Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Top Cited Articles Published in 2020 and 2021
2019 novel coronavirus of pneumonia in Wuhan, China: emerging attack and management strategies
- First Published: 20 February 2020
COVID-19 critical illness pathophysiology driven by diffuse pulmonary thrombi and pulmonary endothelial dysfunction responsive to thrombolysis
- First Published: 13 May 2020
Osteocrin attenuates inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and cardiac dysfunction in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
- First Published: 03 July 2020
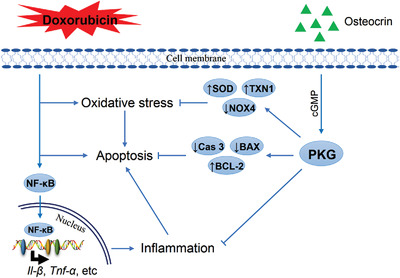
1. OSTN alleviates DOX-induced inflammation, oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. 2. OSTN deficiency exacerbates DOX-induced inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis in vitro. 3. OSTN overexpression attenuates DOX-induced acute and chronic cardiotoxicity in mice. 4. The beneficial effects of OSTN against DOX-induced cardiotoxicity are mediated by PKG activation.
Clinical characteristics and risk factors for mortality among inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China
- First Published: 04 June 2020
COVID-19 diagnostic testing: Technology perspective
- First Published: 22 August 2020
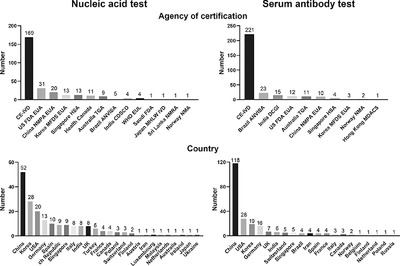
A comprehensive review of the different primary technologies used to test for COVID-19 infection. The review indicates the advantages and disadvantages of each technology, describes technologies that have the potential to accelerate SARS-CoV-2 detection in the future, and discusses the remaining challenges in COVID-19 diagnostic testing.
The clinical potential of gene editing as a tool to engineer cell-based therapeutics
- First Published: 07 February 2020
NLRP3 inflammasome, an immune-inflammatory target in pathogenesis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases
- First Published: 09 April 2020
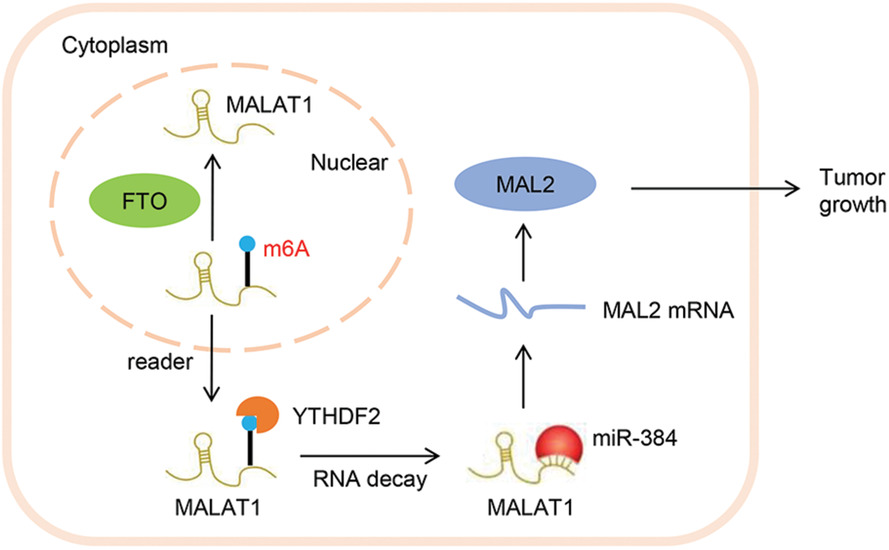
FTO modifies the m6A level of MALAT and promotes bladder cancer progression
- First Published: 01 February 2021
Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of using human menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in treating severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: An exploratory clinical trial
- First Published: 27 January 2021
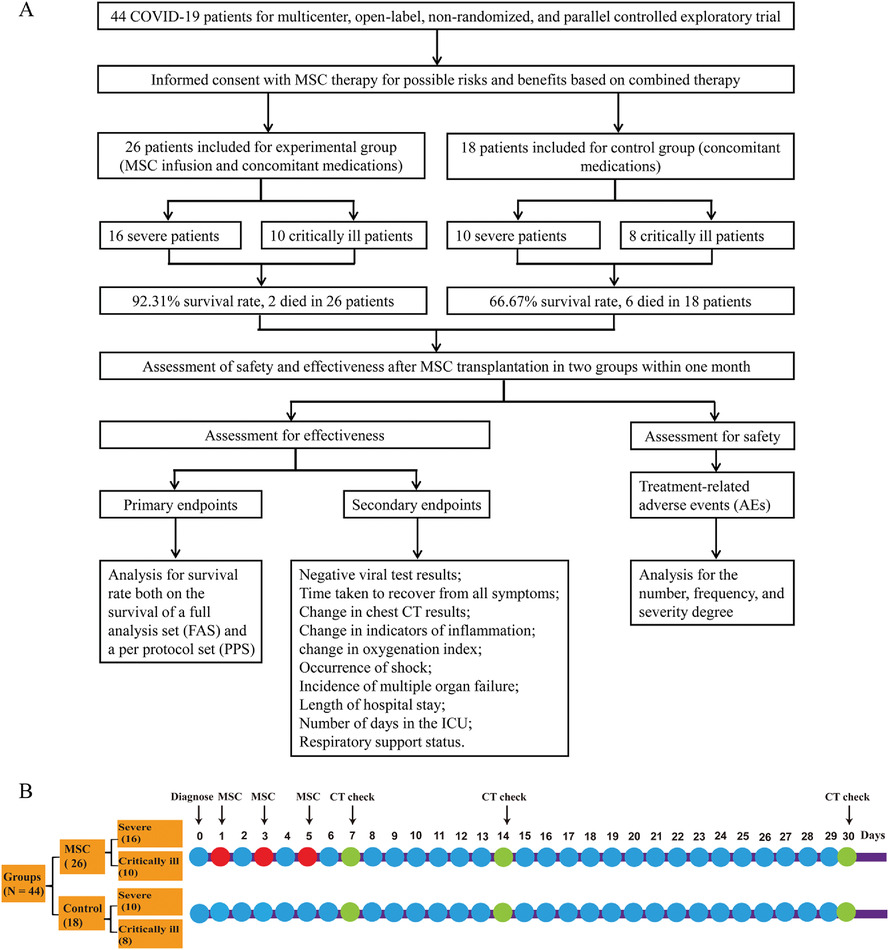
Menstrual blood-derived MSC transplantation significantly lowers the mortality of severe and critical SARS-CoV-2-induced COVID-19.
This prospective and systematic report assessed the ability of menstrual blood-derived MSCs to treat both severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients.
MSC-based therapy may serve in future clinical applications as an alternative way for the treatment of COVID-19
The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 improves osteochondral activity through miR-29b-3p/FoxO3 axis
- First Published: 13 January 2021
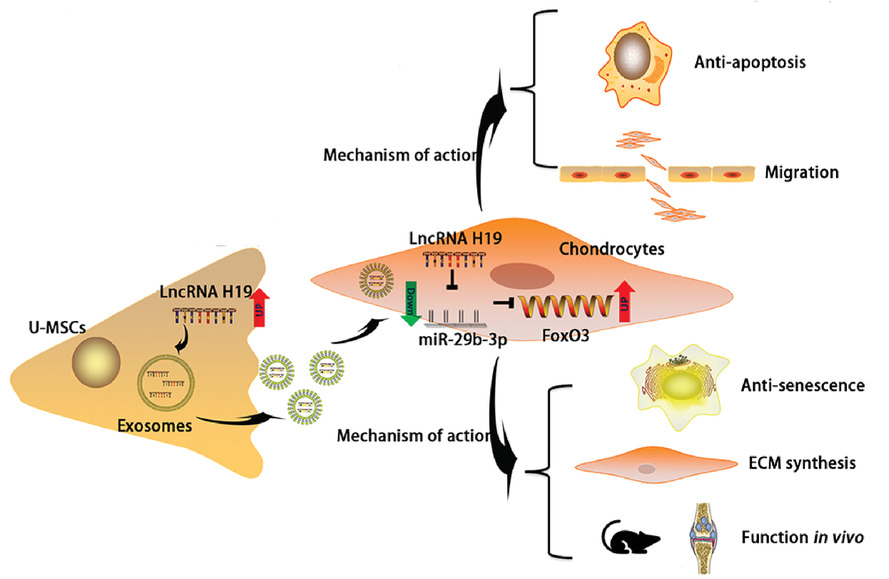
Exosomes derived from UMSCs exhibited the ability to transfer lncRNA H19 to chondrocytes.
Exosomal H19 was found to promote chondrocyte migration, matrix secretion, apoptosis suppression, as well as senescence suppression, both in vitro and in vivo.
The specific mechanism lies in the fact that exosomal H19 acts as a ceRNA against miR-29b-3p to upregulate FoxO3 in chondrocytes.
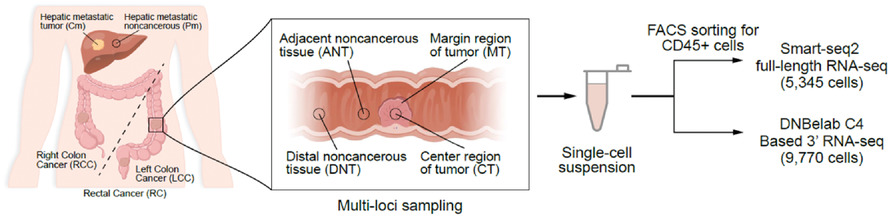
Multiregion single-cell sequencing reveals the transcriptional landscape of the immune microenvironment of colorectal cancer
- First Published: 01 January 2021
The function of LncRNAs and their role in the prediction, diagnosis, and prognosis of lung cancer
- First Published: 05 April 2021
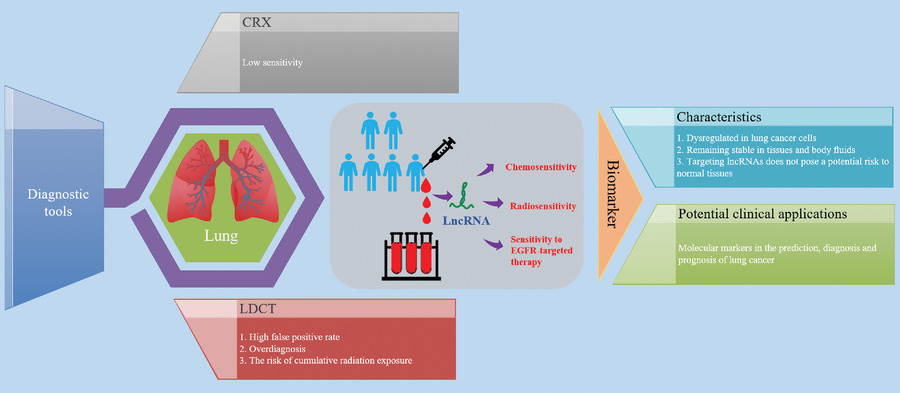
Serum or plasma assay of lncRNAs in blood can be used as a novel detection method to assist low dose CT scan (LDCT) while improving the accuracy of early lung cancer screening. LncRNAs can be used as predictive markers for chemosensitivity, radiosensitivity, and sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted therapy, and as well markers of prognosis. Different lncRNAs have been implicated to regulate chemosensitivity, radiosensitivity and sensitivity to EGFR-targeted therapy through diverse mechanisms.
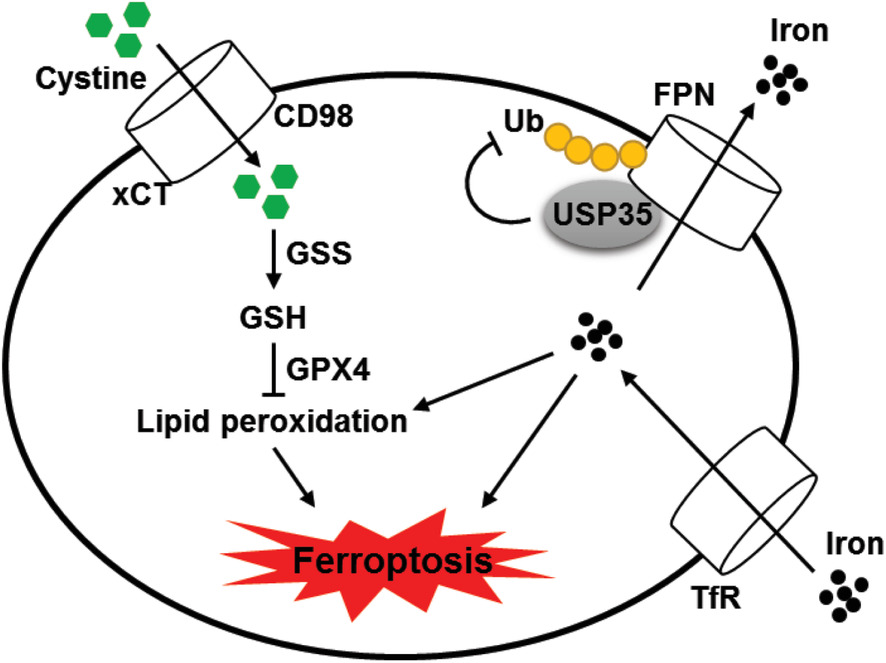
Deubiquitinase USP35 modulates ferroptosis in lung cancer via targeting ferroportin
- First Published: 01 May 2021
m6A modification of lncRNA PCAT6 promotes bone metastasis in prostate cancer through IGF2BP2-mediated IGF1R mRNA stabilization
- First Published: 06 June 2021
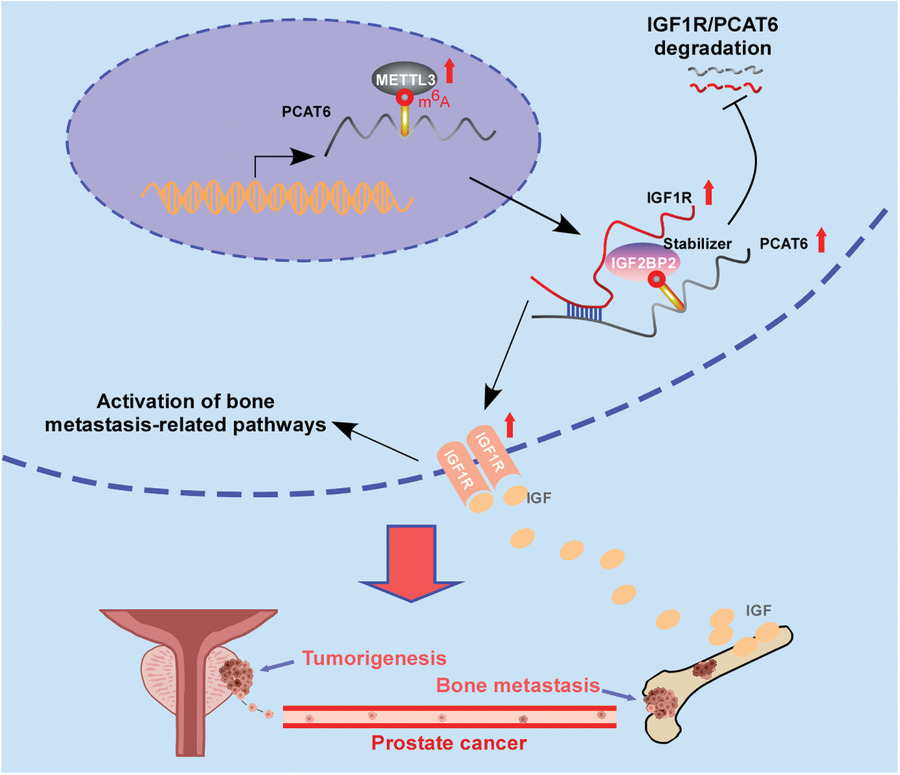
1. PCAT6 is upregulated in bone metastasis-positive prostate cancer and PCAT6 upregulation correlates with poor prognosis in patients with prostate cancer.
2. PCAT6 promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis by stabilizing IGF1R mRNA through interacting with IGF2BP2.
3. METTL3-mediated m6A modification leads to the upregulation of PCAT6 in an IGF2BP2-dependent manner.