Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Extended benchmark set for lattice parameters of inorganic solids
- Pages: 2702-2709
- First Published: 12 August 2024
SOFTWARE NOTE
Clustering one million molecular structures on GPU within seconds
- Pages: 2710-2718
- First Published: 14 August 2024
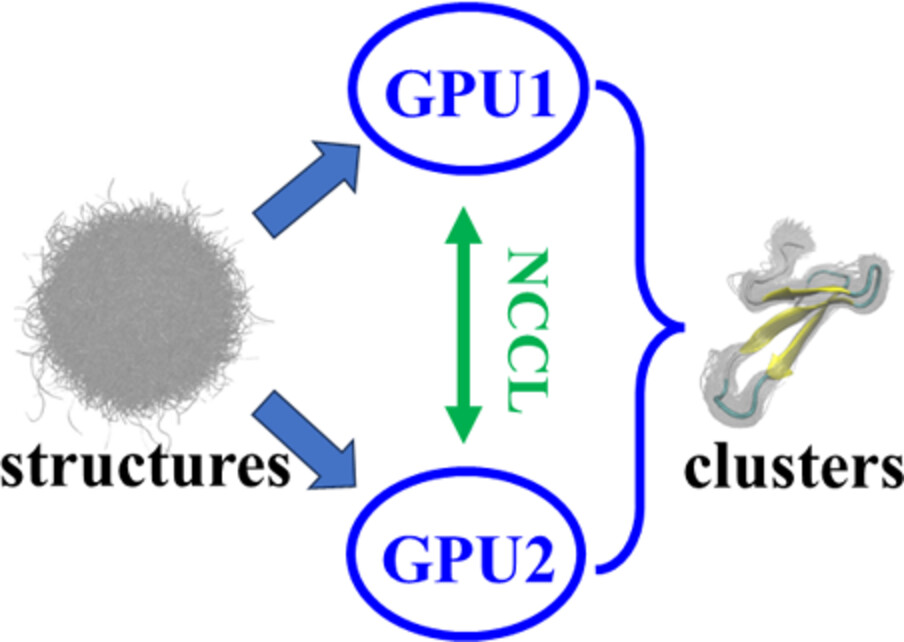
In this paper, we implement a GPU-accelerated molecular structure clustering module in FSATOOL (https://github.com/fsatool/fsatool.github.io). It supports K-medoids method, best-fit RMSD metric, multi-GPU platform and single or double precision data type. The clustering quality is indicated by Davies-Bouldin index (DBI) and Residue-Similarity index (RSI). Performance test shows that the program is able to complete the clustering calculation for one million snapshots of a 33-residue protein in a few seconds. This is hundreds of times faster than CPU. The program can be used as a high-throughput analysis tool for long molecular dynamics simulation trajectories.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Structure and intermolecular interactions in ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide and its aqueous solutions investigated by vibrational spectroscopy and quantum chemical computations
- Pages: 2719-2726
- First Published: 14 August 2024
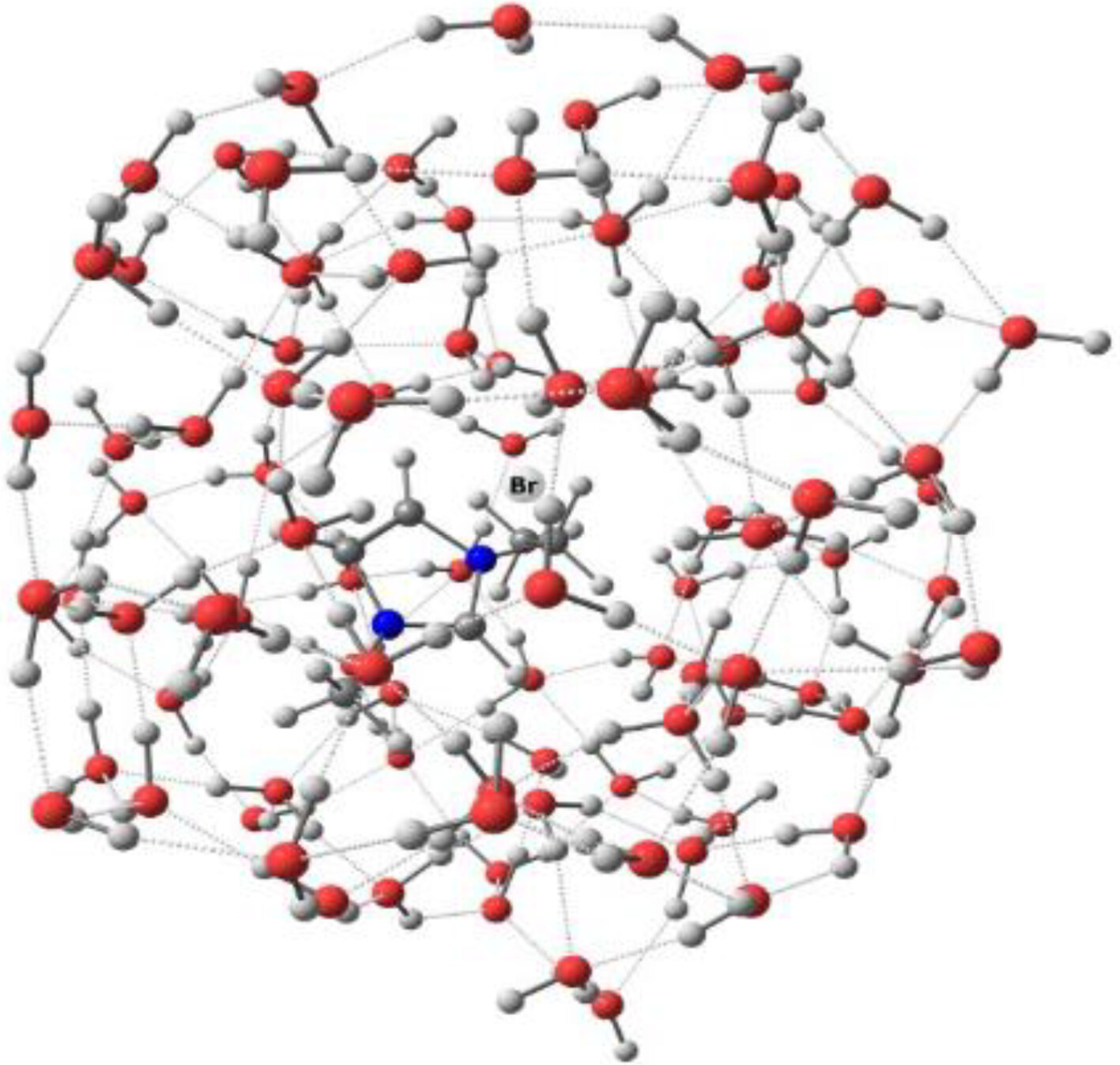
DFT calculations of vibrational spectra of cluster models of ionic liquid (IL) and its aqueous solutions accurately reproduce the experimental spectra. This suggests a close correspondence of the cluster models to actual neat and aqueous IL, and allows to distinguish spectral signatures of contact and solvent-shared ion pairs.
Simulating the full spin manifold of triplet-pair states in a series of covalently linked TIPS-pentacenes
- Pages: 2727-2738
- First Published: 14 August 2024
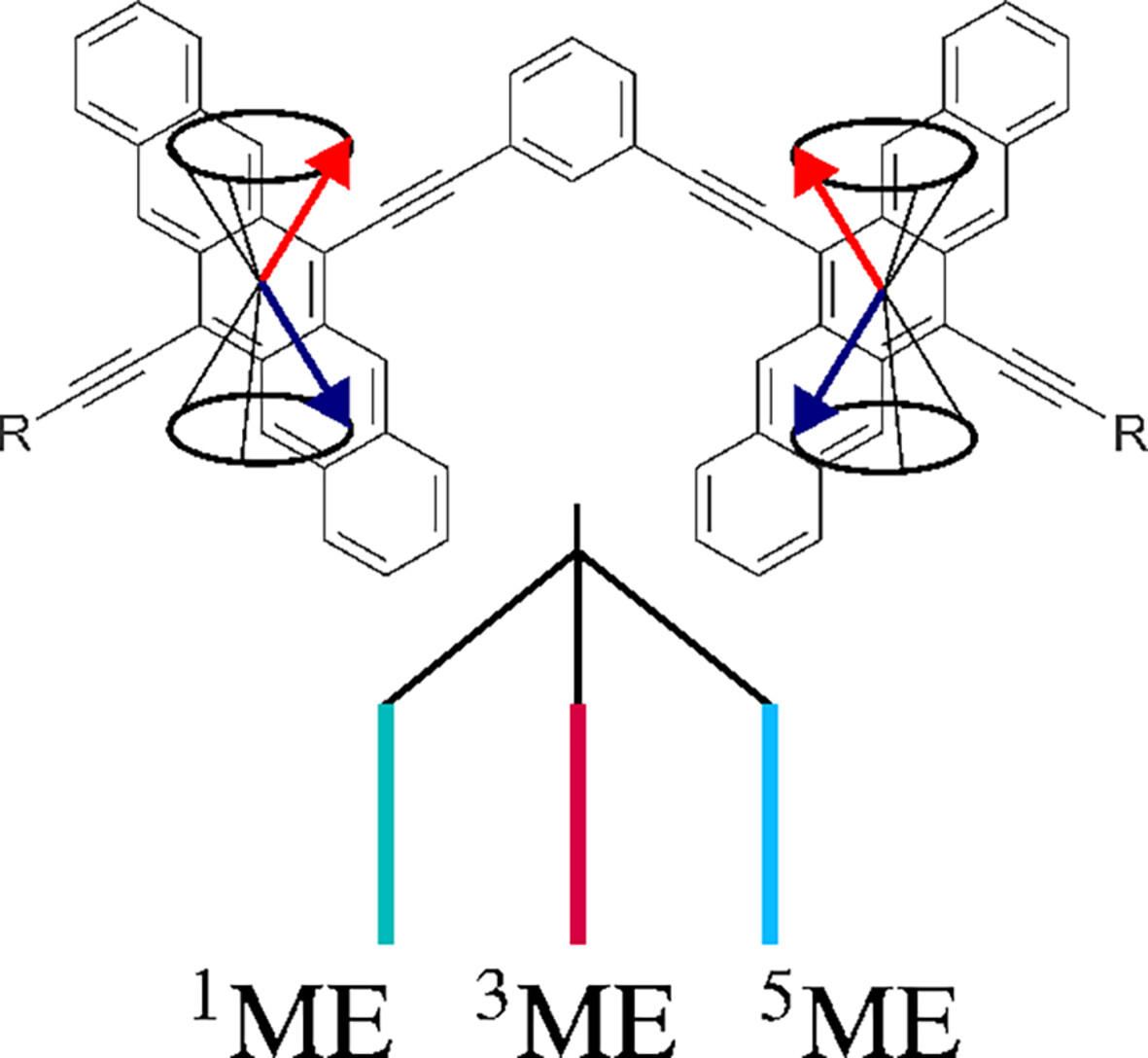
Singlet fission (SF) is a promising pathway to generate multiple charge carriers from a single photon. Possible applications reach from photovolatic cells to quantum computing. A key intermediate in the process is the singlet-coupled triplet pair or multi-excitonic (ME) state. Despite many computational investigations emphasising the ME state, studies exploring the full spin manifold are scarce. This work investigates singlet, triplet and quintet ME species in a series of well-known covalently linked pentacene derivatives.
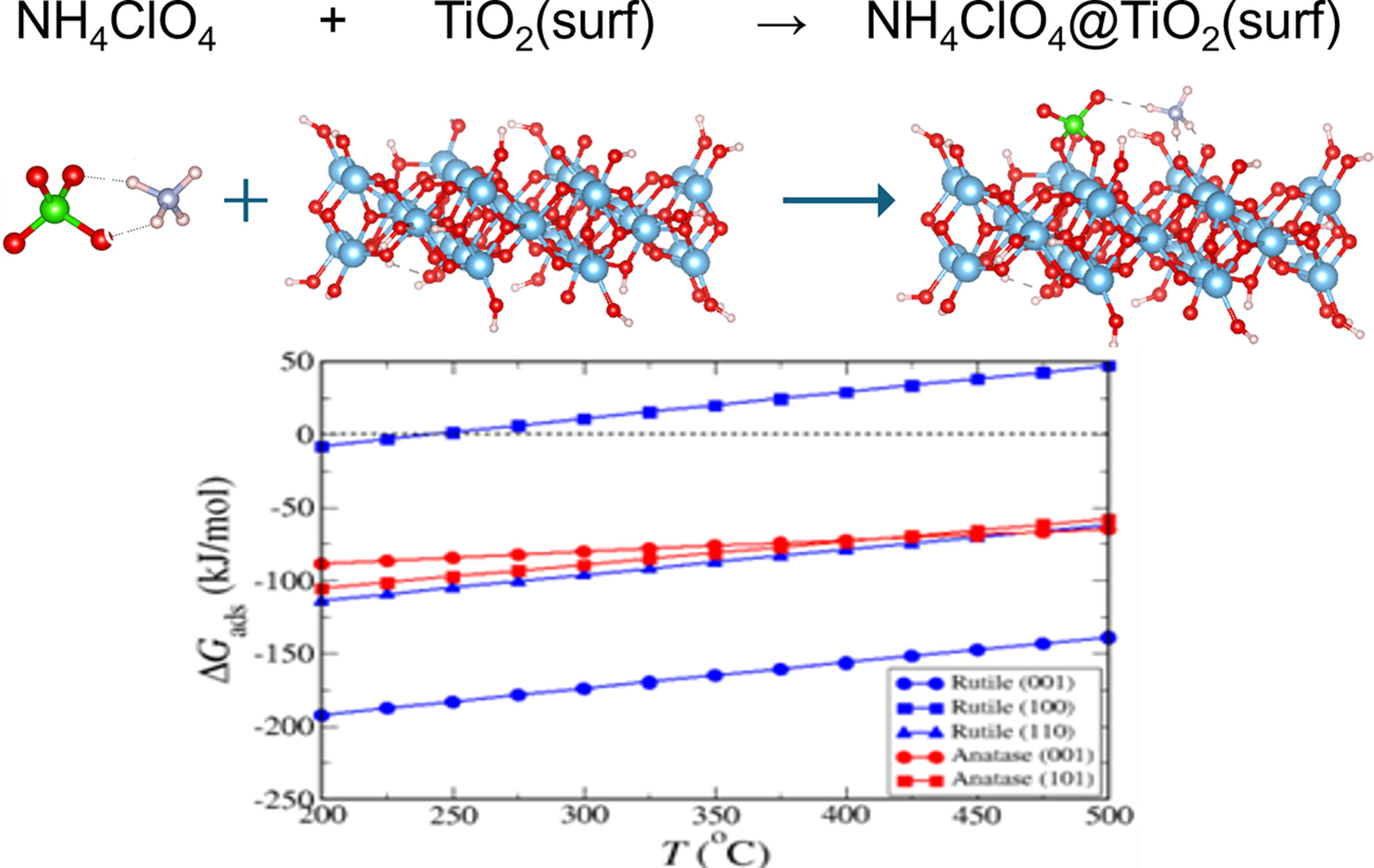
Modeling adsorption reactions of ammonium perchlorate on rutile and anatase surfaces
- Pages: 2739-2748
- First Published: 14 August 2024
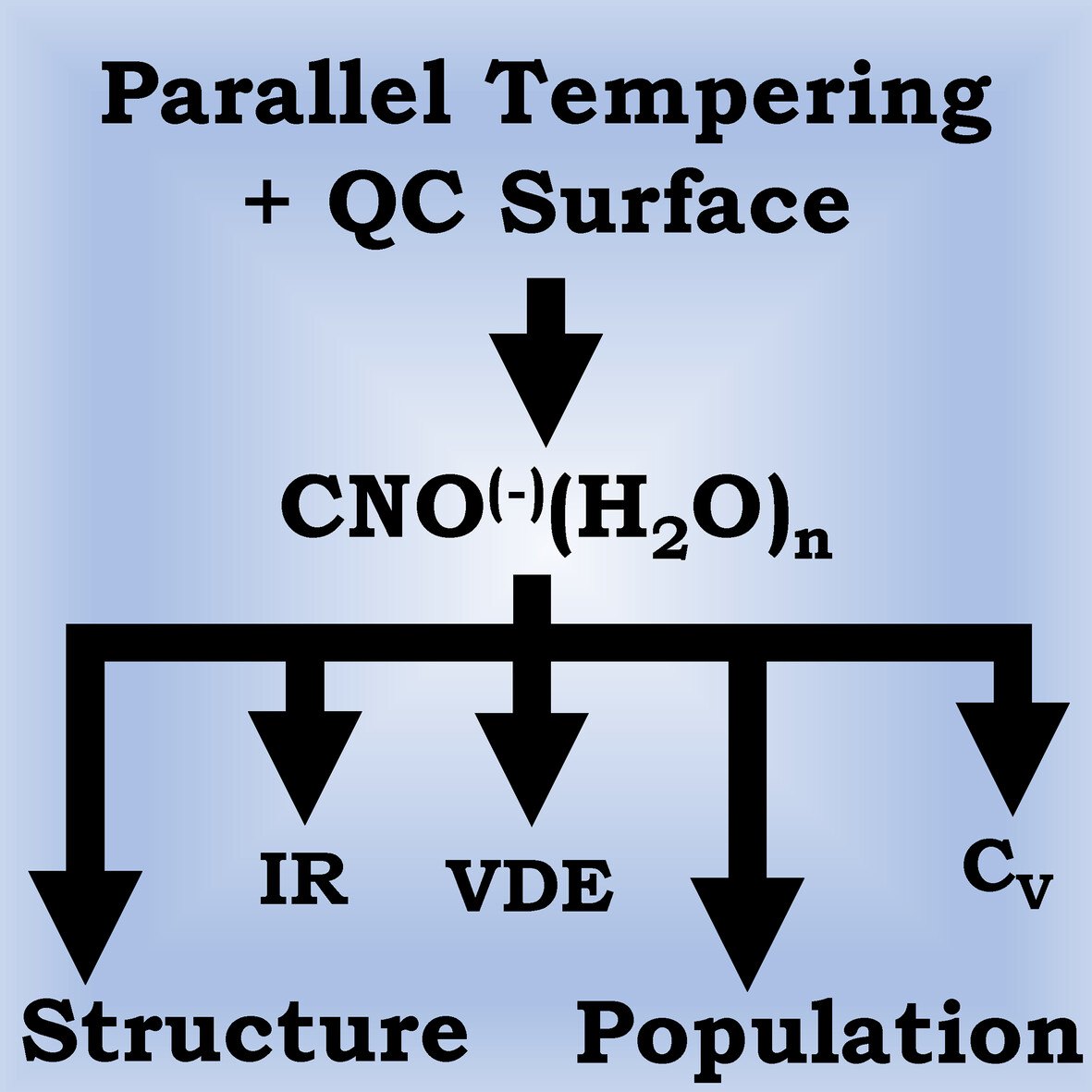
Energetics and spectroscopic studies of clusters and the temperature dependencies of the isomers: An approach based on a combined recipe of parallel tempering and quantum chemical methods
- Pages: 2749-2763
- First Published: 16 August 2024
PGA: A new particle swarm optimization algorithm based on genetic operators for the global optimization of clusters
- Pages: 2764-2770
- First Published: 17 August 2024
The C-terminal self-binding helical peptide of human estrogen-related receptor γ can be druggably targeted by a novel class of rationally designed peptidic antagonists
- Pages: 2771-2777
- First Published: 19 August 2024
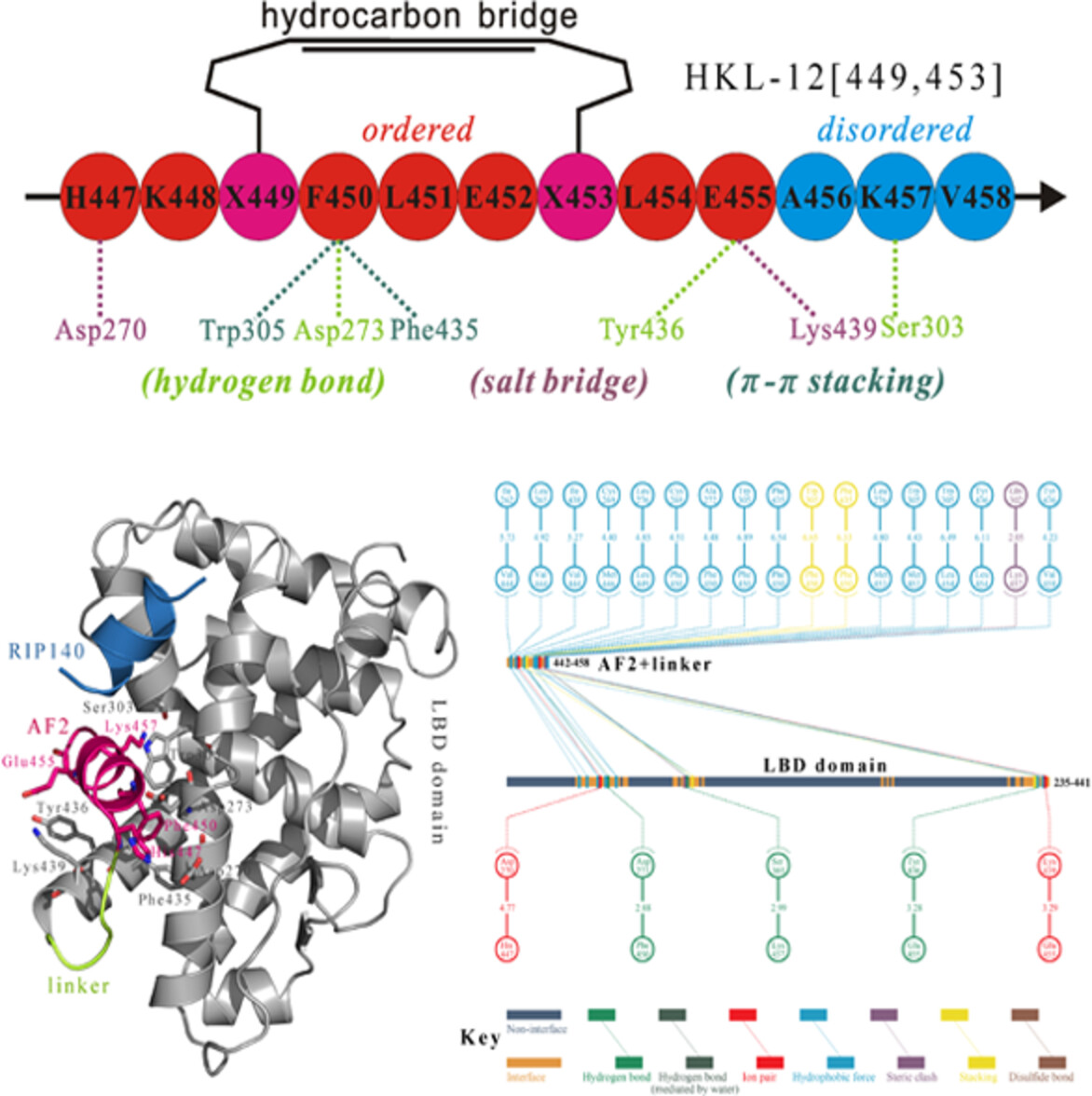
A strategy is described to inactivate ERRγ by competing with the native AF2 helical tail for its cognate binding site on the protein surface of ERRγ ligand-binding domain. A class of peptidic antagonists is derived from the ERRγ AF2 region characterized by a self-binding peptide, which can rebind potently to the AF2-cognate site by reducing its intrinsic disorder with hydrocarbon stapling.
Temperature effects on the branching dynamics in the model ambimodal (6 + 4)/(4 + 2) intramolecular cycloaddition reaction
- Pages: 2778-2785
- First Published: 21 August 2024

Simulations of bifurcation dynamics, emanating from the ambimodal transition state, were conducted across a broad temperature range. The distribution of branching fractions displayed significant dependence on both temperature and potential energy landscapes. As temperature increases, trajectories tend to linger for longer periods in the intermediate region of the potential energy surface.
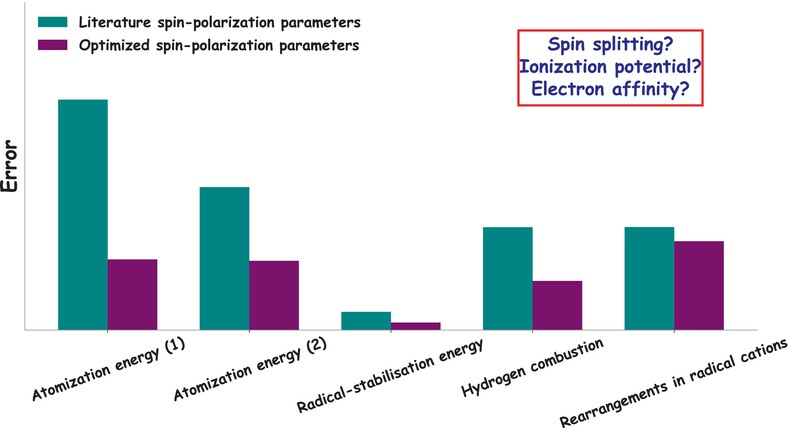
Spin parameter optimization for spin-polarized extended tight-binding methods
- Pages: 2786-2792
- First Published: 22 August 2024
Energy and spectroscopic parameters of neutral and cations isomers of the CnH2 (n = 2–6) families using high-level ab-initio approaches
- Pages: 2793-2804
- First Published: 23 August 2024
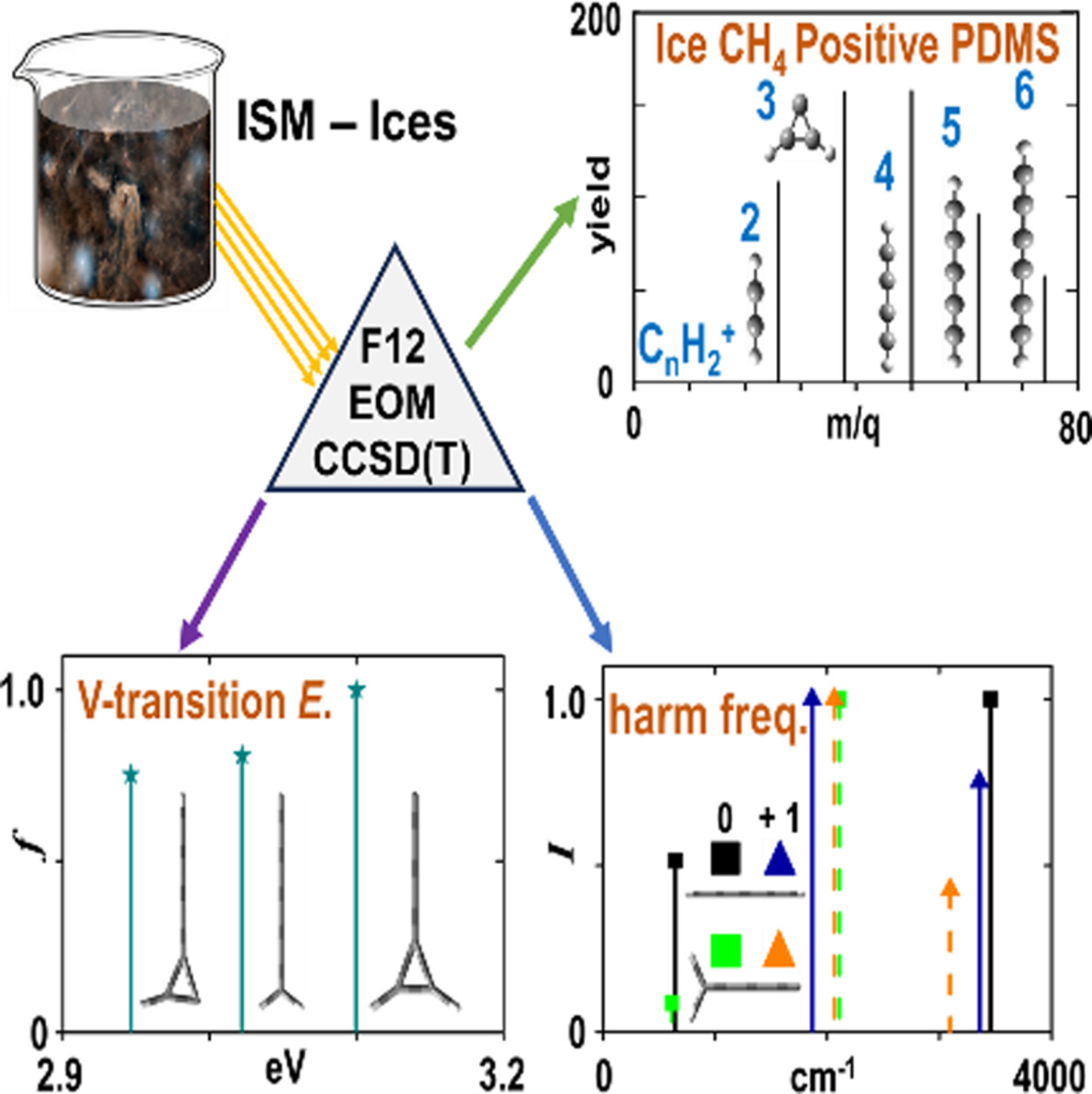
Based on the results of coupled-cluster methodologies, the cationic species of the CnH2 (n = 2 – 6) families, previously detected in the ion-induced desorption of solid methane, were identified. The calculated harmonic vibrational frequencies, vertical transition energies, and oscillator strengths allow for distinguishing between the neutral and cationic CnH2 species. Reliable computational data can facilitate the interpretation of interstellar observations.
Molecular dynamics of liquid–electrode interface by integrating Coulomb interaction into universal neural network potential
- Pages: 2805-2811
- First Published: 23 August 2024
All-body concept and quantified limits of cooperativity and related effects in homodromic cyclic water clusters from a molecular-wide and electron density-based approach
- Pages: 2812-2824
- First Published: 27 August 2024

Cooperativity, defined as intermolecular delocalization of electrons, increases nonlinearly with the size of a cyclic water clusters. O-atoms provide a vast majority of electrons that “travel mainly on a privileged density highway” (⋅⋅⋅O–H⋅⋅⋅O–H⋅⋅⋅O–H⋅⋅⋅) using H-bond density bridges linking water molecules.
GNN-DDAS: Drug discovery for identifying anti-schistosome small molecules based on graph neural network
- Pages: 2825-2834
- First Published: 27 August 2024
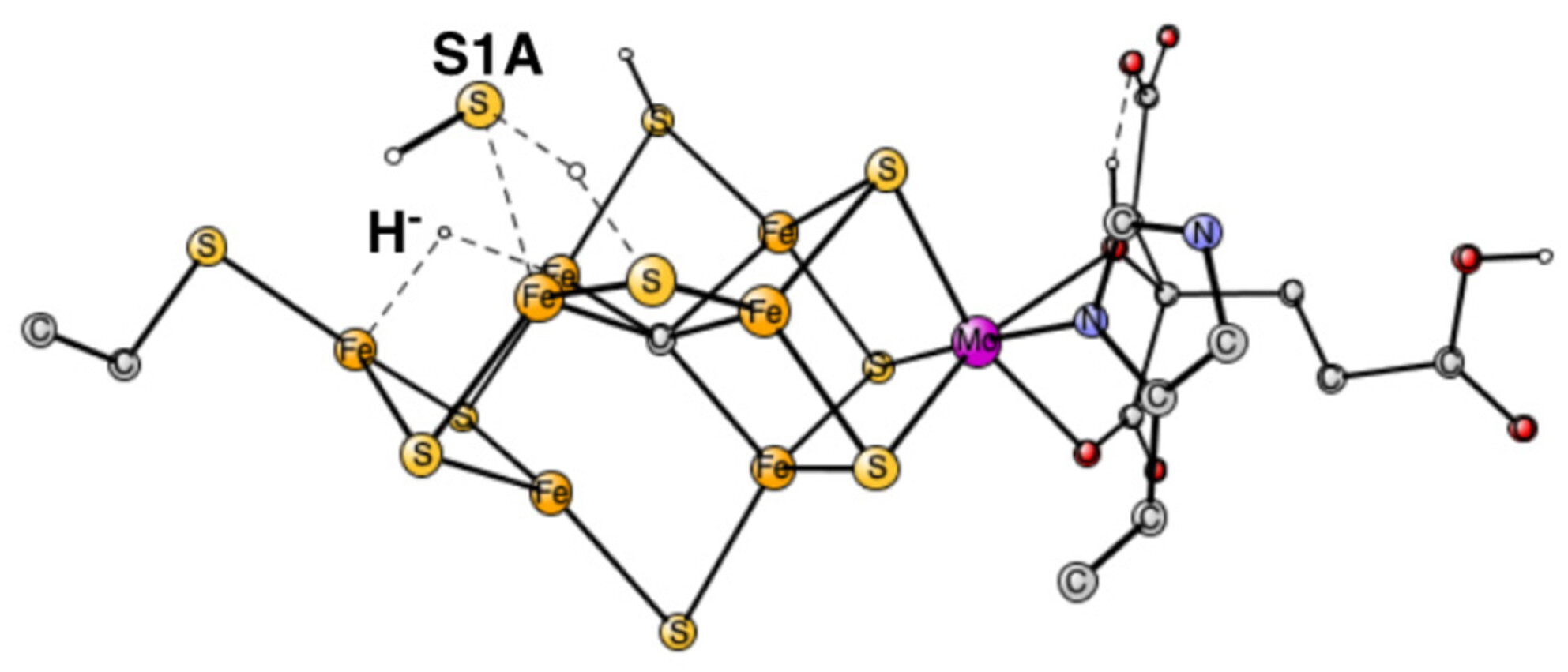
Sulfide release and rebinding in the mechanism for nitrogenase
- Pages: 2835-2841
- First Published: 27 August 2024
Optimized infrared spectrum of mixtures
- Pages: 2842-2847
- First Published: 28 August 2024
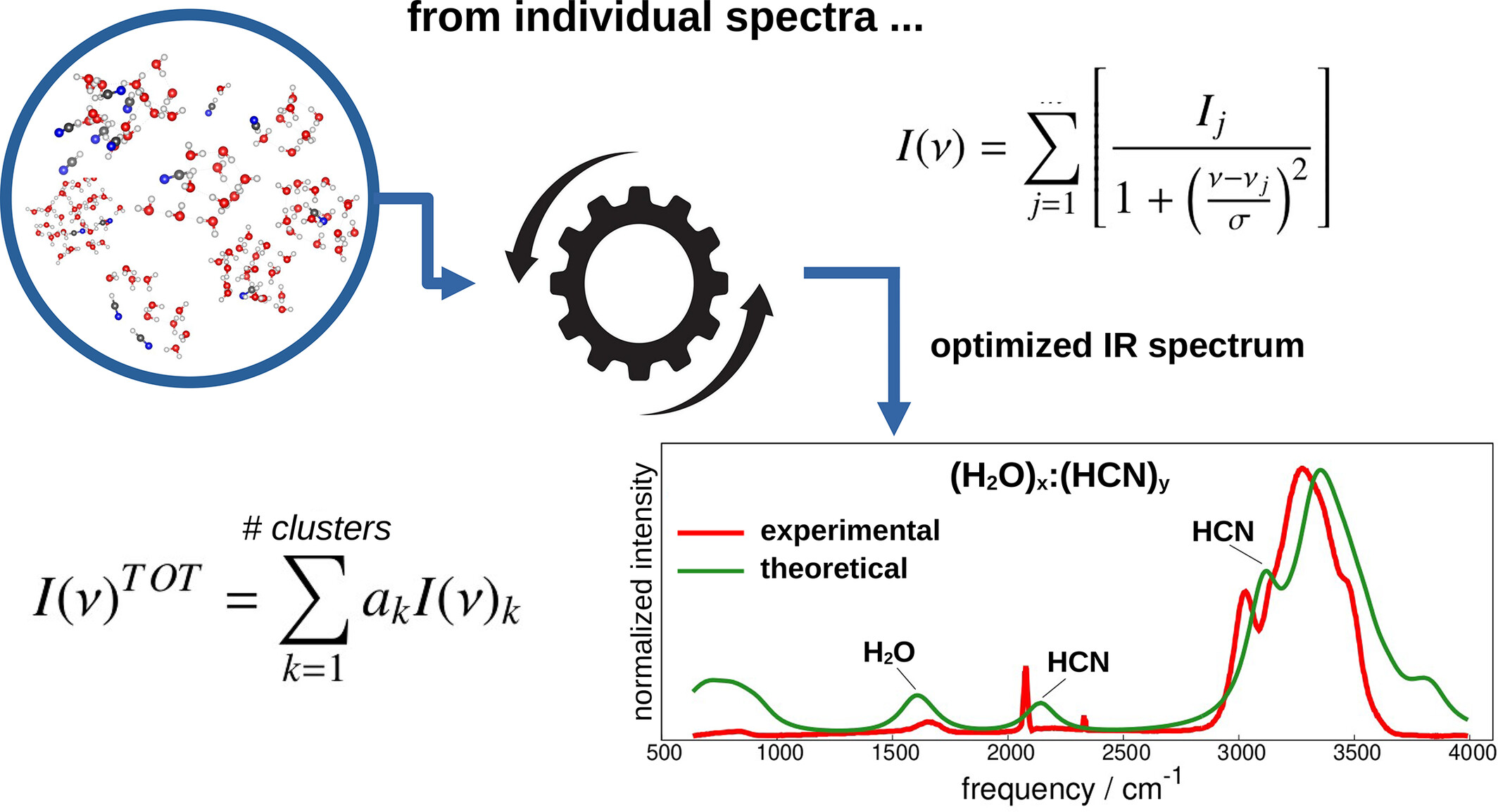
-
Density functional theory including the solvent model has been used for studying the IR spectrum of HO:HCN mixtures.
-
The solvent effect is found crucial to enhance accuracy compared to pure gas-phase modeling.
-
Interestingly, the employed dielectric constant value has shown no significant impact on the final spectrum.
-
A simple methodology is suggested to minimize the root mean square deviation between the calculated and experimental data. This novel approach not only enhances the quality of the final IR spectrum of HO:HCN but suggests itself also for capturing relevant spectral features in the case of other mixtures.
An algorithm for very high pressure molecular dynamics simulations
- Pages: 2848-2861
- First Published: 29 August 2024
Delocalization-ratio analysis of 3-center bonding in position-space for closo-boranes and related systems: Approaching the styx picture and beyond
- Pages: 2862-2877
- First Published: 30 August 2024
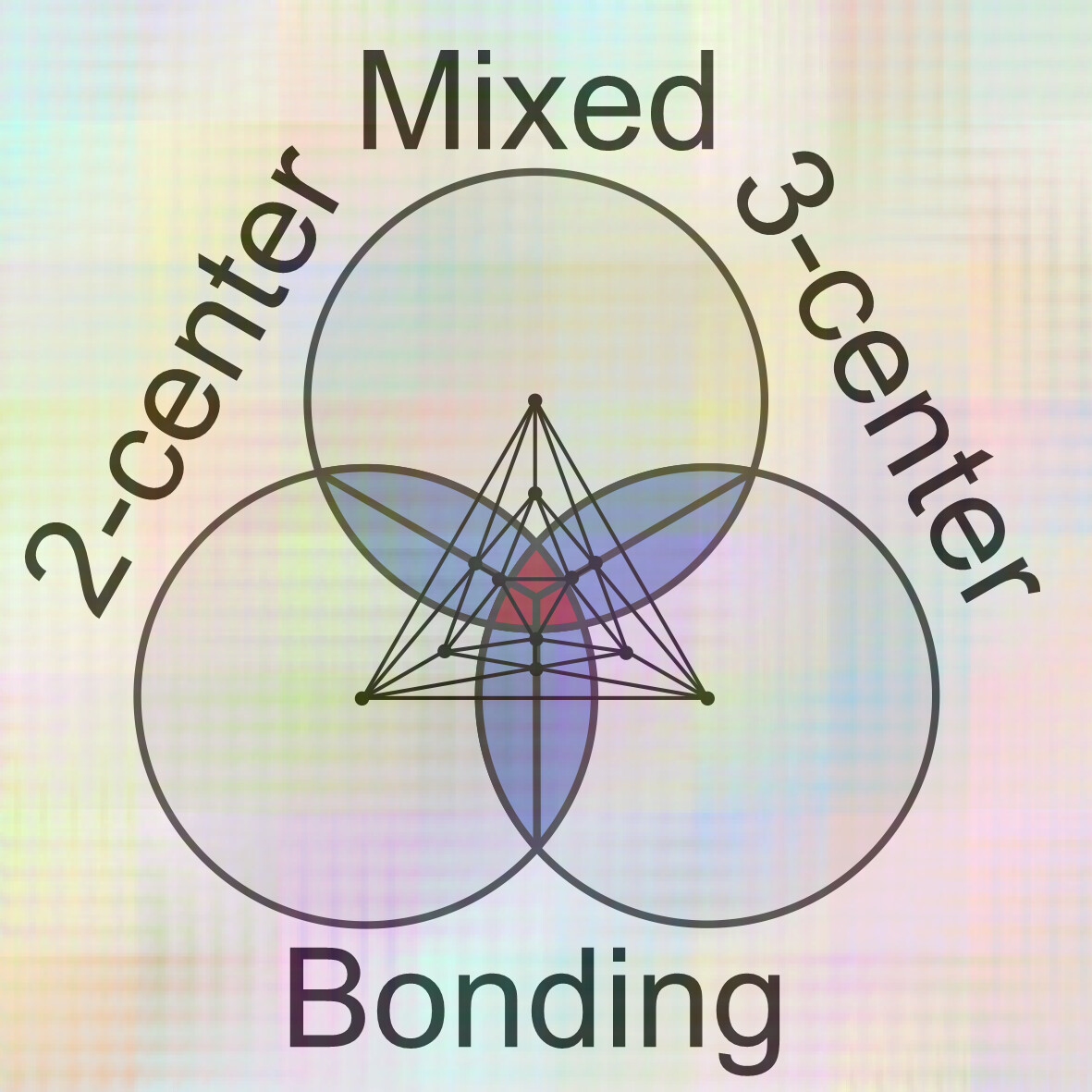
The Wade's rules and Lipscomb's styx approach constitute a conceptual basis of chemical bonding in closo hydroborane clusters and similar compounds. Based on 3-center electron sharing indices obtained from DFT wavefunctions, the DR approach for analysis of multicenter bonding in clusters and intermetallic compounds is presented. By triangulation of multicenter bonding, it is capable characterizing the clusters' global mixed 2- and 3-center type of bonding and decompose it into local bond and triangle contributions.
How accurate can Kohn-Sham density functional be for both main-group and transition metal reactions
- Pages: 2878-2884
- First Published: 30 August 2024
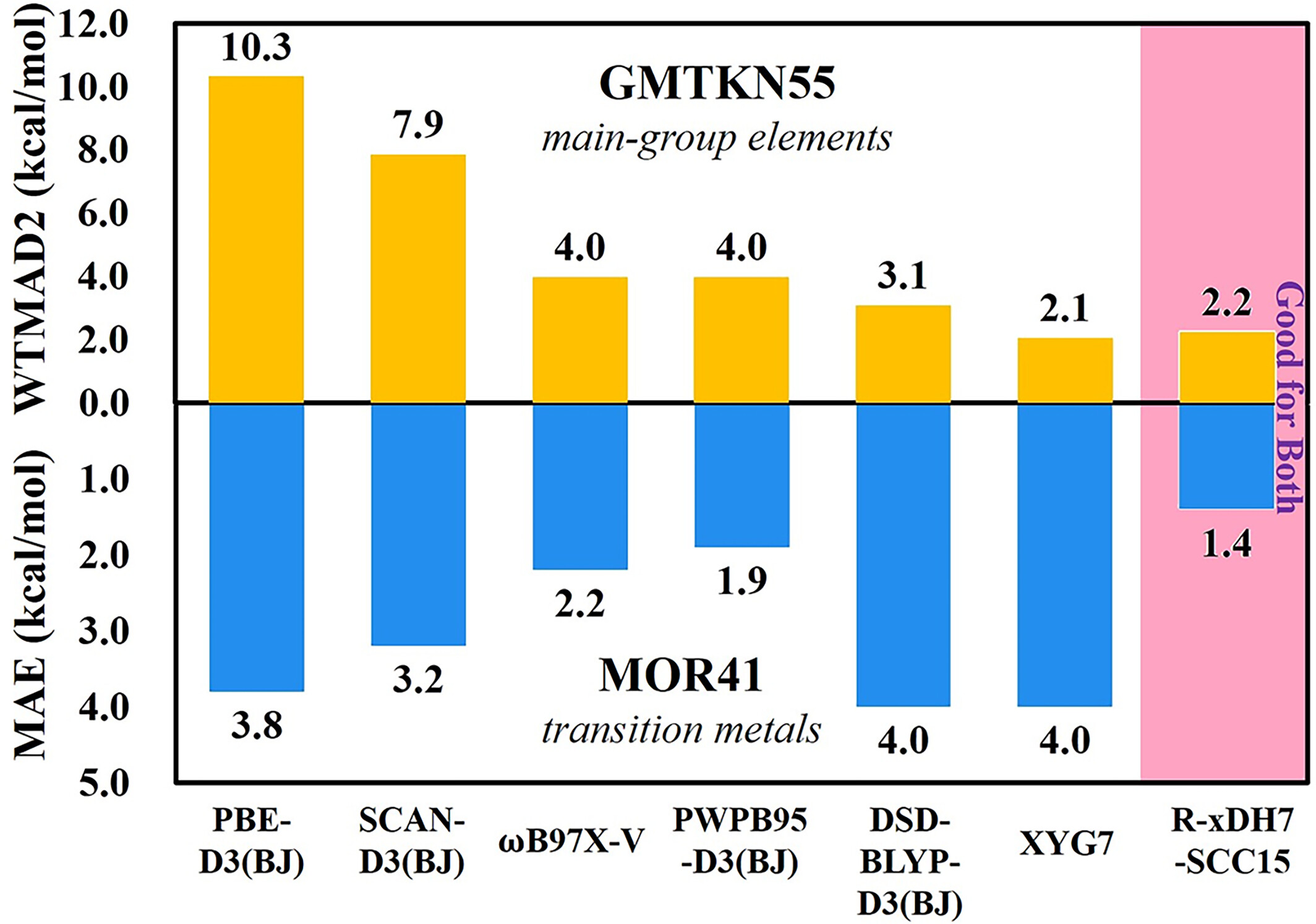
Taking advantage of the Rust-based Electronic-Structure Toolkits (REST), we examine the XYG3-type doubly hybrid (xDH) methods. Our study ushers in a pivotal advance with a renormalized xDH method R-xDH7-SCC15, which not only outperforms other methods for main-group chemistry, but also achieves an unprecedented accuracy for transition-metal chemistry.
Photophysical properties of donor (D)–acceptor (A)–donor (D) diketopyrrolopyrrole (A) systems as donors for applications to organic electronic devices
- Pages: 2885-2898
- First Published: 30 August 2024
Ab initio electronic absorption spectra of para-nitroaniline in different solvents: Intramolecular charge transfer effects
- Pages: 2899-2911
- First Published: 30 August 2024
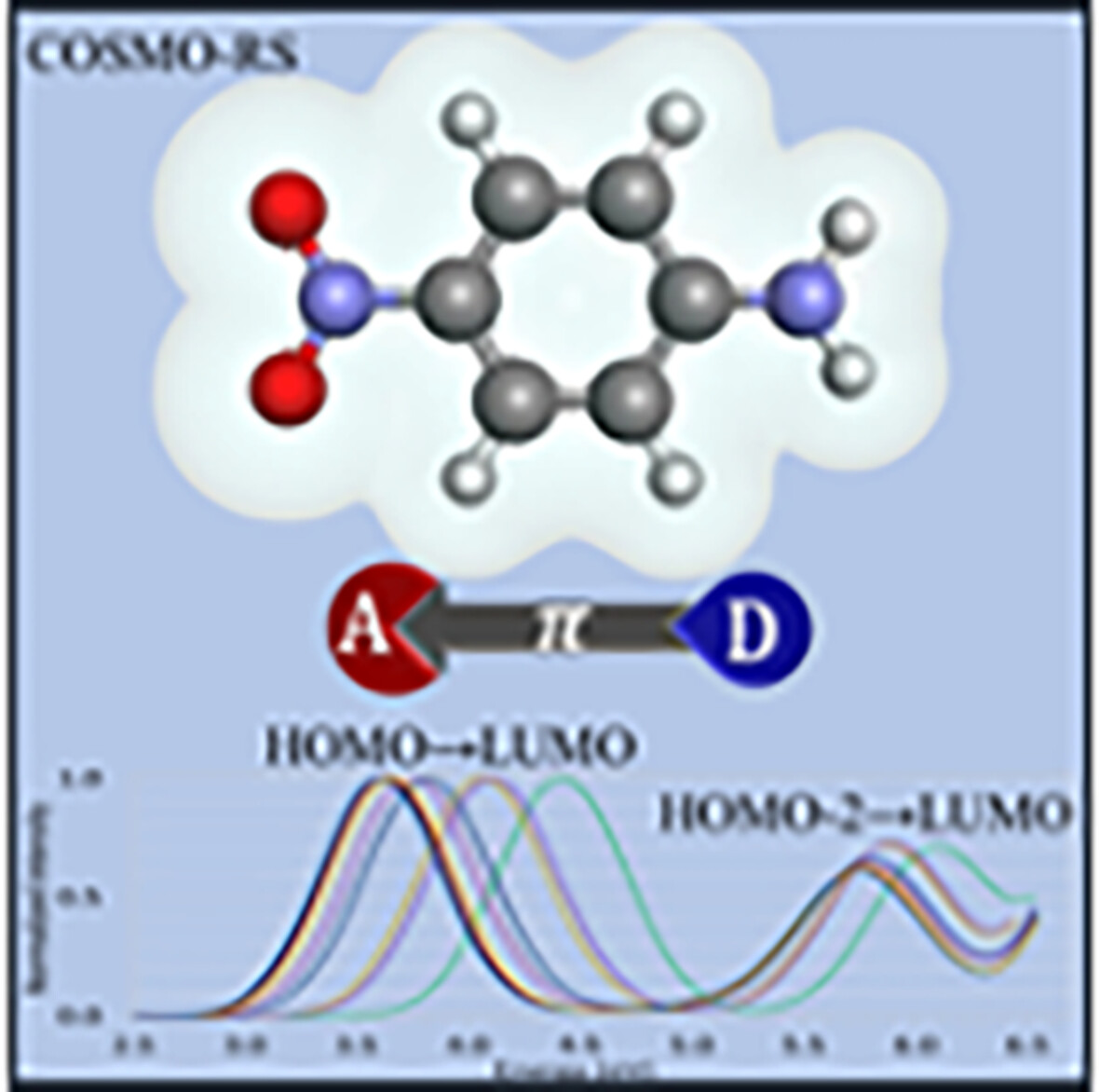
The solvated absorption spectra of p-nitroaniline (pNA), a prototypical push-molecule with electron-withdrawing and electron-donor groups, were investigated focusing on intermolecular charge transfer effects. Eight solvents of different polarities were examined. The ab initio wave function second-order algebraic diagrammatic construction (ADC(2)) combined with implicit and explicit solvation models were employed. For the first time, a second absorption band, not previously measured or computed theoretically, was found and characterized.
SOFTWARE NOTE
Ichor: A Python library for computational chemistry data management and machine learning force field development
- Pages: 2912-2928
- First Published: 31 August 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
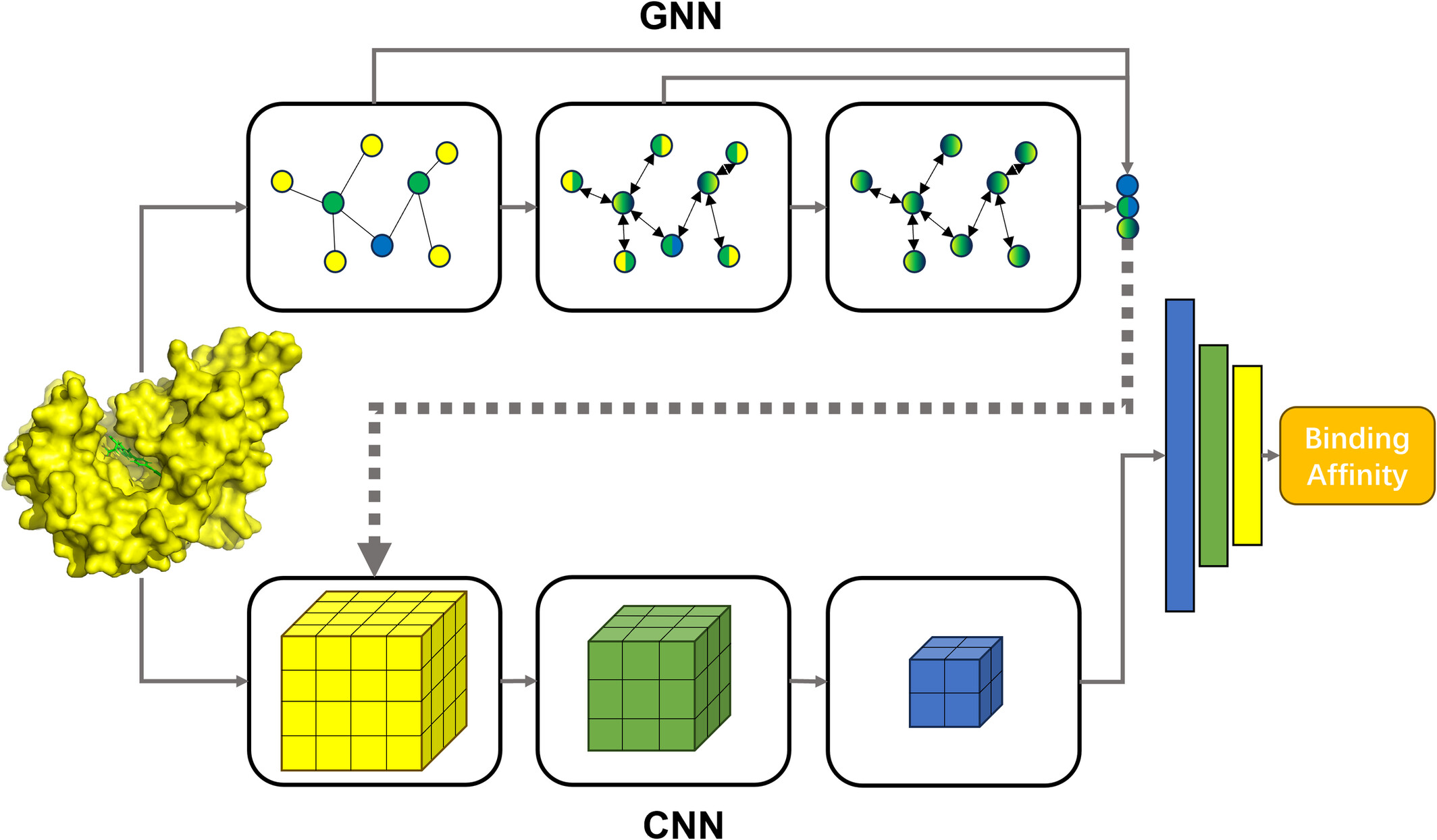
Enhancing protein-ligand binding affinity prediction through sequential fusion of graph and convolutional neural networks
- Pages: 2929-2940
- First Published: 02 September 2024
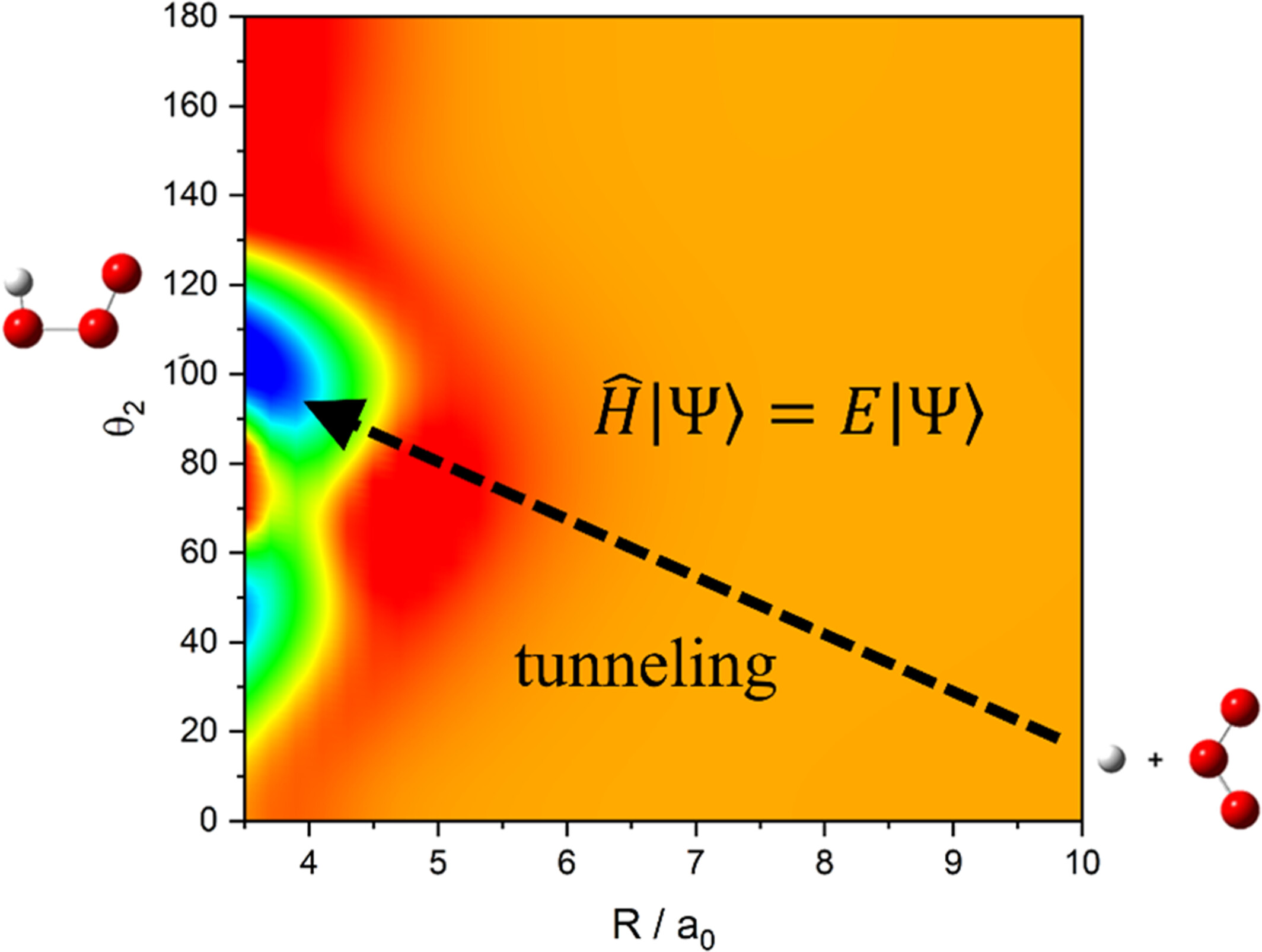
Full-dimensional coupled-channel statistical approach to atom-triatom systems and applications to H/D + O3 reaction
- Pages: 2941-2948
- First Published: 02 September 2024
A machine learning potential construction based on radial distribution function sampling
- Pages: 2949-2958
- First Published: 03 September 2024
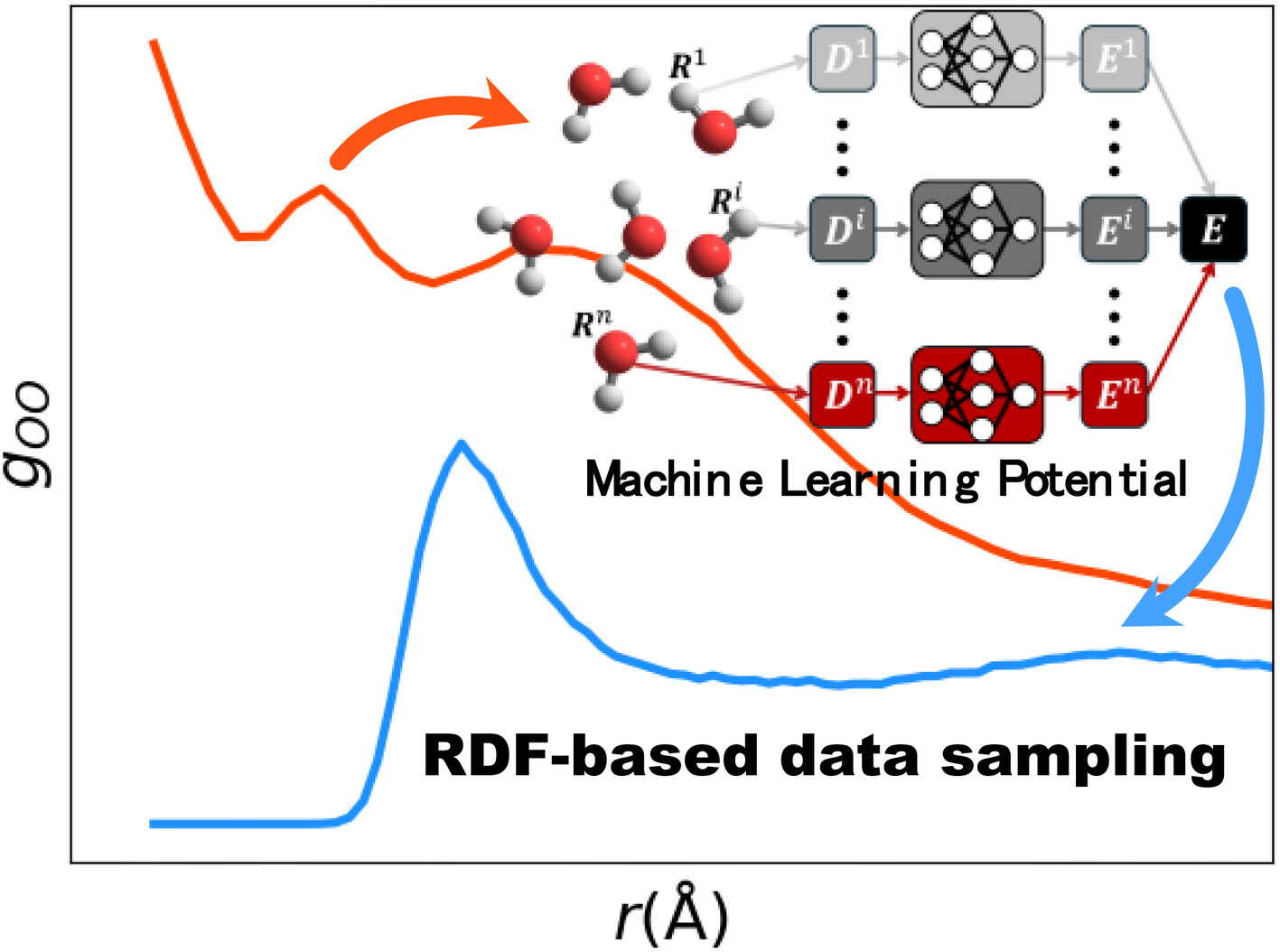
The accuracy of machine learning potentials (MLPs) depends on the quality of training data. MLPs constructed with insufficient data cause unphysical behavior. However, the indiscriminate expansion of the training data is an unwelcome approach from the standpoint of computational cost. This work proposed new training data sampling method, radial distribution function (RDF)-based data sampling, which improves the accuracy of MLPs. The incorporation of new training data via our sampling method led to a notable improvement in the RDFs and other physical properties. Our results demonstrate that this method is useful for constructing MLPs which are robust to extrapolation from molecular cluster system to periodic system.
Quantum chemical investigation of electronic transitions of mitorubrin azaphilones
- Pages: 2959-2968
- First Published: 03 September 2024
Equation-of-motion orbital-optimized coupled-cluster doubles method with the density-fitting approximation: An efficient implementation
- Pages: 2969-2978
- First Published: 05 September 2024
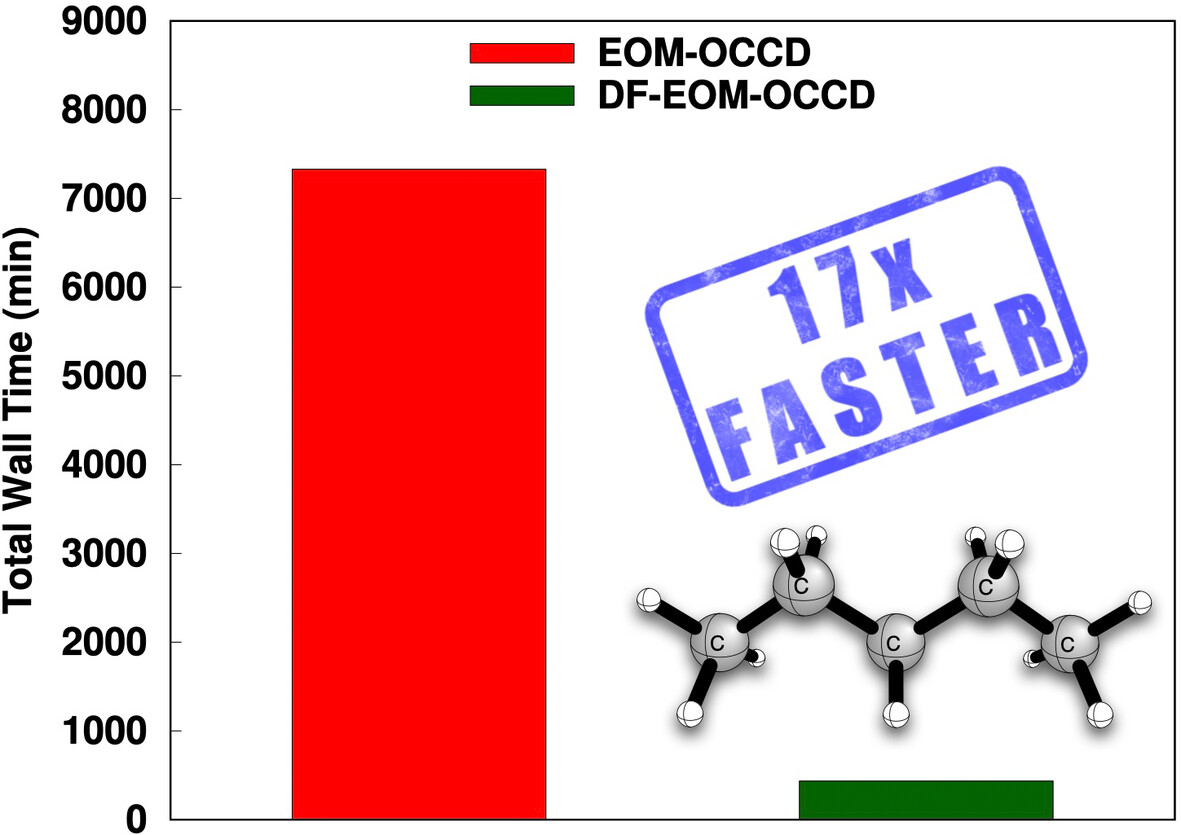
The computational cost of the DF-EOM-OCCD method for excitation energies is compared with that of the conventional EOM-OCCD method. Our results demonstrate that DF-EOM-OCCD excitation energies are dramatically accelerated compared to EOM-OCCD. There are almost 17-fold reductions for the C5H12 molecule in a aug-cc-pVTZ basis set with the RHF reference.
A computational mechanistic study on the formation of aryl sulfonyl fluorides via Bi(III) redox-neutral catalysis and further rational design
- Pages: 2979-2990
- First Published: 06 September 2024
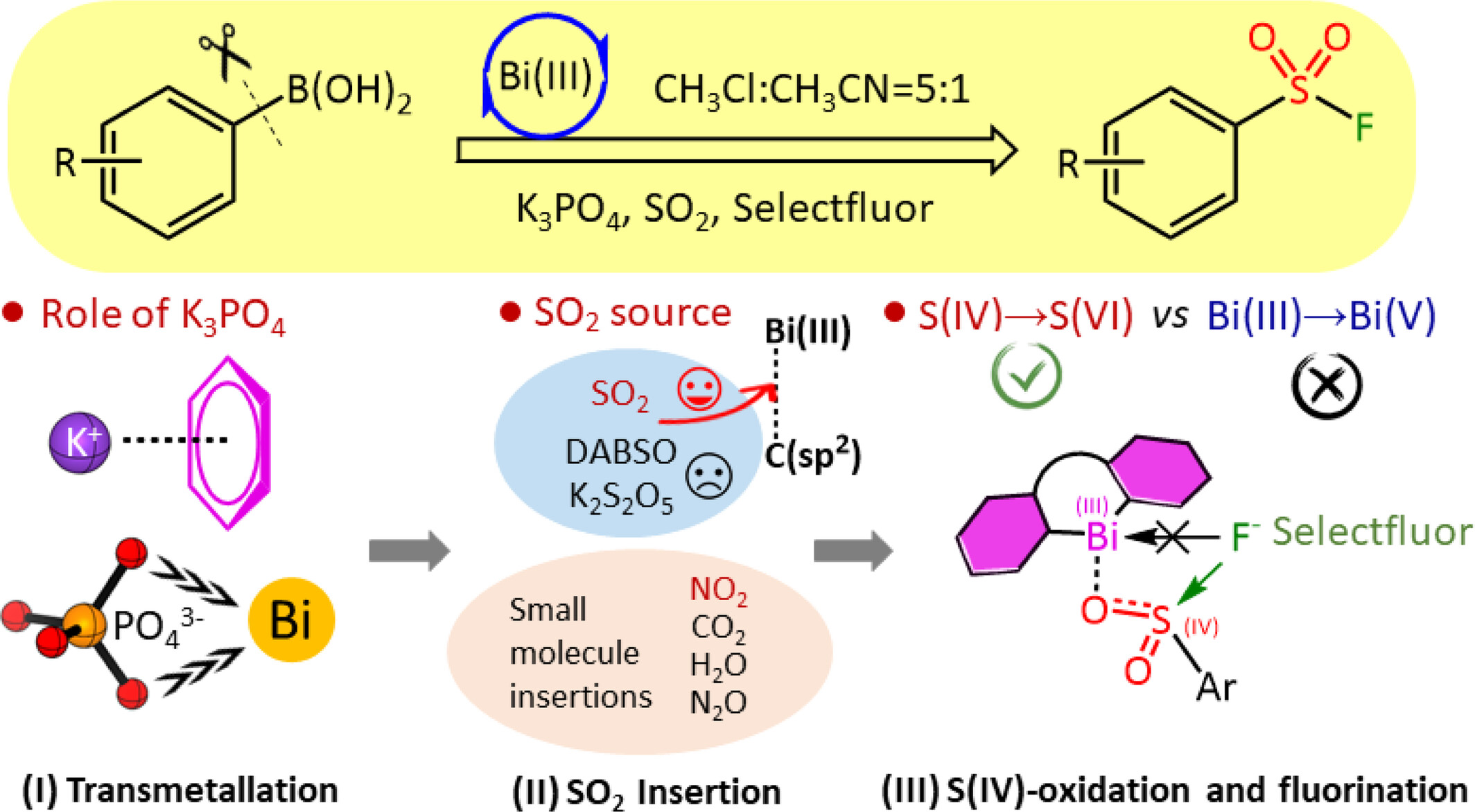
We herein report a DFT mechanistic study on the formation of aryl sulfonyl fluorides via Bi(III) redox-neutral catalysis. The significant role of base K3PO4, the origin of SO2 insertion into the Bi(III)C(sp2) bond, and the competing pathways between S(IV)→S(VI) and Bi(III)→Bi(V) were discussed. Moreover, we rationally design new Bi(III)-catalyzed small molecule (NO2, CO2, etc.) insertion reactions and new Bi(III)/Sb(III)-catalysts for aryl sulfonyl fluoride formation reactions.
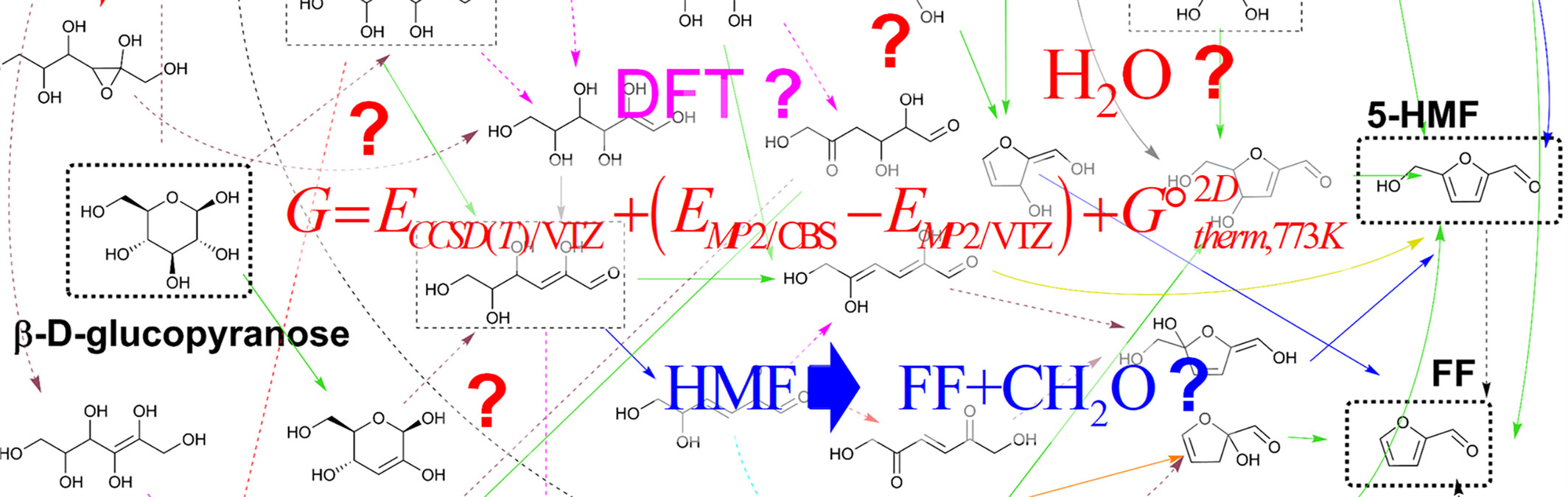
Pyrolytic conversion of glucose into hydroxymethylfurfural and furfural: Benchmark quantum-chemical calculations
- Pages: 2991-3003
- First Published: 09 September 2024
An influence of electronic structure theory method, thermodynamic and implicit solvation corrections on the organic carbonates conformational and binding energies
- Pages: 3004-3016
- First Published: 17 September 2024
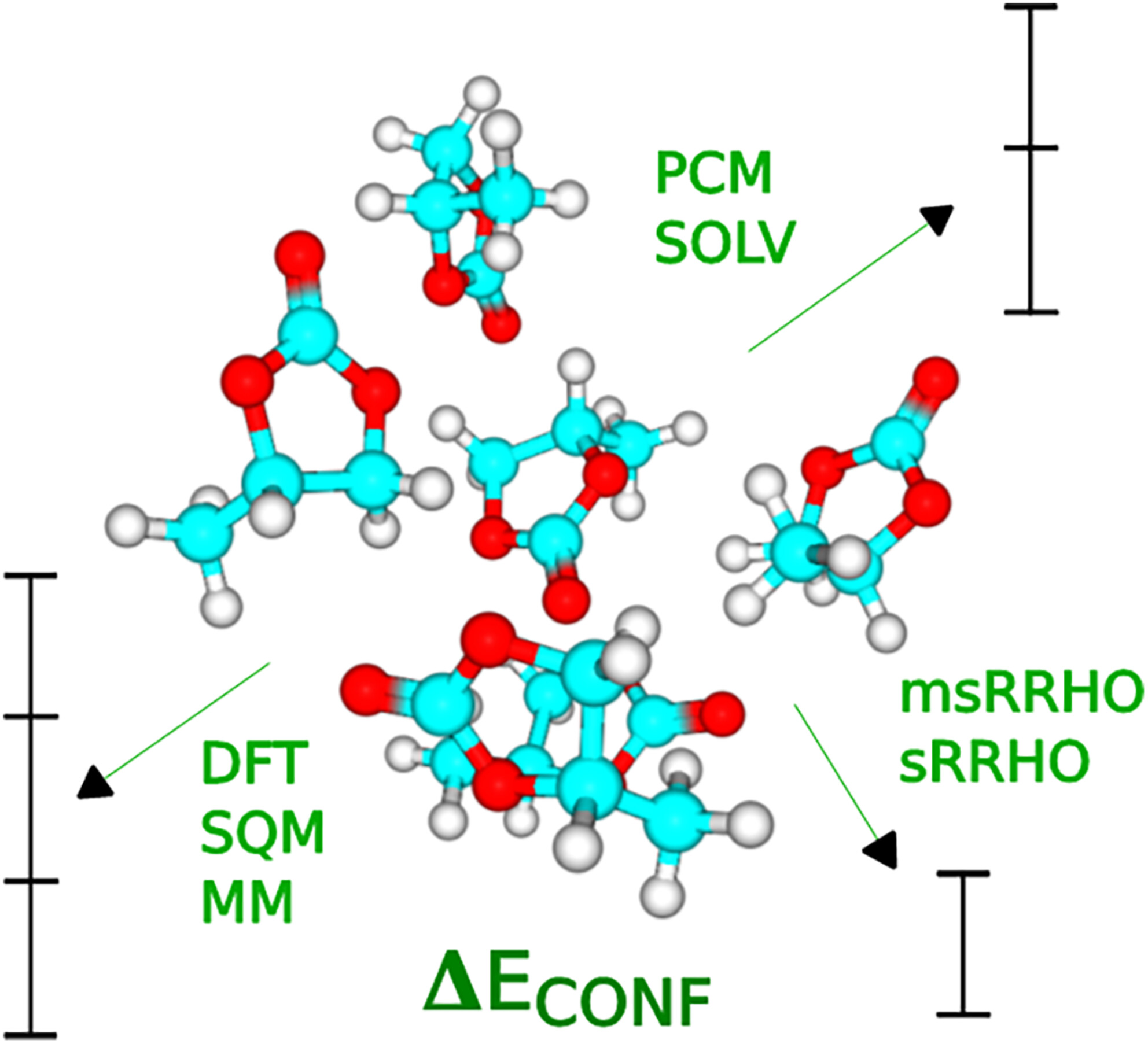
An influence of a battery of electronic structure/force field methods, gas-phase Gibbs free energy thermodynamic correction, and continuum solvation effect on organic carbonate molecular cluster (S)n conformational and binding energies is examined. The results are relevant to molecular modeling of ion transfer in lithium- and sodium-ion batteries for which organic carbonates are primary solvents.