Internalization kinetics and cytoplasmic localization of functionalized diatomite nanoparticles in cancer cells by Raman imaging
Stefano Managò
Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorNunzia Migliaccio
Department of Molecular Medicine and Medical Biotechnology, University Federico II of Naples, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMonica Terracciano
Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMichela Napolitano
Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorNicola M. Martucci
Department of Molecular Medicine and Medical Biotechnology, University Federico II of Naples, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorLuca De Stefano
Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorIvo Rendina
Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Anna Chiara De Luca
Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Correspondence
Anna Chiara De Luca, Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Via P. Castellino 111, 80131 Naples, Italy. Email: [email protected]
Ilaria Rea, Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Via P. Castellino 111, 80131 Naples, Italy. Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAnnalisa Lamberti
Department of Molecular Medicine and Medical Biotechnology, University Federico II of Naples, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ilaria Rea
Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Correspondence
Anna Chiara De Luca, Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Via P. Castellino 111, 80131 Naples, Italy. Email: [email protected]
Ilaria Rea, Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Via P. Castellino 111, 80131 Naples, Italy. Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorStefano Managò
Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorNunzia Migliaccio
Department of Molecular Medicine and Medical Biotechnology, University Federico II of Naples, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMonica Terracciano
Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMichela Napolitano
Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorNicola M. Martucci
Department of Molecular Medicine and Medical Biotechnology, University Federico II of Naples, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorLuca De Stefano
Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorIvo Rendina
Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Anna Chiara De Luca
Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Correspondence
Anna Chiara De Luca, Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Via P. Castellino 111, 80131 Naples, Italy. Email: [email protected]
Ilaria Rea, Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Via P. Castellino 111, 80131 Naples, Italy. Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAnnalisa Lamberti
Department of Molecular Medicine and Medical Biotechnology, University Federico II of Naples, Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ilaria Rea
Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Naples, Italy
Correspondence
Anna Chiara De Luca, Institute of Protein Biochemistry, National Research Council of Italy, Via P. Castellino 111, 80131 Naples, Italy. Email: [email protected]
Ilaria Rea, Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Udr Naples, National Research Council of Italy, Via P. Castellino 111, 80131 Naples, Italy. Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
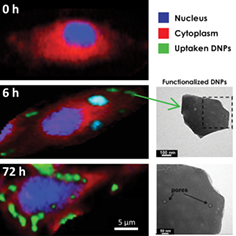
Porous biosilica nanoparticles obtained from diatomites (DNPs) have been recently demonstrated to be non-toxic nanovectors of therapeutic agents in cancer cells. In this work, the internalization kinetics and intracellular spatial distribution of functionalized DNPs incubated with human lung epidermoid carcinoma cell line (H1355) up to 72 hours are investigated by Raman imaging. The label-free Raman results are compared with confocal fluorescence microscopy and photoluminescence (PL) data. Raman bands specifically assigned to DNPs and cellular components provide evidence that the nanovectors are internalized and co-localize with lipid environments. A considerable DNPs uptake in cells is observed within 6 hours, with equilibrium being achieved after 18 hours. The obtained data show the presence of DNPs up to 72 hours, without damage to cell viability or morphology. The PL measurements performed on DNPs not penetrating the cells at different incubation times are strongly correlated with the results obtained by Raman imaging and confocal microscopy analyses.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio201700207-sup-0001-author-biographies.docxapplication/docx, 1.3 MB | Author Biographies |
| jbio201700207-sup-0002-AppendixS1.docxWord 2007 document , 6.2 MB |
Figure S1. Cell viability. The cell viability and cytotoxicity of H1355 cell exposed to functionalized DNPs at concentration of 100 μg/mL were assayed by MTT test at three different incubation times (24, 48 and 72 hours) Figure S2. Raman spectra between 2700 and 3100 cm−1 corresponding to cytosol (red), vesicle+DNPs (green) and DNPs attached to the cell membrane (light blue) Figure S3. MCR-ALS resolved spectra corresponding to nucleus (blue), cytosol (red), vesicle+DNPs (green) and DNPs attached to the cell membrane (light blue) Figure S4. PL spectrum of DNPs. Bare DNPS were deposited on a silicon substrate and irradiated by a 325-nm laser beam |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1A.Wicki, D.Witzigmann, V.Balasubramanian, J.Huwyler, J. Control. Release 2015, 200, 138.
- 2L. K.Bogart, G.Pourroy, C. J.Murphy, V.Puntes, T.Pellegrino, D.Rosenblum, D.Peer, R.Lévy, ACS Nano 2014, 8(4), 3107.
- 3H. Z.Jia, W.Wang, D. W.Zheng, X.Wang, W. Y.Yu, S. Y.Li, R. X.Zhuo, Y. F.Zhao, J.Feng, X. Z.Zhang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8(11), 6784.
- 4J. L.Markman, A.Rekechenetskiy, E.Holler, J. Y.Ljubimova, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1866, 2013, 65(13–14).
- 5J.Liu, T.Wang, D.Wang, A.Dong, Y.Li, H.Yu, Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38(1), 120.
- 6G.Szakacs, J. K.Paterson, J. A.Ludwig, C.Booth-Genthe, M. M.Gottesman, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5(3), 219.
- 7E.Miele, G. P.Spinelli, E.Miele, E.Di Fabrizio, E.Ferretti, S.Tomao, A.Gulino, Int. J. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 3637.
- 8Y.Yang, C.Yu, Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 317.
- 9I.Ruggiero, M.Terracciano, N. M.Martucci, L.De Stefano, N.Migliaccio, R.Tatè, I.Rendina, P.Arcari, A.Lamberti, I.Rea, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 329.
- 10M.Terracciano, M. A.Shahbazi, A.Correia, I.Rea, A.Lamberti, L.De Stefano, H. A.Santos, Nanoscale 2015, 7(47), 20063.
- 11I.Rea, N. M.Martucci, L. De Stefano, I.Ruggiero, M.Terracciano, P.Dardano, N.Migliaccio, P.Arcari, R.Taté, I.Rendina and A.Lamberti, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1840, 3393 (2014).
- 12N. M.Martucci, N.Migliaccio, I.Ruggiero, F.Albano, G.Calì, S.Romano, M.Terracciano, I.Rea, P.Arcari, A.Lamberti, Int. J. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 6089.
- 13I.Rea, M.Terracciano, L.De Stefano, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2017, 6, 1601125.
- 14S.Managò, C.Valente, P.Mirabelli, D.Circolo, F.Basile, D.Corda, A. C.De Luca, Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24821.
- 15B.Kann, H. L.Offerhaus, M.Windebergs, C.Otto, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 89, 71.
- 16N. B.Shah, J.Dong, J. C.Bischof, Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8(1), 176.
- 17E.Tolstik, L. A.Osminkina, C.Matthäus, M.Burkhardt, K. E.Tsurikov, U. A.Natashina, V. Y.Timoshenko, R.Heintzmann, J.Popp, V.Sivakov, Nanomedicine 1931, 2016, 12(7), 1931.
- 18S.Pirkmajer, A. V.Chibalin, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, 272.
- 19A.De Angelis, S.Managò, M. A.Ferrara, M.Napolitano, G.Coppola, A. C.De Luca, J. Spectrosc. 2017, 2017, 9876063.
- 20A. de Juan, R.Tauler, Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2006, 36, 163.
- 21M. A. B.Hedegaard, M. S.Bergholt, M. M.Stevens, J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 542.
- 22X.Zang, A. de Juan, R.Tauler, Appl. Spectrosc. 2015, 69, 993.
- 23A.Alessi, S.Agnello, G.Buscarino, F. M.Gelardi, J. Non Cryst. Solids 2013, 362, 20.
- 24Y.Wang, H.Chen, S.Dong, E.Wang, J. Raman Spectrosc. 2008, 39, 389.
- 25I.Nothinger, Sensors 2007, 7(8), 1343.
- 26I.Nothinger, I.Bisson, J. M.Polak, L. L.Hench, Vib. Spectrosc. 2004, 35, 199.
- 27M.Miljković, T.Chernenko, M. J.Romeo, B.Bird, C.Matthäus, M.Diem, Analyst 2010, 135, 2002.
- 28F. K.Lu, S.Basu, V.Igras, M. P.Hoang, M.Ji, D.Fu, G. R.Holtom, V. A.Neel, C. W.Freudiger, D. E.Fisher, X. S.Xie, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2015, 112(37), 11624.
- 29L.Kou, J.Sun, Y.Zhai, Z.He, Asian J. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2013, 8, 1.
- 30S.Lettieri, A.Setaro, L.De Stefano, M.De Stefano, P.Maddalena, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1257.
- 31K.Murugan, Y. E.Choonara, P.Kumar, D.Bijukumar, L. C. du Toit, V.Pillay, Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2191.
- 32J.Deng, C.Gao, Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 412002.
- 33D.Shao, M.Lu, Y.Zhao, F.Zhang, Y.Tan, X.Zheng, Y.Pan, X.Xiao, Z.Wang, W.Dong, J.Li, L.Chen, Acta Biomater. 2016, 49, 531.
- 34J. A.Champion, S.Mitragotri, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006, 28, 4930.
- 35S.Quignard, G.Mosser, M.Boissière, T.Coradin, Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4431.
- 36M. A.Shahbazi, B.Herranz, H. A.Santos, Biomatter 2012, 2, 1.
- 37S.Quignard, S.Masse, G.Laurent, T.Coradin, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3410.
- 38N. W.Kam, Z.Liu, H.Dai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12492.
- 39T.Wang, L.Wang, X.Li, X.Hu, Y.Han, Y.Luo, Z.Wang, Q.Li, A.Aldalbahi, L.Wang, S.Song, C.Fan, Y.Zhao, M.Wang, N.Che, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18619.
- 40S.Maher, M.Alsawat, T.Kumeria, D.Fathalla, G.Fetih, A.Santos, F.Habib, D.Losic, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25(32), 5107.
- 41I.Rea, M.Terracciano, S.Chandrasekaran, N. H.Voelcker, P.Dardano, N. M.Martucci, A.Lamberti, L.De Stefano, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 405.