Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 7/2017
- Page: 1205
- First Published: 22 June 2017

Large crystals of sodium chloride – macro. Copyright: pzAxe@Shutterstock
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 7/2017
- Page: 1206
- First Published: 22 June 2017
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 7/2017
- Page: 1207
- First Published: 22 June 2017
Highlights
Editorial
Industrial Crystallization: Classical Technology with Steadily Increasing Applications and Importance
- Page: 1210
- First Published: 22 June 2017
Research Articles
Stereoselective Crystallization as a Basis for Single-Enantiomer Drug Production
- Pages: 1211-1220
- First Published: 26 April 2017
Nowadays, single enantiomeric chiral active pharmaceutical ingredients dominate among new drugs. Direct methods for the separation of racemates simplify their preparation. A survey is given on the history of this topic as well as information about actual methods of conglomerate identification and practical implementation options for direct resolutions.
Solubility Study and Thermal Stability Analysis of Calcium Propionate
- Pages: 1221-1230
- First Published: 06 March 2017
Calcium propionate is frequently used as food additive. Basic studies on its solubility and solid-state forms in water and ethanol-water mixtures as well as thermal behavior were performed. The results obtained provide a better understanding of thermal and solubility behavior of calcium propionate and serve as base to improve its crystallization process in the future.
Shape Change and Growth Behavior of Monosodium Urate Monohydrate in a Gout Model
- Pages: 1231-1234
- First Published: 07 April 2017

Needle-shaped monosodium urate monohydrate (MSU) crystals deposited in synovial fluid provoke the acute inflammatory response of gout. The crystallization mechanism of MSU was investigated. Stirring helped to crystallize MSU faster and larger in amount. A high urate concentration enhanced the nucleation of MSU. The results promote the importance of serum urate level control as gout treatment.
Influence of Solution Composition and Temperature on the Crystal Form of Sodium Dehydroacetate
- Pages: 1235-1241
- First Published: 07 April 2017
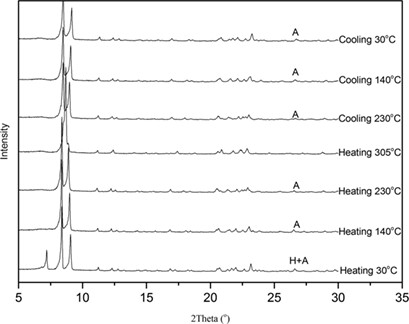
Slurry experiments are common to assess the required amount of water in order to ensure or avoid hydrates in crystallization. The stability of anhydrate and monohydrate I of sodium dehydroacetate was measured at different solvent compositions and temperatures and a new monohydrate II was detected. Explanations for the formation of different sodium dehydroacetate forms are proposed.
Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles by Reductive Crystallization Using Polyethyleneimine
- Pages: 1242-1246
- First Published: 07 April 2017
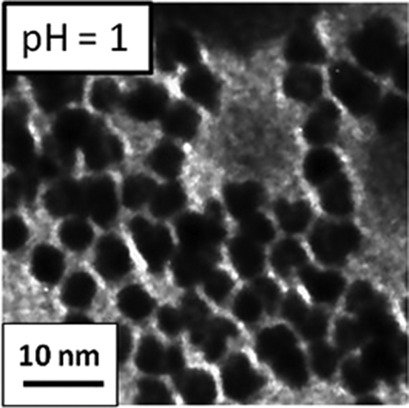
A fast and simple method for synthesizing Pt nanoparticles is required. Monodispersed Pt nanoparticles were successfully synthesized by reductive crystallization using polyethyleneimine as a protective reagent and NaBH4 as a reducing agent. Size and morphology of the Pt nanoparticles were controlled by changing the pH of the reaction field.
Design of Dissolvable Milk Containers for Convenient Handling
- Pages: 1247-1251
- First Published: 10 April 2017

An alternative packaging for milk or condensed milk as an innovative and unique alternative to common plastic jars is introduced. A method is developed to encapsulate milk or condensed milk by means of crystallization. Successful encapsulation is demonstrated creating capsules with a hard and stable crust. Sucrose and erythritol are used to form a crystalline layer.
Model of Temperature Cycle-Induced Deracemization via Differences in Crystal Growth Rate Dispersion
- Pages: 1252-1260
- First Published: 10 April 2017
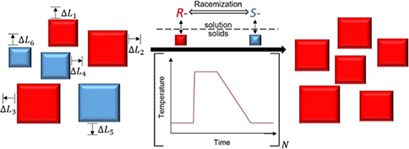
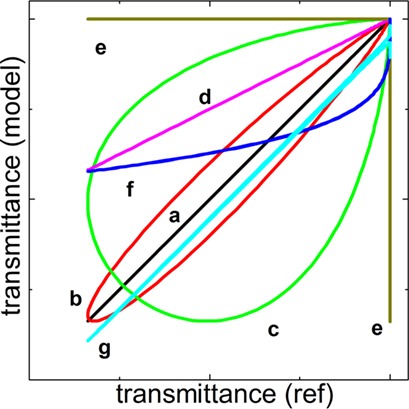
A racemic suspension of conglomerate-forming species can be converted to a homochiral suspension in a fast racemizing solution by temperature cycle-induced deracemization. This process is modeled using the population balance model for the two enantiomorphs, applying the program gCrystal to obtain an accurate simulation of the evolution of the enantiomeric excess in the crystal phase.
Analysis of Hydrocolloids in Crystalline Material
- Pages: 1261-1267
- First Published: 10 April 2017
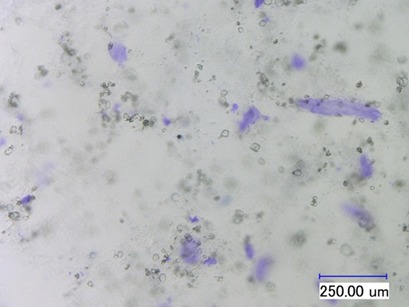
The analysis of gelatin, agar, or carrageenans in crystallized sucrose is an important method to estimate the effects of hydrocolloids on crystallized coated products. An incorporation of these texturants can lead to product changes like storage stability, layer thicknesses, and mouth feeling. All hydrocolloids are incorporated into the coating material during layer formation of coated sweets.
A Contribution to the Solution Thermodynamics of Chiral Lactide
- Pages: 1268-1275
- First Published: 10 April 2017
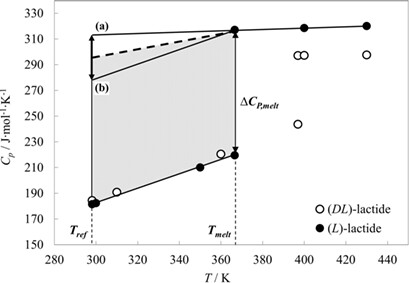
Chiral lactide is a model substance to study the solution thermodynamics of a chiral racemic compound-forming system. The solution enthalpy is considered to consist of three thermodynamic steps: melting of the crystal, transition of the subcooled melt to an infinite dilution, and the subsequent transition to a saturated solution. This model is an alternative way to obtain the solution enthalpy from measured solubilities.
Growth Mechanism of Hollow Sodium Chloride Single Crystals Grown from a Mixed Solvent of Cyclohexane and Acetone
- Pages: 1276-1281
- First Published: 26 April 2017

Hollow sodium chloride crystals are considered as potential high-value-added crystals. Such crystals were successfully synthesized by dropping an aqueous sodium chloride solution into a mixed solvent of cyclohexane and acetone and characterized by X-ray diffraction and optical microscopic imaging. Possible growth mechanisms were proposed to elucidate the formation of the obtained crystals.
Particle Engineering of an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient for Improved Micromeritic Properties
- Pages: 1282-1292
- First Published: 26 April 2017
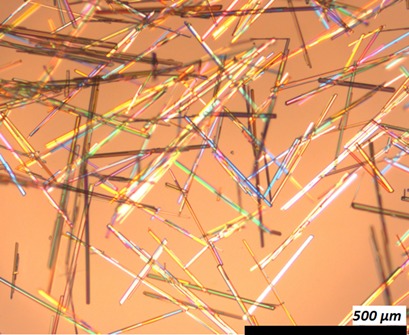
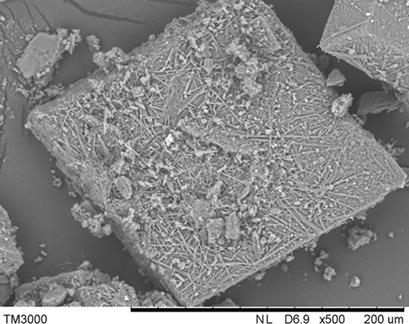
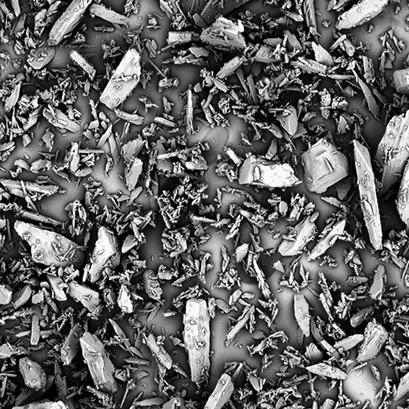
The design and optimization of robust crystal-habit-modification procedures can improve the solid-state properties of an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). A toolbox of techniques is available to develop or optimize crystallization processes in light of the crystal shape, thereby enabling more efficient processing and subsequent formulation.
Effects of Solution Composition and Polymer Additive on the Crystallization of Struvite
- Pages: 1293-1299
- First Published: 26 April 2017
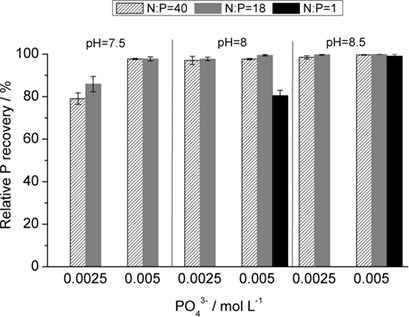
Phosphorus recovered from reject water from a wastewater treatment plant can be used as a phosphate fertilizer. The composition of the wastewater affects the quality of the product, so the effects of solution composition and polymer additive on the crystallization of struvite have been studied. Controlling the crystallization process guarantees the consistent production of struvite with desired properties.
Particle Size Control during Ultrasonic Cooling Crystallization of Paracetamol
- Pages: 1300-1308
- First Published: 04 May 2017

The effects of sonication in the three defined stages of cooling crystallization of paracetamol were evaluated. Tuning of the ultrasonic power density and the exposure time after nucleation resulted in varying crystal sizes, whereas the use of ultrasound before nucleation did not affect the particle size distribution, pointing at enhanced secondary nucleation as the main mechanism.
Control of Polymorphism and Particle Size of Hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane in Drowning-Out Crystallization
- Pages: 1309-1317
- First Published: 03 May 2017
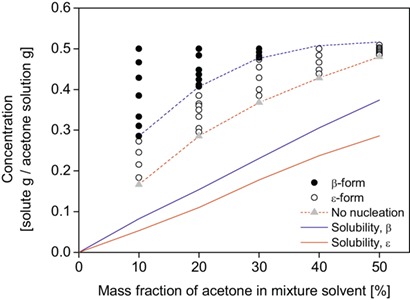
Drowning-out crystallization allows effective control of polymorphism and particle sizes. 2,4,6,8,10-Hexanitro-2,4,6,8,10,12-hexaazaisowurtzitane is used as a model compound to determine laboratory-scale conditions of crystallization for scaling up. The polymorphic β and ε forms were selected by controlling supersaturation and the ratio of components in the solvent mixture.
Polymorph Control of L-ArgHCl on Antisolvent Crystallization by Ultrasonic Irradiation
- Pages: 1318-1322
- First Published: 03 May 2017
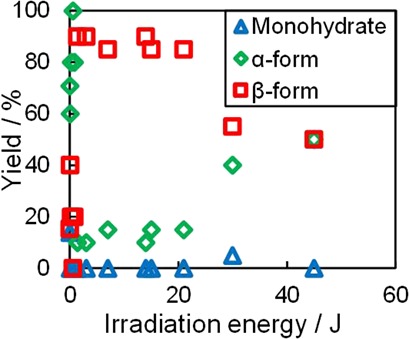
Amino acids are widely utilized as medical raw materials and food additives. Since most of the amino acids exhibit polymorphism, polymorph control is essential in crystallization processes. Polymorph control of L-ArgHCl was achieved by ultrasonic irradiation. Its unstable form was selectively crystallized by ultrasonic irradiation. Irradiation caused a shortening of the induction time.
Optimizing the Crystal Habit of Glycine by Using an Additive for Impinging Jet Crystallization
- Pages: 1323-1331
- First Published: 04 May 2017
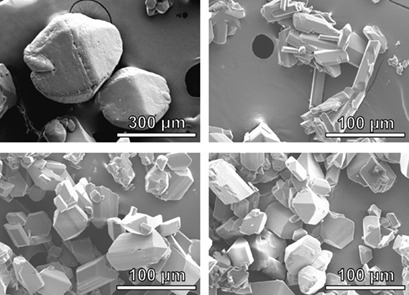
The impinging jet crystallization method was applied for the first time together with different concentrations of potassium chloride as an additive in order to modify the crystal habit of glycine particles. Relevant factors affecting the impinging jet-crystallized product were identified by a 32 full factorial design, revealing the additive concentration and the post-mixing time as important process parameters.
KH2PO4 Production by Cooling Crystallization Using Its Phase Equilibrium in the KH2PO4-KCl-C2H5OH-H2O System
- Pages: 1332-1338
- First Published: 04 May 2017

The KCl-KH2PO4-C2H5OH-H2O system is relevant to process design for the crystallization of KH2PO4. Hence, its solid-liquid phase equilibrium, solubility data, and physicochemical properties were determined at 313.15 K. Drowning-out precipitation of KH2PO4 was carried out in order to observe the crystal morphology, and the effect of KCl on KH2PO4 crystallization was investigated.
Influence of Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation on the Crystallization of L-Menthol from Water
- Pages: 1339-1346
- First Published: 04 May 2017
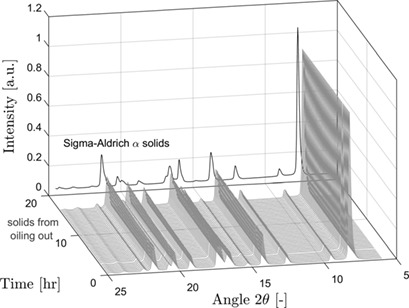
Liquid-liquid phase separation, also termed oiling-out, means a challenge for crystallization processes which is largely unwanted. The influence of oiling-out on crystal properties for a mixture of L-menthol in water was investigated. Solvent inclusions were detected within the L-menthol crystals. Oiling-out crystallization conditions were found to affect the amount of such inclusions.
Photocatalytic Activity of Synthetic N-doped TiO2/Reduced Graphene Oxide Crystalline Composites
- Pages: 1347-1353
- First Published: 16 May 2017
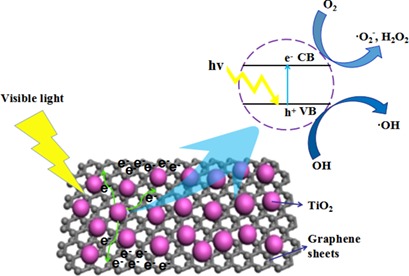
A strategy for analysis of advanced photocatalysts in wastewater treatment is proposed. Electrons are excited from the valence band to the conduction band to form photogenerated electrons, leaving holes in the valence band. Such electrons are transferred to the surface of graphene which reduces the recombination rate of photogenerated electrons and holes and improves the photocatalytic efficiency.
Determination of the Effects of Carboxylic Acids on Calcium Sulfate Dihydrate Crystallization
- Pages: 1354-1361
- First Published: 16 May 2017
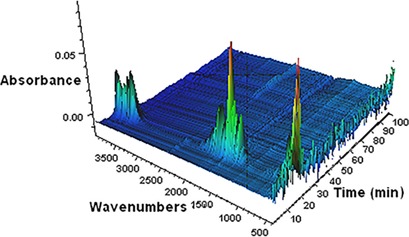
The role of carboxylic acids used as additives in gypsum crystallization is still not clearly clarified. Combined analyses proved that the amount of carboxylic acid adsorbed onto the calcium sulfate dihydrate crystals increased with higher carbonyl group numbers. This affected significantly the morphology, particle size, and filtration characteristics of the calcium sulfate dihydrate crystals.
Control of Continuous Mixed-Solution Mixed-Product Removal Crystallization Processes
- Pages: 1362-1369
- First Published: 16 May 2017
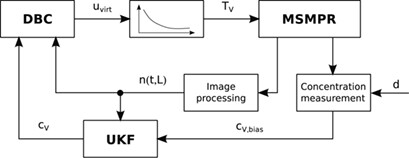
Some aspects like process modeling, monitoring, and control problems in continuous mixed-solution mixed-product removal crystallization are still challenging. An innovative approach for online measurement of the crystal size distribution is proposed. Discrepancy-based control is designed and applied to a nonlinear model taking system nonlinearities into account.
Noninvasive 4D Flow Characterization in a Stirred Tank via Phase-Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Pages: 1370-1327
- First Published: 30 May 2017
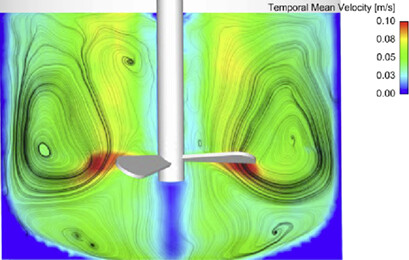
Phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI) applied on rotating systems is highly challenging since a non-ferromagnetic system has to be developed before. The complex 3D unsteady flow in a stirred tank representing a rotating batch crystallizer is considered. The hydrodynamics in space and time could be noninvasively quantified using flow-sensitive PC-MRI.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 7/2017
- Page: 1378
- First Published: 22 June 2017










