Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Consumption of cricket (Acheta domesticus) flour decreases insulin resistance and fat accumulation in rats fed with high-fat and -fructose diet
- First Published: 20 June 2022
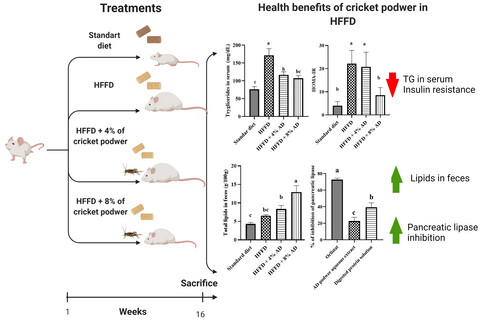
Acheta domesticus (AD) in high-fat and -fructose diet (HFFD) reduces body weight gain and visceral adipose tissue accumulation.
AD in HFFD decreases the serum triglycerides and improves insulin resistance, measured by the HOMA-IR index.
The effects of the addition of AD in an HFFD were related to a greater lipid excretion in feces, and the partial inhibition of pancreatic lipase by the aqueous extract and the hydrolyzed protein obtained from AD.
New alternatives from sustainable sources to wheat in bakery foods: Science, technology, and challenges
- First Published: 19 April 2022
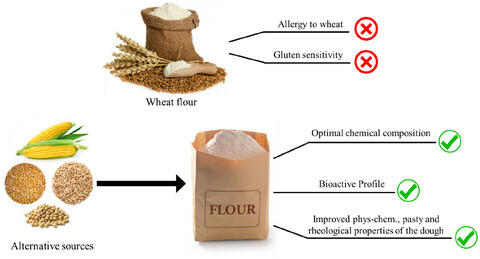
- New alternatives from sustainable sources to wheat in bakery foods as an approach that affects human health.
- Alternatives from sustainable sources are important source of nutrients and bioactive compounds.
- Alternatives from sustainable sources are rising due to nutritional and consumer demand in bakery industry.
- New alternatives from sustainable sources improve physicochemical, pasting, and rheological properties of dough.
- Non-wheat-based foods from non-traditional grains have a potential to increase consumer market acceptance.
A review of thermosensitive antinutritional factors in plant-based foods
- First Published: 02 May 2022
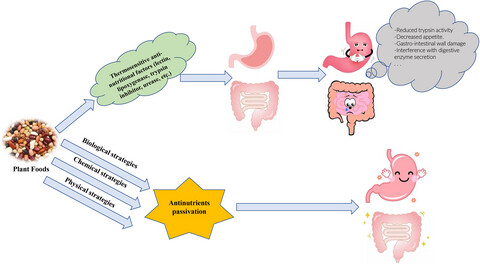
Most plant-based foods (e.g., cereals and legumes) contain thermosensitive anti-nutritional factors such as trypsin inhibitors, lectins, urease and lipoxygenase, the presence of which can cause damage to human such as reduced trypsin activity, decreased appetite, gastro-intestinal wall damage, interference with digestive enzyme secretion and compromised absorption rate of nutrients. Now physical, biological and chemical methods are being used to passivate anti-nutritional factors in foods and improve people health. In this paper, we reviewed the research progress on thermosensitive anti-nutritional factors.
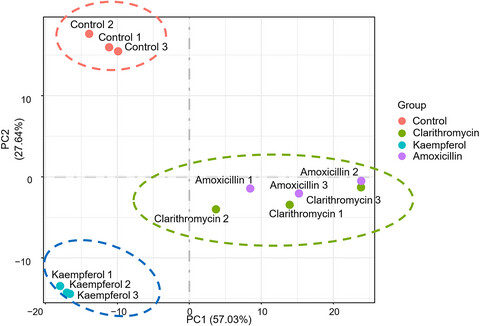
Kaempferol inhibits the growth of Helicobacter pylori in a manner distinct from antibiotics
- First Published: 28 April 2022
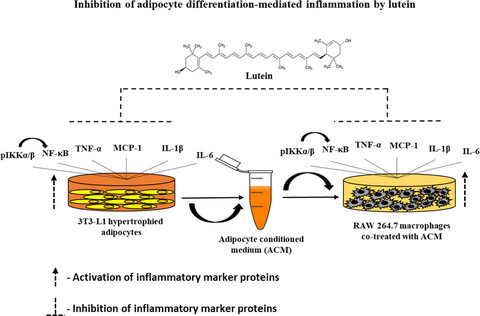
Effective inhibition of adipogenesis-mediated inflammation by a macular carotenoid, lutein in vitro
- First Published: 30 April 2022
Hesperetin and the PI3K/AKT pathway: Could their interaction play a role in the entry and replication of the SARS-CoV-2?
- First Published: 25 April 2022
Major royal jelly proteins alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice model by regulating disordered metabolic pathways
- First Published: 05 May 2022
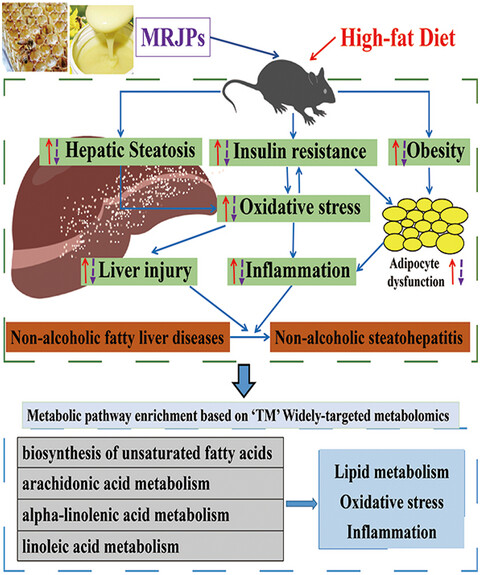
Major royal jelly proteins (MRJPs) were applied to study its effects on improving NAFLD in the NAFLD mouse model. Herein, we demonstrated that intaking of 250–500 mg/kg/day MRJPs significantly decreased the rate of obesity, dyslipidemia, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance. TOF to MRM widely targeted metabolomics indicated that MRJPs alleviated lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammation mainly by regulating the metabolisms of alpha-linolenic acid, linoleic acid, arachidonic acid, and biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids.
The effect of postmortem pH decline rate on caspase-3 activation and tenderness of bovine skeletal muscle during aging
- First Published: 28 April 2022
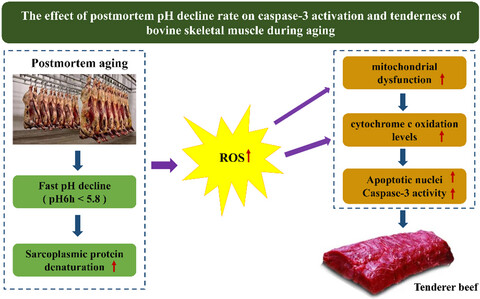
In the present study, the effect of postmortem pH decline rate on mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and bovine muscle tenderness was investigated. The fast pH decline promoted sarcoplasmic protein denaturation and ROS accumulation, which further enhanced mitochondrial dysfunction and cytochrome c oxidation, thereby increasing the proportion of apoptotic nuclei and caspase-3 activity. Thus, the fast postmortem pH decline contributed to the tenderization of bovine muscle via caspase-3 activation.
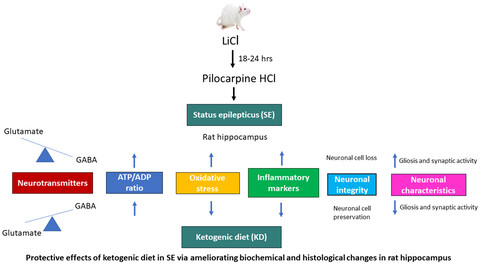
Ameliorating effect of ketogenic diet on acute status epilepticus: Insights into biochemical and histological changes in rat hippocampus
- First Published: 11 May 2022
Anti-breast-cancer activity of self-fermented Bovistella sinensis Lloyd extracts through the mitochondrial ROS-induced apoptosis in vitro
- First Published: 09 May 2022
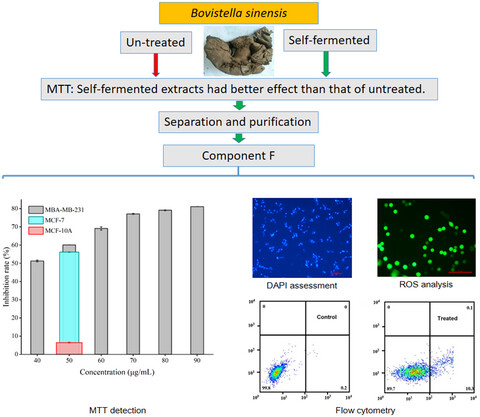
The various extracts of self-fermented Bovistella sinensis (BS) Lloyd showed stronger anti-proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells than that of untreated. Then the ethyl acetate extract of self-fermented BS was further separated and purified to obtain the main component F, which showed the low toxicity in normal cell line, while high cytotoxicity in breast cancer cell line. Apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 cells was found to be taken place in the mitochondrial pathway induced by reactive oxygen species.
In silico evaluation of food-derived carotenoids against SARS-CoV-2 drug targets: Crocin is a promising dietary supplement candidate for COVID-19
- First Published: 11 May 2022
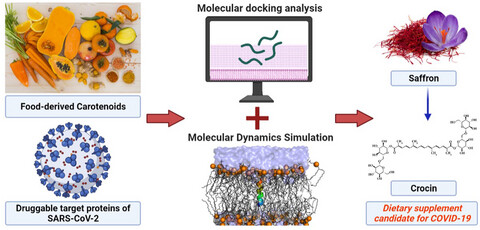
The molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations of carotenoids against multiple SARS-CoV-2 druggable targets revealed that carotenoids are promising therapeutic candidates for COVID-19. Particularly, crocin showed strong binding affinity against multiple drug targets and thus can be considered as a dietary supplement option in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19.
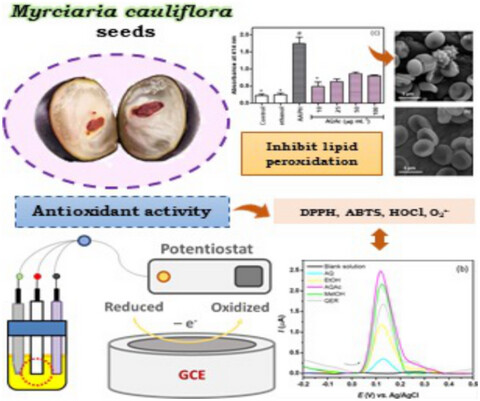
Antioxidant capacity of Myrciaria cauliflora seed extracts by spectrophotometric, biochemical, and electrochemical methods and its protective effect against oxidative damage in erythrocytes
- First Published: 09 May 2022
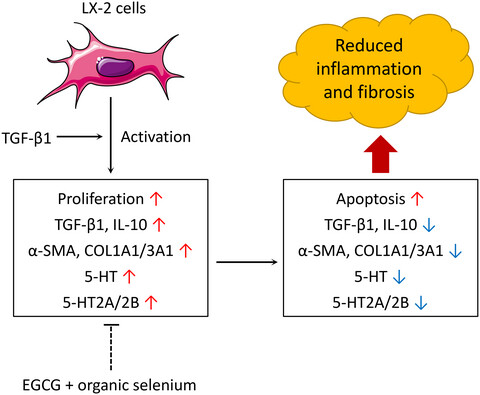
Protective effects of epigallocatechin-3-o-gallate combined with organic selenium against transforming growth factor-beta 1-induced fibrosis in LX-2 cells
- First Published: 19 May 2022
Elucidation of aroma compounds in passion fruit (Passiflora alata Ait) using a molecular sensory approach
- First Published: 13 May 2022
Effect of supplementation with polyphenol extract of Thymus atlanticus on paraoxonase-1 activity, insulin resistance, and lipid profile in high-fat diet-fed hamsters
- First Published: 16 May 2022
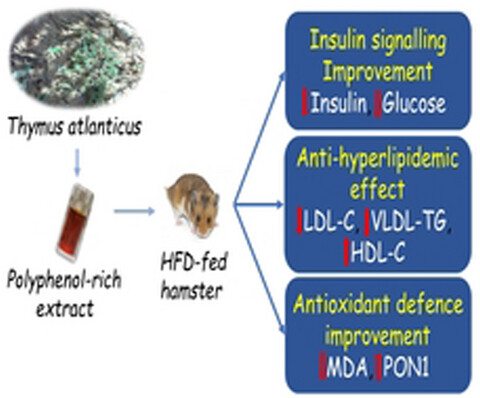
Sixty-three days of supplementation with a polyphenol-rich extract from Thymus atlanticus prevented diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and oxidative stress induced by a high-fat diet (HFD) in hamsters via improving insulin signaling, decreasing the levels of LDL cholesterol and VLDL triglycerides, increasing HDL cholesterol level, and enhancing serum paraoxonase-1 activity.
Investigation of cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of 63 compounds obtained from Salvia species: Promising anticancer agents
- First Published: 24 May 2022
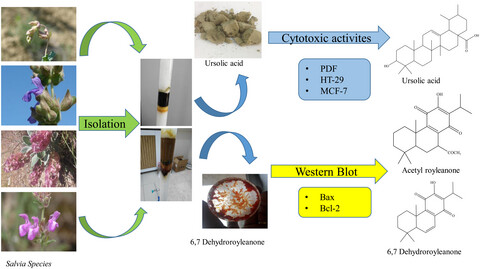
To investigate the effects of 63 secondary metabolites from Salvia species on cell viability and apoptosis were examined using MTT and Western Blot methods. Acetyl royleanone, 6,7-dehydroroyleanone, carnosic acid and cryptotanshinone were found to have anticancer potential based on their modulating effects on the expression levels of Bax and Bcl-2 proteins which play important roles in the regulation of apoptosis.
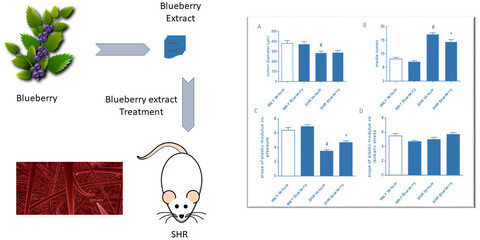
Effects of blueberry polyphenolic extract on vascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- First Published: 22 May 2022
Therapeutic potentials of genistein: New insights and perspectives
- First Published: 17 May 2022
Comparative bioactivity profile of phospholipids from three marine byproducts based on the zebrafish model
- First Published: 16 May 2022
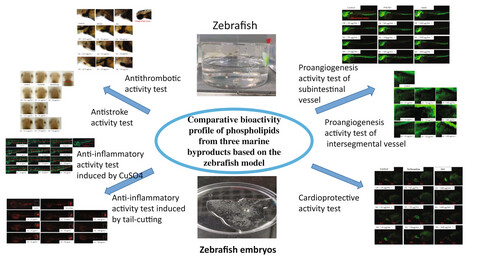
The antithrombotic, antistroke, anti-inflammatory, pro-angiogenic, and cardioprotective activities of phospholipids from shrimp heads, codfish roe, and squid gonads were comprehensively evaluated and compared using the zebrafish model. There were significant differences among these distinct phospholipids in activities. The results lay a foundation for the development of phospholipids in marine byproducts in the future.
Baicalein: A review on its anti-cancer effects and mechanisms in lung carcinoma
- First Published: 11 May 2022
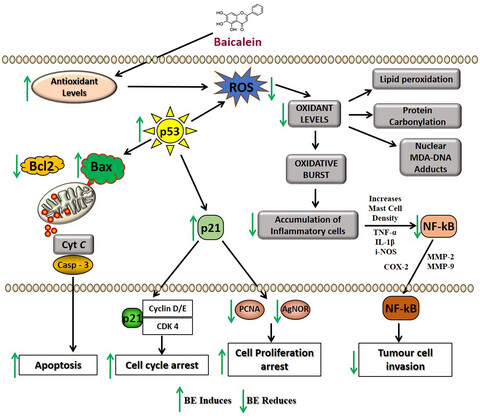
Lung cancer is one of the most common malignancies in the world with a high fatality rate. Several studies have found that Baicalein is an important candidate for treating lung cancer. Its mechanism of action includes regulation of oxidative stress, cell proliferation, metastasis, apoptosis, cell cycle, autophagy, and inflammation. Baicalein could be used as a novel anti-cancer drug for the treatment of lung carcinoma.
Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG fermentation on the structural and functional properties of dietary fiber in bamboo shoot and its application in bread
- First Published: 10 May 2022
Molecular and immunological characterization of cysteine protease from Phaseolus vulgaris and evolutionary cross-reactivity
- First Published: 20 May 2022
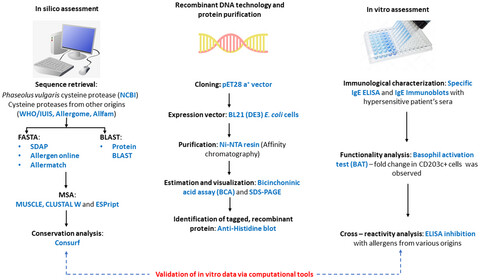
Kidney bean cysteine protease was characterized as a major cross-reacting allergen by in silico and in vitro methods. In computational assessment cross-reactivity and allergenicity of allergen was determined using sequence homology approach. This was followed by cloning and purification of allergen using recombinant DNA technology and affinity chromatography, respectively. Finally, in vitro analysis using food hypersensitive patients' sera validated in silico data, thereby representing cysteine protease as a potential allergen.
Piper retrofractum extract and its component piperine promote lymphangiogenesis via an AKT- and ERK-dependent mechanism
- First Published: 13 May 2022
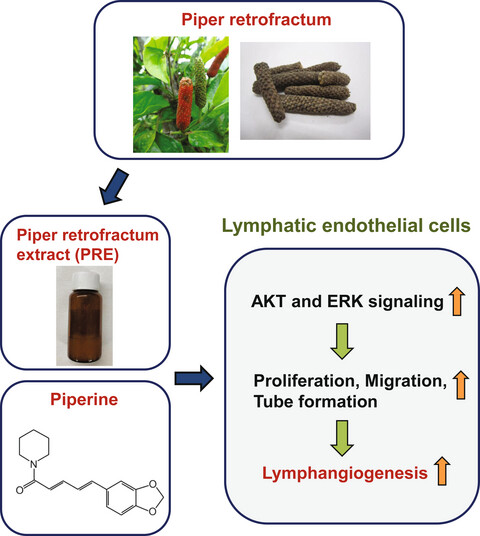
Piper retrofractum extract (PRE) and piperine promoted the proliferation, migration, and tube formation of human dermal lymphatic microvascular endothelial cells (HDLECs). PRE- and piperine-induced lympangiogenesis is AKT and ERK signaling dependent mechanism. PRE has the potential to be used as a novel functional food for improving lymphedema.
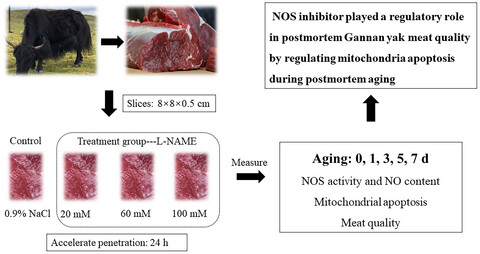
Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on mitochondria apoptosis and meat quality in postmortem Gannan yak (Bos grunniens) meat
- First Published: 24 May 2022
Kidney bean cysteine protease was characterized as a major cross-reacting allergen by in silico and in vitro methods. In computational assessment cross-reactivity and allergenicity of allergen was determined using sequence homology approach. This was followed by cloning and purification of allergen using recombinant DNA technology and affinity chromatography, respectively. Finally, in vitro analysis using food hypersensitive patients' sera validated in silico data, thereby representing cysteine protease as a potential allergen.
An acidic polysaccharide from Oxalis corniculata L. and the preliminary study on its antioxidant activity
- First Published: 17 May 2022
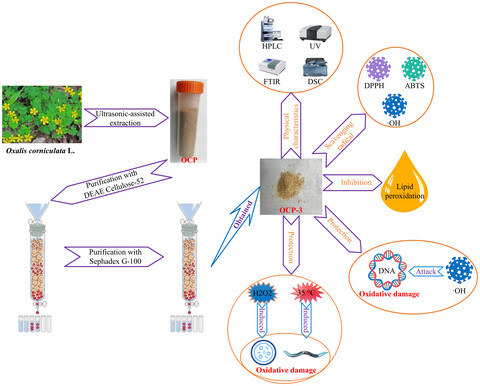
OCP-3, purification from O. corniculata polysaccharide with DEAE Cellulose-52 and Sephadex G-100, was an acidic heteropolysaccharide with 31.5 kDa and exhibited strong antioxidants for scavenging free radical, anti-lipid peroxidation, protecting plasmid DNA, HEK 293 cell, and Caenorhabditis elegans from oxidative damage.
Functional yogurt fermented by two-probiotics regulates blood lipid and weight in a high-fat diet mouse model
- First Published: 31 May 2022
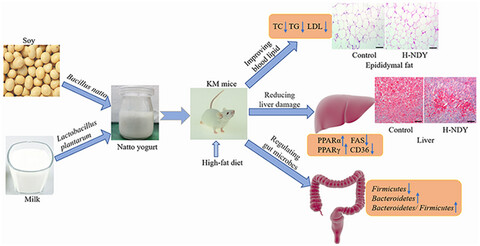
We developed a new dual protein functional yogurt fermented by Bacillus natto and Lactobacillus plantarum with milk and soy as substrates. Our results demonstrated that Natto yogurt could improve blood lipid by inhibiting the de novo synthesis of fatty acids, accelerating the catabolism of fatty acids, reducing liver damage, and increasing the richness of beneficial intestinal microorganisms. Therefore, it is possible that Natto yogurt could prevent and treat hyperlipidemia and obesity as a functional food.
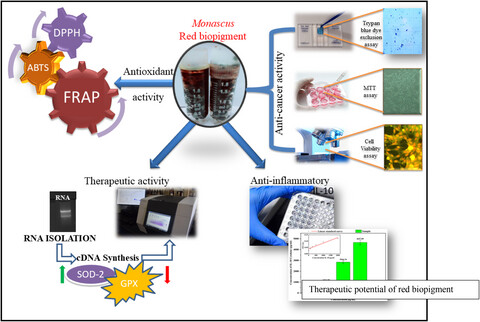
Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties of the red biopigment extract from Monascus purpureus (MTCC 369)
- First Published: 26 May 2022
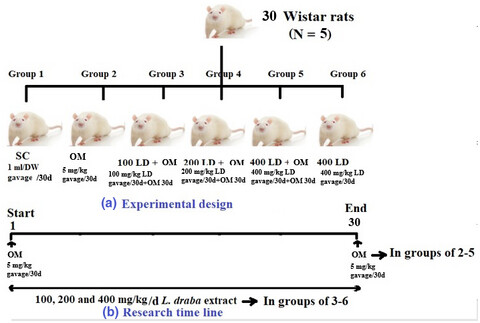
Renoprotective and hepatoprotective activity of Lepidium draba L. extracts on oxymetholone-induced oxidative stress in rat
- First Published: 28 May 2022
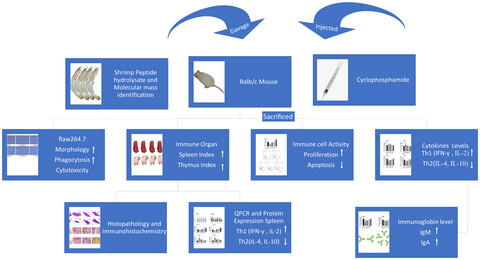
Shrimp peptide hydrolysate modulates the immune response in cyclophosphamide immunosuppressed mice model
- First Published: 28 May 2022
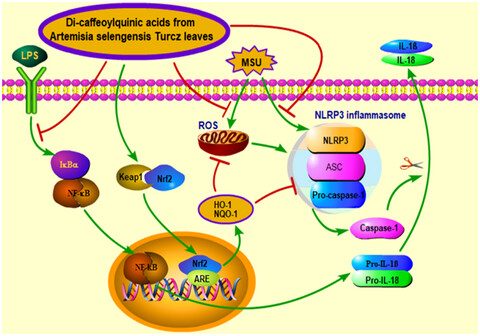
A review of the protective effects of chlorogenic acid against different chemicals
- First Published: 24 May 2022
Alleviation of oxidative stress in pancreatic tissue of hyperglycemic mice by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SCS4
- First Published: 31 May 2022
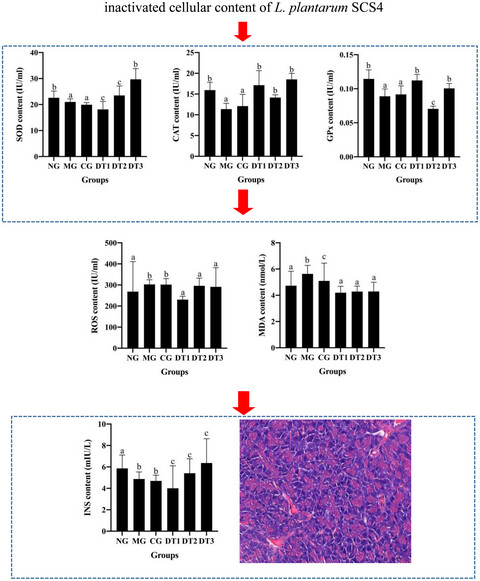
This study shows that after 10 weeks of gavage, the level of INS in DT3 (inactivated cellular content of L. plantarum SCS4) significantly increased and the level of ROS and MDA returned to normal level. The activities of SOD, CAT, and GPx increased. In addition, there is no significant lesion of pancreas in the DT3 group. The results indicate that the inactivated cellular content of L. planetarum SCS4 is more effective in improving oxidative stress in the pancreas of hyperglycemic mice.
Obesity-associated biochemical markers of inflammation and the role of grain phytochemicals
- First Published: 08 June 2022
- Whole forms of cereals, like brown rice, wheat, maize, barley, and millets, like finger, foxtail, proso, kodo, and their effect on inhibition of biochemical markers of adipogenesis and inflammation.
- Role of grain phytochemicals like phenolics, tocopherols, tocotrienols, carotenoids, antioxidants, dietary fiber in obesity-associated biochemical markers of inflammation.
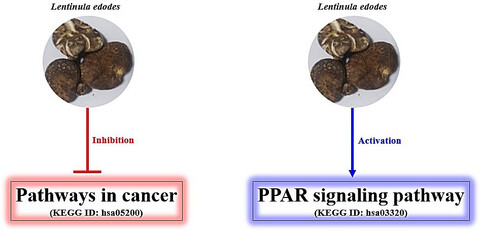
Network pharmacology-based study to identify the significant pathways of Lentinula edodes against cancer
- First Published: 28 May 2022
The effects of dragon fruit (Hylocereus polyrhizus) extract on indomethacin-induced stomach ulcer in rats
- First Published: 18 June 2022
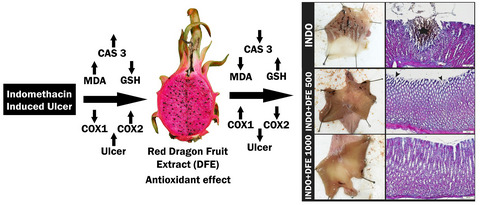
Effect of dragon fruit extract on indomethacin-induced ulcer. Malondialdehyde (MDA), caspase 3 (Cas-3) and Cyclooxygenase 2 (Cox-2) levels was increased, while Glutathione (GSH) and Cyclooxygenase 1 (Cox-1) levels was decreased in indomethacin-induced ulcer. On the other hand, when Dragon Fruit Extract (DFE) was given as a protective agent, the levels of MDA, Cas-3 and Cox-2 decreased, while the levels of (GSH) and Cox-1 decreased. As a result, DFE reduced ulcer foci and shows gastro-protective activity in the stomach.
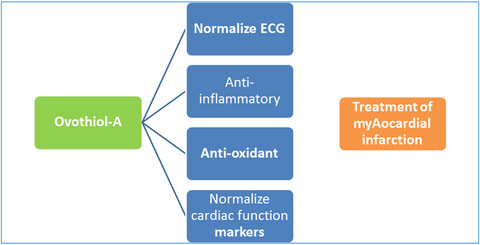
Modulatory effect of Ovothiol-A on myocardial infarction induced by epinephrine in rats
- First Published: 05 July 2022
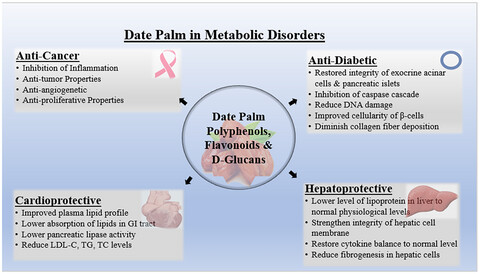
Date fruit as a promising source of functional carbohydrates and bioactive compounds: A review on its nutraceutical potential
- First Published: 27 July 2022
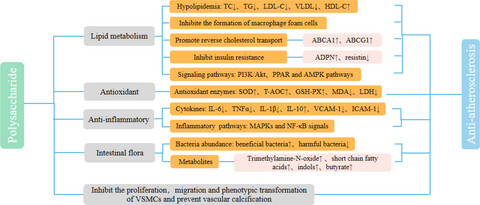
Bioactive polysaccharides and their potential health benefits in reducing the risks of atherosclerosis: A review
- First Published: 09 August 2022
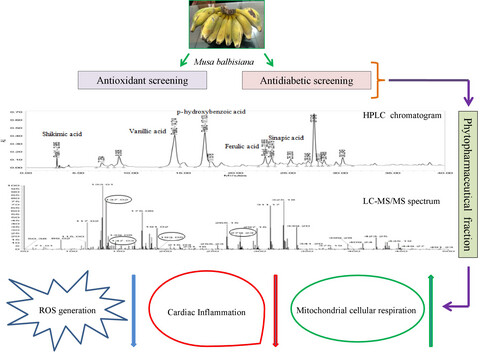
Pharmacologically active chemical composite of Musa balbisiana ameliorates oxidative stress, mitochondrial cellular respiration, and thereby metabolic dysfunction
- First Published: 30 July 2022
A preliminary study on preparation, characterization, and prebiotic activity of a polysaccharide from the edible mushroom Ramaria flava
- First Published: 07 August 2022
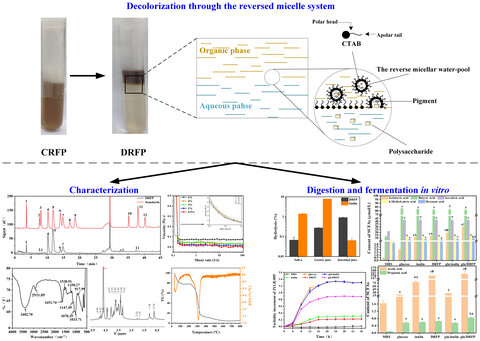
The reversed micelle system consisting of n-hexanol/isooctane and CTAB was an appropriate decolorized method for Ramaria flava polysaccharide. Decolorized R. flava polysaccharide was virtually undegraded after digestion in vitro. Decolorized R. flava polysaccharide stimulated Lactobacillus rhamnosus proliferation and improved SCFA production.
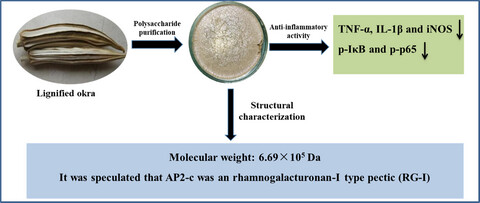
Structural characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of a pectin polysaccharide AP2-c from the lignified okra
- First Published: 17 August 2022