Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
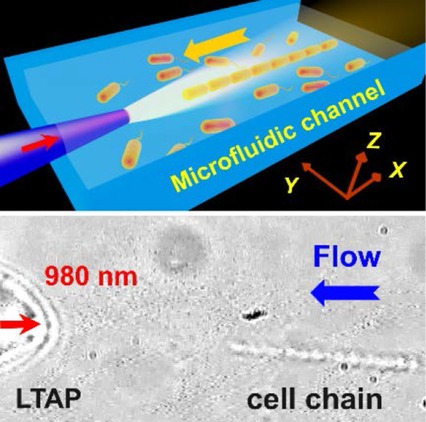
Cover Picture: Optofluidic organization and transport of cell chain (J. Biophotonics 12/2017)
- Page: 1561
- First Published: 05 December 2017

Non-contact optofluidic organization of cell chain were demonstrated by implanting a large-tapered-angle fiber probe (LTAP) into the microfluidic platform, and the organized cell chain can be transported via the adjustment of laser power and flow velocity. Further details can be found in the article by Xiaoshuai Liuet al. on pp. 1627–1635.
Inside Cover: FSOCA-induced switchable footpad skin optical clearing window for blood flow and cell imaging in vivo (J. Biophotonics 12/2017)
- Page: 1562
- First Published: 05 December 2017
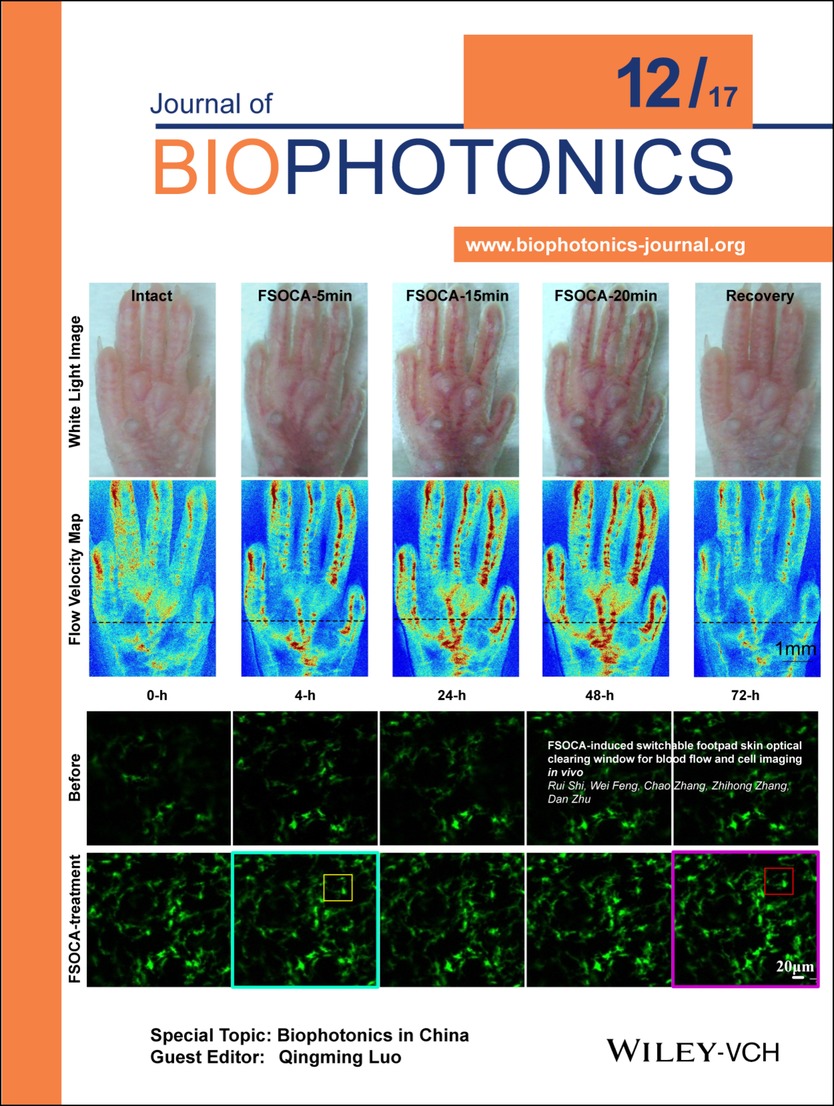
An innovative footpad skin optical clearing agent (FSOCA) has been developed to make the footpad skin transparent with topical treatment, and saline can make the footpad skin recovery. Cover figures show the switchable window permits various optical image to access to cutaneous blood flow with higher contrast, and to cell from deeper depth. The stable distribution and morphological structure of monocyte demonstrates repeated FSOCA treatment could not induce inflammation. Further details can be found in the article by Rui Shi et al. on pp. 1647–1656.
Back Cover: Spectral diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence imaging can perform early prediction of blood vessel occlusion in skin flaps (J. Biophotonics 12/2017)
- Page: 1774
- First Published: 05 December 2017

Spectral diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence imaging data and reconstructed spectra were used to statistically differentiate control flaps, arterially occluded flaps and venously occluded flaps on a rat skin flap model. Our preliminary results suggest that the proposed spectroscopic imaging technique can achieve high classification accuracy thus could detect and differentiate flaps with venous and arterial occlusion accurately at an early time point in a large skin flap. Further details can be found in the article by Shuo Chen et al. on pp. 1665–1675.
Contents
White Papers
Biophotonics in China
- Pages: 1572-1579
- First Published: 05 December 2017

In China, the Biophotonics discipline is often referred to as Biomedical Photonics, under the first-level disciplines Biomedical Engineering or Optical Engineering, and was initiated in the late 1990s. Over the past 20 years, biophotonics research in China expanded extraordinarily and has reached the frontiers of the world-level sciences. This white paper introduces the research groups in the biophotonics field in China, and their representative contributions.
Full Articles
Inverted multiscale optical resolution photoacoustic microscopy
- Pages: 1580-1585
- First Published: 27 January 2017
An inverted optical resolution photoacoustic microscopy system with multiscale FOVs and resolutions is developed. A cylindrically focused transducer and a two-dimensional galvanometric scanner are integrated to achieve a hybrid optical-mechanical scanning mechanism. Black tapes, carbon fibers, and sharp blades are imaged to evaluate the performance of the system, and in vivo multiscale imaging of vasculatures inside the ears and brains of mice is demonstrated using this system.
Enhanced phototoxicity of photodynamic treatment by Cx26-composed GJIC via ROS-, calcium- and lipid peroxide-mediated pathways
- Pages: 1586-1596
- First Published: 18 April 2017

In spite of promising initial treatment responses after PDT, recurrences remain at high level. Consequently, there is need for improvement in the effectiveness of PDT. Our study showed that Cx26-composed GJIC increased PDT phototoxicity in transfected HeLa cells, which was related with ROS, calcium and lipid peroxide-mediated pathways. Our study indicates the possibility that maintenance or increase of Cx26-formed GJIC may be used to increase the efficacy of PDT.
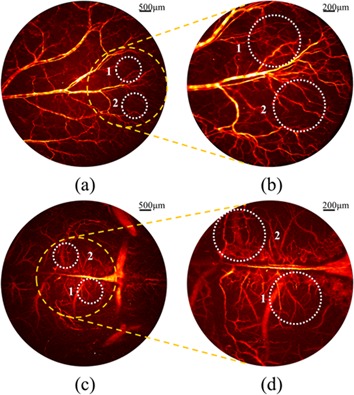
Differential standard deviation of log-scale intensity based optical coherence tomography angiography
- Pages: 1597-1606
- First Published: 30 January 2017
Differential standard deviation of log-scale intensity (DSDLI) based optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) was presented to enhance the contrast of microvasculature maps. The signal noise ratio and the spatial resolution of blood vessels are both improved greatly with our method compared to speckle variance OCT and power intensity method, which suggests a promising application of DSDLI in the disease diagnosis and monitoring.
Cypate-mediated thermosensitive nanoliposome for tumor imaging and photothermal triggered drug release
- Pages: 1607-1616
- First Published: 20 January 2017
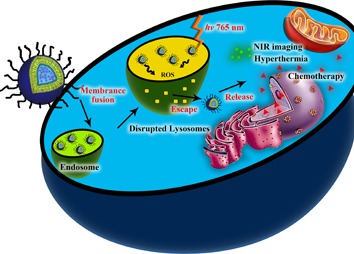
Nanoscale drug delivery systems are attracting considerable attention as an alternative strategy to overcome a lot of limitation. The multifunctional photothermal sensitive liposomes drug-loading system was established, with cypate and DOX carried in it for multi-mechanism diagnosis and treatment of tumor diseases. The attractive features of DOX@PTSL demonstrated here support the anticipation of its promising prospect in cancer therapy.
Editor's Choice
Rapid, label-free identification of cerebellar structures using multiphoton microscopy
- Pages: 1617-1626
- First Published: 02 May 2017
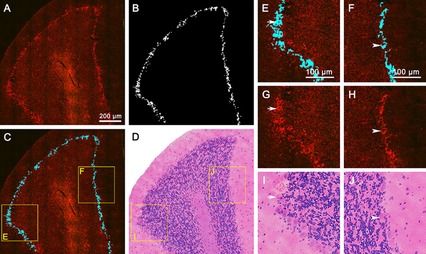
The combination of multiphoton microscopy and custom-developed image processing algorithms was employed as a rapid and label-free method to identify cerebellar structures and pathology. This approach establishes the feasibility of MPM for a direct visualization and rapid pathological diagnosis of unstained cerebellar tissue, which can be provided preliminary proof of principle needed to translate in vivo multiphoton microendoscopes and fiberscopes into clinical use.
Optofluidic organization and transport of cell chain
- Pages: 1627-1635
- First Published: 02 May 2017
Cetuximab-conjugated nanodiamonds drug delivery system for enhanced targeting therapy and 3D Raman imaging
- Pages: 1636-1646
- First Published: 21 June 2017
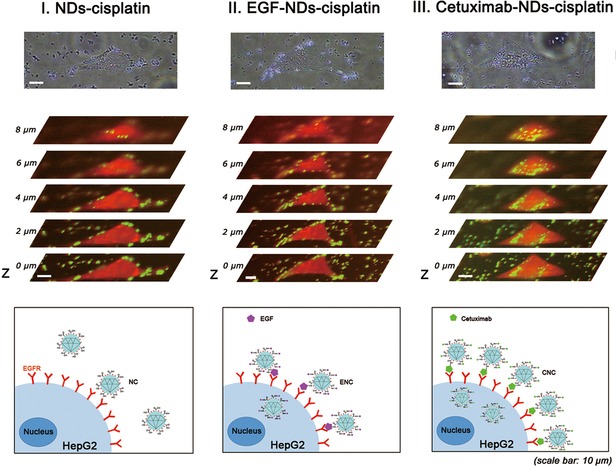
Cetuximab-nanodiamonds (NDs)-cisplatin targeting drug delivery system is developed in this work, which combines specific targeting and enhanced therapeutic efficacy capabilities, incomparison with nonspecific NDs-cisplatin conjugate and specific EGF-NDs-cisplatin bioconjugate. Besides, the three-dimensional Raman imaging technique is utilized to visualize the performance of NDs-based drug delivery system in cancer cell targeting and internalization. These advantageous properties of cetuximab-NDs-cisplatin propose a promising treatment and imaging tool for further clinical application.
FSOCA-induced switchable footpad skin optical clearing window for blood flow and cell imaging in vivo
- Pages: 1647-1656
- First Published: 18 May 2017
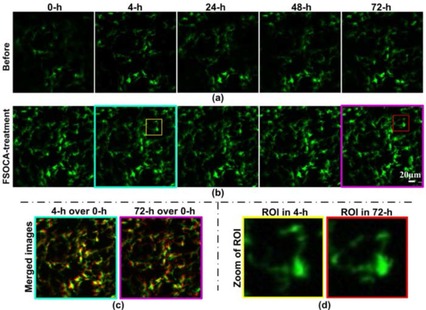
An innovative FSOCA was developed to make the footpad skin transparent, which provided a switchable window for blood flow and cell imaging in vivo. The results showed that the cutaneous blood flow can be monitored with higher contrast, and fluorescent cells can be imaged with higher signal intensity and larger depth after FSOCA treatment. This switchable footpad skin optical clearing window will be significant for microcirculation, immunology, and other diseases studies.
Optomechanical measurement of the role of lamins in whole cell deformability
- Pages: 1657-1664
- First Published: 09 May 2017
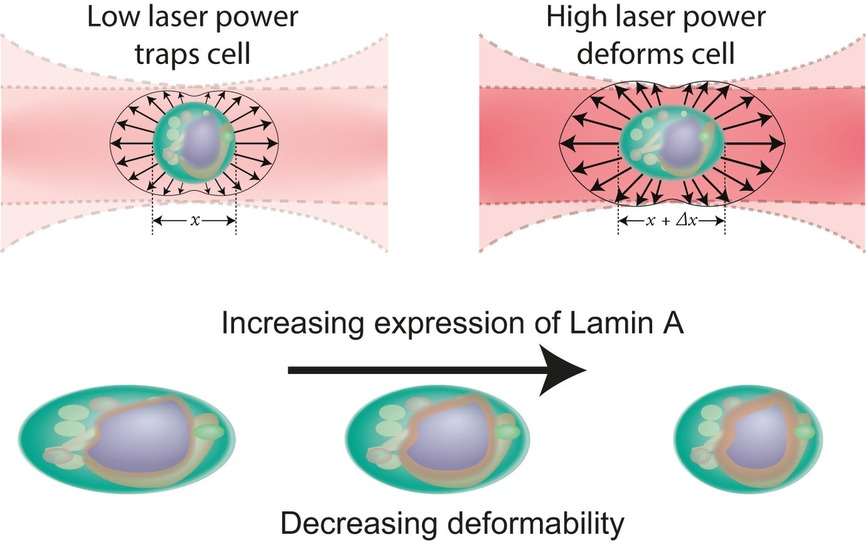
The nuclear lamina provides a physical layer of filamentous protein around a cell's nucleus which can alter the mechanical properties of the cell. We use optical forces to investigate the changing deformability of the whole cell and the nucleus with differing levels of A-type lamins within the nuclear envelope. The optical stretcher provides a detailed measurement of the time-dependent deformation of the cell and nucleus which can be used to investigate the role of lamins.
Spectral diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence imaging can perform early prediction of blood vessel occlusion in skin flaps
- Pages: 1665-1675
- First Published: 17 November 2016
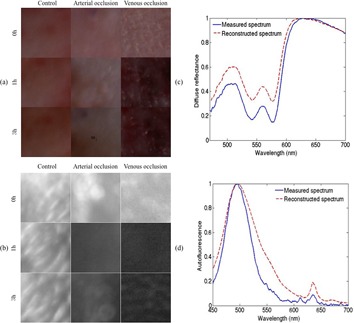
In this study, spectral diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence imaging data and reconstructed spectra were used to statistically differentiate control flaps, arterially occluded flaps and venously occluded flaps in a rat skin flap model. Our preliminary results suggest that the proposed spectroscopic imaging technique can achieve high classification accuracy thus could detect and differentiate flaps with venous and arterial occlusion accurately at an early time point in a large skin flap.
Treatment of tumor in lymph nodes using near-infrared laser light-activated thermosensitive liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin and gold nanorods
- Pages: 1676-1682
- First Published: 18 April 2017
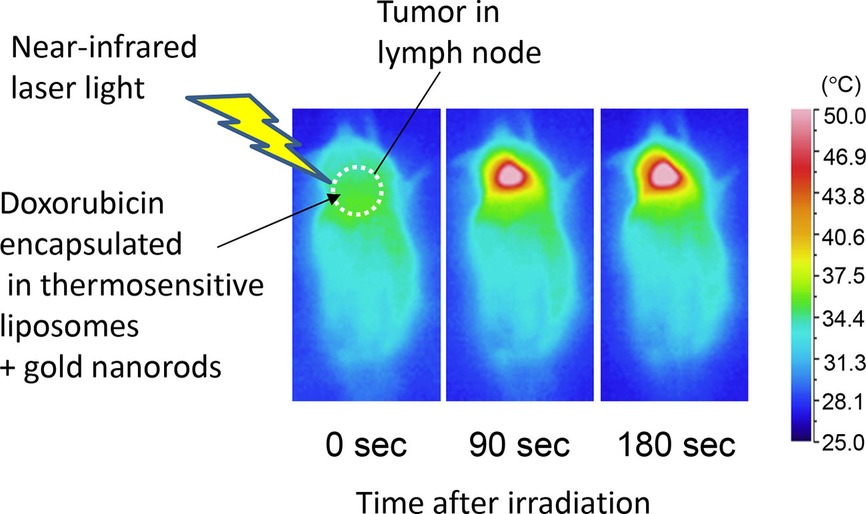
Tumor metastasis to lymph nodes is an important contributory factor for cancer-related deaths despite recent developments in cancer therapy. This study demonstrates that tumor in the lymph node of the mouse can be treated by the external near-infrared laser light to trigger the unloading of doxorubicin encapsulated in thermosensitive liposomes administered together with gold nanorods. This work presents a theranostic approach that has the potential to treat metastatic lymph nodes.
Light-Emitting Diode treatment ameliorates allergic lung inflammation in experimental model of asthma induced by ovalbumin
- Pages: 1683-1693
- First Published: 18 April 2017
Asthma is a multifactorial disease where treatment sometimes is not effective and, in this context new therapies are of great importance. Phototherapy as Light-emitting diode (LED) has emerged as a promisor treatment presenting good results for diseases which are characterized by inflammation. This study open the possibility of a new approach for the asthma treatment showing that drug therapy chould be replaced by LED treatment.
Optical assessment of changes in mechanical and chemical properties of adipose tissue in diet-induced obese rats
- Pages: 1694-1702
- First Published: 02 May 2017
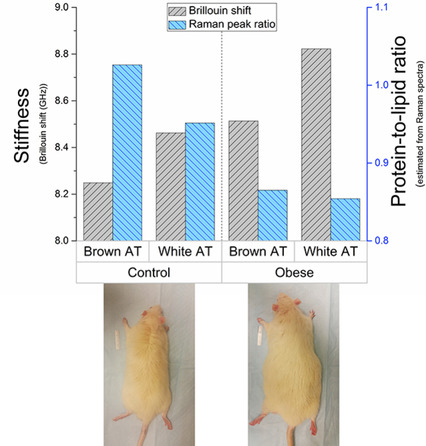
Obesity is associated with tissues’ structural and chemical changes; however, few methods are capable of their concurrent measurement. Using a powerful combination of Brillouin and Raman microspectroscopy, adipose tissue's mechanical and chemical differences between control and obese rats are assessed simultaneously for the first time. The results indicate the adipose tissue experiences an obesity-induced increase in stiffness and lipid content, with brown adipose undergoing a greater change than white adipose.
Development of a classification model for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) using confocal Raman micro-spectroscopy
- Pages: 1703-1713
- First Published: 21 June 2017
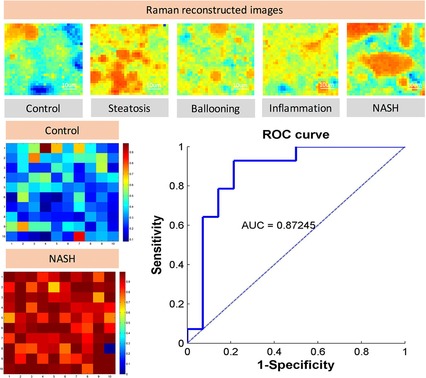
Raman micro-spectroscopy was used to detect and quantify NASH signatures on mice model tissue samples. Quantification of the signatures such as lipid content, using spectrum decomposition and machine learning techniques, revealed their spatiotemporal redistribution as the disease progresses. We identified biochemical changes specific to NASH and show that the classification model could accurately detect NASH (AUC=0.85–0.87). This model can be further validated in clinical samples.
Is the nuclear refractive index lower than cytoplasm? Validation of phase measurements and implications for light scattering technologies
- Pages: 1714-1722
- First Published: 18 April 2017
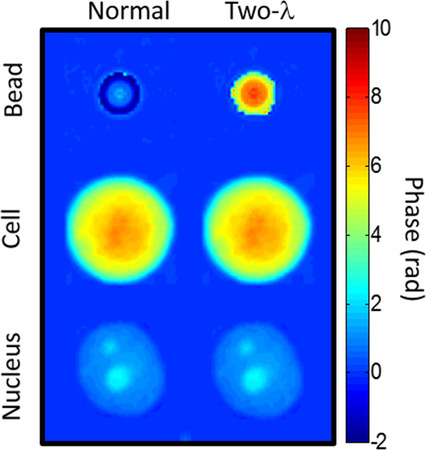
Recent studies using quantitative phase microscopy have suggested that the nuclear refractive index is lower than that of cytoplasm. In this paper, we verify this claim in new cell lines, including non-cancerous and primary lines. We further validate against potential corrupting factors, and examine the impact that a low nuclear index would have on light scattering technologies.
Intracellular localization and delivery of plasmid DNA by biodegradable microsphere-mediated femtosecond laser optoporation
- Pages: 1723-1731
- First Published: 02 May 2017
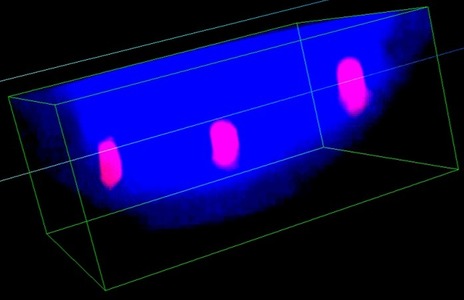
The delivery of plasmid DNA into a nucleus is demonstrated utilizing dielectric microspheres and a femtosecond laser. The transfection is discussed with respect to permeabilization of two main barriers against gene delivery – the cell membrane and nuclear membrane by observing the intracellular localization of plasmid DNA.
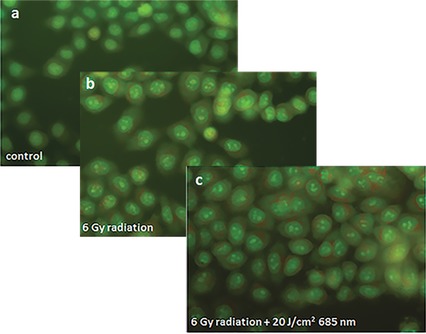
Photobiomodulation leads to enhanced radiosensitivity through induction of apoptosis and autophagy in human cervical cancer cells
- Pages: 1732-1742
- First Published: 02 May 2017
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering analysis of urine from deceased donors as a prognostic tool for kidney transplant outcome
- Pages: 1743-1755
- First Published: 09 May 2017
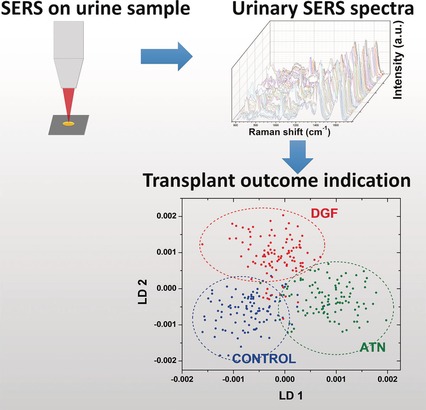
Despite severe shortage of kidney donors, many kidneys from deceased donors (DD) are not transplanted because of real or perceived risk of failure. We show that DD kidneys which functioned well after transplantation despite their perceived risk can be classified by surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) analysis of DD urine. The SERS approach may prove a powerful tool to assist transplant surgeons in utilizing DD kidneys that would otherwise be discarded.
Propagation of Gaussian and Laguerre-Gaussian vortex beams through mouse brain tissue
- Pages: 1756-1760
- First Published: 21 June 2017
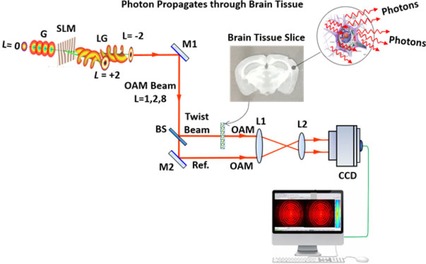
To test the hypothesis that applying Laguerre-Gaussian (LG) vortex beam would obtain higher penetration depth than Gaussian (G) beam for brain imaging, light transmittances of LG beams in mouse brain tissue were measured at different topological charges. Study showed no obvious difference between the transmittances of LG and G beams, which may be due to the interference effects in brain tissue that are not yet fully understood.
Low-level light emitting diode therapy promotes long–term functional recovery after experimental stroke in mice
- Pages: 1761-1771
- First Published: 02 May 2017
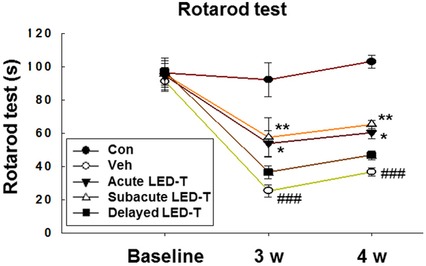
This study aimed to investigate the effects of low-level light emitting diode therapy (LED-T) on the long-term functional outcomes after cerebral ischemia, and the optimal timing of LED-T initiation for achieving suitable functional recovery. we clearly found that LED-T administered during the subacute stage had a positive impact on the long-term functional outcome, probably via neuron and astrocyte proliferation, blood vessel reconstruction, and increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression.