Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 10/2020
- Page: 1903
- First Published: 21 September 2020

Oil Refinery, Petrochemical Plant Equipment. Copyright: Zora Zhuang@Getty Images
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 10/2020
- Page: 1904
- First Published: 21 September 2020
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 10/2020
- Page: 1905
- First Published: 21 September 2020
Highlights
Reviews
Microbial Fuel Cell Membrane Bioreactor in Wastewater Treatment, Electricity Generation and Fouling Mitigation
- Pages: 1908-1921
- First Published: 25 June 2020
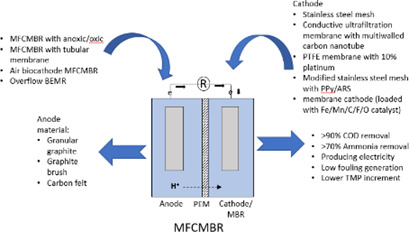
Microbial fuel cells (MFC) and membrane bioreactors (MBR) can be integrated in many ways. MFC-MBR systems usually consist of anode and cathode materials that can produce electricity, treat wastewater, and mitigate fouling. MFC-MBR with higher-conductivity cathodes will produce higher electricity at lower energy input and can remove up to 90 % of the chemical oxygen demand and ammonia in wastewater.
Research Articles
Technical and Economic Analysis of Conventional and Supercritical Transesterification for Biofuel Production
- Pages: 1922-1929
- First Published: 01 July 2020

Two processes of biofuel production from castor oil were investigated. One process was done in the presence of KOH as catalyst and the other one was conducted with supercritical methanol. Both processes were simulated in Aspen HYSYS v10. Final products were biofuel and biodiesel. For validation of the simulation results, the products in the simulation were compared to those of laboratory research.
Simulation Analysis of the Heat Transfer Performance of an N-type Microchannel Heat Exchanger
- Pages: 1930-1938
- First Published: 01 July 2020
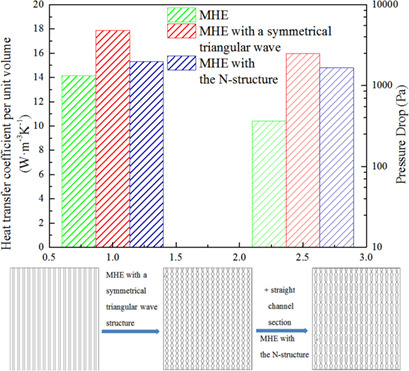
A microchannel heat exchanger with a triangular wave and symmetrical triangular wave structure is introduced. Additionally, an innovative N-type microchannel heat exchanger is developed to balance the heat transfer performance and pressure drop. The degree of disturbance of the fluid is highest in this symmetrical N-structure microchannel, and an excellent heat transfer effect is achieved.
Positron Emission Particle Tracking for Liquid-Solid Mixing in Stirred Tanks
- Pages: 1939-1950
- First Published: 06 July 2020
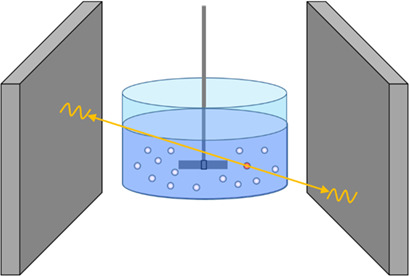
Using data acquired via positron emission particle tracking, detailed methodologies were provided through which the complete suspension speed and homogeneity of solids distribution may be accurately and autonomously measured, even for the case of optically opaque systems, without human interpretation. Full three-dimensional data acquired throughout the interior of a given system are considered.
Hydrodynamic Investigation on Deep Desulfurization of Liquid Fuel at the Microscale
- Pages: 1951-1958
- First Published: 08 July 2020
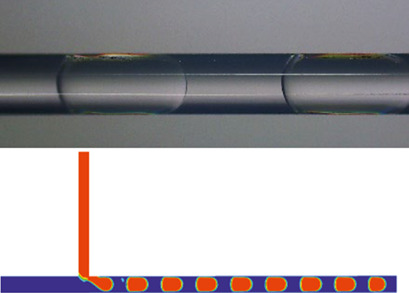
The efficiency of a liquid-liquid microchannel device is significantly influenced by the flow patterns. The occurrence of different flow regimes in microchannels depends strongly on various parameters, which were investigated experimentally and numerically. Reaching a good agreement between both procedures can solve many issues and enhance the development of the microprocess considerably.
Impact of Contact Scaling and Drag Calculation on the Accuracy of Coarse-Grained Discrete Element Method
- Pages: 1959-1970
- First Published: 08 July 2020
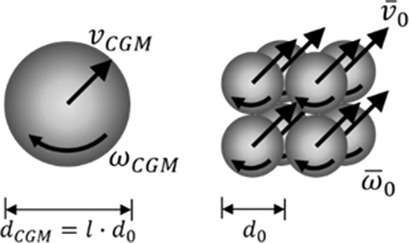
The coarse-grained discrete element method is an efficient and promising numerical method for the simulation of industrial-scale fluidized particle systems. The accuracy of this approach is built on appropriate scaling rules for contact and fluid-particle interaction forces. The impact of different scaling rules and drag models on the accuracy of the model is investigated.
Isothermal by Design: Comparison with an Established Isothermal Nucleation Kinetics Analysis Method
- Pages: 1971-1980
- First Published: 09 July 2020
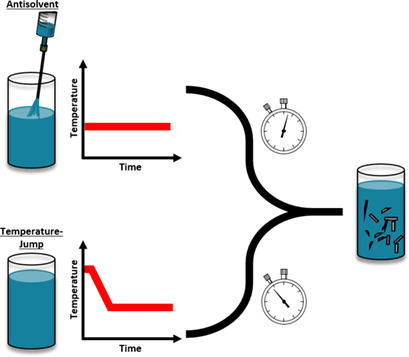
Comparative analysis of the crystallizability of para-aminobenzoic acid using established and antisolvent isothermal methods demonstrates the broad equivalence of the nucleation kinetic parameters determined by both approaches and highlights the importance of solvent selection in optimizing the crystallization behavior.
Biogas Plant Upgrade to CO2-Free Technology: A Techno-Economic Case Study
- Pages: 1981-1993
- First Published: 09 July 2020
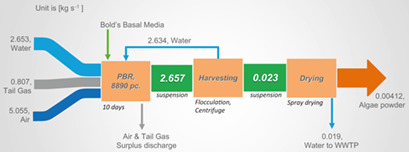
A biogas plant with in-built algae production is introduced, comparing different nutrition techniques for algae cultivation. For each model, a process flow diagram was constructed and mass and energy balances were evaluated. Based on this, economic analyses including sensitivity analyses were made, showing the feasibility of the projects.
3D CFD Simulation of Reaction Cells, Cooling Cells, and Manifolds of a Flatbed Reactor for CO2 Methanation
- Pages: 1994-2006
- First Published: 14 July 2020
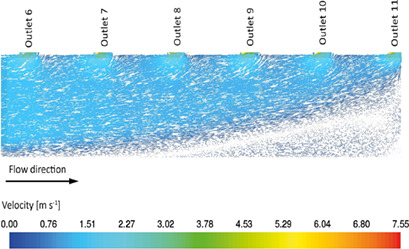
The recent progresses in the development of a novel flatbed reactor for the CO2 methanation are presented. The cells and manifolds of the reactor were designed with predetermined goals. The development was carried out by design strategies, in which the key geometric parameters of the reactor parts were systematically varied. The simulations were performed numerically.
Conversion of Methane Facilitated by Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells
- Pages: 2007-2014
- First Published: 14 July 2020
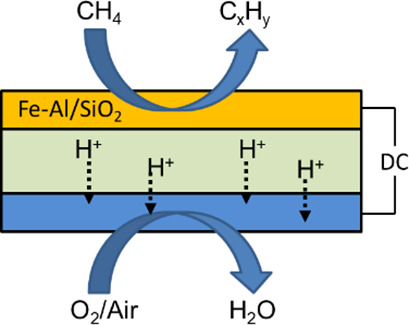
The synthesis of a novel Fe-Al/SiO2 catalyst for direct non-oxidative conversion of methane to ethylene, benzene, and naphthalene is described. Using solid oxide electrolysis cell devices to remove hydrogen effectively from the reaction system helps to improve the efficiency of a non-oxidative methane conversion process, shifting the reaction equilibrium and boosting the methane conversion.
Degradation of Eosin Y in Water by Corona Treatment with a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma
- Pages: 2015-2022
- First Published: 14 July 2020
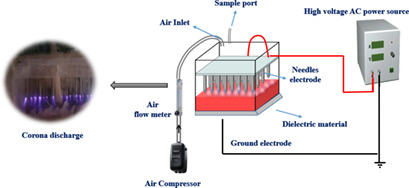
Wastewater contaminated with Eosin Y dye is an environmental threat due to its toxicity, mutagenicity, and difficult degradation. Degradation of Eosin Y in water by treatment with a dielectric barrier discharge plasma was studied in a multineedle point-to-plate mode. The effects of solution conductivity, dye concentration, pH, air gap, number of needles, and electrode materials were investigated.
Activated-Carbon Nanofibers/Graphene Nanocomposites and Their Adsorption Performance Towards Carbon Dioxide
- Pages: 2023-2030
- First Published: 20 July 2020
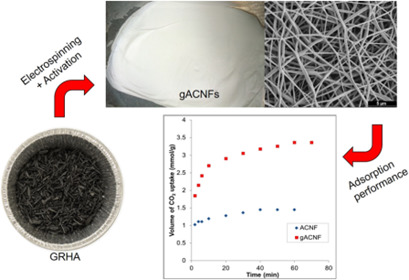
An activated-carbon nanofibers/graphene nanocomposite was developed as adsorbent material with enhanced porous structure and high adsorption performance towards carbon dioxide. The graphene-based material used was synthesized from graphene-derived rice husk ashes, an abundant and cheap agricultural waste, providing an alternative for realizing green technology.
Efficient Removal of Ammonia by Hierarchically Porous Carbons from a CO2 Capture Process
- Pages: 2031-2040
- First Published: 20 July 2020
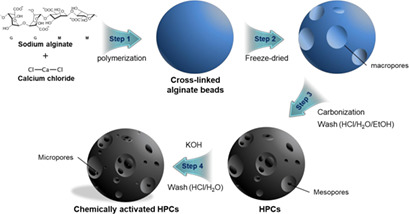
Activated carbon (AC) and hierarchically porous carbon (HPC) preparations were used as adsorbents for the removal of NH3 after an amine-based post-combustion carbon capture process, and their adsorption capacities, adsorption rates, and stabilities were studied. In general, the HPC adsorbents with more mesopores and acid sites showed better performance and stability than the AC ones.
Inhibiting Effect of Ionic Liquids on the Corrosion of Mild Steel in H2S and HCl Solution
- Pages: 2041-2052
- First Published: 20 July 2020
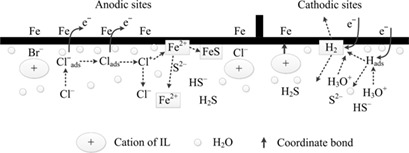
Ionic liquids (ILs) with various alkyl chain lengths were employed to inhibit the corrosion of mild steel in H2S and HCl solution. The IL [NH2ebim]Br exhibited the highest capability of inhibiting corrosion. The long alkyl chain attached to the imidazolium ring of this IL caused a strong adsorption and a high coverage area on the mild steel surface, thereby improving the inhibition ability.
SMART-Reactors: Tailoring Gas Holdup Distribution by Additively Manufactured Lattice Structures
- Pages: 2053-2061
- First Published: 21 July 2020

Additively manufactured lattice structures are used to tailor gas-liquid phase distribution and bubble sizes enhancing the reactor performance of gas-liquid reactions in bubble columns. A closer look on bubble velocities inside the structures helps to understand how structured packings reduce the rising speed, enhancing the residence time of the dispersed phase for a possibly conducted chemical reaction.
Encapsulation of Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract into Zein Nanoparticles
- Pages: 2062-2072
- First Published: 30 July 2020

Antioxidant-rich extracts from Hibiscus sabdariffa were encapsulated by the antisolvent precipitation process, and zein particles with high entrapment efficiency and nanometric size were obtained. Response surface modeling was used to optimize the process variables. The Hibiscus extract in the zein nanoparticles exhibited good stability for 3 months.
Synthesis of Polycaprolactone Nanoparticles through Flow-Focusing Microfluidic-Assisted Nanoprecipitation
- Pages: 2073-2082
- First Published: 30 July 2020
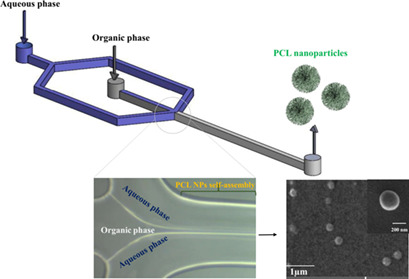
Nanoparticles (NPs) of biodegradable polymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL) have potential as drug delivery systems. PCL NPs were produced in a flow focusing microfluidic device, and their size, polydispersity index, and zeta potential optimized by varying different experimental parameters. The presence of both Tween 80 and polyvinyl alcohol surfactants in aqueous phase resulted in smaller NPs.
Mass Transfer Flux of CO2 into Methyldiethanolamine Solution in a Reactive-Absorption Process
- Pages: 2083-2091
- First Published: 02 August 2020
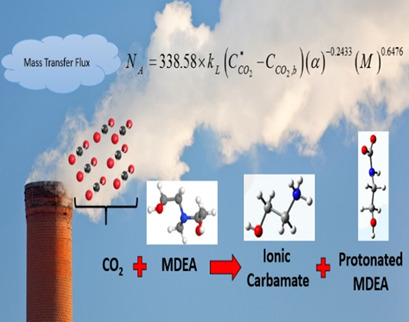
An innovative correlation is proposed based on the Buckingham π theorem for prediction of CO2 mass transfer flux in the reactive-absorption process using methyldiethanolamine solution. Effects of various parameters such as film parameter, CO2 loading, concentration ratio, ratio of partial pressure to total pressure, film thickness ratio, and diffusion ratio are considered in this model.
Optimal Design Issues of a Methanol Synthesis Reactor from CO2 Hydrogenation
- Pages: 2092-2099
- First Published: 02 August 2020
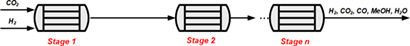
Methanol production by CO2 hydrogenation was studied in fixed-bed reactors with different degrees of reactor staging. The degrees of freedom of the reactor system were the number of stages, the cooling medium temperature, the heat transfer area, and the stage volume. With MeOH production or annual profit maximization as objective, staging of the reactor increases the objective function values to various extents.
Structural Effects of HZSM-5 Zeolite on Methanol-to-Propylene Reaction
- Pages: 2100-2108
- First Published: 02 August 2020
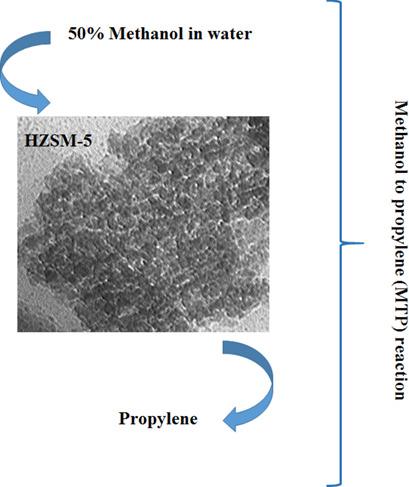
The methanol-to-propylene (MTP) process using zeolite-based catalysts is considered as a suitable solution for propylene production. Morphology variation of the ZSM-5 zeolite by altering the initial gel composition in hydrothermal synthesis is evaluated. Increasing the external surface area and mesopore volume of the HZSM-5 zeolite improves the propylene selectivity in the MTP reaction.
Optimization Investigation on Operating Parameters of a Scrubbing Tower Using a Genetic Algorithm
- Pages: 2109-2117
- First Published: 02 August 2020
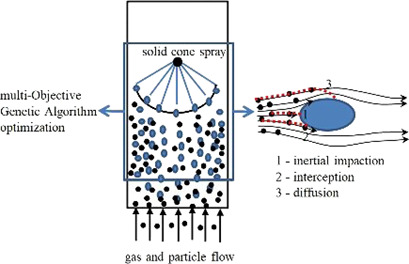
The problem of coke powder entrainment towards the main fractionator in a delayed coking unit can be solved by installing an open scrubbing tower instead of filtration. An innovative numerical method was developed based on a particle scavenging model and liquid wall film model. After response surface analysis, a multiobjective genetic algorithm was applied to optimize the operating conditions.
Preparation of Aqueous Nanodispersions of Disperse Dye by High-Gravity Technology and Spray Drying
- Pages: 2118-2125
- First Published: 02 August 2020
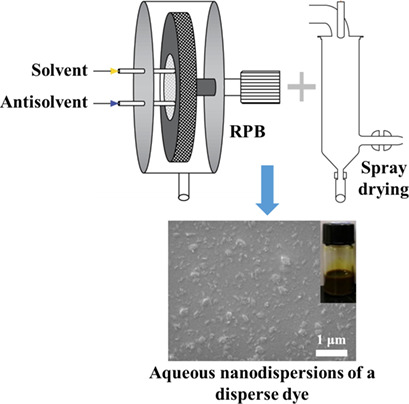
The applicability of disperse dyes is limited since they are poorly water-soluble and difficult to stably disperse in an aqueous medium. A stable aqueous nanodispersion of a water-insoluble disperse dye was prepared by high-gravity technology combined with spray drying, which might offer a general platform. The disperse dye nanodispersion exhibits better dyeing properties than a commercial dye.
Chemical Looping of Manganese to Synthesize Ammonia at Atmospheric Pressure: Sodium as Promoter
- Pages: 2126-2133
- First Published: 10 August 2020
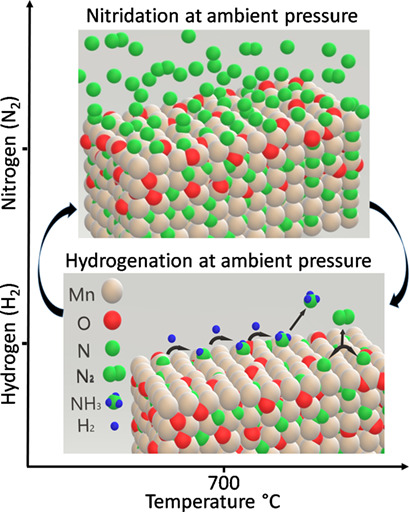
The addition of NaOH as alkali-containing promoter significantly improves yield and kinetics of chemical looping of Mn for NH3 synthesis at atmospheric pressure, thus boosting the ammonia harvesting. Based on the feasible reactions on the Mn surface, Na may increase the N conversion to NH3 instead of N2 whereas the reproducibility of successive reproducible looping implies unflinching.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 10/2020
- Page: 2134
- First Published: 21 September 2020










