Automatic quantification of microscopic heart damage in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy using optical polarization tractography
Abstract
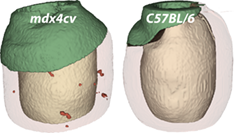
Quantification of microscopic myocardium damage in a diseased heart is important in studying disease progression and evaluating treatment outcome. However, it is challenging to use traditional histology and existing medical imaging modalities to quantify all microscopic damages in a small animal heart. Here, a method was developed for fast visualization and quantification of focal tissue damage in the mouse heart based on the fiber alignment index of the local myofiber organization obtained in optical polarization tractography (OPT). This method was tested in freshly excised hearts of the mdx4cv mouse, a commonly used mouse model for studying Duchenne cardiomyopathy. The hearts of age-matched C57BL/6 mice were also imaged as the normal controls. The results revealed a significant amount of damage in the mdx4cv hearts. Histology comparisons confirmed the damage identified by OPT. This fast and automatic method may greatly enhance preclinical studies in murine models of heart diseases.