Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Articles
Health performance assessment modeling and its application to compact medical communities in China
- First Published: 23 July 2024
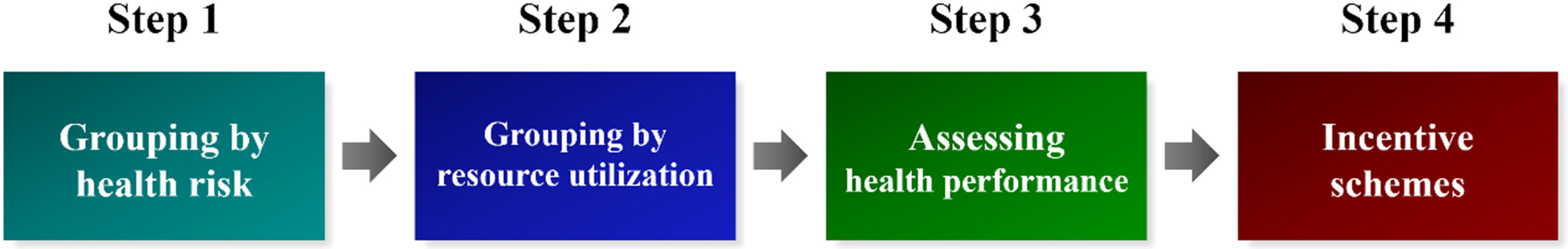
The health performance assessment model comprises four steps: 1. Grouping by health risk; 2. Grouping by resource utilization; 3. Assessing health performance; 4. Incentive schemes. This model could help medical insurance funds allocate capitation budgets for various populations in accordance with variations in health risks and provide incentives to compact medical communities which are successful in promoting health.
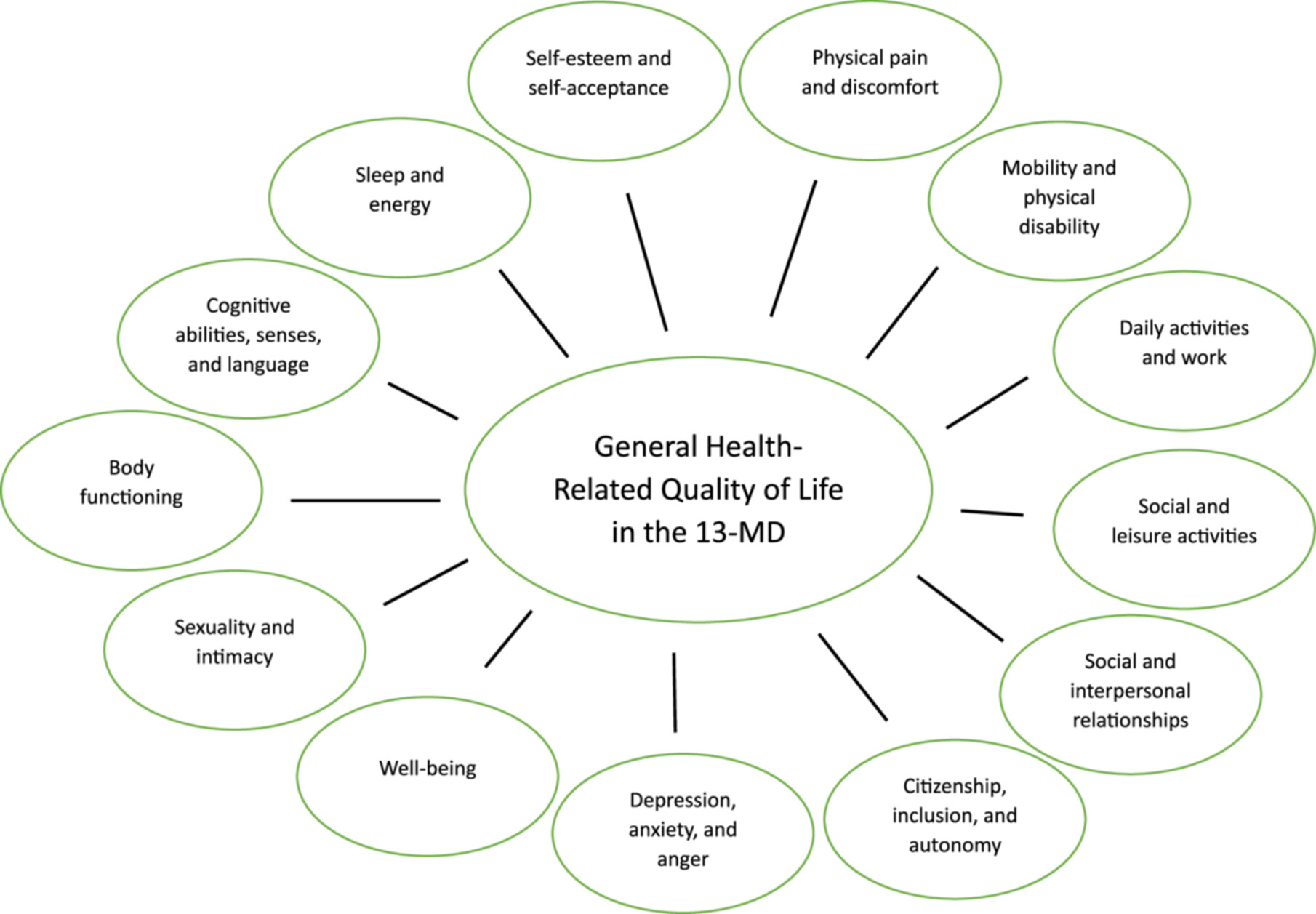
Confirmatory analysis of the 13-MD and ranking of its meta-dimensions and items
- First Published: 04 August 2024
Evaluation of the McGill-Tongji Blended Education Program for Teacher Leaders in General Practice: The importance of partnership and contextualization in International Primary Care Training Initiatives
- First Published: 12 August 2024
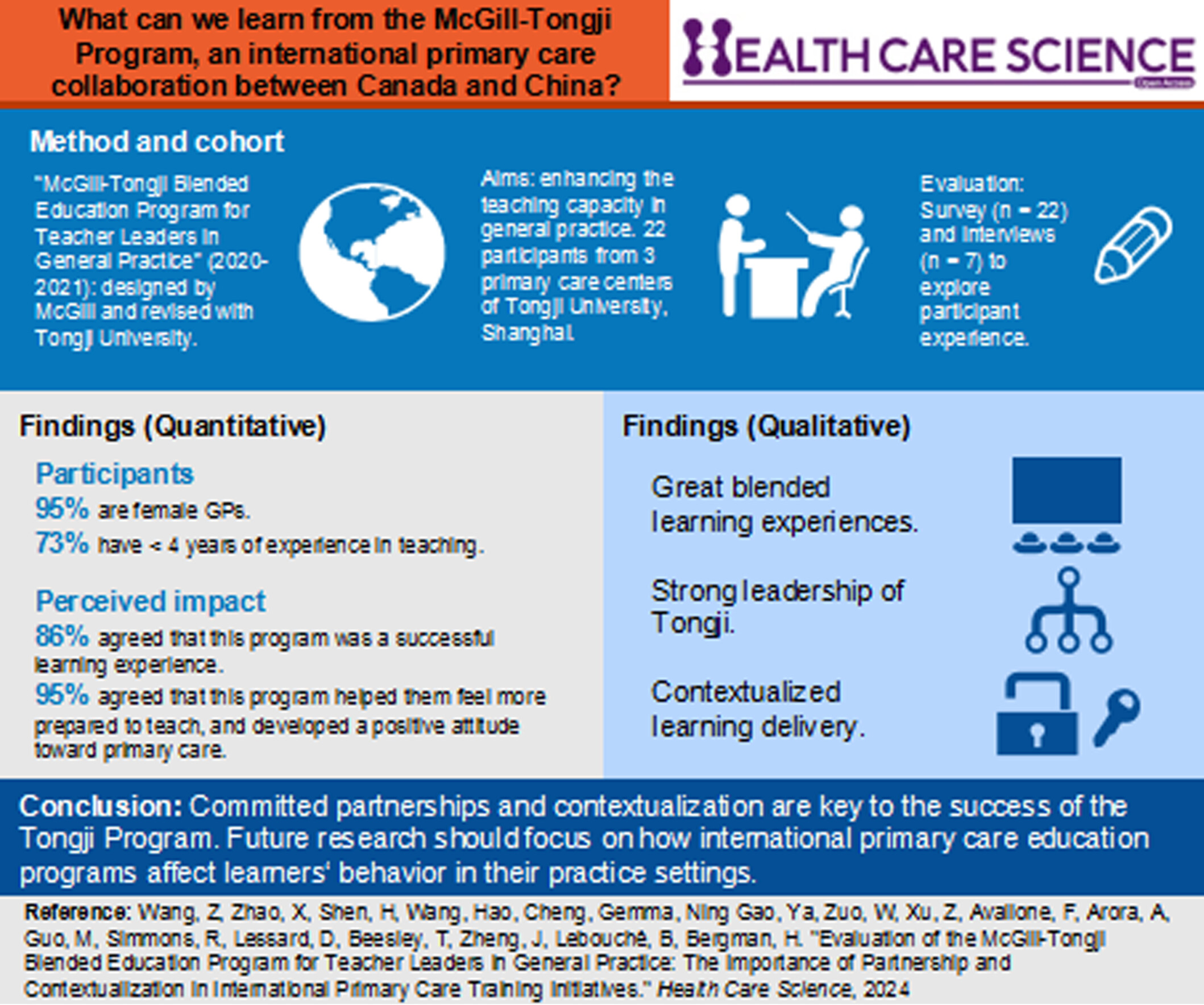
We presented an evaluation study of the McGill-Tongji Blended Education Program for Teacher Leaders in General Practice (Tongji Program). This program was considered a successful learning experience by most participants in terms of subjective learning experiences and outcomes. Committed international partnerships and contextualization were key to the success of the Tongji Program.
Formulation of a CITE metric for evaluating the clinical implications of medical studies and their originating hospitals in China
- First Published: 06 August 2024
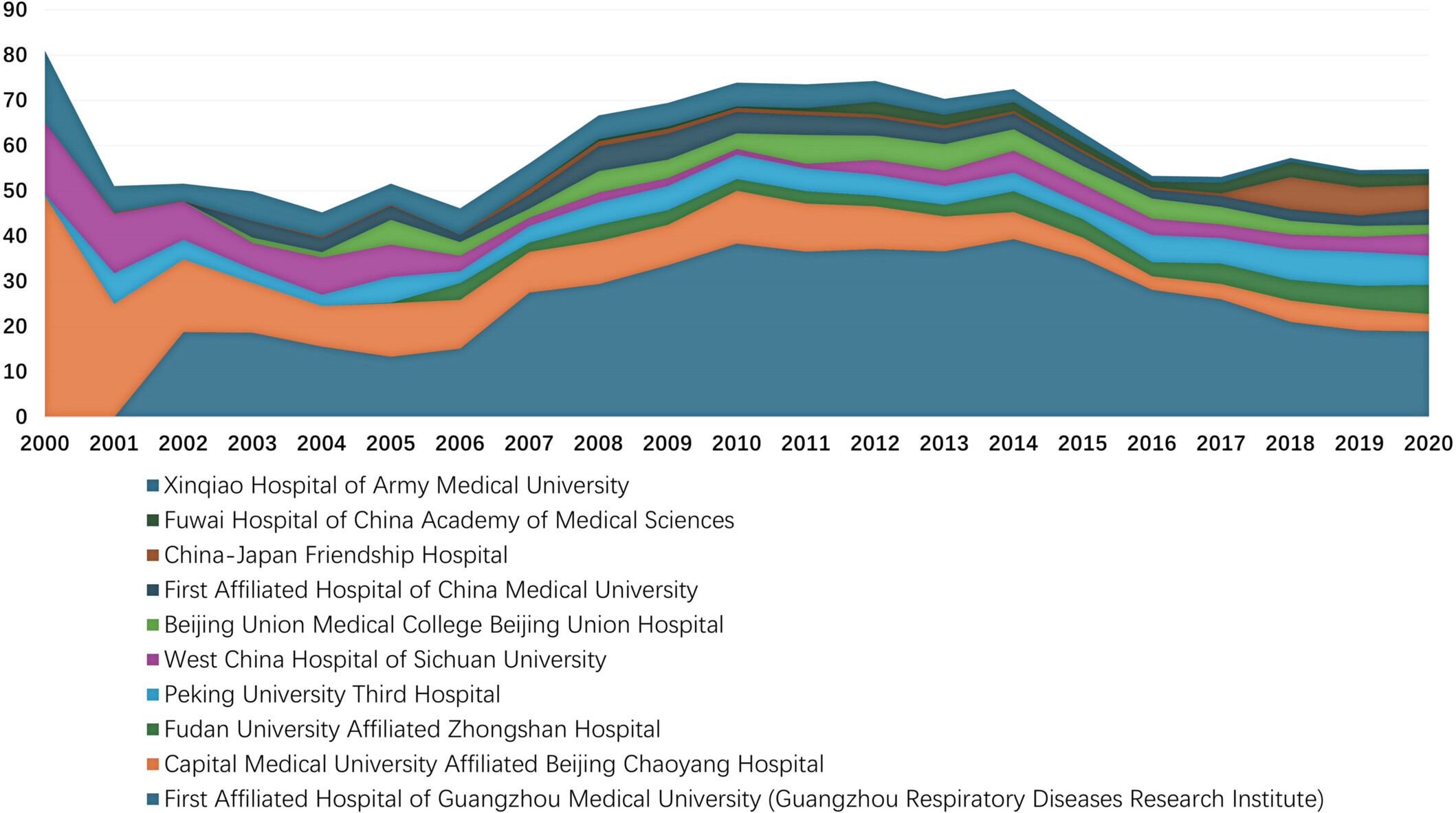
This study introduced the “Clinical Influence and Timeliness Evaluation (CITE)” metric to assess the clinical significance of a medical research and the clinical influence of the medical research outputs of domestic hospitals based on the premise that meaningful medical research should be valuable for clinical practice. The CITE metric was applied to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, incorporating 78,636 articles from 2000 to 2020 and incorporated 499 hospitals in China, in which the top 10 hospitals of most clinical influence were shown here.
Theranostic scope of monometallic selenium and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in biomedicine: A review
- First Published: 13 August 2024
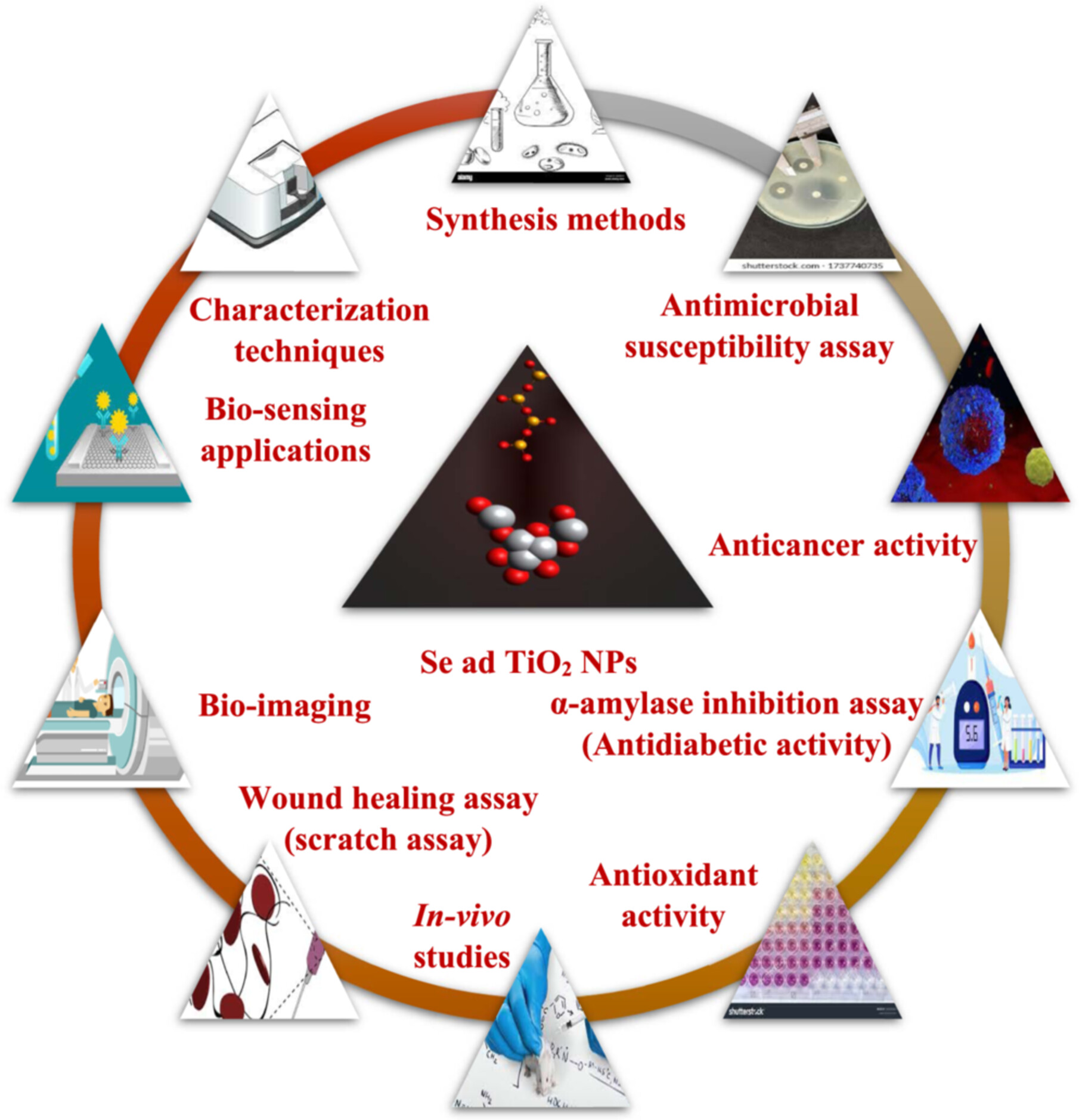
The nanoparticles (NPs) of metals and metal oxides constitute significant components of technology in terms of monometallic NPs (MNPs). Throughout the last 10 years, the most fascinating and in-depth uses of NPs have been found in the biomedical field, which has demonstrated the therapeutic potential of these particles. Significant strides were made in the application of nanotechnology in a variety of industries, including biomedical sciences. In biomedicine, the two most important applications of NPs are in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Given their ability to deliver specific drugs, these next-generation NPs provide safe and effective pharmacotherapies for a wide range of disorders. A comprehensive review on MNPs like selenium (metal-based) and titanium dioxide (metal-oxide based), their synthesis methods, nanoscale physicochemical properties, and the definition of specific industrial applications in the various fields of applied nanotechnology, including biomedicine, is discussed.
Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants KP.2 and KP.3 sparks concerns: What should we do?
- First Published: 06 August 2024
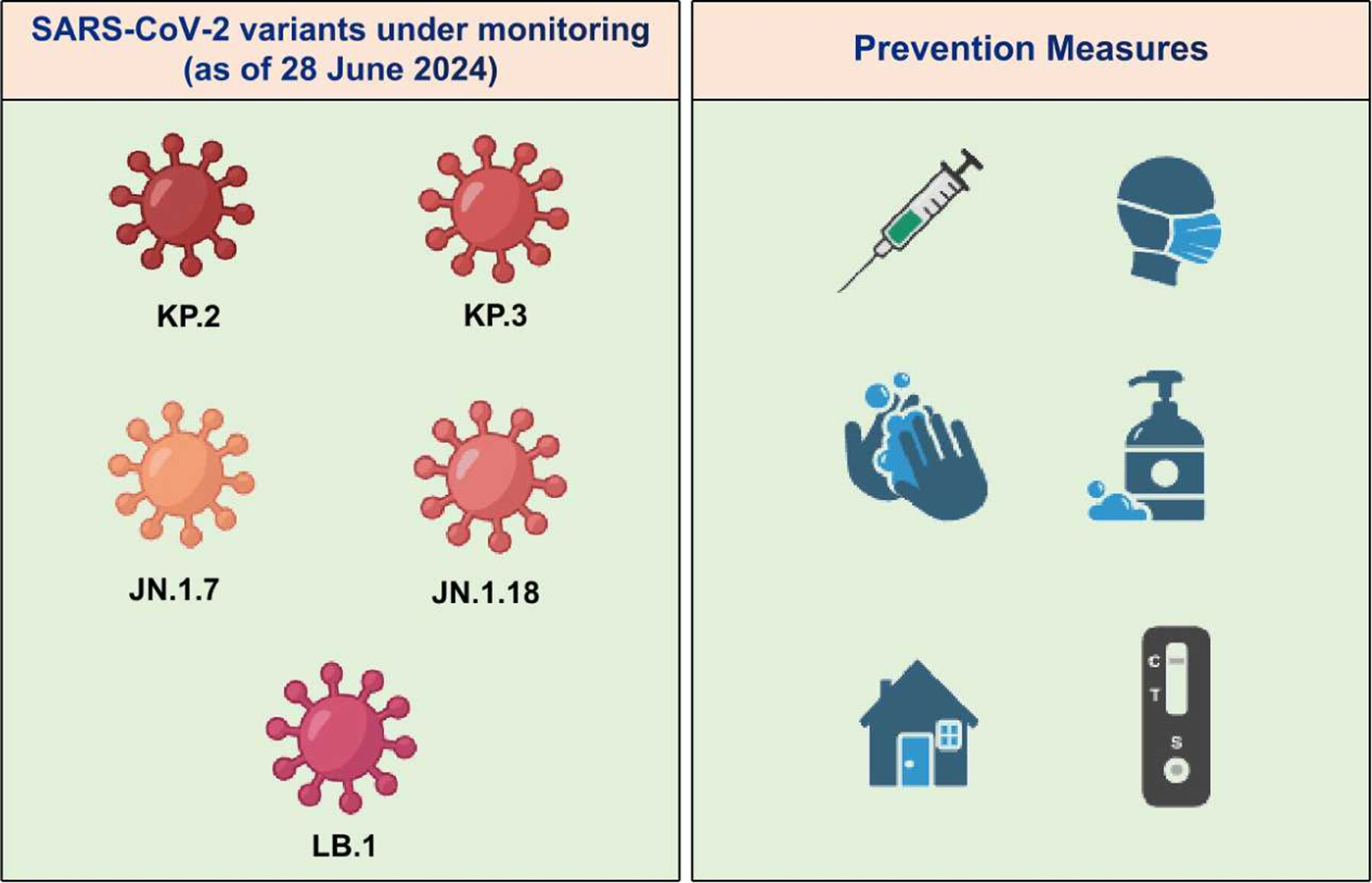
SARS-CoV-2 continues to evolve and circulate globally. In recent weeks, variants such as KP.2 and KP.3 have been rapidly increasing in many countries. Prevention strategies such as receiving updated COVID-19 vaccines, wearing masks when recommended, washing hands frequently, getting tested if symptoms appear, and staying home when sick can help protect individuals and others from COVID-19.
Early-onset scoliosis in children aged 4–7 years in Nanjing, China: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 18 August 2024
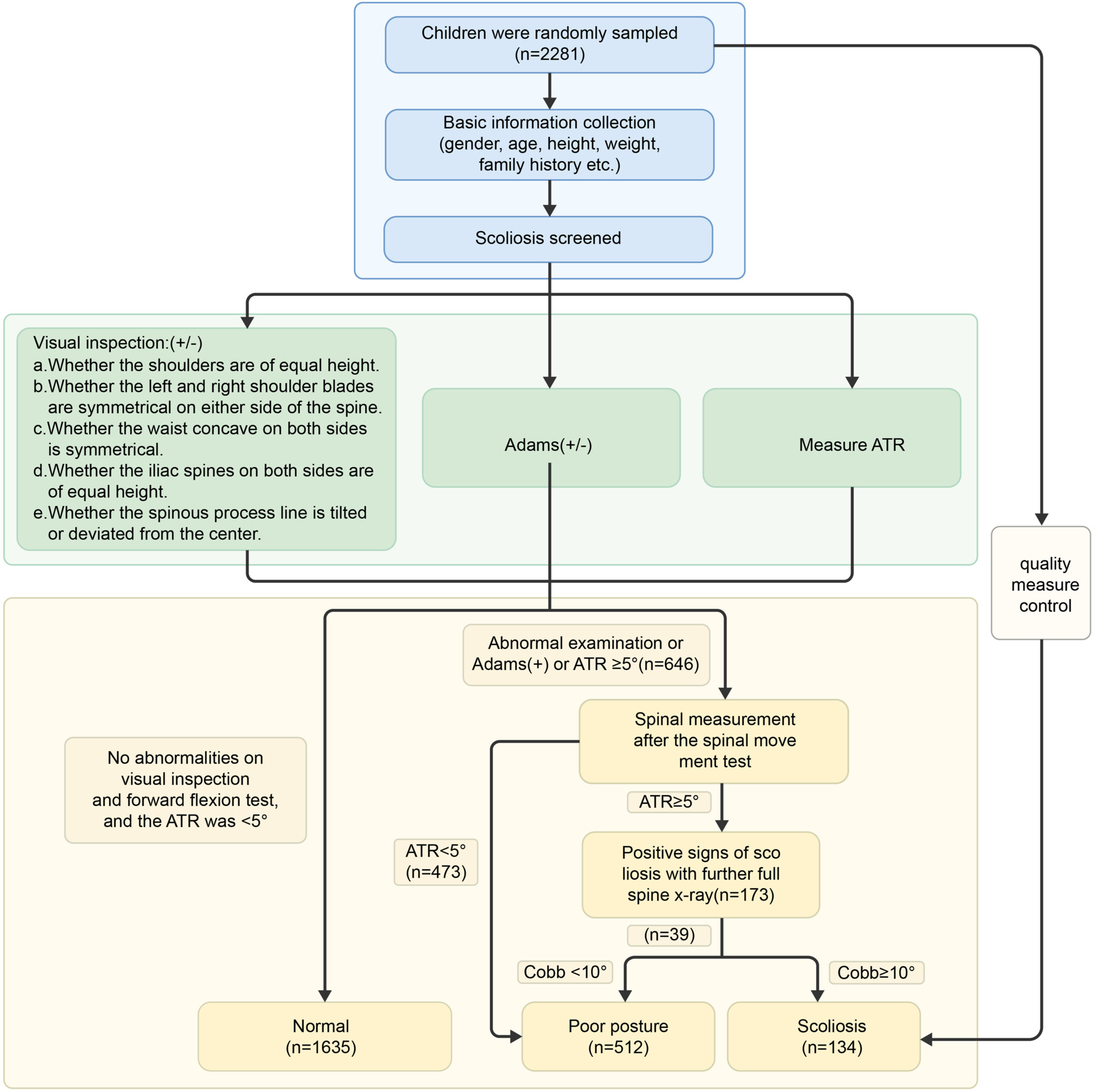
The combination of visual assessment, the Adams forward bend test, and angle of trunk rotation (ATR) angle measurement provides an accurate and efficient screening method for scoliosis. Regular spinal check-ups are advised for children with an ATR angle of 4.5° or higher. Children with a lower body mass index are more susceptible to scoliosis.
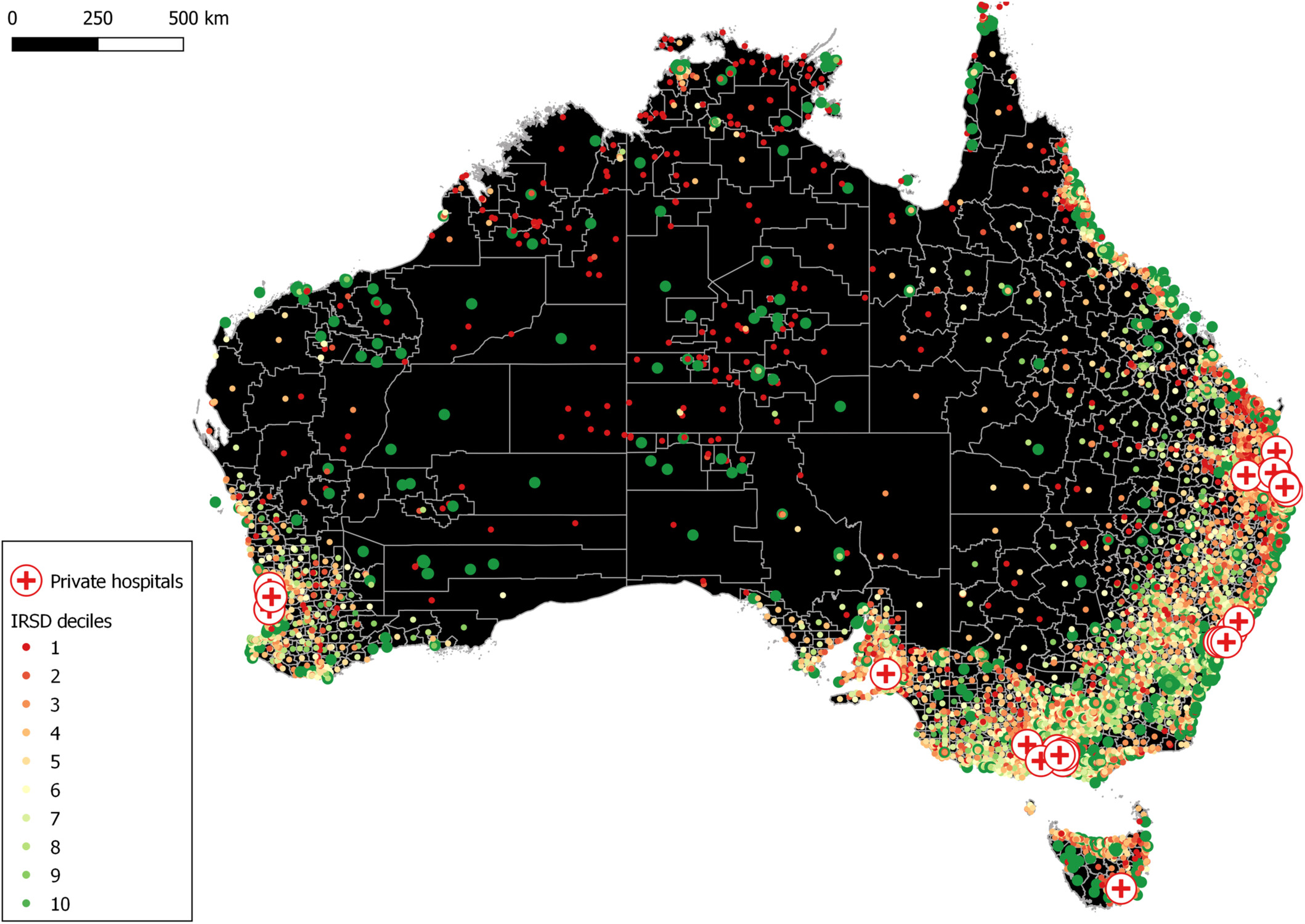
Are private hospital emergency departments in Australia distributed to serve the wealthy community?
- First Published: 18 October 2024
Reporting ethical approval in case reports and case series in 12 consecutive years: A systematic review
- First Published: 04 October 2024
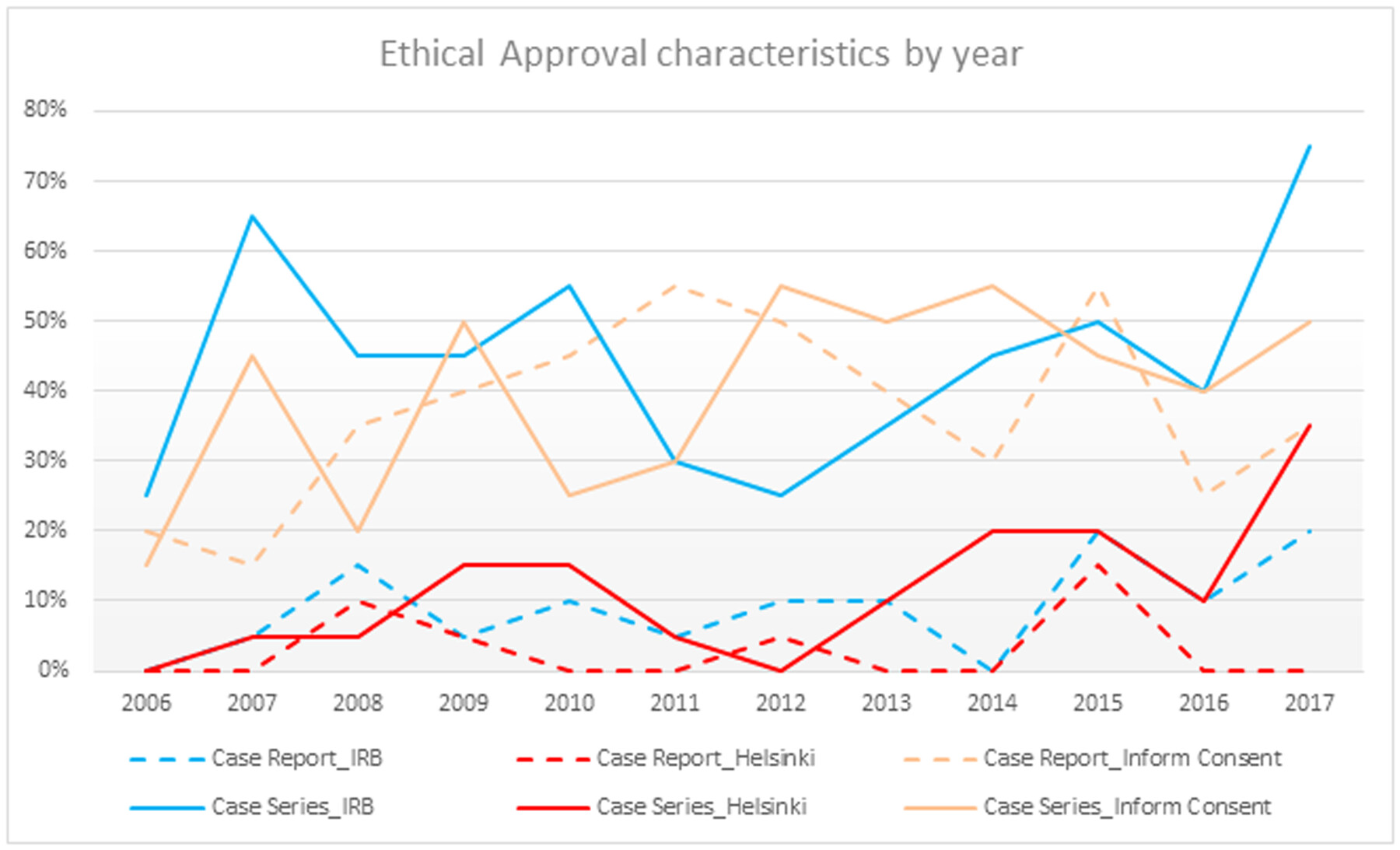
Ethical reporting practices in case reports and case series remained consistently suboptimal over a 12-year period. Despite the importance of informed consent, institutional review board (IRB) approval, and adherence to the Helsinki Declaration, our analysis revealed low rates of reporting for these crucial elements (38.5%, 26.9% and 7.3% respectively). Furthermore, the disproportionate in informed consent reporting rate (52.3%) within IRB-approved case series studies suggests potential misuse of IRB approval as a surrogate for obtaining patient consent.
Toward real-world deployment of machine learning for health care: External validation, continual monitoring, and randomized clinical trials
- First Published: 14 October 2024
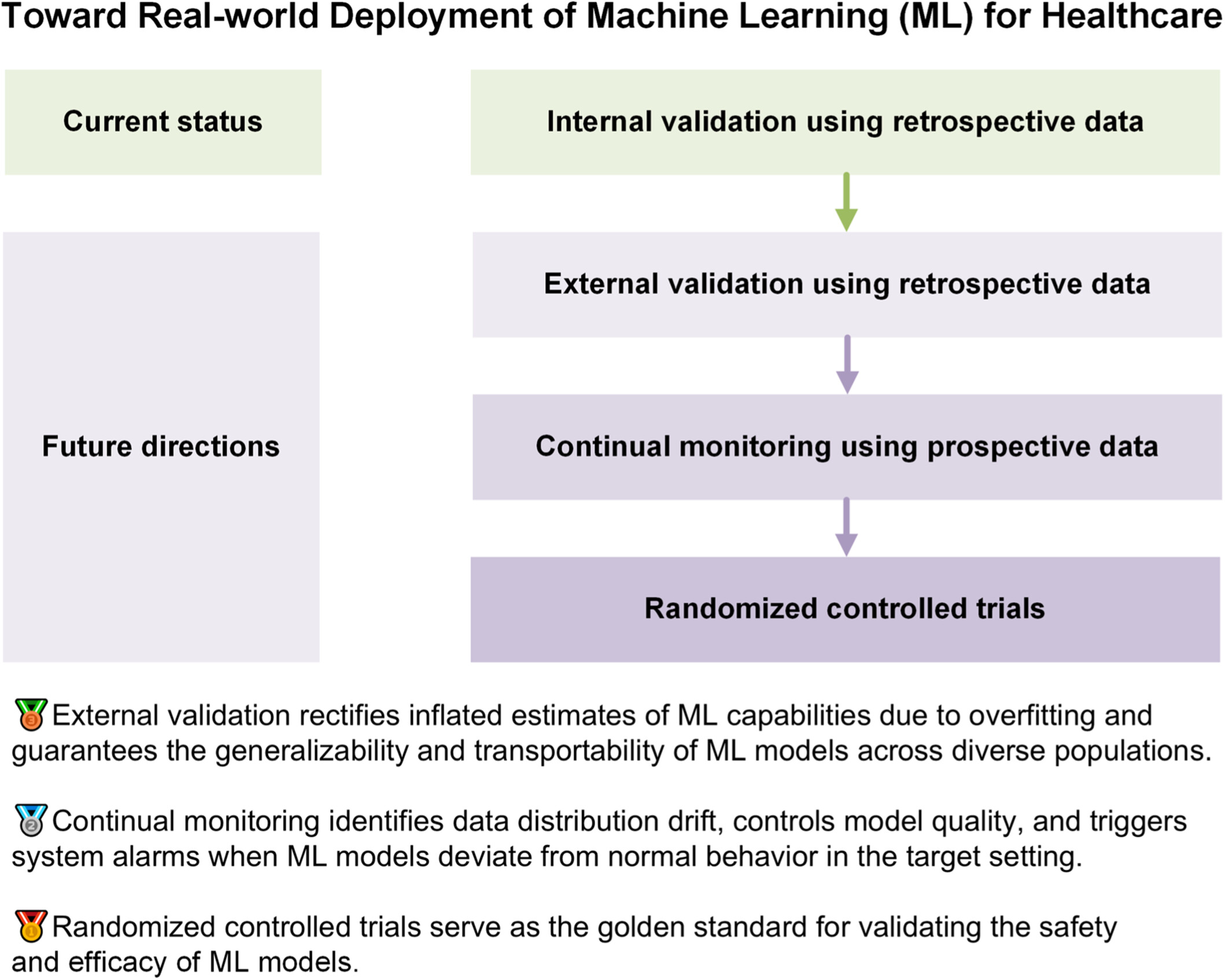
In this commentary, we elucidate three indispensable evaluation steps toward the real-world deployment of machine learning within the healthcare sector and demonstrate referable examples for diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic tasks. We encourage researchers to move beyond retrospective and within-sample validation, and step into the practical implementation at the bedside rather than leaving developed machine learning models in the dust of archived literature.
Revolutionizing healthcare and medicine: The impact of modern technologies for a healthier future—A comprehensive review
- First Published: 09 October 2024
The way medical professionals diagnose, treat, and manage diseases has changed dramatically due to several innovative technologies that have emerged in recent years. Thanks to sophisticated algorithms that examine enormous volumes of patient data to find patterns and predict outcomes, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have become increasingly potent instruments that enable more precise diagnoses. Telemedicine has increased access to healthcare, particularly in rural regions, by facilitating remote monitoring and consultations. Furthermore, wearable technology and IoMT have enabled people to track their health parameters in real-time, offering insightful information to patients and healthcare professionals. Moreover, personalized therapies have become possible thanks to genomics and personalized medicine developments, which use a patient's genetic information to create exact medications. Together, these technologies have improved healthcare delivery systems’ efficiency and patient-centeredness while raising the standard of care.
Improving transitional care after acute myocardial infarction: A scoping review
- First Published: 13 October 2024
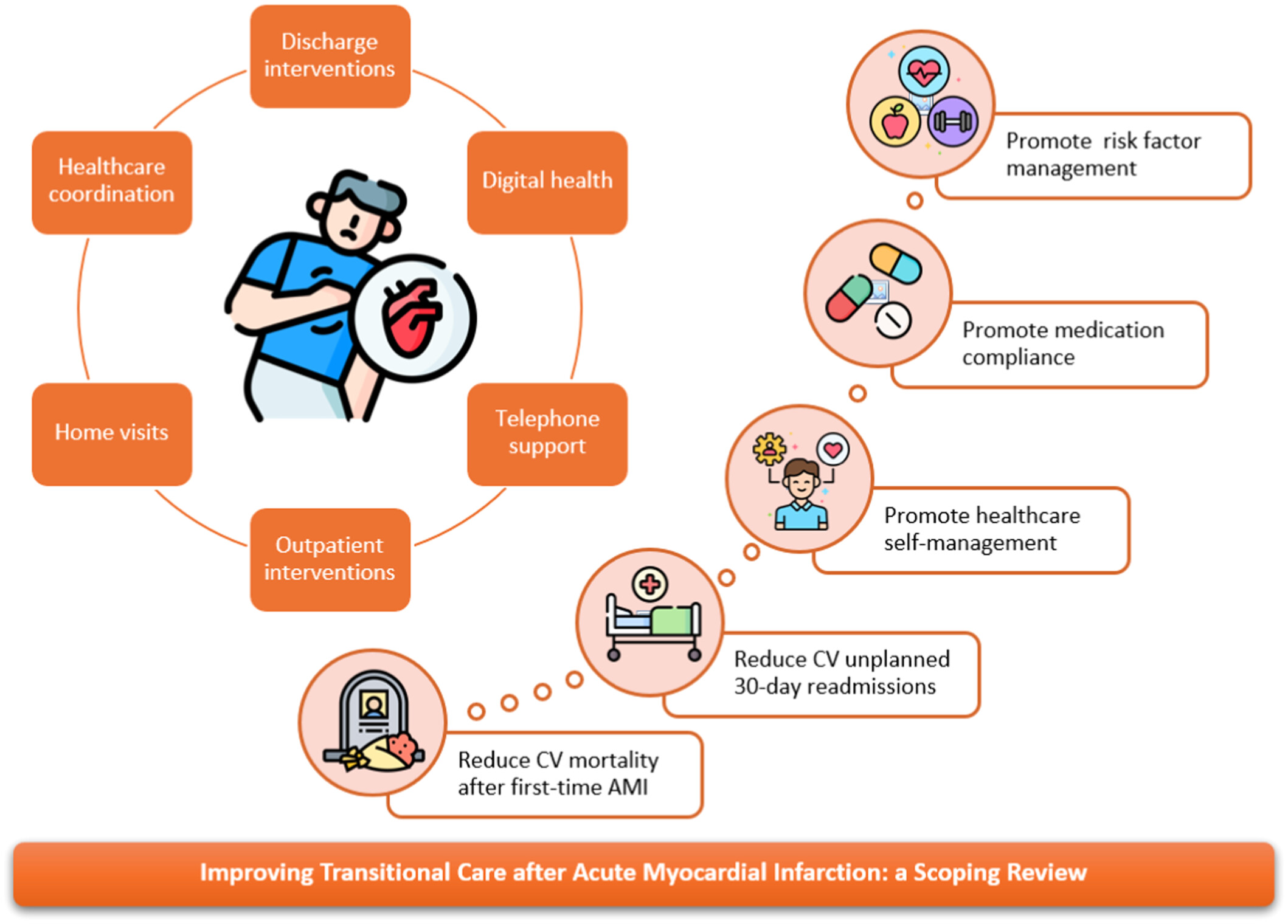
It synthesizes evidence on various components of transitional care. The need for multifaceted interventions required to improve long-term outcomes. Identifies the role of each healthcare professional and the integration of different interventions. Integrative healthcare programs facilitate continuity and care coordination post-discharge after acute myocardial infarction.
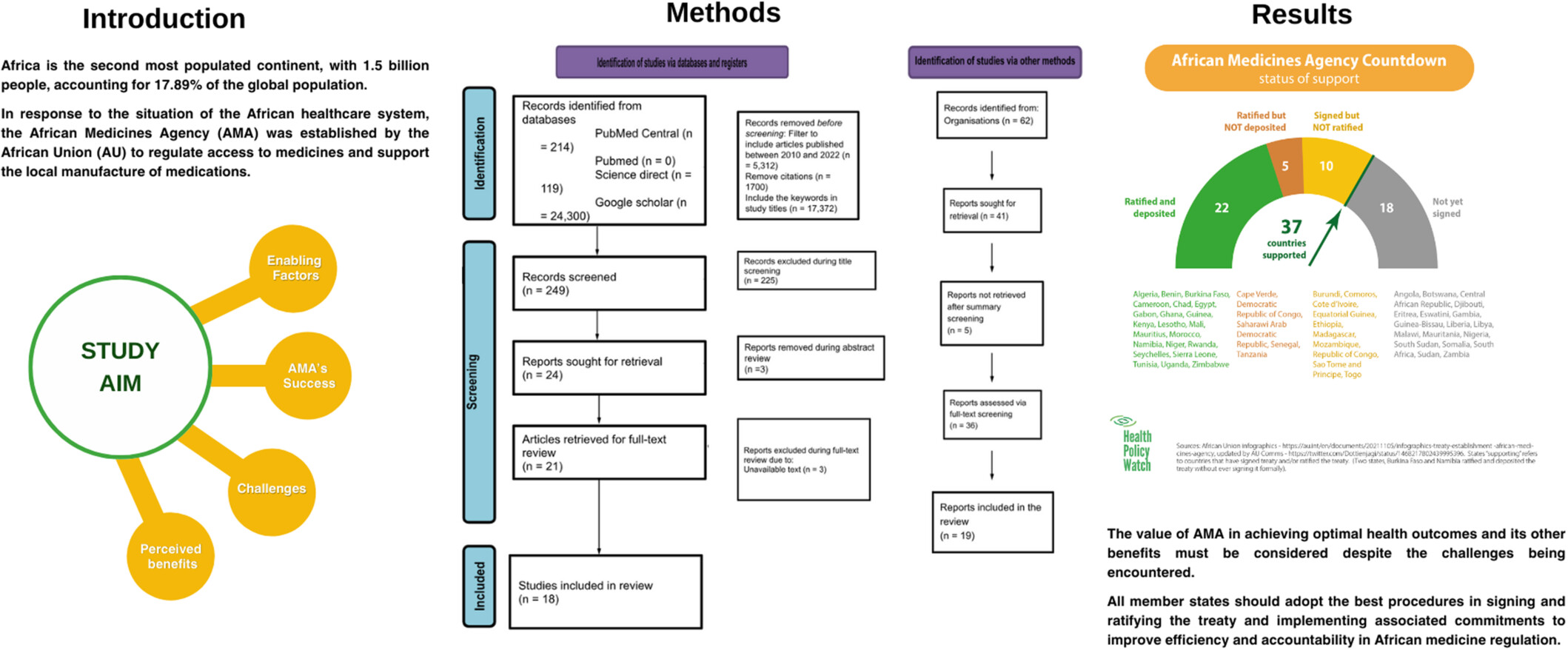
The African Medicines Agency and Medicines Regulation: Progress, challenges, and recommendations
- First Published: 10 October 2024
Advancing digital health in China: Aligning challenges, opportunities, and solutions with the Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH)
- First Published: 17 October 2024

We summarized the unique challenges that China faced in digital health due to its large population, regional disparities, and uneven distribution of medical resources. Under the guidance of the Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) released by WHO, we proposed corresponding solutions that address infrastructure, data, terminology, technology and security.
Leveraging anatomical constraints with uncertainty for pneumothorax segmentation
- First Published: 15 December 2024
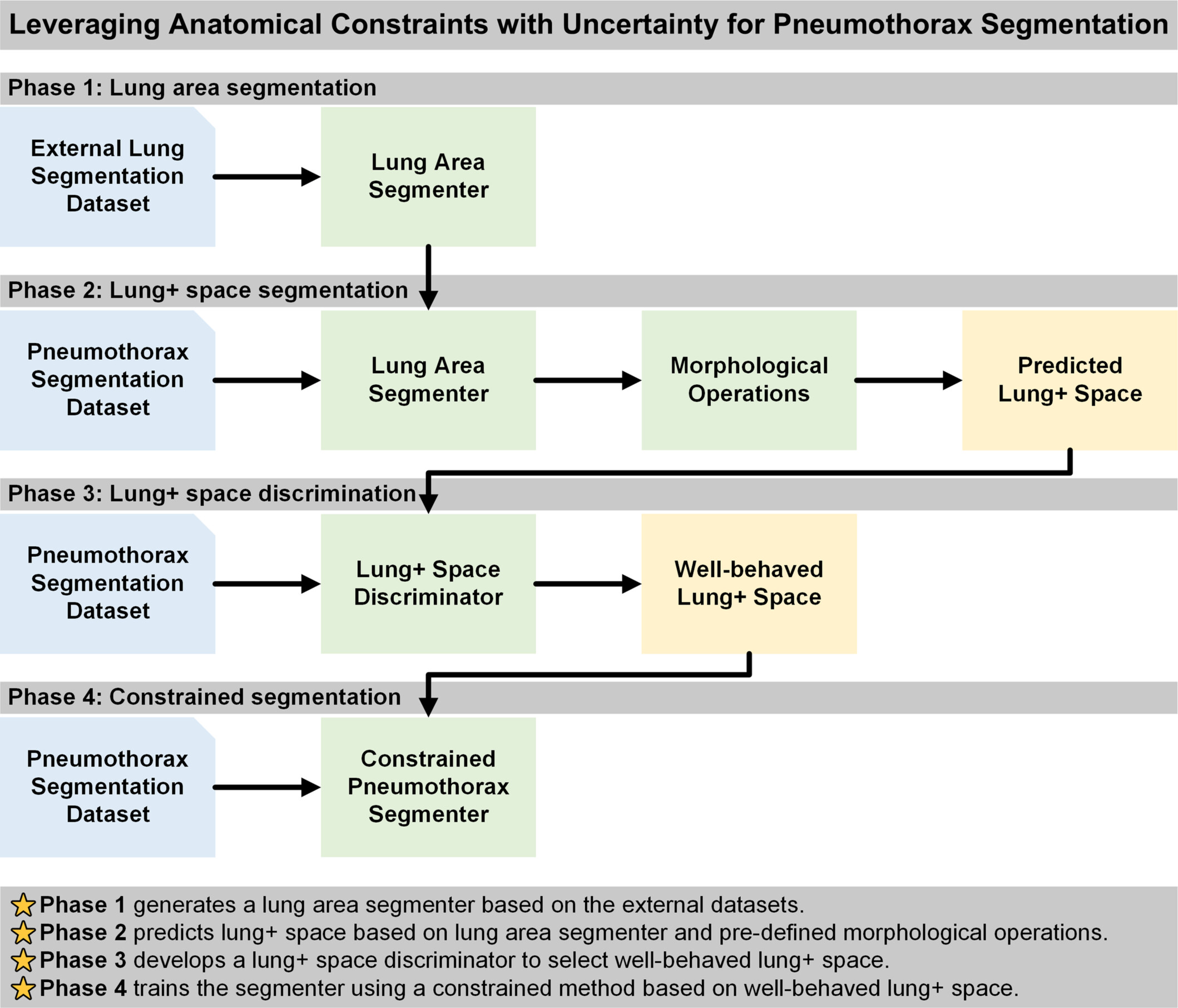
We proposed a novel approach that incorporates the lung + space as a constraint during deep learning model training for pneumothorax segmentation on 2D chest radiographs. We utilized external datasets and an auxiliary task of lung segmentation to generate a specific constraint of lung + space for each chest radiograph, circumventing the need for additional annotations. We incorporated a discriminator to eliminate unreliable constraints caused by the domain shift between the auxiliary and target datasets. Our results demonstrated consistent improvements across six baseline models built on three segmentation architectures and two convolutional neural networks backbones.
Explainable machine learning model for pre-frailty risk assessment in community-dwelling older adults
- First Published: 10 December 2024
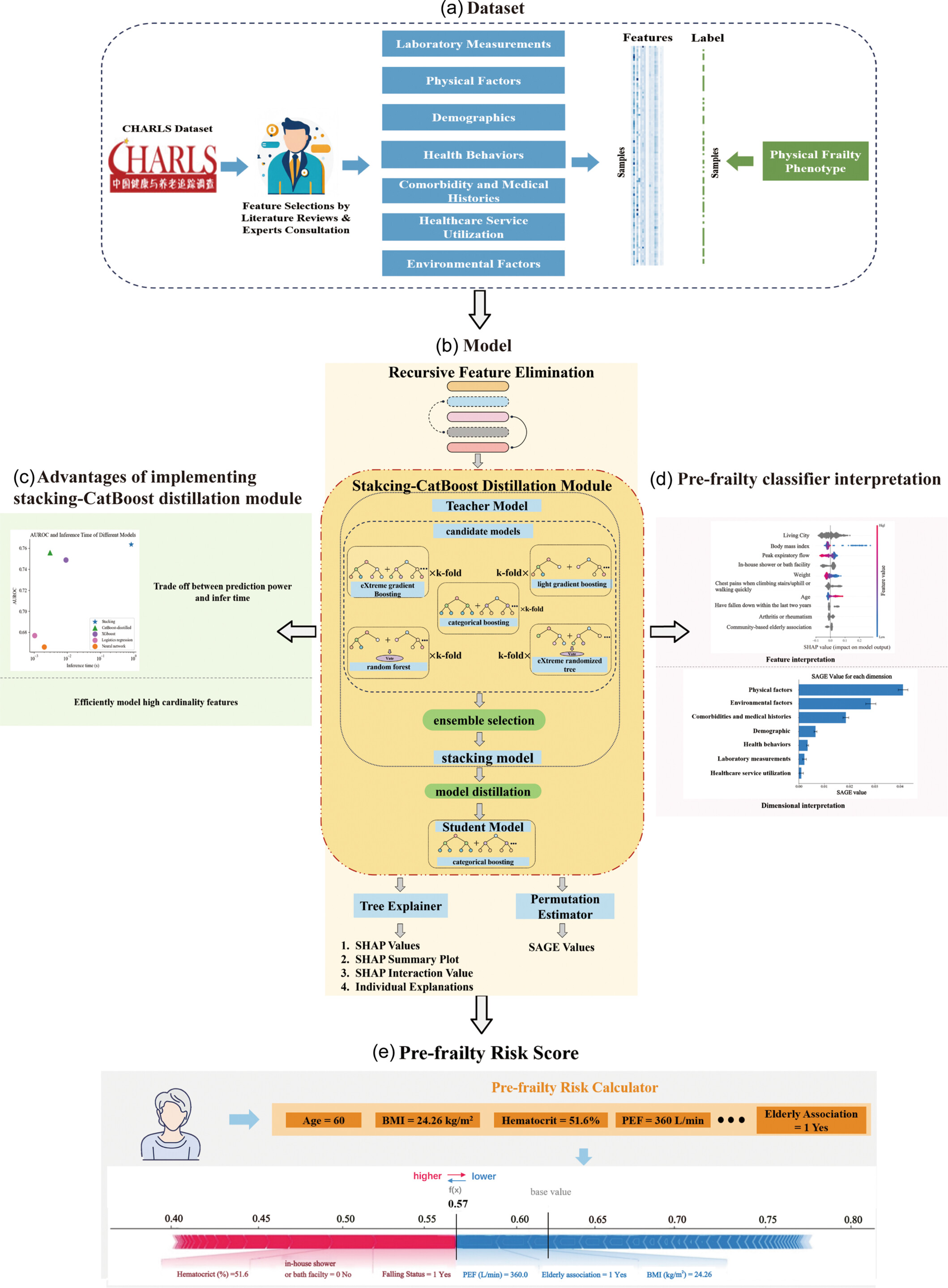
The PACIFIC framework utilizes the CHARLS (2011) data set, which consists of 80 features organized into seven dimensions, and integrates an efficient recursive feature elimination method with a stacking-CatBoost distillation module and explainable AI techniques to analyze pre-frailty risk. By employing Tree Explainer for SHAP values and SAGE values for feature contribution, PACIFIC provides individualized explanations that highlight the impact of each risk factor on the overall risk score, thereby enhancing clinical credibility.
SkinSage XAI: An explainable deep learning solution for skin lesion diagnosis
- First Published: 28 November 2024
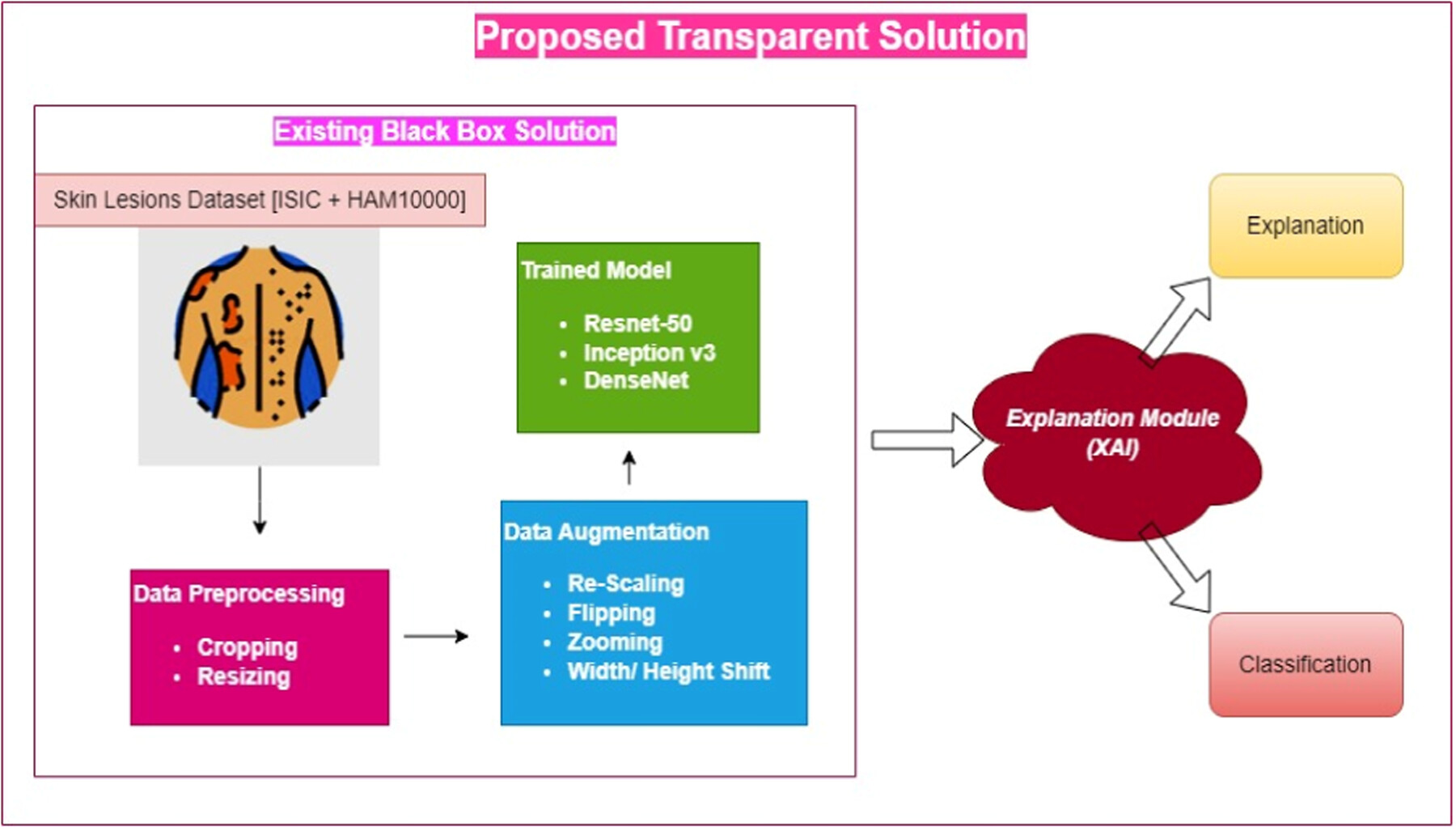
The research was meant to disentangle the difficulties of skin lesion diagnosis using a multimodal approach. Our suggested technique offers unparalleled levels of transparency and interpretability in skin lesion categorization and marks a substantial improvement in the area via methodical methodology and meticulous refining. The research focuses on proposing.
- i.
A straightforward and reliable technique for the categorization of a variety of skin lesions.
- ii.
Explore different deep learning (DL) models in the diagnosis of skin lesions and evaluate their performance and effectiveness.
- iii.
Enhanced DL model's interpretability and transparency in dermatology with the help of explainable artificial intelligence techniques.
- iv.
Helping DL models to be easily incorporated into clinical practice further supporting in skin cancer prevention, management, and improved patient outcome.
Innovative public strategies in response to COVID-19: A review of practices from China
- First Published: 18 December 2024
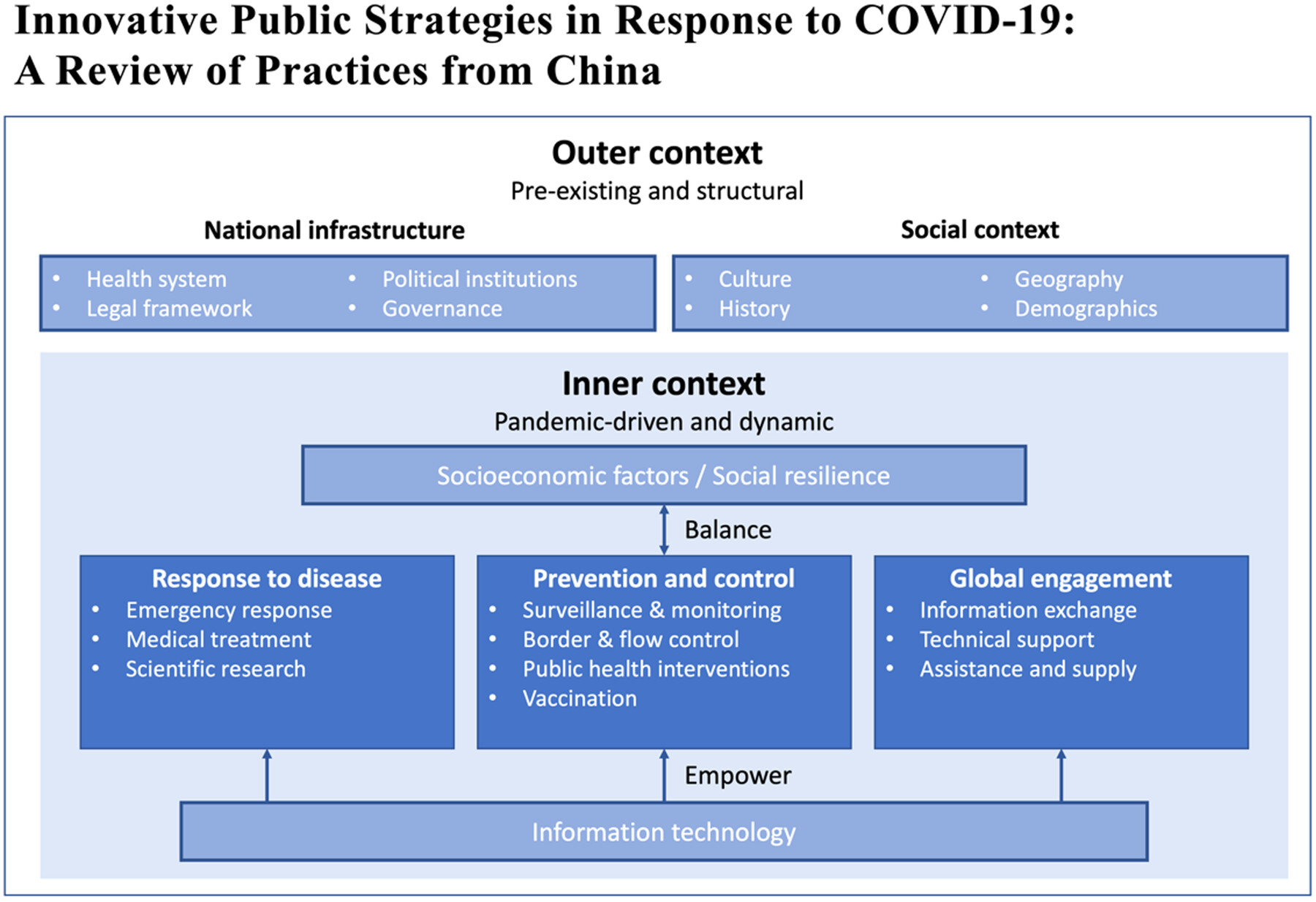
China's COVID-19 response: infrastructure, medical care, prevention, resilience, and global health engagement. Highlighted China's top-down command system, intersectoral coordination, and social governance effectiveness. Focused on coordinated emergency response, evidence-based treatment, strategic vaccine rollout, and IT support in healthcare.
A novel ensemble ARIMA-LSTM approach for evaluating COVID-19 cases and future outbreak preparedness
- First Published: 15 December 2024
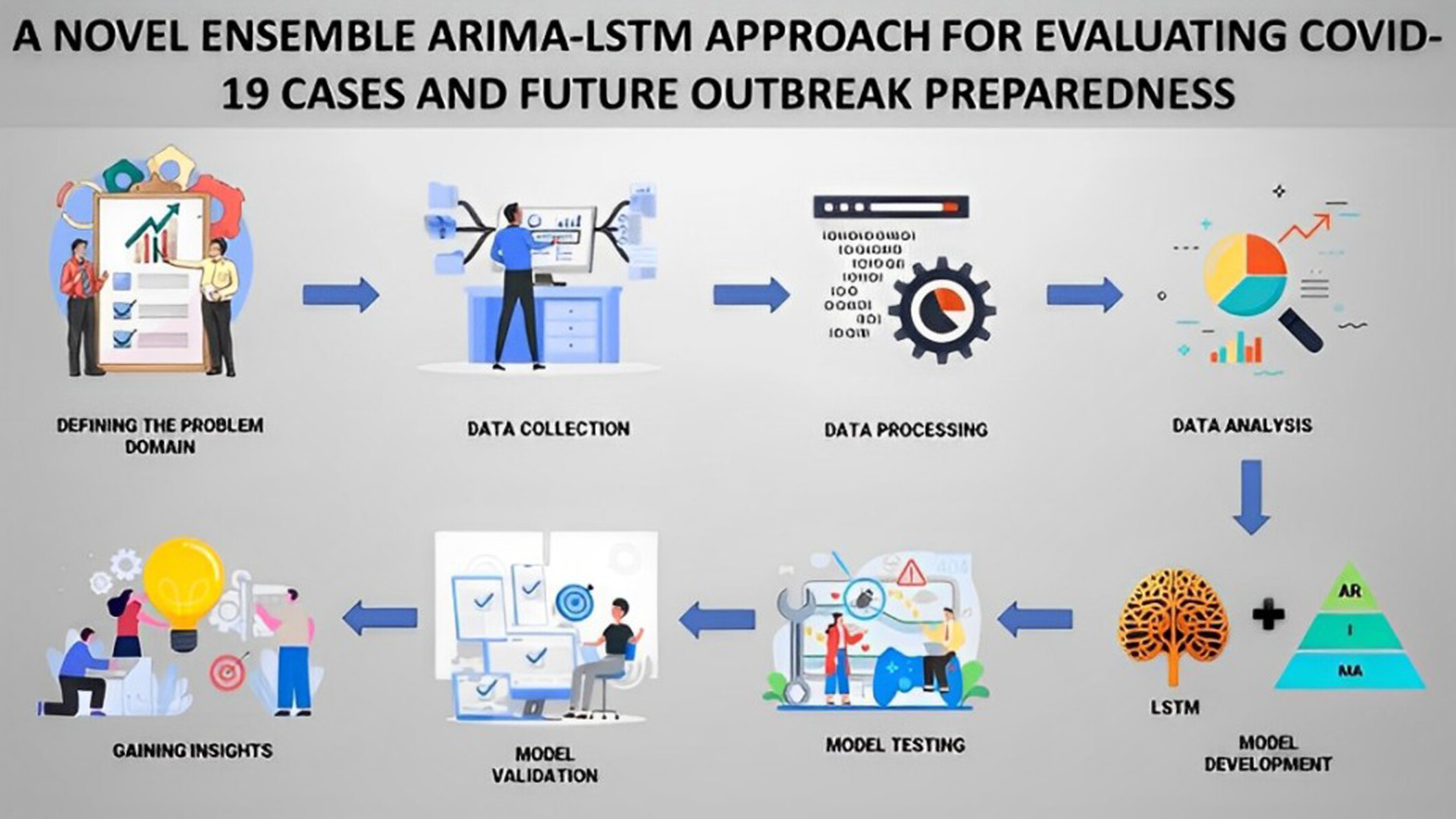
A novel ensemble model that combines auto-regressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) and long short-term memory (LSTM) models is proposed to improve the forecasting accuracy of COVID-19 cases. The proposed ensemble model achieves superior performance compared to individual ARIMA, LSTM, and other baseline forecasting models. This approach has the potential to enhance preparedness for future outbreaks by providing more accurate forecasts of COVID-19 cases.
Caregiving in Asia: Priority areas for research, policy, and practice to support family caregivers
- First Published: 18 December 2024
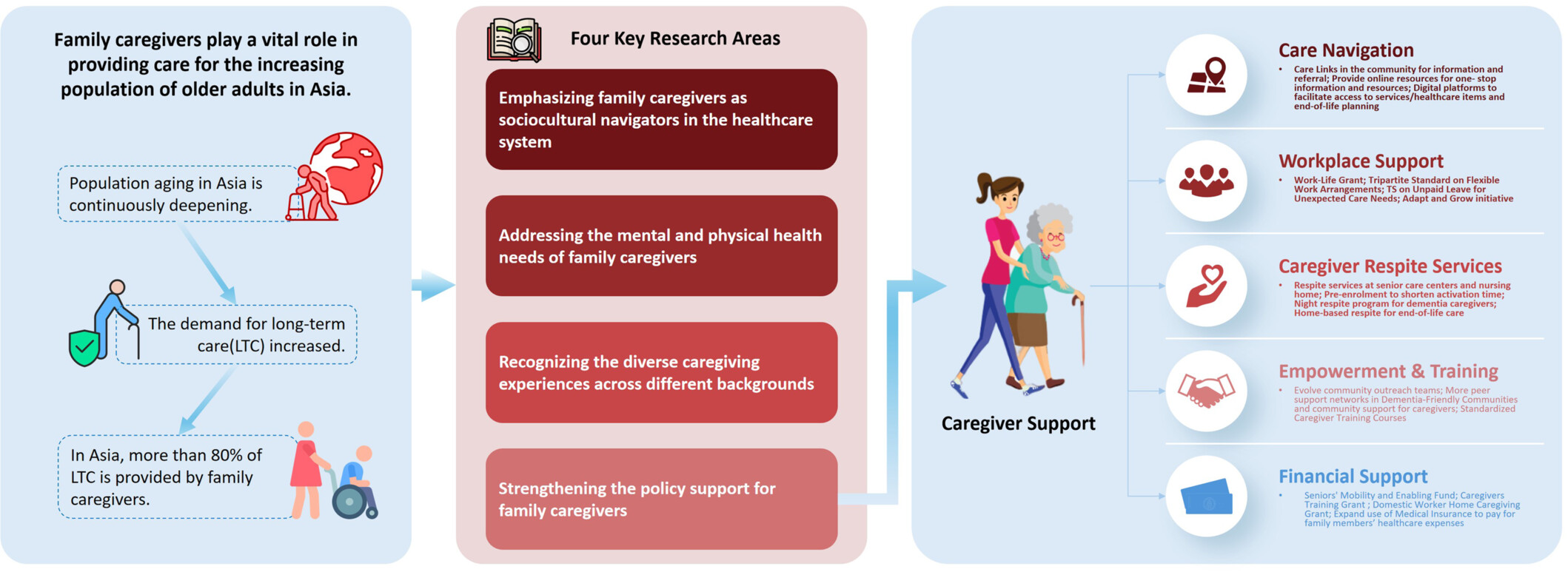
In this review, we identify four key priority areas to advance research, practice, and policy related to family caregivers in Asia: (1) Emphasizing family caregivers as sociocultural navigators in the healthcare system; (2) addressing the mental and physical health needs of family caregivers; (3) recognizing the diverse caregiving experiences across different cultural backgrounds, socioeconomic status, and countries of residence; and (4) strengthening policy support for family caregivers. We propose cross-country knowledge exchange and capacity development for better serving both the aging population and their caregivers.