Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 5/2019
- Page: 948
- First Published: 18 April 2019

Parallel catalytic reactors for CO/CO2 hydrogenation, located at SINOPEC Shanghai Research Institute of Petrochemical Technology (SRIPT). Copyright: Su Liu@SRIPT
Activated carbon-supported Mo-Co-K sulfide catalysts, prepared by stepwise impregnation, were used in the synthesis of higher alcohols via CO2 hydrogenation. The catalysts with Mo contents of 9∼12 wt %, a K/Mo molar ratio of 0.9, and a Co/Mo molar ratio of 0.3 showed relatively high CO2 conversions and high selectivity to total alcohols and C2+ alcohols. Moreover, the influence of calcination conditions on the sulfidation states and catalytic performance was studied. The surface sulfur runoff of the supported catalysts can be suppressed effectively by online calcination.
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 5/2019
- Page: 950
- First Published: 18 April 2019
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 5/2019
- Page: 951
- First Published: 18 April 2019
Highlights
Reviews
Agro Food Wastes and Innovative Pretreatments to Meet Biofuel Demand in Europe
- Pages: 954-961
- First Published: 15 February 2019
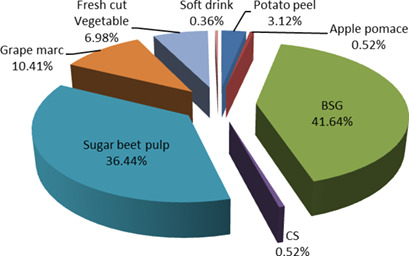
Owing to the rising energy demand and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, interest in biofuels is increasing. This review assesses the use of agricultural residues and agro-food waste such as Brewer's spent grains (BSG) and coffee silverskin (CS) as potential feedstocks for the production of ethanol and butanol as biofuels in the European framework and for a local scenario (Campania, Italy).
Research Articles
Activated Carbon-Supported Mo-Co-K Sulfide Catalysts for Synthesizing Higher Alcohols from CO2
- Pages: 962-970
- First Published: 29 January 2019
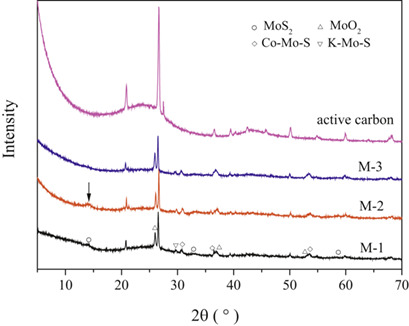
Activated carbon-supported Mo-Co-K sulfide catalysts were prepared by stepwise impregnation in a more economical and environmentally friendly way compared to the bulk-phase MoS2-based catalyst and applied for the synthesis of higher alcohols via CO2 hydrogenation. Optimization of the Mo loading content, Co/Mo and K/Mo molar ratios further improved the performance of the catalysts.
Ultrasonic Fabrication of Polymer Plate Reactors with a Surface Coating
- Pages: 971-979
- First Published: 21 December 2018

A polymer plate reactor was generated from two different polymers. By ultrasonic fabrication, a transparent polymer plate was welded with a chemically inert polymer layer. The leak-tight reactor system can withstand all tested flow rates and resulting pressures, with rapid and efficient mixing in the range of milliseconds.
Evaluation of Operational Cycles for Long-Term Run of a Tar Removal Catalytic System
- Pages: 980-986
- First Published: 13 December 2018
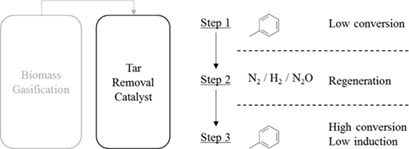
The poor stability of tar removal catalysts is a challenge in biomass gasification processes. An efficient method is proposed for performing long-term test operations with a commercial catalyst based on Pt supported on Ce-Zr-Al. A regeneration procedure is recommended for the success of long-term runs. The operation using the concept of cycles allows for cost reduction and higher health security.
Mixing and Heat Transfer of Granular Materials in an Externally Heated Rotary Kiln
- Pages: 987-995
- First Published: 15 February 2019
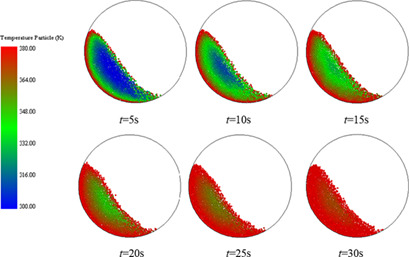
The effect of mixing on the heat transfer of particles in an externally heated rotary kiln was studied based on a heat transfer model, which was validated by experiments. High rotation speeds and low filling rates are beneficial for both mixing and heat transfer. The mean temperature differences between particles and between the particles and the drum wall dominate the heat transfer.
Effect of the Co-SiO2 Mesoporous Layer Coating Step on the Performance of Liquid Fuel Dimethyl Amino Ethyl Azide Dehydration
- Pages: 996-1001
- First Published: 15 February 2019
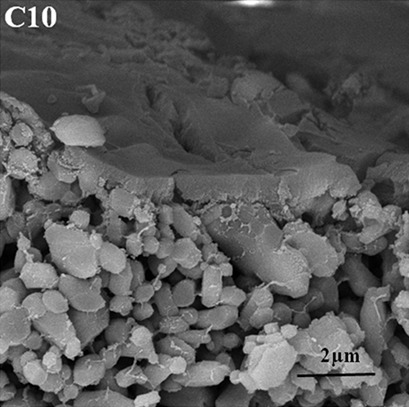
The sol-gel method is commonly applied via colloidal and polymeric routes for ceramic membrane preparation. Co-SiO2 ceramic membranes based on mullite discs were successfully synthesized and employed for dehydration of the liquid fuel dimethyl amino ethyl azide (DMAZ) via pervaporation process. These membranes are promising candidates to be applied in large-scale pervaporation dehydration of DMAZ.
Pervaporation-Assisted Esterification of Caproic Acid with Isobutanol in Conventional, In Situ, and Ex Situ Reactors
- Pages: 1002-1010
- First Published: 13 February 2019
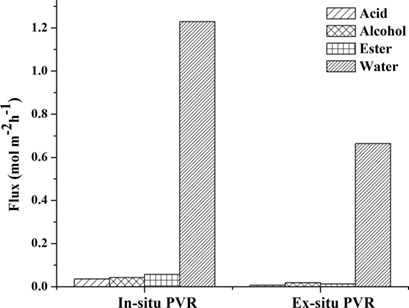
A pervaporation (PV) membrane separates close boiling, azeotropic liquid mixtures and enhances the reaction conversion of equilibrium-limited reactions. The effect of PV-assisted esterification of caproic acid and isobutanol is compared in conventional batch, in situ PV, and ex situ PV reactors. The ratio of water removal rate to the water production rate determines the performance of PV reactors.
Colorimetric Methods for Determining Fe, V, and Ni Contents in Coke and Anodes
- Pages: 1011-1017
- First Published: 13 February 2019
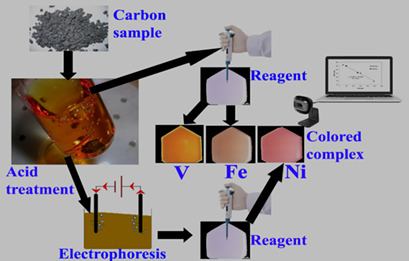
High concentrations of transition metal impurities (Fe, V, Ni) in coke increase the carbon anode reactivity, thus increasing carbon consumption, cost, and greenhouse gas emissions. Simple and easy-to-use tools to measure the concentration of impurities in coke and anodes were developed, enabling the industry to preselect anode raw materials or to blend cokes in order to reach their targets.
Deactivation Analysis of Industrial Spent Catalysts Applied to Lube Oil Hydrotreating in a Pilot Plant
- Pages: 1018-1026
- First Published: 25 February 2019
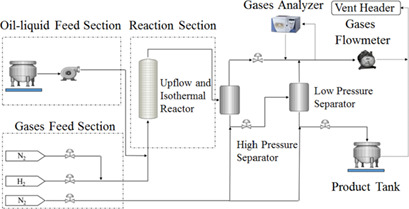
Industrial spent catalyst evaluation tests revealed a nonlinear deactivation through a hydrotreating reactor. Different main deactivation causes were determined depending on the location of the industrial spent catalyst samples. Poisoning by silicon, arsenic, and iron was the main cause at the top of the reactor, while coke deposition at the reactor bottom.
Modification of a Poly(tetrafluoroethylene) Porous Membrane to Superhydrophilicity with Improved Durability
- Pages: 1027-1036
- First Published: 25 February 2019
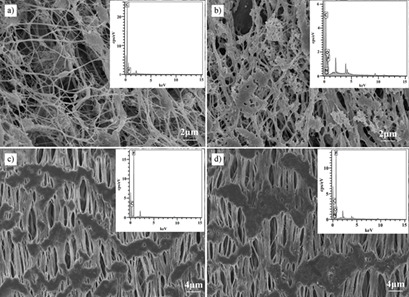
Hydrophobic flat-sheet and hollow-fiber poly(tetrafluoroethylene) membranes were modified by a commercial fluorocarbon surfactant to reach superhydrophilicity. The superhydrophilic membranes are characterized by enhanced wetting stability and resistance to acid and alkali solutions together with good filtration performance and antifouling property. A facile and effective route of modification is provided.
Flow Regimes of Viscous Immiscible Liquids in T-Type Microchannels
- Pages: 1037-1044
- First Published: 25 February 2019
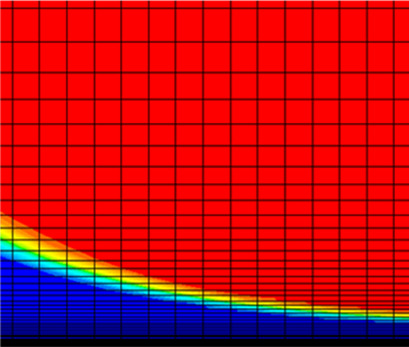
A computational and experimental study of flow regimes of a mixture of paraffin and castor oils with high viscosity in a T-shaped microchannel was performed for the first time. Parallel, rivulet, plug, slug, and droplet flow regimes were identified and a flow regime map was constructed for this mixture depending on Weber numbers. Experimental data were compared with numerical simulation results.
Direct Contact Membrane Distillation Applied to Colored Reactive or Disperse Dye Solutions
- Pages: 1045-1052
- First Published: 25 February 2019
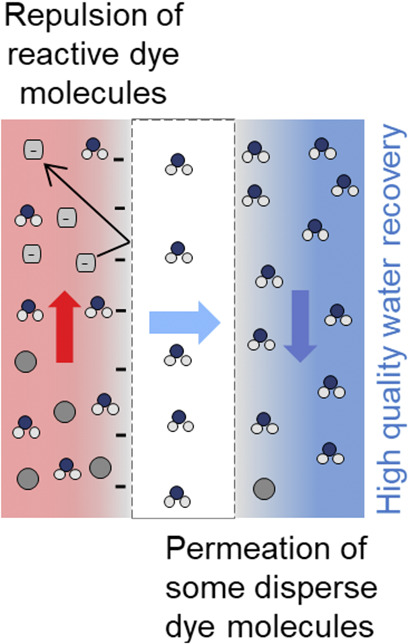
Dye classes provide different results of permeability in direct contact membrane distillation as demonstrated by using a commercial polypropylene flat-sheet membrane in the treatment of reactive and disperse dye solutions. Reactive and disperse dye solutions with different colors in direct contact membrane distillation for the treatment of dyeing wastewater were compared for the first time.
Enhanced Droplet Size Control in Liquid-Liquid Emulsions Obtained in a Wire-Guided X-Mixer
- Pages: 1053-1058
- First Published: 25 February 2019
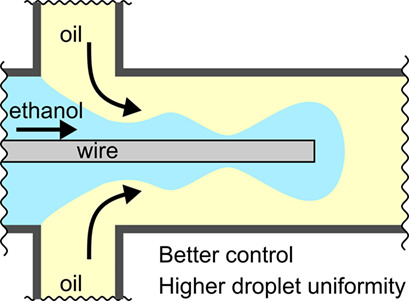
A simple and efficient method was proposed to control the droplet size in a liquid-liquid emulsion. Placing a metal wire along the centerline of the X-mixer changes the droplet formation mechanism. The wire improves droplet uniformity and provides additional control over the droplet size via the wire diameter and the position of the wire tip.
Experimental Study of Air Entrainment Rates due to Inclined Liquid Jets
- Pages: 1059-1069
- First Published: 01 March 2019
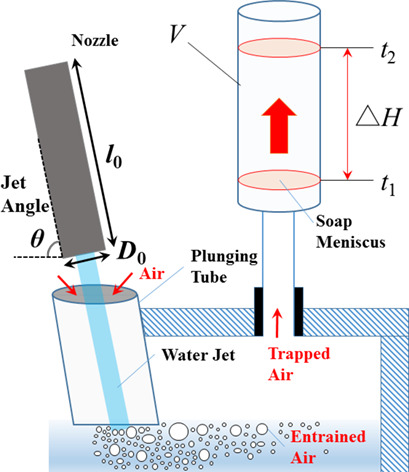
Air entrainment due to inclined plunging jets was analyzed experimentally with three types of fluids, nozzles with different inner diameters, and various inclination angles and liquid jet velocities. The air entrainment rate depends notably on the Weber number. An empirical model dependent on the Weber number and Laplace length scale is proposed to predict the air entrainment flow rate.
Efficient Removal of Anionic Organic Dyes from Aqueous Solution with Cu-Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 1070-1077
- First Published: 27 February 2019
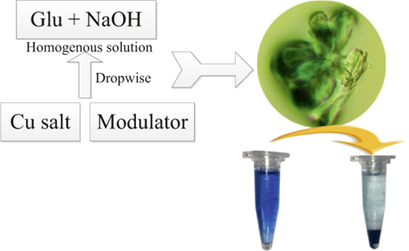
Metal-organic frameworks are emerging adsorption materials for a wide range of applications. A Cu-organic framework was synthesized rapidly at room temperature in aqueous solution and applied to remove organic dyes from aqueous solutions. The maximum adsorption capacities for dyes were higher than the data in previous reports. This framework can be easily regenerated and reused several times.
Integrating Biogas Plants into Microgrids for Bridging Temporary Power Supply Interruptions
- Pages: 1078-1087
- First Published: 01 March 2019
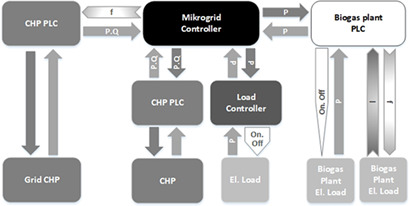
Until now, renewable energies have not become a part of a grid restoration process. They can be integrated into such process by building small island grids after a blackout. The usability of loads of a biogas plant for demand-side management and a control architecture for the integration of the bioenergy-based microgrid are described on the example of the microgrid of a farm with a biogas plant.
Alternatives for the Purification of the Blend Butanol/Ethanol from an Acetone/Butanol/Ethanol Fermentation Effluent
- Pages: 1088-1100
- First Published: 12 March 2019
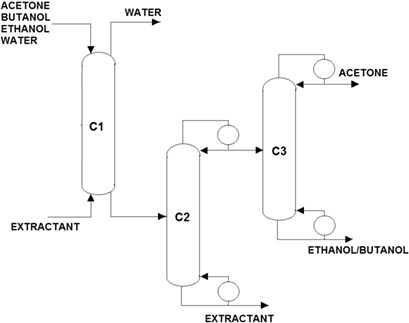
Alternative purification structures are proposed for an acetone/butanol/ethanol mixture, obtaining acetone and a butanol/ethanol blend as main products. Intensified sequences are also developed. The designs are optimized in terms of economic and environmental objectives, and safety indexes are assessed. The main effect of the production of the butanol/ethanol blend is on the safety index.
Mixing of Oil in Water Through Electrical Resistance Tomography and Response Surface Methodology
- Pages: 1101-1115
- First Published: 25 February 2019
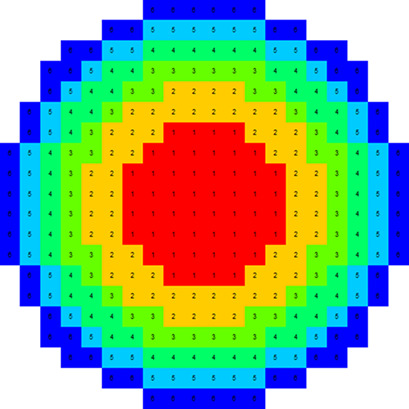
The mixing performance of two immiscible liquids in an agitated tank was investigated using an electrical resistance tomography system to evaluate the axial mixing index. An experimental design with response surface methodology was applied. The most effective factors were oil type and oil volume fraction. A linear relationship was found between the dispersed-phase viscosity and mixing index.
Economic and Risk Analyses of an Industrial N,N-Dimethylformamide Recovery Process
- Pages: 1116-1126
- First Published: 12 March 2019
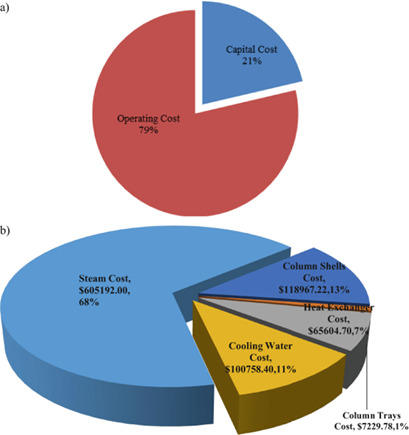
Industrial dimethylformamide recovery plants are usually based on a two-column sequence. The proposed dividing-wall column (DWC)-based plant avoids the remixing effect and has lower utility duties and CO2 emissions compared to the conventional system, in addition to lower total annual costs and a higher profitability index. The DWC can also increase the chance of earning the profit.
Generation of Coarse Bubbles and Flow Instability Control by Means of a Bubble Generator
- Pages: 1127-1134
- First Published: 07 March 2019
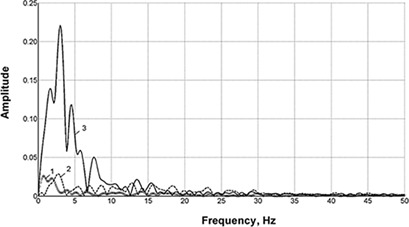
Pulsating flows have potential applications in membrane filtration and water treatment. Millimeter-sized bubbles were produced by a bubble generator, and pressure oscillations in the exit section of the device were captured and analyzed for two-phase flows with fine and coarse bubbles. Installing a pin in the exit section resulted in drastic changes in the structure of the pressure oscillations.
Enhanced Conversion in the Direct Synthesis of Diethyl Carbonate from Ethanol and CO2 by Process Intensification
- Pages: 1135-1143
- First Published: 14 March 2019
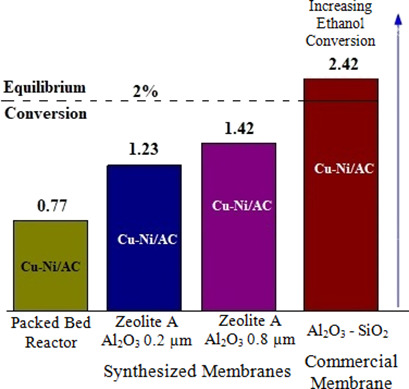
Direct synthesis of diethyl carbonate in a membrane reactor packed with Cu-Ni:3-1/AC was evaluated. Improved ethanol conversion to diethyl carbonate was obtained in all membrane reactors. Ethanol conversions higher than equilibrium were attained in a membrane reactor prepared with commercial SiO2/Al2O3 membrane. The enhancement of ethanol conversion resulted from H2O permeation through the membrane.
Adsorbent Regeneration by Non-thermal Plasma for Elimination of Odorous Compounds from Indoor Air
- Pages: 1144-1152
- First Published: 14 March 2019
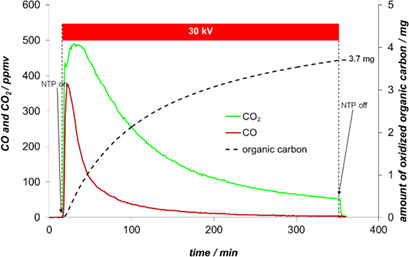
Odorous compounds are removed from indoor air by a combined concept of adsorption and plasma regeneration. Regeneration is carried out by non-thermal plasma oxidation. The concept was successfully demonstrated for model compounds and real odors. Adsorbed compounds could be eliminated to a high degree by regenerating the adsorber. A combination with ozone removal and CO post-oxidation is favored.
Biomass Gasification Integrated with Chemical Looping System for Hydrogen and Power. Coproduction Process – Thermodynamic and Techno-Economic Assessment
- Pages: 1153-1168
- First Published: 14 March 2019
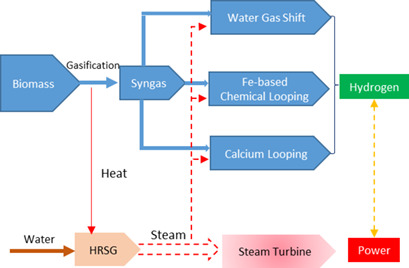
Three different biomass gasification-based processes for hydrogen and power cogeneration are proposed and simulated using Aspen Plus. Energy and exergy analyses as well as techno-economic evaluations for these processes are carried out and compared with each other. Parametric analyses are conducted to study the effect of some key parameters on the process performance indicators.
Communications
Minimum Cross Diameter for C6–C10 Aromatic Compounds
- Pages: 1169-1173
- First Published: 20 March 2019
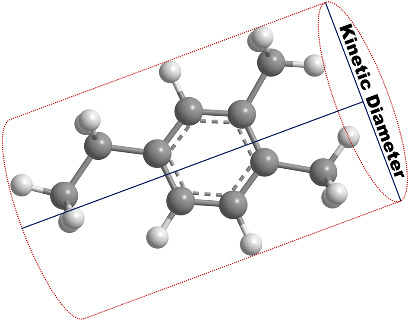
A simple and verifiable method to determine the kinetic diameter of 21 aromatic compounds was developed using the commercial software ChemBio3D Ultra. In addition to the commonly known BTX species, other heavy aromatics such as ethyltoluene, trimethylbenzene, diethylbenzene, and ethylxylene were included in the study. Some heavy aromatics presented similar sizes to o-xylene and m-xylene.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 5/2019
- Page: 1174
- First Published: 18 April 2019










