Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
High post-chemotherapy TIL and increased CD4+TIL are independent prognostic factors of surgically resected NSCLC following neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- First Published: 09 February 2023
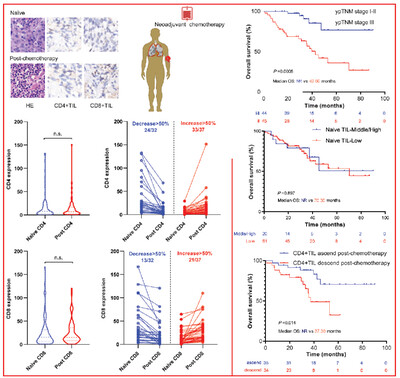
NCT remodeled the infiltrating level of CD4+TIL and CD8+TIL in individuals, which is important for antitumor immunity and associated with the prognosis of NCT-NSCLC. The ypTNM stage, post-chemotherapy TIL, and CD4+TIL ascend post-chemotherapy is independent prognostic factors of NCT-NSCLC. This study indicated that TIME remodeled by chemotherapy has a better prognostic value than the naïve TIME.
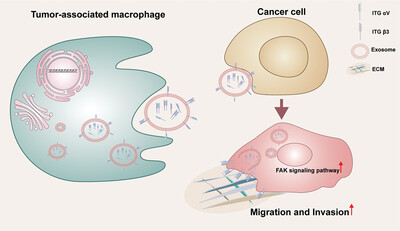
M2-like macrophage-derived exosomes facilitate metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer by delivering integrin αVβ3
- First Published: 23 December 2022
Cryo-EM structure of orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR21
- First Published: 25 January 2023
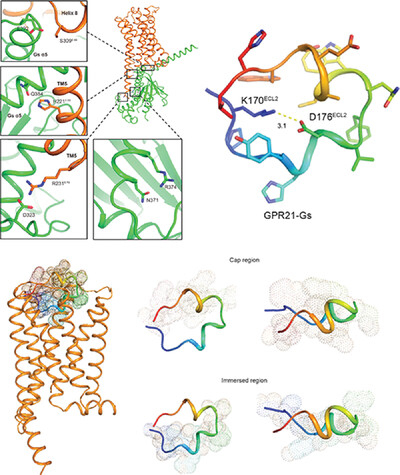
The high-resolution structure of GPR21-Gαs complexes was resolved. GPR21 ECL2 exhibited highly stable conformation and is inserted deeply into the orthosteric ligand-binding pocket of GPR21. The immersed region of ECL2 was constrained in position via an intra-loop salt bridge (K170ECL2 and D176ECL2). The new structure data reveal a novel signaling cascade of GPR21 mediated by ECL2.
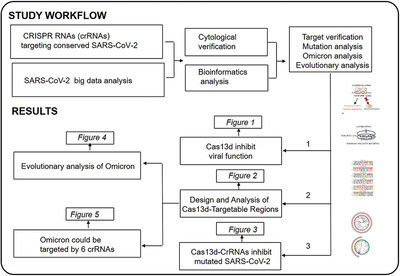
CRISPR-Cas13d effectively targets SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Delta and Omicron, and inhibits viral infection
- First Published: 31 January 2023
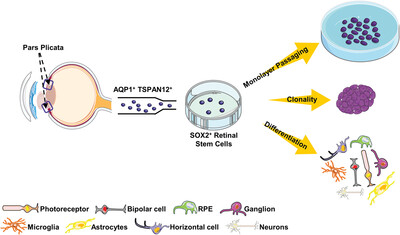
SOX2-positive retinal stem cells are identified in adult human pars plicata by single-cell transcriptomic analyses
- First Published: 24 December 2022
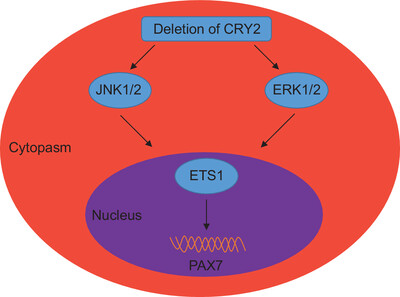
Loss of CRY2 promotes regenerative myogenesis by enhancing PAX7 expression and satellite cell proliferation
- First Published: 09 January 2023
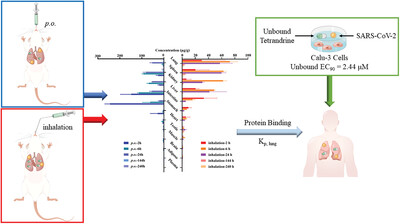
Antiviral effects and tissue exposure of tetrandrine against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19
- First Published: 19 January 2023
REVIEWS
Multifunctional nanoparticle for cancer therapy
- First Published: 11 January 2023
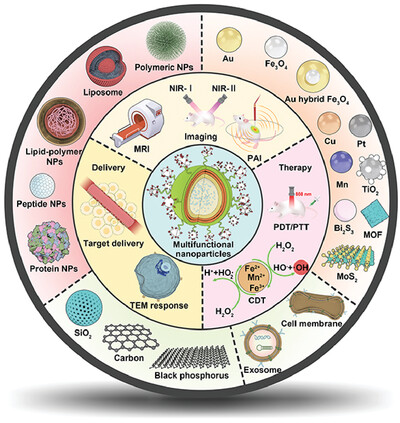
Cancer is a complex disease associated with a combination of abnormal physiological processes affecting multiple systems. The single nanocarriers are not satisfy complex cancer diseases. However, multifunctional nanoparticles are upgraded versions of the original function and involve a sophisticated system with a proper backbone. Here, the construction strategies and application advances of multifunctional nanoparticles are systemically summarized.
DNA replication: Mechanisms and therapeutic interventions for diseases
- First Published: 05 February 2023
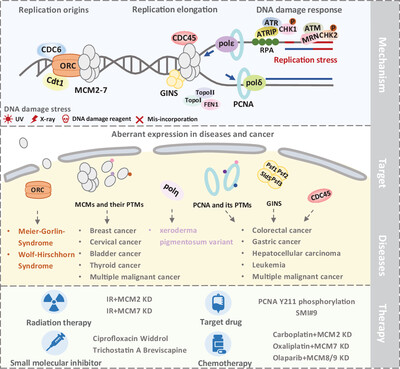
Accurate DNA replication is modulated by multiple replication-associated proteins, which is fundamental to preserve genome stability. Abundant replication proteins are involved in tumorigenesis and development, implying these proteins act as therapeutic targets in clinical. Replication-target cancer therapy emerges as the times require. Furthermore, the novel posttranslational modification of replication proteins in response to replication stress, which seems to be a promising strategy to eliminate diseases.
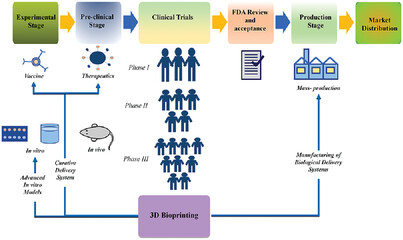
3D bioprinting and its innovative approach for biomedical applications
- First Published: 24 December 2022
Neural stem/progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A novel therapy for neurological diseases and beyond
- First Published: 07 February 2023
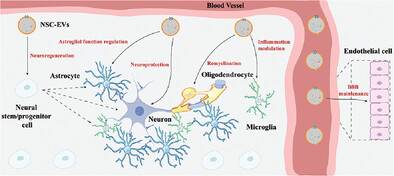
After administration, NSC-EVs can be internalized by various brain cells and vascular endothelial cells to exert their therapeutic effects. After being internalized by different types of brain cells, NSC-EVs promote the regenerative potential of endogenous NSCs, inhibit the excessive activation and neurotrophin production of astrocytes, rescue neuronal and synaptic damage from oxidative stress, promote remyelination capacity of oligodendrocytes, modulate inflammatory responses of resident microglia, and stimulate endothelial cell vascular regeneration, therefore ameliorating neurological disorders and accelerating post-disease recovery.
Aldehyde dehydrogenase in solid tumors and other diseases: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 16 January 2023
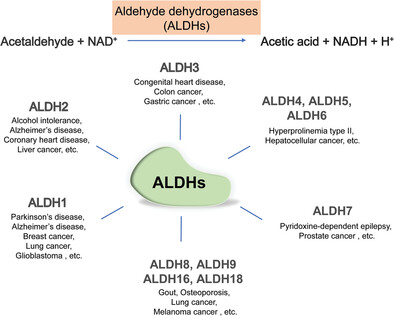
The human aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) superfamily comprises 19 isozymes and can be divided into 11 distinct families. ALDHs are a group of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+)-dependent enzymes that could catalyze the reversible oxidation of endogenous and exogenous aldehydes to their corresponding carboxylic acids. However, ALDHs are frequently dysregulated and associated with various diseases like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and especially solid tumors. Different ALDH isoenzymes are believed to be potential biomarkers or therapeutic targets in different diseases.
Hypoxia signaling in cancer: Implications for therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 23 January 2023
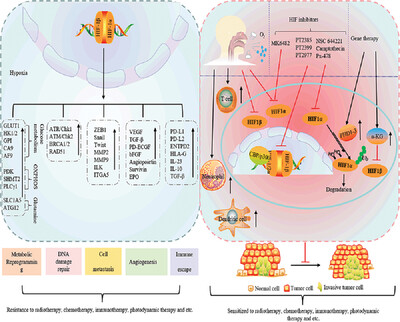
Solid tumors gradually form a hypoxic malignant microenvironment during growth, which promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis by affecting metabolism, angiogenesis, and immune escape, and finally leads to therapeutic resistance. In recent years, hypoxia-inducible factor inhibitors, direct targeting of hypoxic cells, and respiratory hyperoxia have been widely used to improve the hypoxic microenvironment of tumors and enhance the sensitivity of tumor therapy.
Dietary patterns and cardiometabolic health: Clinical evidence and mechanism
- First Published: 05 February 2023
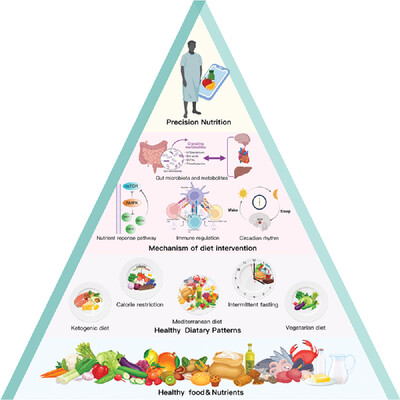
The research process for analyzing nutrition and cardiometabolic health is shown in a bottom–up manner. Phase 1: identification of essential nutrients and healthy foods, such as vegetables and fruits, whole grains, and plant-based oils (tier 4). Phase 2: establishment and development of different types of dietary patterns, such as vegetarian diets, Mediterranean diets, ketogenic diets, calorie restriction, and intermittent fasting (tier 3). Phase 3: exploration of the molecular mechanisms of dietary interventions, including nutrient response pathways, immune regulation, the role of gut microbiota and metabolites, and circadian rhythms (tier 2). Phase 4: providing personalized dietary strategies to cardiometabolic disease patients based on diet–genetic interactions (tier 1).
Vascular calcification: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 03 January 2023
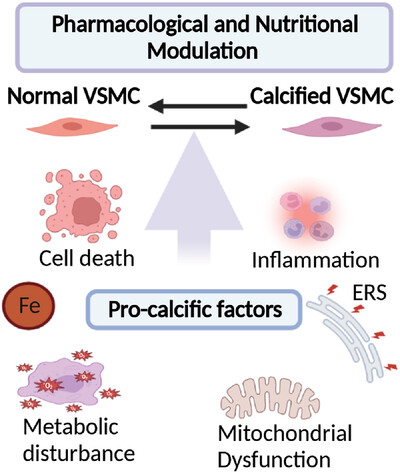
Vascular calcification is caused by the imbalance of vascular microenvironment. The pro-calcific factors include chronic inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, iron homeostasis, programed cell death, and other cellular metabolic dynamics. However, the pharmacological and nutritional modulations, such as CCBs, ACEI/ARB, and vitamins, may provide potential therapeutic strategies on vascular calcification.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of pediatric sepsis in PICUs of China: A national cross-sectional study
- First Published: 11 February 2023
Myeloid dendritic cells are increased in the lesional skin and associated with pruritus in patients with prurigo nodularis
- First Published: 11 February 2023
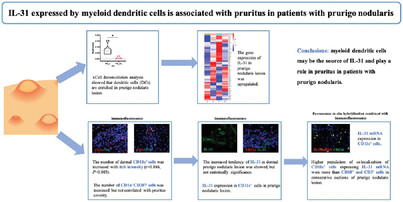
The number of dermal mDCs (CD11c+ cells) was increased with itch intensity (r = 0.886, p = 0.003) using immunofluorescence (IF). On IF, CD11c+ mDCs expressed IL-31 in lesional PN skin. Fluorescence in situ hybridization combined with IF also confirmed IL-31 mRNA expression by mDCs in PN lesion. Higher population of colocalization of CD11c+ mDCs expressing IL-31 mRNA were more than CD68+ macrophages and CD3+ T cells in consecutive sections of PN skin lesion. HC, healthy control; PN, prurigo nodularis; SPN, PN with severe pruritus (itch NRS score ≥7 points); MPN, PN with mild pruritus (itch NRS score <3 points); NRS, Numeric Rating Scale; AD, atopic dermatitis; mDC, myeloid dendritic cell.
Effectiveness and safety of four different beta-blockers in patients with chronic heart failure
- First Published: 06 January 2023
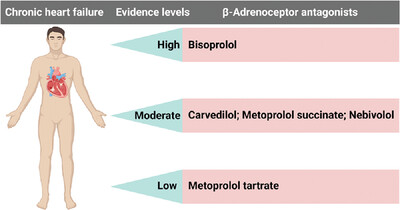
In this study, we evaluated the effectiveness and safety of bisoprolol, metoprolol, carvedilol, and nebivolol in the treatment of chronic heart failure. The results demonstrated that bisoprolol improved the prognosis of chronic heart failure in comparison with carvedilol, and carvedilol exerted similar effects as metoprolol succinate and nebivolol and better effect than metoprolol tartrate (evidence levels: bisoprolol > carvedilol = metoprolol succinate = nebivolol > metoprolol tartrate; “ > ” means “prior to”).
ERRATUM
Correction to: Interference of miR-107 with Atg12 is inhibited by HULC to promote metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 31 January 2023