Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 4/2019
- Page: 710
- First Published: 25 March 2019
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 4/2019
- Page: 711
- First Published: 25 March 2019
Highlights
Editorial
CHISA – Worldwide Meeting for Chemical Engineers in the Heart of Europe
- Page: 714
- First Published: 25 March 2019
Reviews
W/O/W Multiple Emulsions as the Functional Component of Dairy Products
- Pages: 715-727
- First Published: 23 January 2019
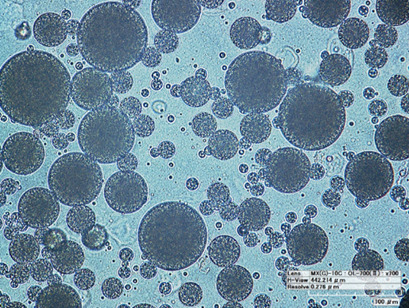
Functional food is experiencing increasing interest. Water-in-oil-in-water emulsions are remarkable systems bringing innovative opportunities to this field. They could allow for enjoying favorite fat products because of lower fat content and eventually other nutritional benefits. This review discusses the technology and research of such emulsions with potential applications in dairy products.
Research Articles
Life Cycle of Wash Oil for Benzol Absorption from Coke Oven Gas
- Pages: 728-734
- First Published: 21 January 2019
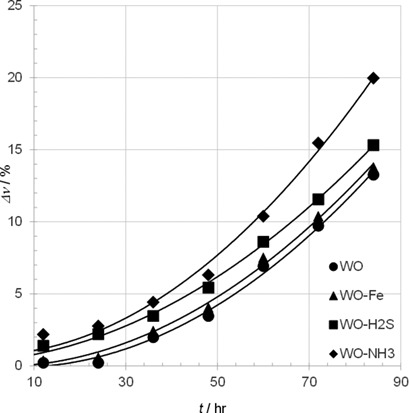
Coke oven gas is an important source of benzol. The process of benzol scrubbing and stripping was examined and the physicochemical properties of wash oil were monitored under natural technological conditions. Laboratory experiments simulated the exposition by coke oven gas impurities. Optimal conditions for wash oil regeneration could be estimated based on the presented results.
Rapid Models for Predicting the Low-Temperature Behavior of Diesel
- Pages: 735-743
- First Published: 21 January 2019
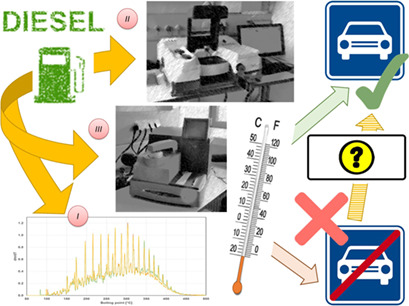
Three very rapid and accurate models for the prediction of the cold filtration plugging point were developed and correlated with the standard method for its assessment. Each model has its own particular advantages that suit it to a particular type of diesel sample and a specific stage of the diesel production process. These models could improve the optimization of diesel fuel production.
Effect of the ZIF-8 Distribution in Mixed-Matrix Membranes Based on Matrimid® 5218-PEG on CO2 Separation
- Pages: 744-752
- First Published: 21 January 2019

Mixed-matrix membranes based on Matrimid®, PEG 200, and ZIF-8 were successfully prepared by the traditional and the non-dried metal-organic framework method. The membrane preparation procedure played an important role for the separation properties of the membranes, at least in the dispersion of the filler across the membrane. The incorporation of ZIF-8 nanoparticles increased the CO2 permeability.
Economic Evaluation and Environmental Assessment of the Shale Gas Sweetening Process
- Pages: 753-760
- First Published: 18 January 2019
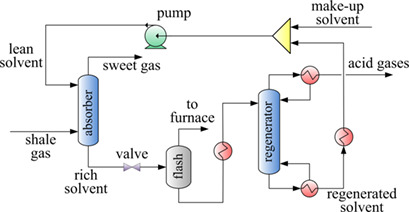
Shale gas is an emerging unconventional energy with enormous reserves. The shale gas sweetening process and Claus process are coupled by energy integration. A framework of economic evaluation and environmental assessment on the coupled process is established. The economic and environmental performance is investigated and distributions of different pollutant emissions by sources are discussed.
Population Balance Model Simulation of the Particle Effect on Flow Hydrodynamics in Slurry Beds
- Pages: 761-768
- First Published: 18 January 2019

A modified interphase drag model is proposed to describe the interactions between gas phase and slurry phase considering the presence of particles. Flow hydrodynamics in a slurry-bed reactor is studied by a computational fluid dynamics-population balance model with the modified drag force model. Simulation results demonstrate the accuracy of the model in predicting the hydrodynamics.
Separation of Trimethyl Borate from a Liquid Mixture by Pervaporation
- Pages: 769-773
- First Published: 18 January 2019
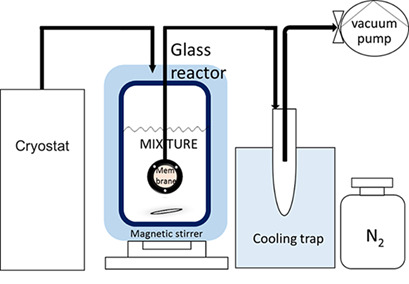
Separation of methanol/trimethyl borate using industrial membranes was performed, with PERVAPTM 4155-30 reaching the best separation results from all tested membranes. Due to the strong affinities of these membranes to different compounds, methanol preferentially passed through PERVAPTM 4155-30 whereas trimethyl borate was favorably pervaporated from the mixture by PERVAPTM 4060.
Practical Application of the Probabilistic-Statistical Model of the Suspension Separation in Hydrocyclones
- Pages: 774-779
- First Published: 18 January 2019
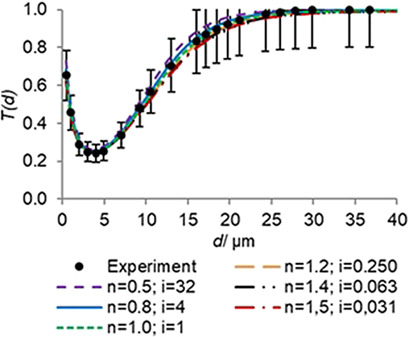
Probabilistic-statistical methods are increasingly used in the theoretical description of processes in hydrocyclones to meet modern chemical engineering requirements. The use of the property of statistical self-similarity is proposed to reduce the scope of field experiments and provide an opportunity to define the relationship between random components and flow hydrodynamics in a hydrocyclone.
Fatty Acid Deoxygenation in Supercritical Hexane over Catalysts Synthesized Hydrothermally for Biodiesel Production
- Pages: 780-787
- First Published: 18 January 2019
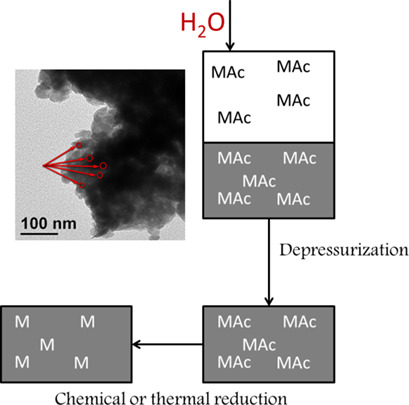
Supported metal catalysts play an important role in chemical technology, and hydrothermal synthesis of catalysts has recently attracted much attention. Cobalt and nickel nanoparticles were deposited on a hyper-cross-linked polystyrene matrix by a hydrothermal method, and the catalytic activity of the resulting catalysts was evaluated in the deoxygenation of fatty acids in supercritical n-hexane.
Influence of Impeller Diameter on Crystal Growth Kinetics of Borax in a Mixed Dual-Impeller Batch-Cooling Crystallizer
- Pages: 788-796
- First Published: 23 January 2019

Crystallization kinetics of borax decahydrate in a batch-cooling dual-impeller crystallizer at different impeller diameters was evaluated. Hydrodynamic conditions were analyzed by mixing time and simulations of the fluid flow pattern by computational fluid dynamics. A strong relation between the hydrodynamics and the properties of the final product of crystallization was detected.
Simulation of Post-Combustion CO2 Capture, a Comparison among Absorption, Adsorption and Membranes
- Pages: 797-804
- First Published: 23 January 2019
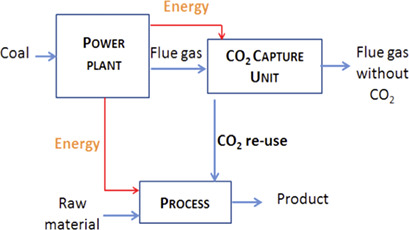
Based on systems modeling, three post-combustion CO2 capture processes – membrane, absorption, and adsorption – were compared regarding energy consumption, design, and efficiency. The membrane process is revealed as the most efficient one in terms of energy consumption, but reaches lower recovery rates than the other two processes and a significantly smaller CO2 purity than the absorption process.
Synthesis-Gas Absorption under Real Process Conditions: Thermodynamic Aspects
- Pages: 805-811
- First Published: 23 January 2019
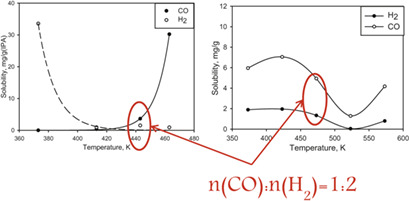
Solubilities of gases in liquids are needed to interpret rate data in gas-liquid, gas-liquid-liquid, and gas-liquid-solid reactions. Hence, CO and H2 solubility under the conditions of liquid-phase Fischer-Tropsch synthesis were measured and thermodynamic parameters calculated. The SRK equation of state can be used to predict optimal process conditions for liquid-phase Fischer-Tropsch reactions.
A Probabilistic-Statistical Model of Change of Particle Size Distribution in Settlers and Tanks
- Pages: 812-817
- First Published: 29 January 2019
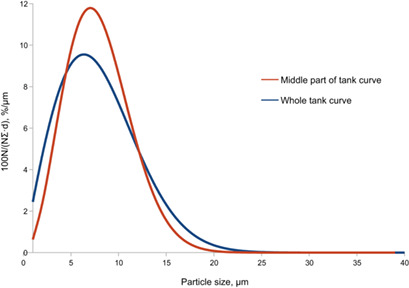
The solid particle distribution in a liquid inside a tank in the presence of sedimentation and random perturbing forces caused particularly by convective motion is considered. The behavior of particles can be described by a diffusion-type equation, the Fokker-Planck-Kolmogorov equation. Stationary particle distributions over the height and horizontal cross sections of the tank were obtained.
Direct Coal Liquefaction Using Iron Carbonyl Powder Catalyst
- Pages: 818-826
- First Published: 29 January 2019
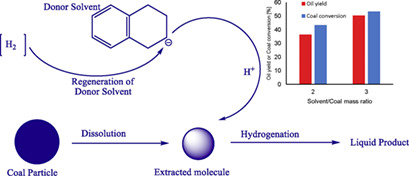
Thermal dissolution and hydrogenation of coal was performed under mild reaction conditions with a carbonyl iron powder catalyst. The yield of preasphaltenes, asphaltenes, and oils were strongly influenced by the solvent-to-coal mass ratio and temperature. Carbonyl iron powder is an effective catalyst for first-stage direct coal liquefaction, replacing the dangerous iron pentacarbonyl catalyst.
Effect of Particle Image Velocimetry Setting Parameters on Local Velocity Measurements in an Agitated Vessel
- Pages: 827-834
- First Published: 29 January 2019
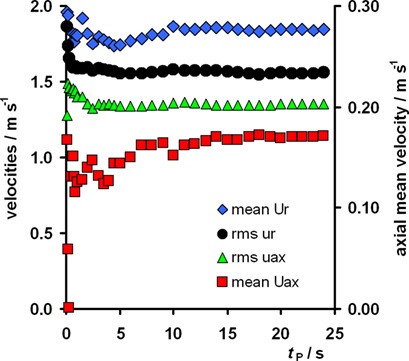
The impact on turbulence characteristics of the main particle image velocimetry setting parameters was investigated for a Rushton turbine impeller. To obtain the relevant data for velocities and fluctuation gradients, a minimum recording time is needed. No effect of sampling frequency was observed if the sampling frequency was higher than approx. 17 times the impeller frequency.
What the Combustion Engineer Gains from CFD Modeling: Gas Furnace
- Pages: 835-842
- First Published: 29 January 2019

The expectations of combustion engineers who use CFD tools are put into perspective by two instructive examples. The first one is an extensive parametric study of NOx emissions, and the second one a prediction of local heat loads in a water-cooled furnace. Both examples are validated by reliable measured data and provide an indication of the typical degree of accuracy.
Experiments on Bubble Breakup Induced by Collision with a Vortex Ring
- Pages: 843-850
- First Published: 29 January 2019
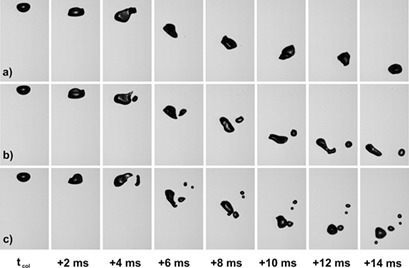
The collision of single bubbles with single vortex rings of defined energy was studied experimentally. The intention was to investigate if the model case of a free rising bubble that interacts with a controlled liquid jet can be used as an alternative source of breakup parameters for population balance modeling of multiphase flows where bubble breakup occurs.
Activated Carbon from Renewable Material as an Efficient Support for Palladium Oxidation Catalysts
- Pages: 851-858
- First Published: 06 February 2019
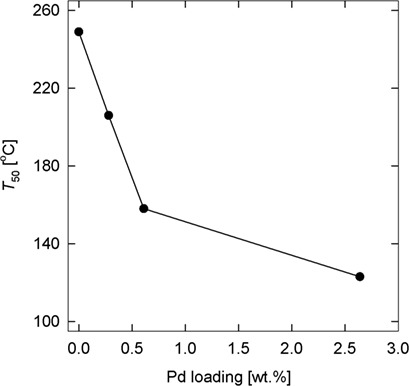
Activated carbon was prepared from agricultural waste (cocoa pod husk) with ZnCl2 as an activating agent and employed as a green support for Pd oxidation catalysts. Pd nanoparticles were introduced by impregnation with Pd acetate in the presence of citric acid. The catalysts were tested in ethanol gas-phase oxidation and their performance correlated with their physicochemical properties.
Numerical Simulation of Sterilization Processes for Shear-Thinning Food in Taylor-Couette Flow Systems
- Pages: 859-866
- First Published: 04 February 2019
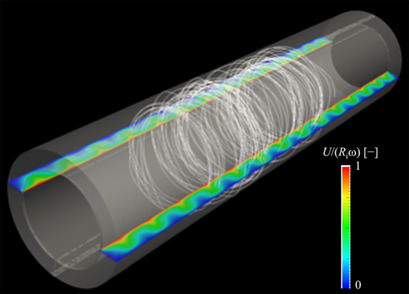
Thermal sterilization still holds a dominant position in the food industry. The performance of a Taylor-Couette flow apparatus as sterilizer for food was numercically investigated. The destruction of spores of Clostridium botulinum and retention of thiamine served as model reactions. The proposed flow sterilizer has the potential for process intensification in heat sterilization processes.
Electrodialysis Application of the Ultrafiltration Permeate of Milk Before and After Reverse Osmosis
- Pages: 867-873
- First Published: 06 February 2019
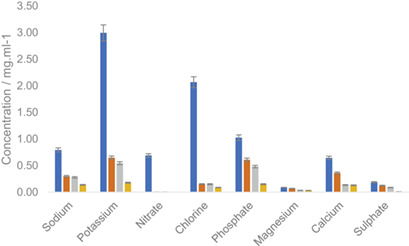
Electrodialysis of secondary milk products, i.e., the ultrafiltration permeate and its concentrated form by reverse osmosis, was performed to achieve different levels of desalination. Ion analysis showed that electrodialysis of milk permeate, particularly after reverse osmosis, improves the handling characteristics and may offer advantages for further processing of secondary dairy products.
A Kinetic Model of Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Employing a Hole Scavenger
- Pages: 874-881
- First Published: 06 February 2019
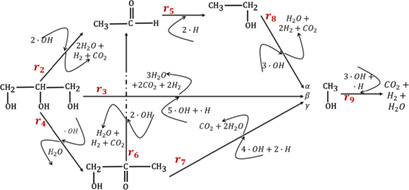
As a fuel, hydrogen has a high heating value and is environmentally friendly, and thus, a hydrogen production process must be sustainable and inexpensive. Photocatalytic processes meet these requirements. An improved multi-response kinetic model based on experimental observations is presented for the photocatalytic production of hydrogen.
Catalytic Evaluation of CuO/[Si]MCM-41 in Fenton-like Reactions
- Pages: 882-888
- First Published: 06 February 2019
![Catalytic Evaluation of CuO/[Si]MCM-41 in Fenton-like Reactions](/cms/asset/50d918bb-8c52-4640-a75c-003b7c83912c/ceat201800593-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts have potential applications in treating dye-containing effluents. Hence, CuO catalysts supported on mesoporous silica MCM-41 were synthesized and evaluated in a Fenton-like reaction for the decolorization of the azo dye methyl orange. Catalytic activity at different pH values and the influence of copper content on catalyst activity were also investigated.
Energy, Thermal, and Economic Analysis of Air Heat Pumps for Hot Water
- Pages: 889-895
- First Published: 04 February 2019
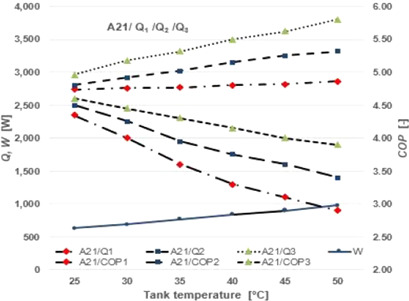
The air heat pump for domestic hot water is an ideal solution for heating systems equipped with solid fuel boilers. It is a maintenance-free, economical, and environmentally friendly system outside the heating season. Such heat pump should be used primarily in systems with solid fuel boilers that are not turned on outside the heating season, and installations with electric utility water preparation.
Features of Multicomponent Mass Transfer in Gas Mixtures Containing Hydrocarbon Components
- Pages: 896-902
- First Published: 06 February 2019

The characteristics of transition from a diffusion process to the concentration gravitational convection in multicomponent gas mixtures containing hydrocarbon components are evaluated. A computational model for the study of isothermal transfer in a ternary mixture by means of 2D modeling in a vertical channel of finite size is proposed and the results are compared with experimental data.
Determination of Breakage Parameters in Turbulent Fluid-Fluid Breakage
- Pages: 903-909
- First Published: 13 February 2019
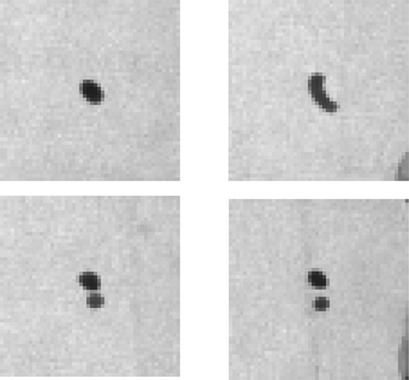
The definitions adopted in breakage experiments of single fluid particles are significant for the reported values. The impact of the two main definitions of fluid particle breakage on those values like breakage time, daughter sizes, and daughter numbers is investigated. An image analysis procedure is presented and the procedure for extracting the parameters from a series of images is elucidated.
Isothermal Adsorption Behavior of Cesium Ions in a Novel Chitosan-Prussian Blue-Based Membrane
- Pages: 910-917
- First Published: 13 February 2019
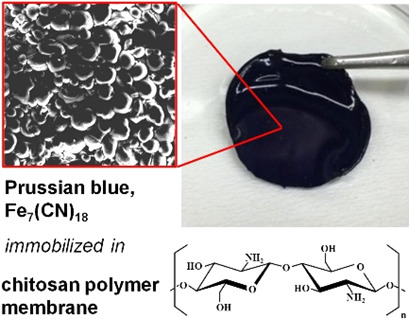
A novel chitosan-Prussian blue-based membrane was successfully prepared through addition/removal of polyethylene glycol. The membrane exerts a high immobilizing stability as well as attractive adsorption characteristics for the selective removal of cesium ions, e.g., from water resources. High amounts of immobilized Prussian blue improve the adsorption ability of the membrane.
Nanosized Composite Pt-Ru Catalysts for Production of Modern Modified Fuels
- Pages: 918-924
- First Published: 15 February 2019
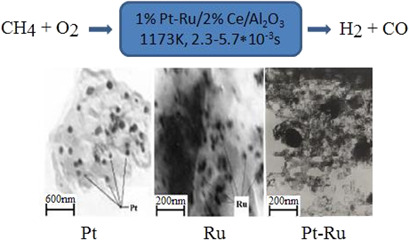
Innovative thermostable high-performance catalysts for selective production of synthesis gas from CH4 at short contact times were developed. Nanosized Pto, Ruo, and PtRu clusters provide optimum selective oxidation. The relationship of physicochemical characteristics of catalysts with their catalytic properties was evaluated. Quantum chemical modeling of CH bond activation in CH4 on clusters was conducted.
Improvement of Centrifugal Cryoconcentration by Ice Recovery Applied to Orange Juice
- Pages: 925-931
- First Published: 15 February 2019
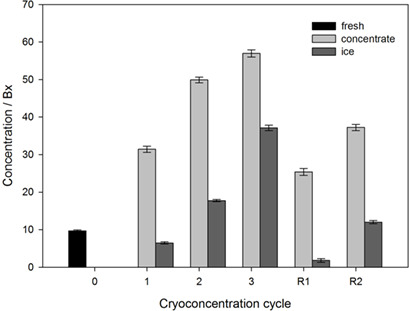
Cryoconcentration is a relatively new emerging and environmentally friendly non-thermal technology. The improvement of centrifugal cryoconcentration through concentrate recovery from the ice fraction applied to orange juice was evaluated. The solid concentration increased by six times compared to the initial concentration of solids in fresh orange juice after three cycles.
Full-Loop Simulation of Gas-Solids Flow in a Pilot-Scale Circulating Fluidized Bed
- Pages: 932-939
- First Published: 13 February 2019
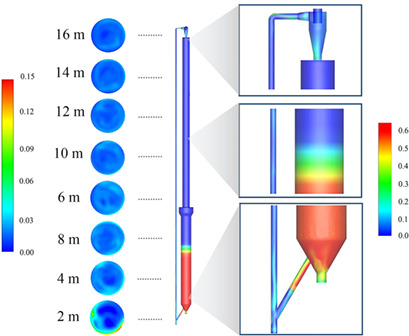
A 3D full-loop simulation was conducted for a pilot-scale circulating-fluidized bed to study the gas-solids flow behavior. The system hydrodynamics such as pressure balance, distribution of solids holdup and velocity as well as instantaneous circulating rates were investigated, and the effects of operating conditions on the system were evaluated to get a comprehensive understanding of the system.
Kinetics and Equilibrium Modeling of Sterol Adsorption on Styrene-Divinylbenzene Cation-Exchange Resins
- Pages: 940-946
- First Published: 18 March 2019
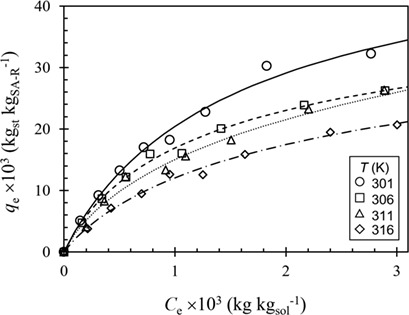
A styrene-divinylbenzene cation-exchange resin with sulfonic acid group is a promising adsorbent for phytosterol recovery from fatty acid methyl esters. The behavior of stigmasterol adsorption on this resin is analyzed. Simple pseudo-second-order kinetics and a modified Langmuir isotherm with corresponding parameters are proposed for prediction of adsorption rate and adsorption capacity of the resin.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 4/2019
- Pages: 947-948
- First Published: 25 March 2019











