Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
HIGHLIGHTS
Potential mechanisms by which impaired ketogenesis links metabolism to T-cell dysfunction in patients with severe COVID-19
- First Published: 30 September 2022
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Cryo-EM structure of G-protein-coupled receptor GPR17 in complex with inhibitory G protein
- First Published: 10 September 2022
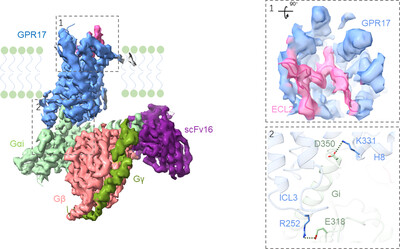
GPR17 is a class A orphan G protein-coupled receptor. The 3.02 Å resolution structure elucidates the activated GPR17 in complex with the Gαi, Gβ, Gγ, and scFv16 in the ligand-free state. The ECL2 of GPR17 occupies the orthosteric binding pocket to promote its self-activation. Meanwhile, the residues D350 and E318 of Gαi form two salt bridges with K3318.49 and R252 of GPR17, respectively, which play a prominent role in the assembly of complex.
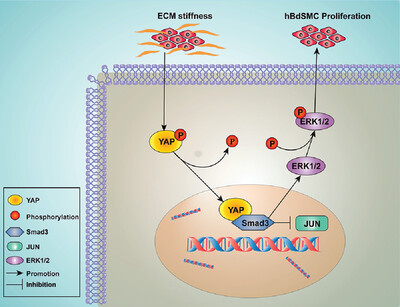
YAP/Smad3 promotes pathological extracellular matrix microenviroment-induced bladder smooth muscle proliferation in bladder fibrosis progression
- First Published: 15 September 2022
REVIEWS
Targeting cancer cachexia: Molecular mechanisms and clinical study
- First Published: 10 September 2022
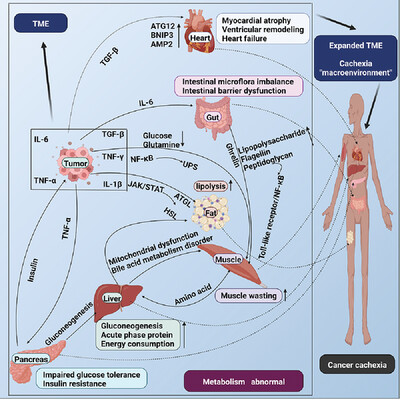
Signal communications among tumor and muscle, fat, liver, heart, pancreas, and the intestinal tract aggravate the process of cachexia. Moreover, the functions of multiple organs gradually decline in the presence of metabolic disorders, which constitutes the “macroenvironment of cancer cachexia” along with the TME. The “macroenvironment” plays an important role in the occurrence and development of cancer cachexia.
Targeting epigenetic regulators for inflammation: Mechanisms and intervention therapy
- First Published: 15 September 2022
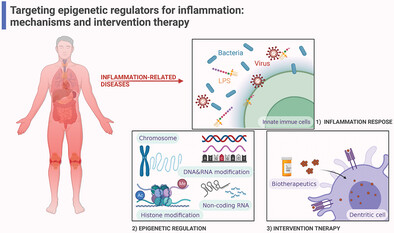
Innate immune system responds to stimulus (bacteria, virus, lipopolysaccharide) firstly; nevertheless, exaggerated immune response results in a variety of inflammation-related diseases. Epigenetic modifications including chromatin remodeling, DNA modifications, RNA modifications, Histone modifications, noncoding RNA, and regulate multiple signaling pathways of chemokines and cytokines released by immune cells in inflammation response. Biotherapeutics targeting epigenetics regulators have been studied as an important clinically effective treatments for inflammation-related diseases.
PERSPECTIVES
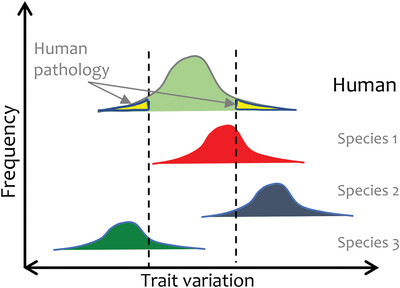
The value of broad taxonomic comparisons in evolutionary medicine: Disease is not a trait but a state of a trait!
- First Published: 22 September 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Systematic metabolic characterization of mental disorders reveals age-related metabolic disturbances as potential risk factors for depression in older adults
- First Published: 30 September 2022
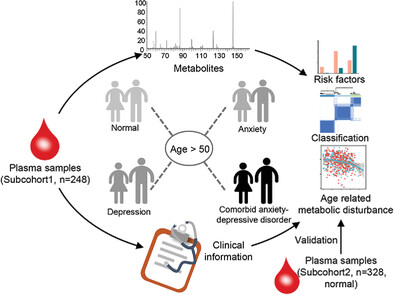
Based on plasma metabolomics and lipidomics, we identified numerous potential risk factors for older adults with anxiety, depression, or comorbid anxiety-depressive symptoms. Molecular classification revealed the clinical relevance of metabolic perturbations associated with these mental disorders. In addition, the incidence of depression increases with age. We revealed that the changes of depression-related metabolites were significantly correlated with age, indicating the interplay among age, metabolic disturbances, and depression.
REVIEWS
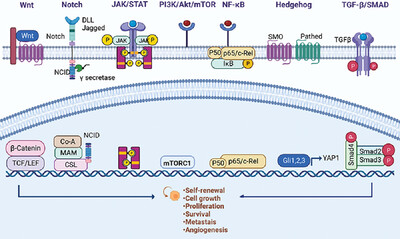
Signaling pathways in the regulation of cancer stem cells and associated targeted therapy
- First Published: 05 October 2022
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
The safety and short-term outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with donor vaccination for COVID-19
- First Published: 05 October 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Integrated analyses of brain and platelet omics reveal their common altered and driven molecules in Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 13 October 2022
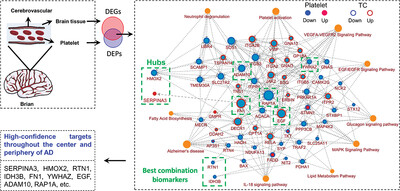
By employing multiple statistical analyses plus machine learning, we identified and validated multiple deregulated central and peripheral network in AD patients, which provided rich resources for understanding the pathogenesis of AD and large-scale biomarker validation. We also highlighted the key-driven role of HMOX2 and SERPINA3 in the AD pathogenesis, and the potential diagnostic value of RTN1 and IDH3B for AD.
REVIEWS
Small molecule inhibitors targeting the cancers
- First Published: 13 October 2022
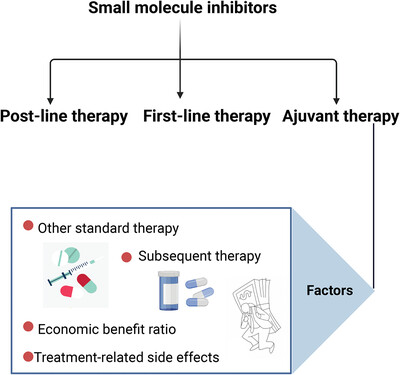
Small molecule inhibitors have been permitted to be used in post-line therapy, first-line treatment, and adjuvant therapy. Compared with post-line and first-line treatment, attempts at adjuvant therapy are just beginning. Several factors should be considered in the adjuvant setting, including other standard treatments, subsequent therapy, financial benefit ratio, and treatment-related side effects.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Transcription factor CASZ1 increases an oncogenic transcriptional process in tumorigenesis and progression of glioma cells
- First Published: 20 October 2022
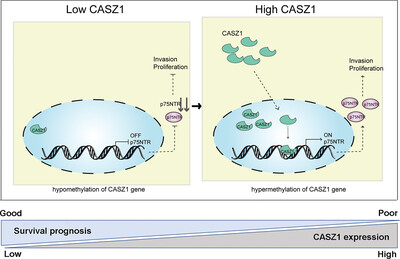
CASZ1 overexpressed is inversely correlated with the unfavorable prognosis of glioma patients, which was confirmed as a new predictive indicator. The CASZ1/p75NTR signaling axis is vital in the development and progression of glioma, being a novel potential target for glioma therapy. CASZ1 is hypo-methylated in gliomas, and its status is negatively correlated with CASZ1 mRNA level.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Pan-cancer analysis revealing DAAM1 as a novel predictive biomarker for PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- First Published: 27 October 2022
REVIEWS
Role of protein phosphorylation in cell signaling, disease, and the intervention therapy
- First Published: 03 November 2022
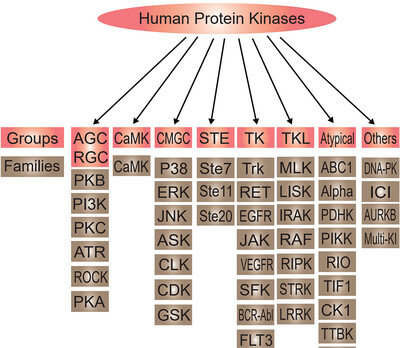
Human protein phosphorylation kinases were divided into eight groups and nearly 50 families, and delineated their main regulatory pathways, upstream and downstream targets. We analyzed more than 300 small-molecule protein phosphorylation inhibitors listed by Food and Drug Administration or in clinical research for classification, generalization, and analysis. This review takes newly developed drugs as entry point, aiming to clarify the regulatory network and relationship of each pathway, as well as their roles in disease intervention, and provide a direction for future drug development.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Tumor-associated N1 and N2 neutrophils predict prognosis in patients with resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A preliminary study
- First Published: 03 November 2022
Obstructive sleep apnea predicts pathologic response to neoadjuvant therapy in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 11 November 2022
HIGHLIGHTS
Adagrasib: A landmark in the KRASG12C-mutated NSCLC
- First Published: 25 November 2022
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: ENKUR recruits FBXW7 to ubiquitinate and degrade MYH9 and further suppress MYH9-induced deubiquitination of β-catenin to block gastric cancer metastasis
- First Published: 25 November 2022
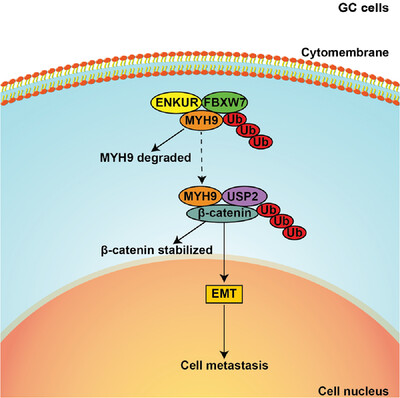
ENKUR inhibits MYH9 expression by recruiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 to promote its protein ubiquitinated degradation. Downregulated MYH9 further increased the degradation of β-catenin protein by reducing the recruitment of the deubiquitinase USP2 and finally decreased EMT signaling to inhibit GC cell metastasis.
ERRATUM
Correction to: SENP3-mediated TIP60 deSUMOylation is required for DNA-PKcs activity and DNA damage repair
- First Published: 01 December 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Distribution of intra-host variations and mutations in the genomes of SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on detection and therapeutics
- First Published: 02 December 2022
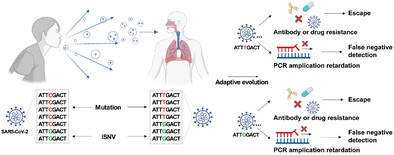
The distributions of mutations and iSNVs in the genomes of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs were characterized. The potential correlation between mutations and iSNVs of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs was evaluated. Analysis results of both mutations and iSNVs provided some helpful implications to SARS-CoV-2 detection and therapeutics.
Mixed formulation of mRNA and protein-based COVID-19 vaccines triggered superior neutralizing antibody responses
- First Published: 02 December 2022
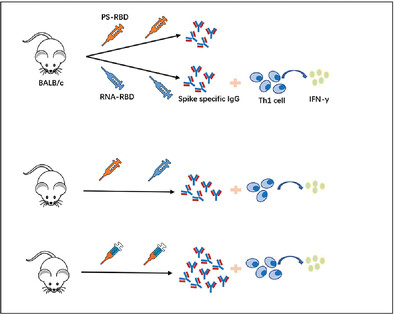
The immunogenicity of vaccines can be enhanced by the optimization of immunization strategies. In this paper, we investigated the immunogenicity of different combined regimens with the mRNA vaccine RNA-RBD and protein subunit vaccine PS-RBD. The result showed that compared with homologous immunization, heterologous prime-boost strategies for mRNA and protein subunit vaccines failed to simultaneously enhance NAb and Th1 cellular response, but immunizing the mice with the mixed formulation of the two aforementioned vaccines in various proportions further significantly enhanced the NAb responses and Th1 cellular response.
HIGHLIGHTS
Circadian-rhythm-regulating hormones: Key factors to regulate breast cancer metastasis via circulating tumor cells
- First Published: 02 December 2022
REVIEWS
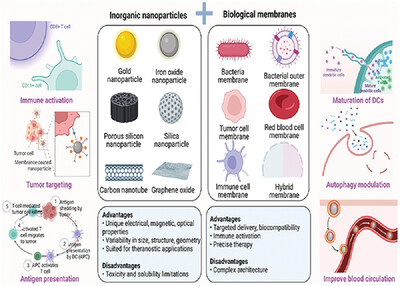
Targeting inorganic nanoparticles to tumors using biological membrane-coated technology
- First Published: 08 December 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals distinct cell response between acute and chronic pulmonary infection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- First Published: 08 December 2022
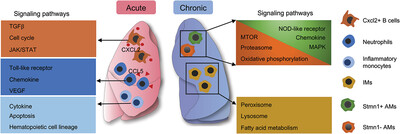
Mouse lung cell subtypes with the most significant gene expression changes in acute and chronic pulmonary infection. In the acute infection condition, activated receptors and their involved biological pathways in Cxcl2+ B cells, neutrophils, and inflammatory monocytes are indicated by the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and CellChat analysis. In contrast, signaling pathways in the Stmn1+ alveolar macrophages (AMs) and Stmn1– AMs are illustrated by the gene set enrichment analysis. Besides, in the chronic infection condition, expansion of interstitial macrophages and related signaling pathways are shown by the KEGG analysis.
REVIEWS
Long COVID: The latest manifestations, mechanisms, and potential therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 08 December 2022
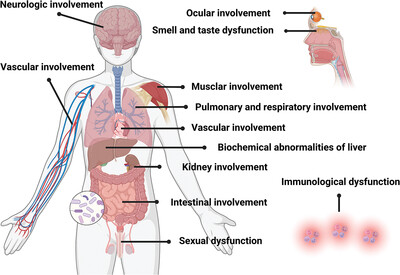
Long COVID manifests in different organs of different patients. In this manuscript, symptoms, mechanism, and potential interventions of long COVID in different organs were discussed as follows: pulmonary and respiratory involvement, neurological involvement, smell and taste dysfunction, vascular involvement, muscular involvement, cardiac involvement, intestinal involvement, immunological dysfunction, kidney involvement, biochemical abnormalities of liver, ocular involvement, and sexual dysfunction. In addition, the differences in symptoms and frequency of long COVID caused by breakthrough infection after vaccination and infection with different variants of concern are discussed in the manuscript.