Spectral diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence imaging can perform early prediction of blood vessel occlusion in skin flaps
Abstract
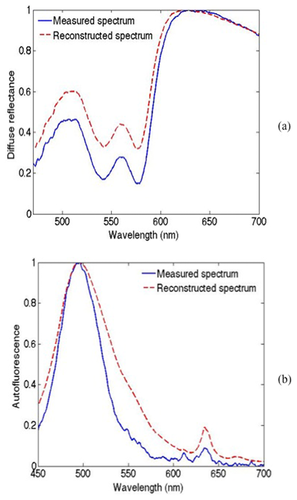
Flap transfer has become a common technique in reconstructive surgery. However, a significant number of compromised skin flaps are not successfully salvaged because the current clinical method for flap assessment relies heavily on the clinician's experience. Vascular occlusion is the major reason for flap failure, thus the accurate and objective early prediction of blood vessel occlusion is vitally important. Our parallel point measurement study has demonstrated the great potential of joint diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence spectroscopy in the early detection and differentiation of venous and arterial occlusion in skin flaps. Unfortunately, the technique of point measurements is not suitable to examine a large skin flap when a high spatial resolution is required. In this study, we attempted to overcome this problem by performing spectral diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence imaging on a rat skin flap model. Both imaging data and reconstructed spectra were used to statistically differentiate control flaps, arterially occluded flaps and venously occluded flaps. Our preliminary results suggest that the technique of joint diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence spectroscopic imaging can achieve high classification accuracy thus could be used to detect and differentiate flaps with venous and arterial occlusion accurately at an early time point in a large skin flap.