging of gastrointestinal tracts
- First Published: 08 August 2017
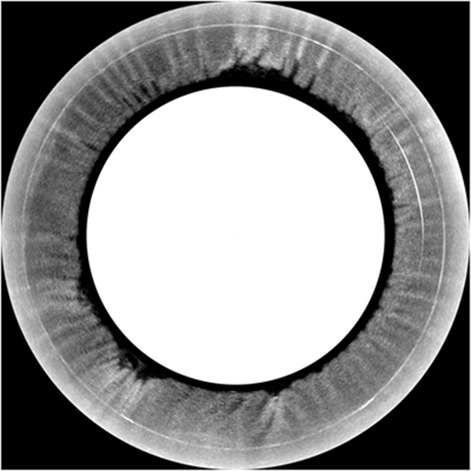
This article presents a micro-optical coherence tomography (μOCT) endomicroscopy system capable of acquiring cellular-level details of gastrointestinal (GI) tissues through circumferential scanning with 2.48-μm axial resolution and 4.8-μm transverse resolution along the depth-of-focus of ~150 μm. The imaging results demonstrate the feasibility of this fiber-optic μOCT system for visualizing cellular-level morphological features, which paves the way for the surveillance, detection and treatment of GI tract diseases.
Compressed sensing approach for wrist vein biometrics
- First Published: 13 October 2017
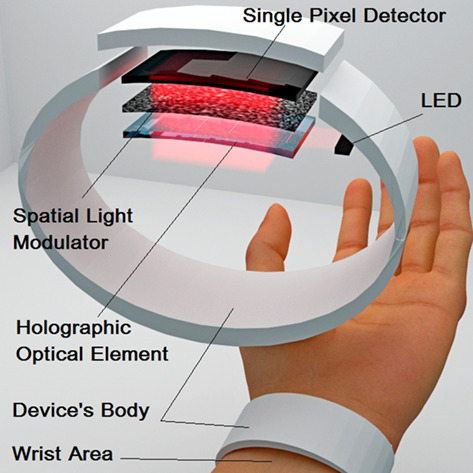
Compressed sensing (CS) approach is capable of resolving some issues which complicate development of wrist vein biometrics system, including low resolution and misalignment sensitivity. In our work we demonstrate the advantages of the CS by reconstructing wrist vein pattern with use of different types of spatial light modulation - based upon liquid crystals and diffusely scattering medium.
Insight into plant cell wall chemistry and structure by combination of multiphoton microscopy with Raman imaging
- First Published: 12 October 2017
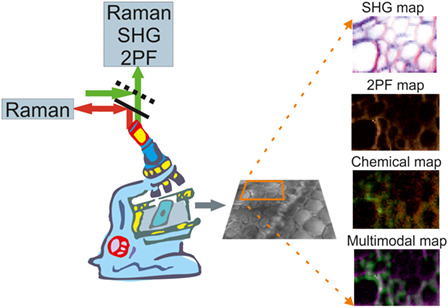
Spontaneous Raman, polarization-resolved second harmonic generation (SHG) and 2-photon excited fluorescence were used simultaneously for multimodal mapping to obtain chemical, structural and orientational information of cell walls in sorghum leaf and root cross-sections, extending current vibrational imaging and multiphoton microscopies. The distribution of chemical components and the structure of the cell walls were investigated with the help of multivariate methods, and the use of polarization-resolved SHG signals revealed the supramolecular structure of the cell walls.
A rapid bio-optical sensor for diagnosing Q fever in clinical specimens
- First Published: 10 October 2017
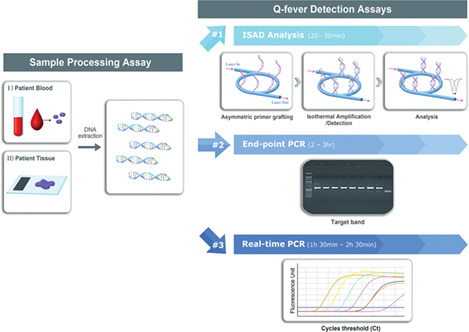
Schematic representation of the 3 detection methods including the conventional assays and the bio-optical sensor for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue and blood plasma samples. The bio-optical sensor can simultaneously amplify and detect the target DNA in a label-free and real-time manner (#1). The conventional assays (end-point and real-time PCRs) are composed of DNA amplification and detection step separately (#2 and #3)
Identification of polystyrene nanoparticle penetration across intact skin barrier as rare event at sites of focal particle aggregations
- First Published: 27 November 2017
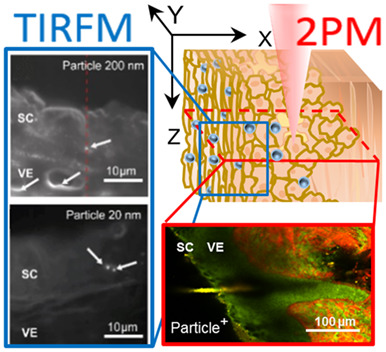
wide-field 2-photon microscopy allows for penetration studies of fluorescently tagged nanoparticles in full-thickness skin without invasive sample preparation. Twenty and 200 nm nanoparticles were preferentially found in the upper stratum corneum and in hair follicle openings. At sites of focal particle aggregations, rare events of deeper penetration were observed. Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy selectively detected single and clustered nanoparticles, thereby confirming the specificity of 2-photon microscopy.
Low-power laser irradiation decreases lipid droplet accumulation in the parotid glands of diabetic rats
- First Published: 07 November 2017
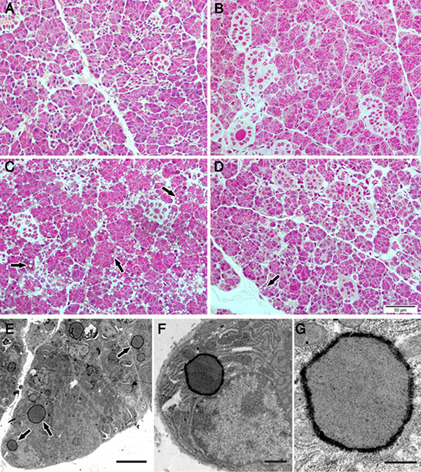
Lipid droplet accumulation observed in secretory cells of salivary glands has been related to salivary gland hypofunction and, consequently, to a reduction in patient's quality of life. In this study, it was observed a reduction in lipid droplet accumulation of parotid glands of streptozotocin-induced diabetic animals, after irradiation with a low-power laser. In addition, it was observed a decrease in intracellular calcium concentration and an increased expression of calmodulin.
Dual-wavelength-assisted thermal hemostasis for treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia
- First Published: 19 September 2017
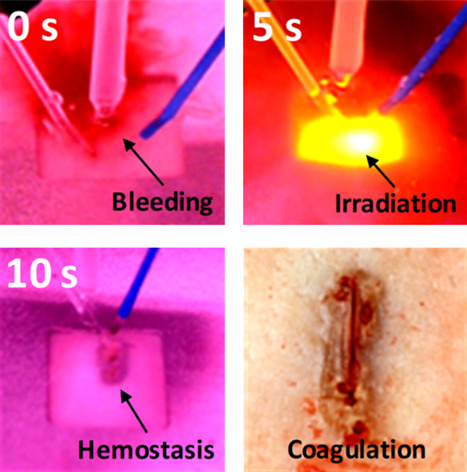
An eye-catching color image. Dual-wavelength application is evaluated to achieve rapid hemostasis for laser prostatectomy. Ex vivo kidney testing shows that the dual-wavelength creates deeper and wider coagulation areas than a single wavelength does. Perfused phantom testing verifies that the simultaneous irradiation yields the complete hemostasis with larger coagulation areas. The proposed dual-wavelength irradiation can be a feasible method to obtain effective thermal hemostasis on bleeders.
Multicontrast endomyocardial imaging by single-channel high-resolution cross-polarization optical coherence tomography
- First Published: 22 November 2017
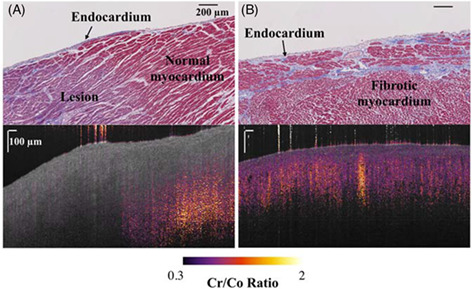
The ratio between the cross- and co-polarization channel intensities is a typical cross-polarization-optical coherence tomography (CP-OCT) contrast. Difference in CP-OCT contrasts of ablated lesion, normal myocardium and fibrotic myocardium suggests the feasibility of using CP-OCT for delineation of myocardial fibrosis in human myocardium.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Near-infrared human finger measurements based on self-calibration point: Simulation and in vivo experiments
- First Published: 13 November 2017
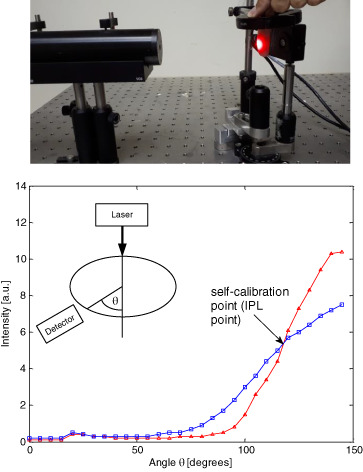
When measuring a tissue, such as earlobe, fingertip, lip and pinched tissue, one angle is indifferent to the scattering properties of the tissue. Furthermore, this point is indifferent to the tissue orientation, and it depends on the effective radius of the elliptic tissue cross section. This angle, that is, the IPL point, may act as a self-calibration point for accurate assessment of tissue oxygenation.
FULL ARTICLES
Optical emission of 223Radium: in vitro and in vivo preclinical applications
- First Published: 20 October 2017
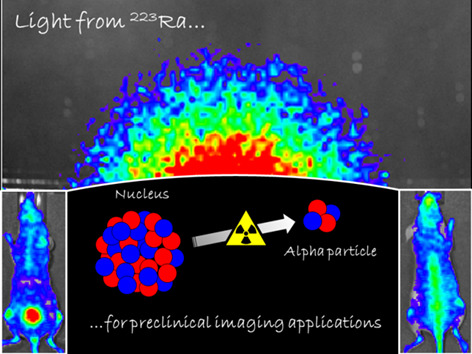
This study shows the decay of 223Radium (223Ra) as source of optical light. The emission, mostly generated by its short-lived daughter nuclides, is compatible with Cerenkov radiation (CR). The uptake of 223Ra, especially in bones, is shown here by whole body optical imaging technique in mice. This discovery will provide a new tool for in vivo tracking of 223Ra with widely available optical instruments for preclinical research.
Bayesian sparse-based reconstruction in bioluminescence tomography improves localization accuracy and reduces computational time
- First Published: 09 November 2017
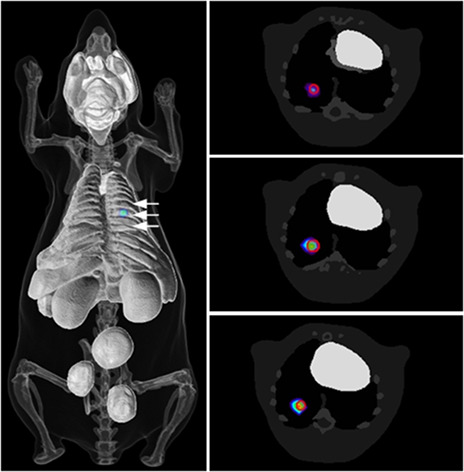
The primary limitations of an application of bioluminescence tomography in preclinical studies are the inaccurate localization of sources and high computational cost. This article develops a new reconstruction algorithm by taking advantage of the sparsity and multispectral data. The algorithm can accurately recover source distribution in heterogeneous and complex tissues, while at the same time reducing the computation time in reasonable time limit.
Detection of depth-depend changes in porcine cartilage after wear test using Raman spectroscopy
- First Published: 11 December 2017
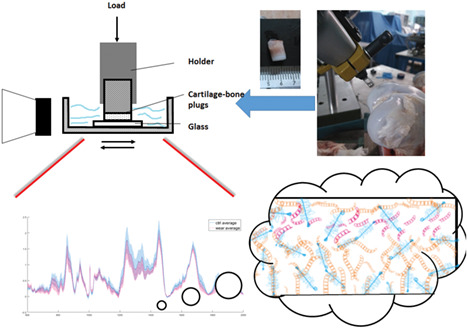
With the advantages of high-spatial resolution and easy characterization, Raman microspectroscopy was employed to characterize full-depth changes in the cartilage extracellular matrix after wear test in this study. Collagen content damage and loss were detected at depth 20% to 30% relative to the cartilage surface.
Confocal Raman spectroscopic imaging for in vitro monitoring of active ingredient penetration and distribution in reconstructed human epidermis model
- First Published: 16 November 2017
Perfusion-based fluorescence imaging method delineates diverse organs and identifies multifocal tumors using generic near-infrared molecular probes
- First Published: 05 December 2017
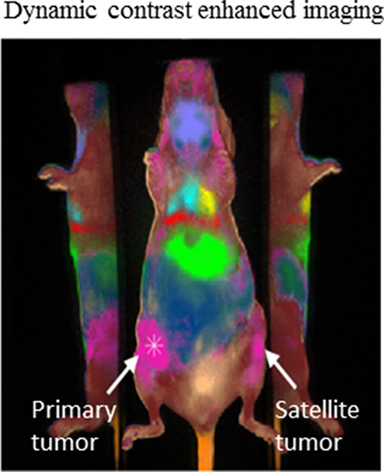
Some tumors have multiple nodules in different positions in the same organ, making their detection challenging. Here, different tissue structures and organs were identified within minutes post injection of a generic near infrared fluorescence dye using dynamic contrast enhanced imaging. Satellite tumors were detected once the primary tumor was known based on the similarity in their perfusion properties, highlighting the possibility of rapidly visualizing multiple tumors from a primary cancer.
Towards automated cancer screening: Label-free classification of fixed cell samples using wavelength modulated Raman spectroscopy
- First Published: 28 December 2017
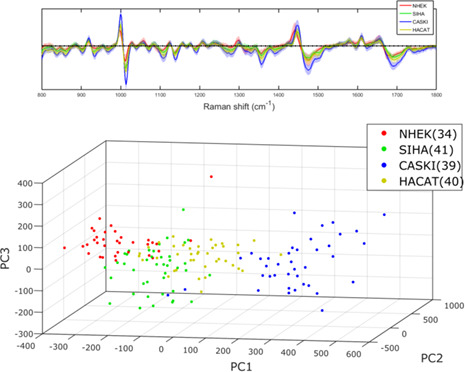
Molecular pathology shows significant promise for improving the cost, time and subjectivity of current cervical screening practice. This paper explores the use of Raman spectroscopy for the automatic categorisation of fixed cells through analysis of their intrinsic molecular vibrations. The addition of wavelength modulation to the laser provides autofluorescence rejection and a marked improvement in both the sensitivity and specificity of cell line classification.
Microscopic investigation of" topically applied nanoparticles for molecular imaging of fresh tissue surfaces
- First Published: 11 December 2017
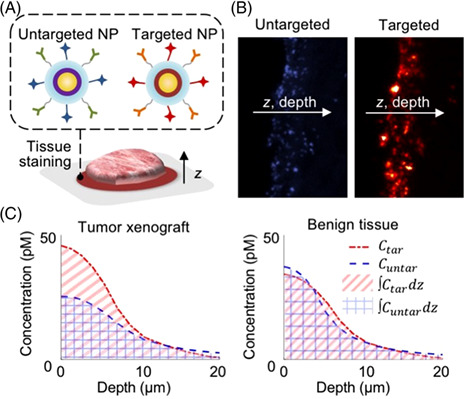
A microscopic investigation of a nanoparticle-based molecular imaging strategy is presented, which is used to inform the design of larger nanoparticles that exhibit reduced diffusion and improved binding to cell-surface biomarkers when topically applied onto the surfaces of fresh tissue specimens. Data and preliminary modeling suggest the presence of a binding-site barrier that restricts the diffusion of biomarker-targeted nanoparticles in comparison to untargeted control nanoparticles.
Portable optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy for volumetric imaging of multiscale organisms
- First Published: 24 October 2017
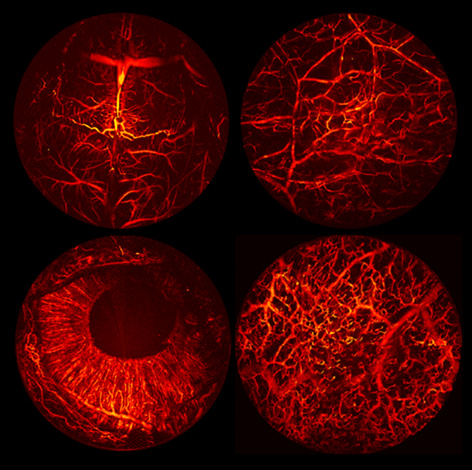
In this study, we describe a portable optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy system for 3-dimensional imaging of small-to-large rodents and humans with a high spatiotemporal resolution and a large field of view. Its easy-to-use, multiscale resolution; and portability provide significant advantages over existing optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopies in biomedical and clinical research. This technology is promising for universal biomedical studies: from fundamental biology to clinical diseases.
Optical effects on the surrounding structure during quantitative analysis using indocyanine green videoangiography: A phantom vessel study
- First Published: 29 November 2017
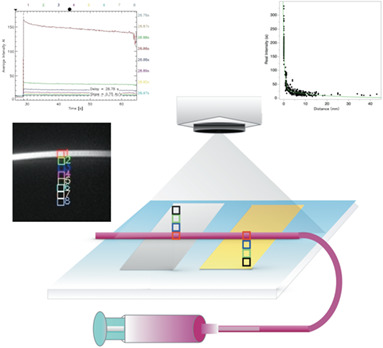
Basic research on cerebral blood flow (CBF) evaluation using intraoperative fluorescence test is reported. Recently, clinical CBF evaluation using indocyanine green (ICG) was performed, but quantitative evaluation using luminance is rare. When ICG is administered to the peripheral vein, it flows into the cerebral artery. However, ICG becomes highly concentrated in the artery. The resulting effect on luminance evaluation of the brain cortex was investigated.
Tendinopathy diagnosis and treatment monitoring using attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- First Published: 21 November 2017
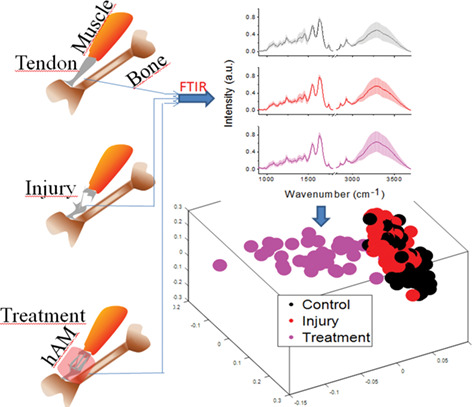
Tendinopathy is a common sports injury that afflicts athletes as well as general public, resulting in heavy economic losses. The current study proposes the use of Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) as a diagnostic and treatment monitoring tool for this ailment. We show that this technique can not only identify normal, injured and treated tendons but also the phases of healing.
Automatic quantification of microscopic heart damage in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy using optical polarization tractography
- First Published: 04 January 2018
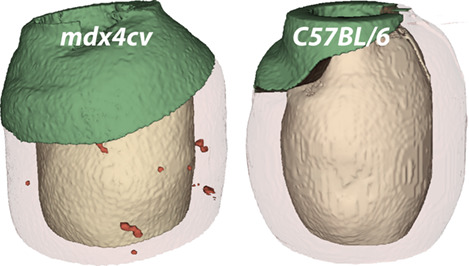
A technology was developed for fast and automatic visualization and quantification of microscopic damage in an intact mouse heart based on optical polarization tractography. This method was applied to image heart damages in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The results were compared with standard histology. This new method may be valuable in preclinical studies of murine models of heart diseases.
Ex vivo confocal microscopy features of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 11 December 2017
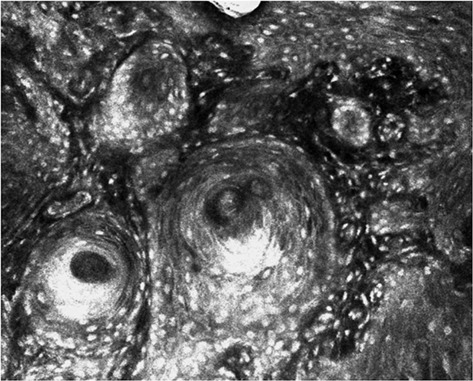
Ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy (ex vivo CLSM) enables perioperative histopathological examination. Tissue probes from invasive and in situ cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma were analyzed in order to assess tumor invasiveness and tumor differentiation. The study proves that ex vivo CLSM is suitable for evaluation of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and might help to accelerate therapeutic decisions in skin surgery in the future.
Reconnectable fiberscopes for chronic in vivo deep-brain imaging
- First Published: 17 October 2017