Microscopic investigation of" topically applied nanoparticles for molecular imaging of fresh tissue surfaces
Soyoung Kang
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
Search for more papers by this authorYu “Winston” Wang
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
Search for more papers by this authorXiaochun Xu
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, Illinois
Search for more papers by this authorEric Navarro
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, Illinois
Search for more papers by this authorKenneth M. Tichauer
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, Illinois
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jonathan T. C. Liu
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
Correspondence
Jonathan T. C. Liu, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorSoyoung Kang
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
Search for more papers by this authorYu “Winston” Wang
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
Search for more papers by this authorXiaochun Xu
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, Illinois
Search for more papers by this authorEric Navarro
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, Illinois
Search for more papers by this authorKenneth M. Tichauer
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, Illinois
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jonathan T. C. Liu
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
Correspondence
Jonathan T. C. Liu, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
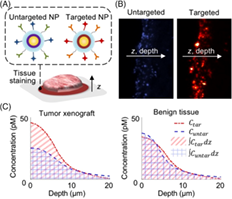
Previous studies have shown that functionalized nanoparticles (NPs) topically applied on fresh tissues are able to rapidly target cell-surface protein biomarkers of cancer. Furthermore, studies have shown that a paired-agent approach, in which an untargeted NP is co-administered with a panel of targeted NPs, controls for the nonspecific behavior of the NPs, enabling quantitative imaging of biomarker expression. However, given the complexities in nonspecific accumulation, diffusion, and chemical binding of targeted NPs in tissues, studies are needed to better understand these processes at the microscopic scale. Here, fresh tissues were stained with a paired-agent approach, frozen, and sectioned to image the depth-dependent accumulation of targeted and untargeted NPs. The ratio of targeted-to-untargeted NP concentrations—a parameter used to distinguish between tumor and benign tissues—was found to diminish with increasing NP diffusion depths due to nonspecific accumulation and poor washout. It was then hypothesized and experimentally demonstrated that larger NPs would exhibit less diffusion below tissue surfaces, enabling higher targeted-to-untargeted NP ratios. In summary, these methods and investigations have enabled the design of NP agents with improved sensitivity and contrast for rapid molecular imaging of fresh tissues.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio201700246-sup-0001-author-biographies.docxapplication/docx, 15.1 KB | Author Biographies |
| jbio201700246-sup-0002-Figures.pdfPDF document, 1,004.6 KB |
Figure S1. Wide-area nanoparticle-based molecular imaging (NMI) of fresh tissue topically stained with SERS NPs. A 10-mW 785-nm diode laser illuminates tissue with a spot size of 0.5 mm. A custom spectrometer disperses the collected signal onto a cooled deep-depletion spectroscopic CCD. Raster-scanned spectral imaging of the sample is performed by scanning the tissue sample, while keeping the fiberbundle imaging probe stationary. A direct classical least-squares (DCLS) algorithm is used to compute the relative SERS NP weights and the weights of all broadband background components. The ratio of the weights of targeted vs untargeted SERS NPs is used to obtain a ratiometric image of the tissue specimen. Additional details about the imaging system have been described previously [1–6] Figure S2. TEM images of (A) unconjugated NPs and (B) antibody-conjugated NPs with uniform size distribution around 120-nm in diameter Figure S3. We hypothesize that the design of conjugated NPs with larger sizes could reduce the diffusion of the NPs and therefore reduce the nonspecific accumulation of the NPs in tissue. This could in turn allow for molecular imaging of fresh tissue surfaces with higher NP ratios (targeted vs untargeted) compared with our original 120-nm NPs Figure S4. In order to ensure that the relative brightness of the fluorescence from each of the NP sizes was well matched, the NP concentrations used in the conjugation reactions were tuned such that total surface area of the NPs was identical to that of the 120-nm NPs used in previous experiments. Here, we used a spectrofluorometer to show that the different NP sizes exhibit comparable levels of fluorescence for aliquots with identical total NP surface areas. Background subtraction was applied using the fluorescence intensity of stock NPs that have not been reacted with fluorophores Figure S5. Flow cytometry validation of conjugated NPs of various sizes with cell lines of varying biomarker (EGFR) expression levels. Flow cytometry experiments were performed to verify that the binding of the EGFR-targeted NPs to EGFR-positive cell lines was comparable in magnitude for various NP sizes when staining cells with NP concentrations that were matched in terms of total NP surface areas. EGFR-NPs and isotype-NPs of various sizes were individually used to stain 3T3 (top row, EGFR−), U251 (middle row, EGFR+), or A431 (bottom row, EGFR++). The columns are separated by NP size (120, 200, and 300-nm diameter). The fourth column shows the mean fluorescence intensity between the EGFRtargeted NP vs untargeted NP to compare binding levels of the various NP sizes Figure S6. A mathematical model of the diffusion of NPs topically applied in fresh tissue. (A) An illustration of our simplified model of NP diffusion and binding. The NP solution is an infinite reservoir that establishes a constant NP concentration at the tissue surface. NPs are allowed to diffuse into the tissue, where they bind to cell-surface biomarkers or remain unbound. (B) A representation of our mathematical model showing targeted and untargeted NPs diffusing into the tissue with diffusion coefficient D, where the targeted NPs bind to and unbind from cell-surface biomarkers with rate constants ka and kd, respectively. The compartments in the reaction network are defined as unbound targeted NPs, Ctu; bound targeted NPs, Ctb; and untargeted NPs, Cuu. The total concentration of targeted NPs is Ctar = Ctu + Ctb, while the concentration of untargeted NPs is Cuntar = Cuu. (C) Our kinetic model was run using the implicit and unconditionally stable Crank-Nicolson method and fit to the concentration curves obtained experimentally with the micro-NMI method (Figure 4) using a nonlinear least-squares algorithm (lsqnonlin in MATLAB). We note that this simple model of diffusion and binding of topically stained NPs on fresh tissue, while not a perfect fit to our experimental data, does predict a binding-site barrier for tumor tissue. Improved fitting of the model with our experimental data may potentially be achieved by taking into account the nonspecific binding of NPs to cell-surface receptors with a nonspecific binding compartment for both targeted and untargeted NPs, as previously described in the literature [7] APPENDIX S1. REFERENCES |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1Y. E.Choi, J. W.Kwak, J. W.Park, Sensors 2010, 10(1), 428.
- 2A. O.Saarela, T. K.Paloneva, T. J.Rissanen, H. O.Kiviniemi, J. Surg. Oncol. 1997, 66(4), 248.
10.1002/(SICI)1096-9098(199712)66:4<248::AID-JSO5>3.0.CO;2-B CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 3E. K.Valdes, S. K.Boolbol, J. M.Cohen, S. M.Feldman, Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14(3), 1045.
- 4L.Xing, N. W.Todd, L.Yu, H.Fang, F.Jiang, Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23(8), 1157.
- 5H.Jaafar, Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 13(1), 4.
- 6J. M.Jorns, D.Visscher, M.Sabel, T.Breslin, P.Healy, S.Daignaut, J. L.Myers, A.Wu, Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 138(5), 657.
- 7C.Rua, P.Lebas, P.Michenet, L.Ouldamer, Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2012, 93(11), 871.
- 8G. M. van Dam, G.Themelis, L. M. A.Crane, N. J.Harlaar, R. G.Pleijhuis, W.Kelder, A.Sarantopoulos, J. S. de Jong, H. J. G.Arts, A. G. J.vander Zee, J.Bart, P. S.Low, V.Ntziachristos, Nat. Med. 2011, 17(10), 1315.
- 9A. L.Vahrmeijer, M.Hutteman, J. R.vander Vorst, C. J. H.vande Velde, J. V.Frangioni, Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10(9), 507.
- 10D. J.Yang, E. E.Kim, T.Inoue, Ann. Nucl. Med. 2006, 20(1), 1.
- 11L. R.Yates, M.Gerstung, S.Knappskog, C.Desmedt, G.Gundem, P.Van Loo, T.Aas, L. B.Alexandrov, D.Larsimont, H.Davies, Y.Li, Y. S.Ju, M.Ramakrishna, H. K.Haugland, P. K.Lilleng, S.Nik-Zainal, S.McLaren, A.Butler, S.Martin, D.Glodzik, A.Menzies, K.Raine, J.Hinton, D.Jones, L. J.Mudie, B.Jiang, D.Vincent, A.Greene-Colozzi, P. Y.Adnet, A.Fatima, M.Maetens, M.Ignatiadis, M. R.Stratton, C.Sotiriou, A. L.Richardson, P. E.Lènning, D. C.Wedge, P. J.Campbell, Nat. Med. 2015, 21(7), 751.
- 12D.Zardavas, A.Irrthum, C.Swanton, M.Piccart, Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12(7), 381.
- 13Y.Barenholz, J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117.
- 14S.Biffi, R.Voltan, E.Rampazzo, L.Prodi, G.Zauli, P.Secchiero, Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1837.
- 15R.Gray, B.Pockaj, E.Garvey, S.Blair, Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 18.
- 16A.Shadfan, H.Darwiche, J.Blanco, A.Gillenwater, R.Richards-Kortum, T.Tkaczyk, Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 1525.
- 17M.Ferrari, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 161.
- 18M.Han, X.Gao, J. Z.Su, S.Nie, Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19(7), 631.
- 19J. V.Jokerst, S. S.Gambhir, Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44(10), 1050.
- 20S.Ramírez-García, M.Baeza, M.O’Toole, Y.Wu, J.Lalor, G.Wallace, D.Diamond, Talanta 2008, 77, 436.
- 21X.Zhang, Q.Guo, D.Cui, Sensors 2009, 9, 1033.
- 22L. R.Lorenzo, L.Fabris, R. A.Alvarez-Puebla, Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 745, 10.
- 23X.Qian, X. H.Peng, D. O.Ansari, Q. Y.Goen, G. Z.Chen, D. M.Shin, L.Yang, A. N.Young, M. D.Wang, S.Nie, Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 83.
- 24Y.Wang, S.Kang, J. D.Doerksen, A. K.Glaser, J. T. C.Liu, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2016, 22(4), 6802911 .
- 25Y. W.Wang, A.Khan, M.Som, D.Wang, Y.Chen, S. Y.Leigh, D.Meza, P. Z.McVeigh, B. C.Wilson, J. T. C.Liu, Dent. Tech. 2014, 2(2), 118.
10.1142/S2339547814500125 Google Scholar
- 26Y. W.Wang, A.Khan, S. Y.Leigh, D.Wang, Y.Chen, D.Meza, J. T. C.Liu, Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5(9), 2883.
- 27Y.Wang, B.Yan, L.Chen, Chem. Rev. 2013, 113(3), 1391.
- 28C. L.Zavaleta, E.Garai, J. T. C.Liu, S.Sensarn, M. J.Mandella, D.Van de Sompel, S.Friedland, J.Van Dam, C. H.Contag, S. S.Gambhir, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110(25), E2288.
- 29B.Sharma, R. R.Frontiera, A. I.Henry, E.Ringe, R. P. V.Duyne, Mater. Today 2012, 15(1–2), 16.
- 30J.Qi, J.Li, W. C.Shih, Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4(11), 1289.
- 31M.Li, J.Lu, J.Qi, F.Zhao, J.Zeng, J. C. C.Yu, W. C.Shih, J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 19(5), 050501.
- 32M.Natan, Surface Enhanced Spectroscopy-Active Composite Nanoparticles, XXX, XXX 2003.
- 33H. N.Xie, R.Stevenson, N.Stone, A.Hernandez-santana, K.Faulds, D.Graham, Angew. Chem. 2012, 51, 8509.
- 34S. L.Kleinman, B.Sharma, M. G.Blaber, A.i.Henry, N.Valley, R.Gri, M. J.Natan, G. C.Schatz, R. P. V.Duyne, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 301.
- 35T. P.Tyler, A. I.Henry, R. P. V.Duyne, M. C.Hersam, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 218.
- 36L.Fabris, ChemNanoMat 2016, 2, 249.
- 37J. V.Jokerst, T.Lobovkina, R. N.Zare, S. S.Gambhir, Nanomedicine 2011, 6(4), 715.
- 38S.Kang, Y.Wang, N. P.Reder, J. T. C.Liu, PLoS One 2016, 11(9), 1.
- 39Y.Wang, S.Kang, A.Khan, G.Ruttner, S. Y.Leigh, M.Murray, S.Abeytunge, G.Peterson, M.Rajadhyaksha, S.Dintzis, S.Javid, J. T.Liu, Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21242.
- 40Y. W.Wang, J. D.Doerksen, S.Kang, D.Walsh, Q.Yang, D.Hong, J. T. C.Liu, Small 2016, 12(40), 5612.
- 41Y. W.Wang, S.Kang, A.Khan, P. Q.Bao, J. T. C.Liu, Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6(10), 3714.
- 42M. F.Kircher, J. V.Jokerst, C. L.Zavaleta, P. J.Kempen, E.Mittra, K.Pitter, R.Huang, C.Campos, R.Sinclair, C. W.Brennan, I. K.Mellinghoff, S. S.Gambhir, P.Program, Nat. Med. 2012, 18(5), 829.
- 43J. V.Jokerst, Z.Miao, C. L.Zavaleta, Z.Cheng, S. S.Gambhir, Small 2012, 7(5), 625.
- 44J.Li, P.Zrazhevskiy, X.Gao, Small 2016, 12, 1035.
- 45S.Harmsen, R.Huang, M. A.Wall, H.Karabeber, J. M.Samii, M.Spaliviero, J. R.White, S.Monette, R. O.Connor, K. L.Pitter, S. A.Sastra, M.Saborowski, E. C.Holland, S.Singer, K. P.Olive, S. W.Lowe, R. G.Blasberg, M. F.Kircher, Cancer Imaging 2015, 7(271), 1.
- 46K.Fujimori, D. G.Covell, J. E.Fletcher, J. N.Weinstein, J. Nucl. Med. 1990, 31(7), 1191.
- 47T. T.Goodman, J.Chen, K.Matveev, S. H.Pun, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 101(2), 388.
- 48T. T.Goodman, P. L.Olive, S. H.Pun, Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2(2), 265.
- 49L.Miao, J. M.Newby, C. M.Lin, L.Zhang, F.Xu, W. Y.Kim, M. G.Forest, S. K.Lai, M. I.Milowsky, S. E.Wobker, L.Huang, ACS Nano 2016, 10(10), 9243.
- 50G. M.Thurber, R.Weissleder, PLoS One 2011, 6(9), 1.
- 51A. L.Kholodenko, J. F.Doughlas, Phys. Rev. E 1995, 51(2), 1081.
- 52R.Siegel, K.Miller, A.Jemal, CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65(1), 29.
10.3322/caac.21254 Google Scholar
- 53H.Lee, H.Fonge, B.Hoang, R. M.Reilly, C.Allen, Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7(4), 1195.
- 54S. D.Perrault, C.Walkey, T.Jennings, H. C.Fischer, W. C. W.Chan, Nano Lett. 2009, 9(5), 1909.
- 55C.Wong, T.Stylianopoulos, J.Cui, J.Martin, V. P.Chauhan, W.Jiang, Z.Popović, R. K.Jain, M. G.Bawendi, D.Fukumura, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2011, 108(6), 2426.
- 56J.Cheng, B. A.Teply, I.Sherifi, J.Sung, G.Luther, F. X.Gu, E.Levy-nissenbaum, A. F.Radovic-Moreno, R.Langer, O. C.Farokhzad, Biomaterials 2007, 28, 869.
- 57Y. W.Wang, N. P.Reder, S.Kang, A. K.Glaser, Q.Yang, M. A.Wall, S. H.Javid, S. M.Dintzis, J. T.Liu, Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4506.