Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Formation, Structure, and Mechanical Performance of Silk Nanofibrils Produced by Heat-Induced Self-Assembly
- First Published: 05 February 2021

Front Cover: In article number 2000435 by Shengjie Ling, Ying Pei, and co-workers, the kinetic behavior of the heat-induced self-assembly of silk fibroin (SF) is studied. The formation of silk nanofibrils (SNFs) occurs through nucleation-dependent aggregation. SF shows inherent fractal growth, and this trend is critical for the short-term assembly. The longterm assembly of SF mainly involves an elongation growth process, which shows bright iridescent colors under polarized light.
Inside Front Cover
Lignin-Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes: Lignin-Graft-Poly(ethylene glycol)
- First Published: 05 February 2021

Inside Cover: In article number 2000428, Hoyong Chung, Daniel Hallinan Jr., and coworkers graft-copolymerized biomass lignin with poly(ethylene glycol) through eco-friendly and low energy-consuming photo-redox catalysis that can be performed under natural sunlight. The new solid polymer electrolyte is designed to be used for safe battery applications. With enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, the new polymer demonstrates excellent ionic conductivity at both ambient and elevated temperatures.
Back Cover
Rate-Limited Reaction in TEMPO/Laccase/O2 Oxidation of Cellulose
- First Published: 05 February 2021

Back Cover: In article number 2000501 by Yimin Fan and co-workers, the TEMPO/laccase/O2 system is an environmentally friendly option for cellulose oxidation to prepare nanofibers. The whole oxidation is divided into separated reactions to calculate each reaction rate at different pH values. The rate-limited reaction in this system at pH 4.5 is cellulose oxidation by TEMPO+.
Masthead
Guest Editorial
Reviews
Mechanical Recycling of Packaging Plastics: A Review
- First Published: 30 September 2020

Degradation during mechanical recycling remains the largest barrier to efficient recycling. This review presents innovations in plasticizers, fillers, stabilizers, chain extenders, and blending technologies to reverse extrusion-induced degradation for packaging polymers. Secondary uses of lower quality recyclates are also briefly discussed in order to curb land-fill.
Sustainable Photopolymers in 3D Printing: A Review on Biobased, Biodegradable, and Recyclable Alternatives
- First Published: 18 November 2020
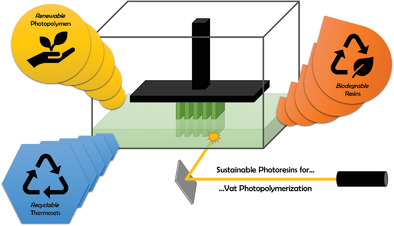
In view of the growing demand for 3D printing materials, the availability of environmentally friendly alternatives is vital. The field of sustainable materials for vat photopolymerization is evolving rapidly from biobased resins and biodegradable photopolymers to repairable and reprocessable thermosets. This review article strives to give an overview of recent advances in the last decade.
Lignin-Based Polyurethane: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives
- First Published: 18 November 2020
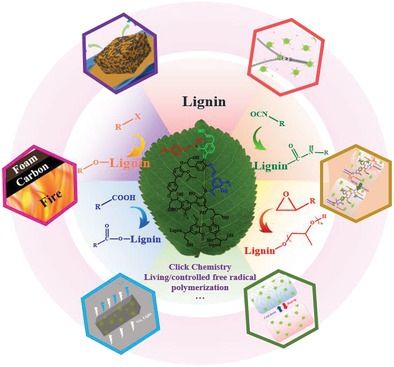
The consumption of petrochemical resources and the aggravation of environmental pollution make biomass as a replacement to petrochemicals a crucial means for sustainable development. As an excellent natural substance, scientists have applied lignin in various fields. This review focuses on recent progress, challenges, and opportunities in the design, synthesis, and functionalization of lignin-based polyurethanes.
Production and Polymerization of Biobased Acrylates and Analogs
- First Published: 12 January 2021
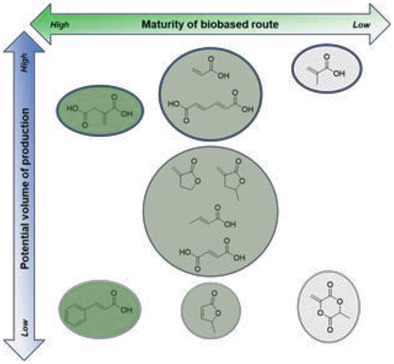
Acrylates and analogs are widely used monomers that can now be derived from renewable resources. This review aims at identifying which biobased routes are the most mature ones in the perspective of potential commercialization. Challenges in the polymerization of those potentially green monomers are also highlighted and their wide applicability is demonstrated.
Synthesis of Sustainable Polyesters via Organocatalytic Ring-Opening Polymerization of O-carboxyanhydrides: Advances and Perspectives
- First Published: 26 November 2020

Sustainable polyesters can be furnished via ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of O-carboxyanhydrides (OCAs). In this mini review, the recent progress on the organocatalytic ROP of OCAs, including the usage of thiourea-based bifunctional single-molecule organocatalysts for eliminating epimerization in OCAs polymerization is summarized.
Feature Article
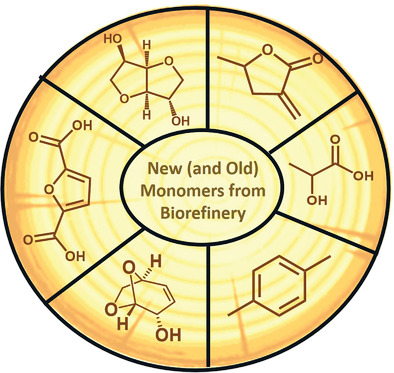
New (and Old) Monomers from Biorefineries to Make Polymer Chemistry More Sustainable
- First Published: 18 November 2020
Research Article
Thermal Stability of Bio-Based Aliphatic-Semiaromatic Copolyester for Melt-Spun Fibers with Excellent Mechanical Properties
- First Published: 18 December 2020
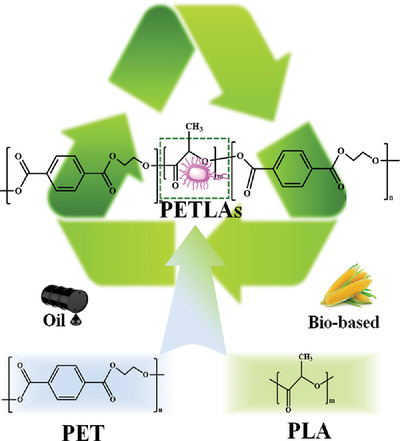
Bio-based flexible aliphatic poly(lactic acid) is introduced into polyethylene terephthalate through copolymerization to prepare poly(ethylene terephthalate-co-lactic acid) random copolyesters (PETLAs). PETLA-10 fiber has good thermal stability, and the initial decomposition temperature can reach 394 °C. Meanwhile, the mechanical properties are excellent, the breaking strength and the breaking elongation can reach 260 MPa, 130%, respectively.
Communications
Formation, Structure, and Mechanical Performance of Silk Nanofibrils Produced by Heat-Induced Self-Assembly
- First Published: 16 November 2020
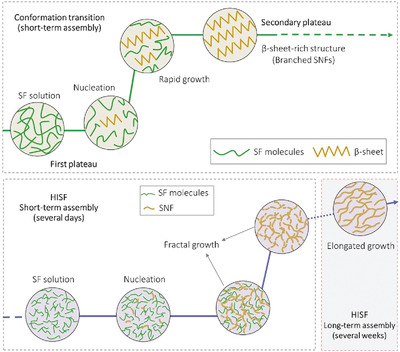
A heat-induced self-assembly (HISA) process is developed to produce water-dispersed silk nanofibril (SNF) solutions, due to its advantages, such as accessibility, scalability, and environmental friendliness. However, the assembly, and structure and physical features of HISA-SNF have not yet been studied in detail. This work, therefore, investigates the fundamental issues regarding the formation, structure, and mechanical performance of HISA-SNF.
Lignin-Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes: Lignin-Graft-Poly(ethylene glycol)
- First Published: 07 October 2020
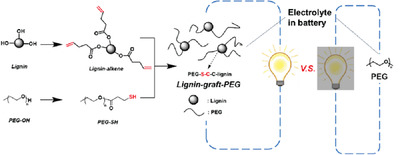
Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) is grafted onto natural lignin to synthesize a new solid polymer electrolyte, lignin-graft-PEG. The new polymer is biomass-based and a promising candidate in lithium battery applications. The lignin-graft-PEG shows higher ionic conductivity than homopolymer PEG at ambient temperature. This feature solves low conductivity issue of homoPEG at ambient temperature.
Rate-Limited Reaction in TEMPO/Laccase/O2 Oxidation of Cellulose
- First Published: 23 November 2020
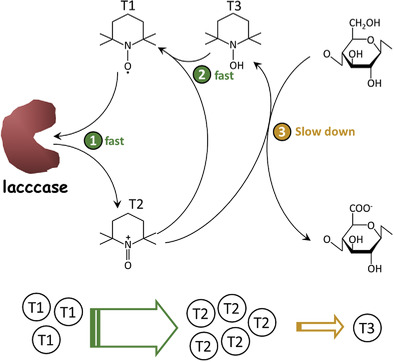
The 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy (TEMPO)/laccase/O2 oxidation is divided into individual reactions and the kinetics rate constant of each reaction is evaluated. The oxidation rate of TEMPO by laccase decreases when pH increases from 4.5 to 6.8, meanwhile the other reaction rates increase. The rate-limited reaction in the whole system is supposed to be the oxidation of cellulose by TEMPO+.
Synthesis of a Renewable, Waste-Derived Nonisocyanate Polyurethane from Fish Processing Discards and Cashew Nutshell-Derived Amines
- First Published: 09 August 2020

Fish oil extracted from waste streams is epoxidized via acid catalysis using H2O2 and reacted with CO2 using tetrabutylammonium bromide and ascorbic acid to produce a viscous organic carbonate (CFO) in excellent yields. Curing CFO with cashew nutshell-derived amine forms nonisocyanate polyurethane. Except for catalysts, solvents, and H2O2, all reacting components can be obtained from waste.
Electrical Writing to Three-Dimensional Pattern Dynamic Polysaccharide Hydrogel for Programmable Shape Deformation
- First Published: 17 August 2020
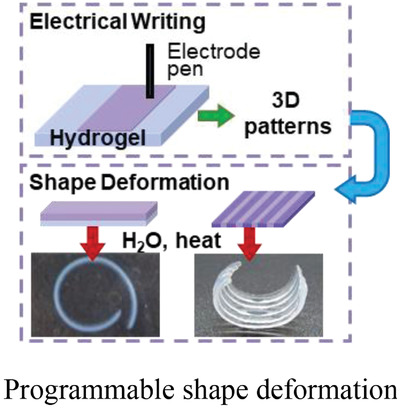
A three-dimensional pattern is formed in the chitosan/agarose hydrogel by a simple electrical writing process. By controlling the stroke of the electrical writing and changing the writing pattern, various shapes and deformations of the hydrogel can be programmed. This work provides a favorable design concept for sustainable polymer hydrogel actuators, which show great potential in soft robots and other aspects.
Organocatalytic Synthesis of Alkyne-Functional Aliphatic Polycarbonates via Ring-Opening Polymerization of an Eight-Membered-N-Cyclic Carbonate
- First Published: 09 September 2020
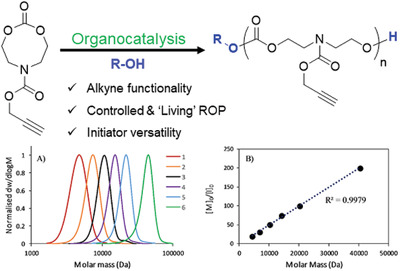
The synthesis of well-defined propargyl-functional aliphatic polycarbonates is achieved using organocatalytic ring-opening polymerization of a newly reported monomer, prop-2-yn-1-yl 2-oxo-1,3,6-dioxazocane-6-carboxylate (P-8NC) using a range of commercially available or easy-to-prepare, shelf-stable organocatalysts. The resulting homopolymers show low dispersities and end-group fidelity, with the versatility of the system demonstrated by the synthesis of telechelic copolymers and block copolymers of high molar mass.
Fully Renewable Non-Isocyanate Polyurethanes via the Lossen Rearrangement
- First Published: 16 September 2020
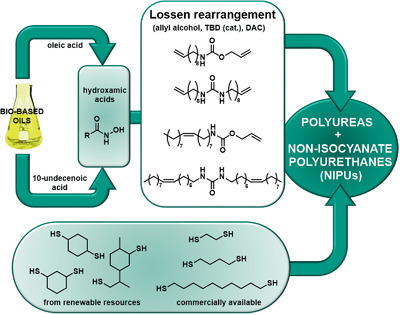
A modified procedure of the Lossen rearrangement enables the synthesis of fatty acid derived carbamates and ureas bearing two-terminal olefins. These monomers are polymerized via the highly efficient thiol–ene reaction with both renewable and commercially available dithiols to yield non-isocyanate polyurethanes as well as polyureas in a simple and straightforward fashion.
Cellulose Nanocrystal (CNC)–Latex Nanocomposites: Effect of CNC Hydrophilicity and Charge on Rheological, Mechanical, and Adhesive Properties
- First Published: 12 October 2020
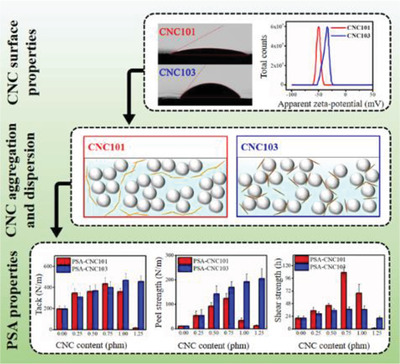
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) with different surface properties are in situ incorporated in emulsion polymerization of pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs). CNCs with less hydrophilicity and lower surface charge better associate with latex particles, form shorter aggregates (enhanced dispersion), and produce high peel strength PSAs. The more hydrophilic CNCs form longer aggregates and lead to elevated shear strength (highly elastic PSAs).
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Vitrimer: Robust Mechanical Performance and Facile Hydrothermal Decomposition in Pure Water
- First Published: 23 November 2020
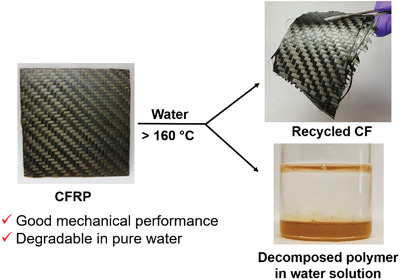
A readily recyclable and external catalyst free conventional carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) is developed. This CFRP possesses comparable tensile property to commercial analogues and exhibits shape changing property due to the thermally induced transesterification. The matrix of the CFRP is efficiently degraded in water at above 160 °C. The method developed in this work may setup a framework for the development of recyclable CFRP.
Enabling Oxygen–Sulfur Exchange Reaction to Produce Semicrystalline Copolymers from Carbon Disulfide and Ethylene Oxide
- First Published: 18 November 2020
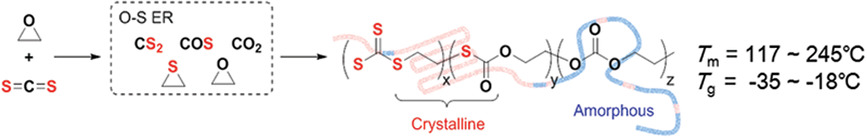
Semicrystalline poly(thiocarbonate)s from ethylene oxide and carbon disulfide are synthesized with catalysis of organic Lewis pair. The oxygen–sulfur exchange reaction during the copolymerization controlled by the type of Lewis base and the reaction conditions is harnessed to produce the polythiocarbonate with various chain microstructure and the crystalline properties.
Viability of Low Molecular Weight Lignin in Developing Thiol-Ene Polymer Electrolytes with Balanced Thermomechanical and Conductive Properties
- First Published: 16 November 2020

Softwood pine Kraft lignin and wheat straw/Sarkanda grass soda lignin are fractionated into low molecular weight fractions, functionalized, and characterized, then used in thiol-ene polymerizations to create gel polymer and solid polymer electrolytes. Thermomechanical and electrochemical properties are evaluated. Utilization of the low molecular weight lignins in this application yields conductive thiol-ene polymer electrolytes with beneficially high cationic transport.
Water-Borne Isocyanate-Free Polyurethane Hydrogels with Adaptable Functionality and Behavior
- First Published: 12 October 2020
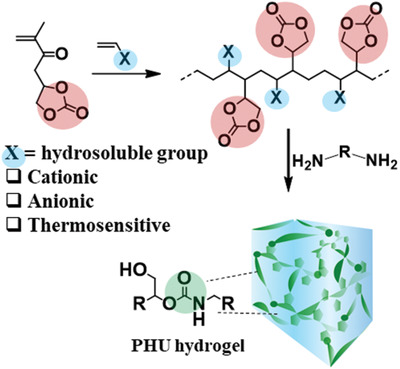
A large palette of anionic, cationic, or neutral non-isocyanate polyurethane hydrogels is prepared in water at room temperature without catalyst from readily available diamines and new hydrosoluble polymers bearing cyclic carbonates. The partial hydrolysis of cyclic carbonates is exploited to generate CaCO3 particles that reinforce the hydrogel. Thermoresponsive hydrogels are also prepared from new thermoresponsive cyclic carbonate bearing polymers.
Highly Isoselective Ring-Opening Polymerization of rac-Lactide Using Chiral Binuclear Aluminum Catalyst
- First Published: 16 November 2020
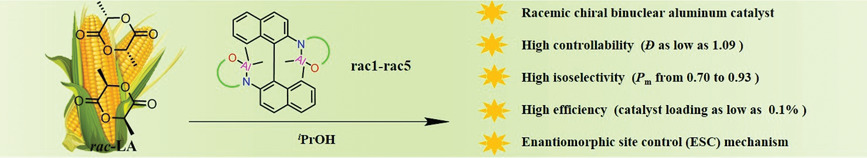
Five binaphthalene-based chiral binuclear aluminum complexes are synthesized and characterized, which exhibit highly polymerization activity and isoselectivity toward the polymerization of rac-lactide (Pm up to 0.93). Even with a 0.1% catalyst loading, polylactide with Pm of 0.83 can still be obtained. These binuclear aluminum catalysts followed the enantiomorphic site control mechanism.
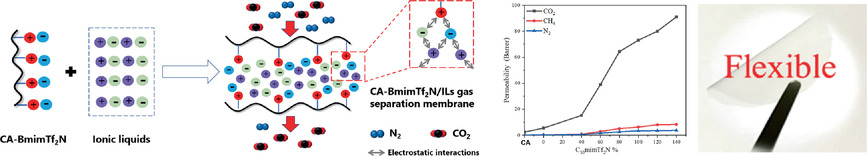
Immobilization of Ionic Liquids with a New Cellulose Ester Containing Imidazolium Cation for High-Performance CO2 Separation Membranes
- First Published: 18 November 2020
Synthesis and Fluorescent Thermoresponsive Properties of Tetraphenylethylene-Labeled Methylcellulose
- First Published: 18 November 2020
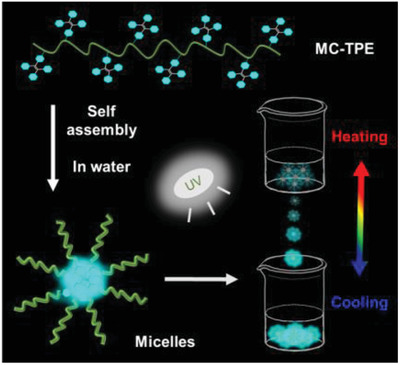
Methylcellulose (MC) is labeled by tetraphenylethylene (TPE) to obtain the water-soluble fluorescent MC-TPE. MC-TPE self-assembles into micelles in aqueous solution and shows thermoresponsivity and thermoreversibility in size, transmittance, and fluorescence. Moreover, MC-TPE exhibits nontoxicity and biocompatibility to be applied in cell imaging.
Green Fabrication of Highly Conductive Paper Electrodes via Interface Engineering with Aminocellulose
- First Published: 16 November 2020
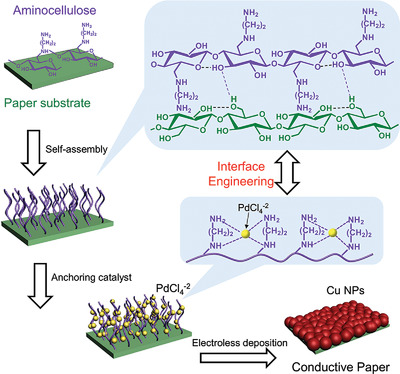
Aminocellulose is successfully utilized as interface layers for the fabrication of conductive paper electrodes by full solution-processed electroless deposition. It can not only anchor the catalysts but also bind the deposited Cu nanoparticles with paper substrates, leading to highly conductive and stable papers.
Insight into Morphology Change of Chitin Microspheres using Tertiary Butyl Alcohol/H2O Binary System Freeze-Drying Method
- First Published: 18 November 2020

The present work explores the morphology change of chitin microspheres over the tertiary butyl alcohol/H2O binary system freeze-drying route. Especially, 20 wt% tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) freeze-drying route is found to be conducive to split chitin microspheres and other polysaccharides microspheres, this opens a window for observing the internal structure of microscale materials. The underlying mechanism of all morphology change is thoroughly studied.
Aqueous Polymer Modification of Cellulose Nanofibrils by Grafting-Through a Reactive Methacrylate Group
- First Published: 18 November 2020
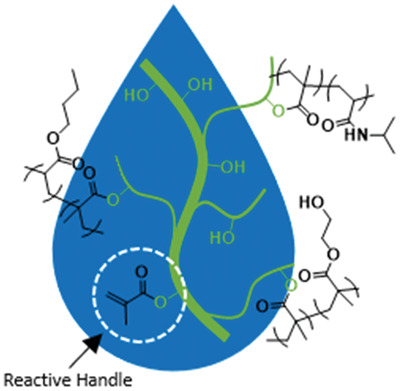
An entirely aqueous modification of cellulose nanofibrils with a diverse range of (meth)acrylamide and (meth)acrylate monomers by grafting-through polymerization of a reactive methacrylate handle is shown. The degree of functionalization of the resulting products is tuned by varying monomer to cellobiose mole ratio. Polymer modifications retain nanoscale fibril morphology.
Enantioselective Crystallization of Diglycerol Dicarbonate: Impact of the Microstructure on Polyhydroxyurethane Properties
- First Published: 25 November 2020

The enantioselective crystallization of diglycerol dicarbonate (DGDC) is performed in specific conditions, yielding two types of crystals, respectively, square transparent and needle-like crystals, which can be easily separated. From these DGDC crystals, a series of poly(hydroxyurethane)s, suppress the second polyhydroxyurethanes, are prepared that exhibit different features and properties with respect to the DGDC microstructure.
Synergetic Effect of Dopamine and Alkoxysilanes in Sustainable Non-Isocyanate Polyurethane Adhesives
- First Published: 26 November 2020
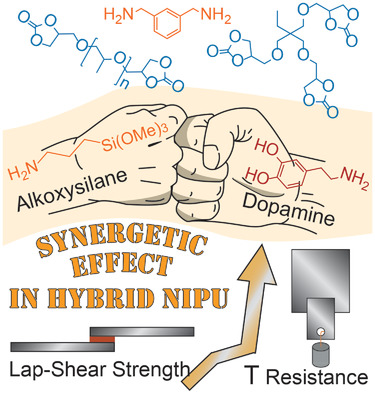
Hybrid non-isocyanate polyurethanes are prepared through polyaddition of dicarbonates and an aromatic diamine. Dopamine and an alkoxysilane compound are added, enhancing the adhesive, lap-shear strength, as well as shear adhesion failure temperature, and rheological properties. Moreover, the importance of the hard/soft monomer balance in the formulation to obtain optimal performances is demonstrated.