Editor-in-Chief: David Huesmann, Publisher: Kirsten Severing
We feature contributions on membranes, sensors, sustainability, composites, fibers, foams, 3D printing, actuators as well as energy and electronic applications. As a trusted home for polymer science research, our journal is managed by experienced in-house editors who ensure a fast and fair handling of all manuscripts.
Journal Metrics
- 8.9CiteScore
- 4.6Journal Impact Factor
- 53%Acceptance rate
- 23 days Submission to first decision
On the Cover
Articles
Characterization and Drug Delivery Potential of Biodegradable PCL/PLA Scaffolds Fabricated via Solvent‐Cast Direct‐Writing
- 21 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
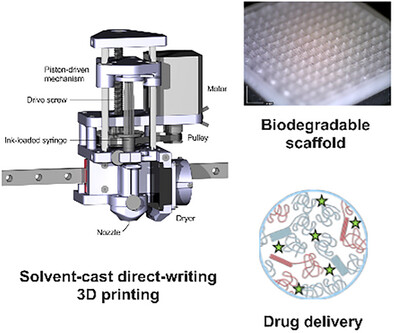
A novel solvent-cast direct-writing method is demonstrated for 3D printing biodegradable scaffolds for drug delivery. This technique enables the fabrication of intricate biodegradable architectures loaded with thermosensitive drugs. Thermal, physical, mechanical, and dissolution studies highlight how polymer composition influences drug release, expanding the potential of this fabrication method for advanced tissue engineering and drug delivery applications.
Mesenchymal Stem Cell‐Engrafted Bacterial Cellulose and Graphene Oxide Scaffolds Enhance Peripheral Nerve Repair in a Rat Model
- 21 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
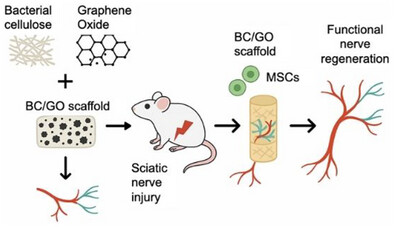
This study investigates the use of graphene oxide-decorated bacterial cellulose (BC/GO) scaffolds combined with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to enhance axonal regeneration after sciatic nerve injury in rats. Graphene oxide is embedded monodispersely into the BC fibrillar matrix. The composite scaffold shows potential to support functional nerve regeneration by improving cellular interactions and tissue repair.
Nanofiber‐Coated CF/PEEK Composite: Boosting Osteogenesis for Enhanced Bone Grafting
- 18 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
Front Cover: This illustration depicts the integration of 3D printing and electrospinning to fabricate nanofiber-coated scaffolds. Incorporating hydroxyapatite-loaded nanofibers significantly boosts osteogenesis, hydrophilicity, and cell compatibility. This multifunctional surface engineering strategy offers a powerful route toward next-generation bone graft substitutes with tailored mechanical strength, improved bioactivity, and enhanced osteogenesis. More details can be found in article 2400286 by Norbert Radacsi and co-workers.
Plasma Carbonization of Sustainable Lignin Fiber‐Derived Papers for Supercapacitor Electrodes
- 16 July 2025
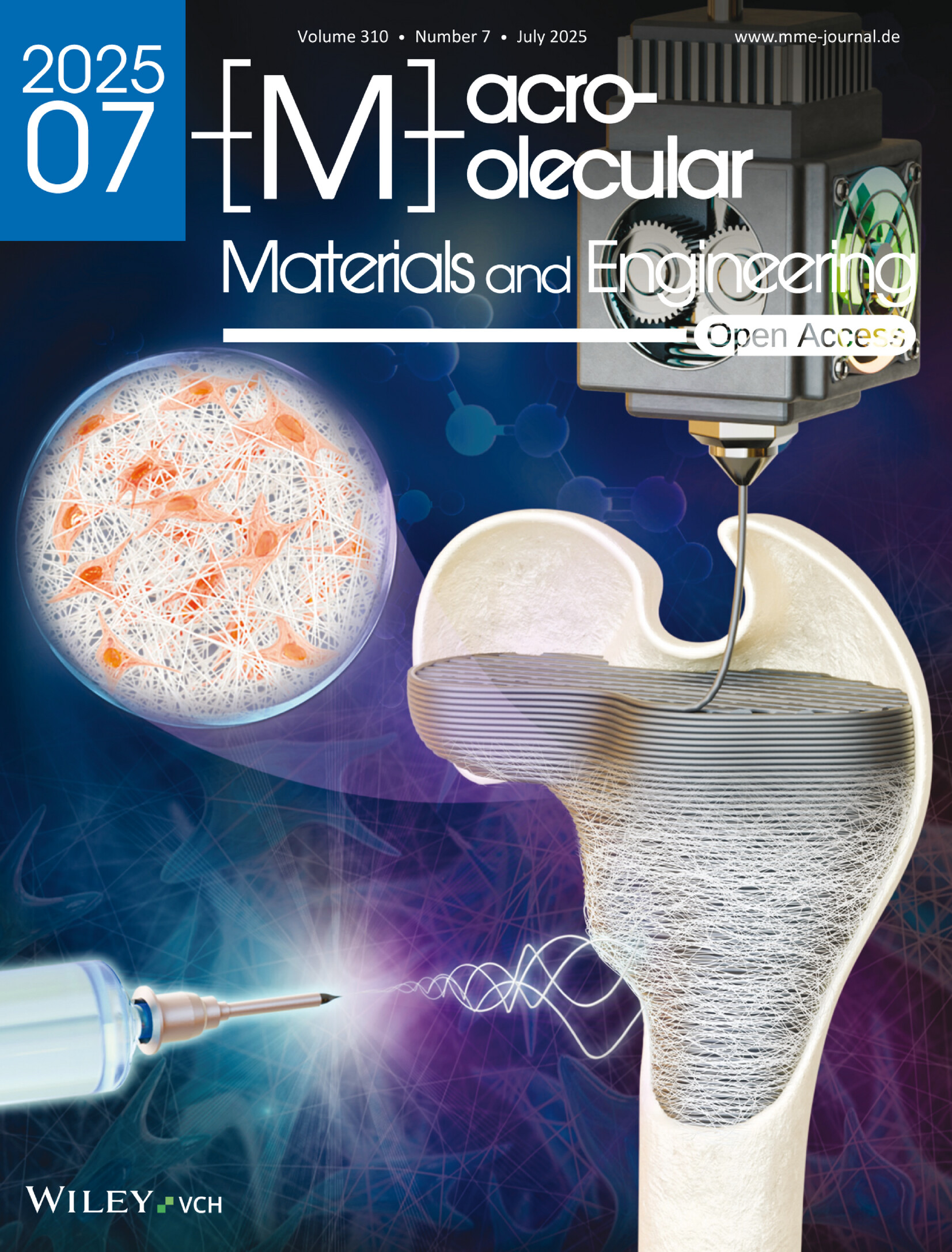
Processing Characteristics of High Molecular Weight Polyethylene in Laser Sintering: The Role of Carbon Black Concentration and Processing Strategy for Diode Laser Sintering Machines
- 13 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
Because of its high viscosity, HMWPE needs an exact adjustment between material and processing parameters as well as printing strategy. The concentration of carbon black fillers influences the processability of HMWPE in PBF-LB/P. The mechanical properties of printed parts can be optimized by volume energy density and absorption at the optimum carbon black concentration.
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
Biofibres, biodegradable polymers and biocomposites: An overview
- 1-24
- 24 May 2000
Progress Report on Natural Fiber Reinforced Composites
- 9-26
- 19 June 2013
Graphical Abstract
Recent economic and ecological issues have encouraged the development of new materials with less environmental impact, produced from renewable resources with a high level of biodegradability. Therefore, all over the world, there is rising acceptance in materials demonstrating efficient use of renewable resources. Natural fiber reinforced bio-based polymers can replace synthetic composites with cost equivalence and better properties. This Review focuses on progress made on natural fiber reinforced composites in recent years.
Advances in Piezoelectric Polymer Composites for Energy Harvesting Applications: A Systematic Review
- 27 November 2018
Graphical Abstract
The versatility of different piezoelectric materials for energy harvesting applications is explored throughout this review while giving special attention to piezoelectric polymers and composites. It has been revealed that these materials could be a better alternative to piezo-ceramics, in terms of mechanical flexibility, suitable voltage with sufficient power output, lower manufacturing cost, and rapid processing.
A Review: Natural Fiber Composites Selection in View of Mechanical, Light Weight, and Economic Properties
- 10-24
- 2 September 2014
Graphical Abstract
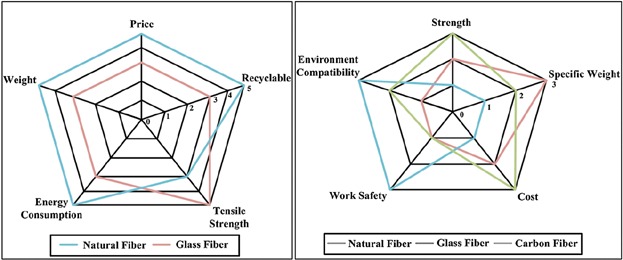
Due to light weight, low cost, and reasonable strength, natural fiber are replacing synthetic fibers and because of these properties their applications in automobile industries were increased. Comparisons of material indices are made to investigate the possibility to use natural fiber composites instead of some conventional and non-conventional materials for beam and panel structures.
Latest news
Recent issues
- Volume 310, Issue 7July 2025
- Volume 310, Issue 6June 2025
- Volume 310, Issue 5May 2025
- Volume 310, Issue 4April 2025