Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cinnamon, an effective anti-obesity agent: Evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis
- First Published: 01 April 2022
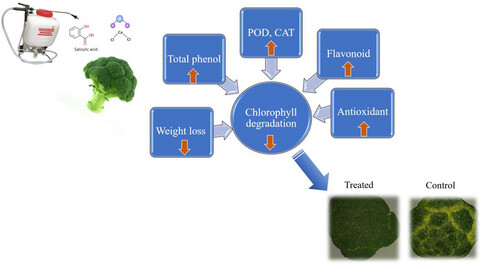
Foliar application of salicylic acid and calcium chloride delays the loss of chlorophyll and preserves the quality of broccoli during storage
- First Published: 05 April 2022
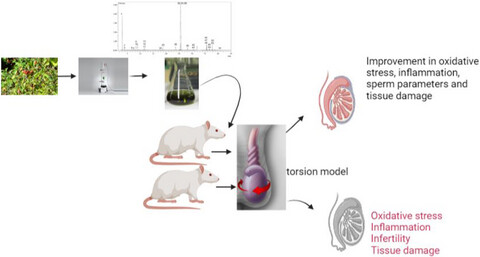
Protective effect of Smilax excelsa L. pretreatment via antioxidant, anti-inflammatory effects, and activation of Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway in testicular torsion model
- First Published: 29 March 2022
Corn oligopeptides inhibit Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway and inflammatory factors to ameliorate CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice
- First Published: 11 April 2022
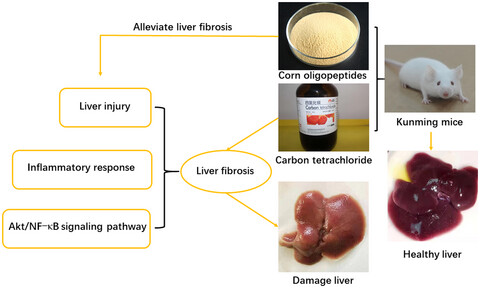
The liver fibrosis model of Kunming mice was established by intragastric administration of carbon tetrachloride. However, gavage of corn oligopeptides can improve liver fibrosis caused by carbon tetrachloride by alleviating liver injury, relieving inflammation and inhibiting the expression of Akt/NF-KB signaling pathway.
Protective effect of isopsoralen on UVB-induced injury in HaCaT cells via the ER and p38MAPK signaling pathways
- First Published: 12 April 2022
Antidepressant-like effects of aqueous extracts of miswak (Salvadora persica) and date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) on depression-like behaviors using CUMS model in male rats
- First Published: 29 March 2022
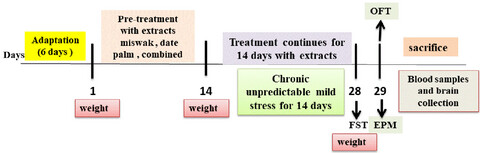
Aqueous extracts of miswak (Salvadora persica) and date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) and their combination effectively ameliorated depressive-like behaviors, body weight loss, and oxidative stress induced by CUMS in the rat model of depression and restored serotonin and cortisol secretion to normal levels. Furthermore, the studied extracts improved the levels of plasma pro-inflammatory cytokines and CREB and BDNF mRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex. These findings suggest their possible application as an effective treatment for stress-induced depression-like behaviors.
Chrysin abrogates gibberellic acid-induced testicular oxidative stress and dysfunction via the regulation of antioxidants and steroidogenesis- and apoptosis-associated genes
- First Published: 05 April 2022
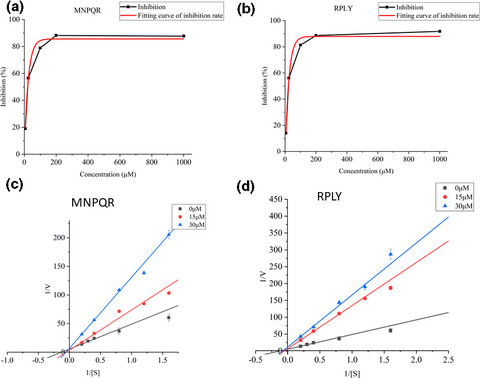
Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory mechanism of peptides from Macadamia integrifolia antimicrobial protein 2 (MiAMP2)
- First Published: 08 April 2022
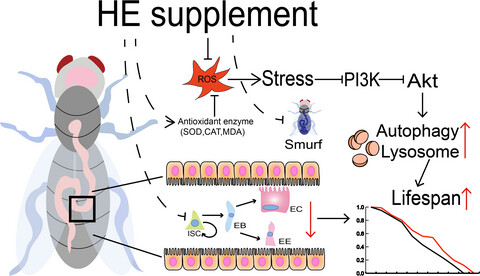
Hawthorn extract inhibited the PI3k/Akt pathway to prolong the lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster
- First Published: 05 April 2022
Anti-adipogenic β-sitosterol and lupeol from Moringa oleifera suppress adipocyte differentiation through regulation of cell cycle progression
- First Published: 11 April 2022
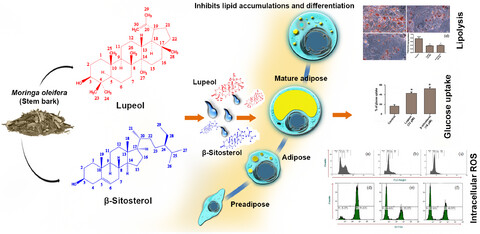
Triterpenes and phytosterols have been extracted and separated from Moringa oleifera stem bark. Dose-dependent reduction of cell viability found when lupeol and β – sitosterol administered and showcasing increased G1 phase cell accumulation while reducing other cell cycle phases (S and G2/M) and significant lowering of intracellular lipid accumulation.
Aqueous extract of Solanum macrocapon Linn leaf abate diabetic cardiomyopathy by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation in rats
- First Published: 18 April 2022
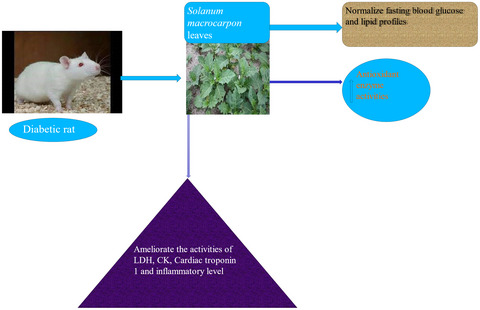
Administration of different doses of Solanum macrocarpon (SM) aqueous leaf extract to diabetic rats demonstrated normoglycemia, normolipidemia, reduced the activities of lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase, cardiac troponin I, and inflammatory levels as well as an increase in the antioxidant enzyme activities. Hence, the results suggest that SM aqueous leaf extract ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Low temperature delays degreening of apple fruit by inhibiting pheophorbide a oxygenase (PAO) pathway and chlorophyll oxidation during ripening
- First Published: 06 April 2022
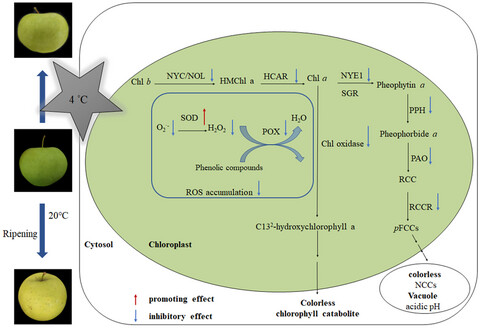
Low temperature (LT) treatment reduced activities of MDcase and PPH in chloroplast and differentially reduced MdCCGs expression in apple peel during ripening. LT might also reduce ROS accumulation by inhibiting Chl-POX and Chl oxidase activities and enhancing SOD activity in chloroplast of apple peel during ripening. These results indicated that LT treatment might delay Chl degradation through inhibiting PAO pathway and Chl oxidation during ripening of apple fruit.
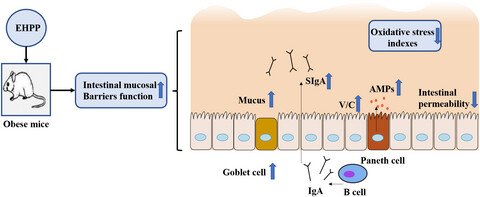
Enzymatic hydrolysate of porphyra enhances the intestinal mucosal functions in obese mice
- First Published: 04 May 2022
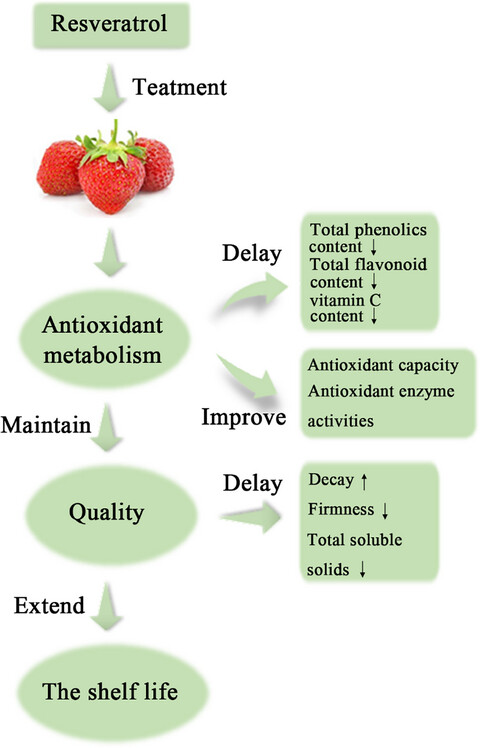
Effects of resveratrol treatment on quality and antioxidant properties of postharvest strawberry fruit
- First Published: 08 April 2022
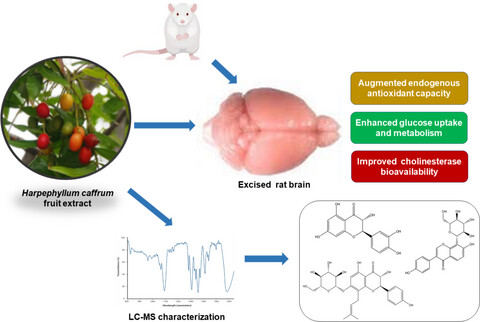
Harpephyllum caffrum fruit (wild plum) facilitates glucose uptake and modulates metabolic activities linked to neurodegeneration in isolated rat brain: An in vitro and in silico approach
- First Published: 09 April 2022
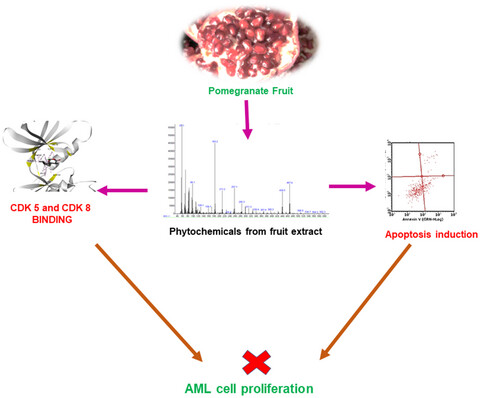
GC/MS characterization and computational kinome-wide screening of pomegranate fruit extract identifies key phytochemicals interacting to CDK kinases implicated in acute myeloid leukemia cells
- First Published: 22 April 2022
Heme oxygenase-1 induction by gallic acid-g-chitosan is an important event in modulating adipocyte differentiation
- First Published: 08 April 2022
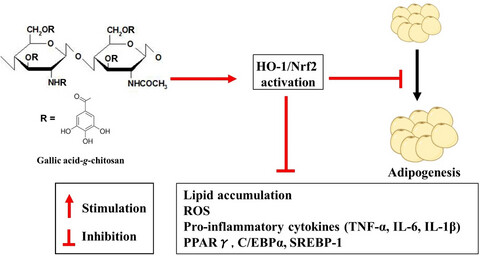
- Gallic acid was grafted onto the chitosan to prepare gallic acid-g-chitosan (GAC) with anti-adipogenesis effects.
- GAC inhibited lipid accumulation, reactive oxygen species generation, pro-inflammatory cytokines production (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β), and adipocyte gene expression (PPARγ, C/EBPα, and SREBP-1).
- GAC exhibited an anti-adipogenic effect through the induction of HO-1.
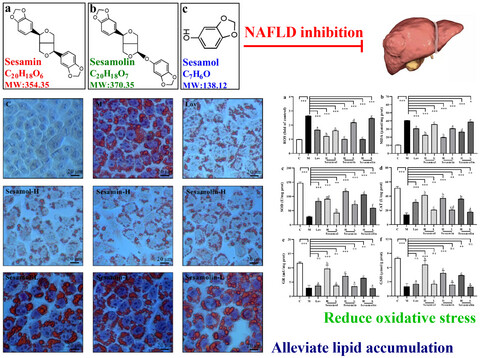
Comparative effects of sesame lignans (sesamin, sesamolin, and sesamol) on oxidative stress and lipid metabolism in steatosis HepG2 cells
- First Published: 09 April 2022
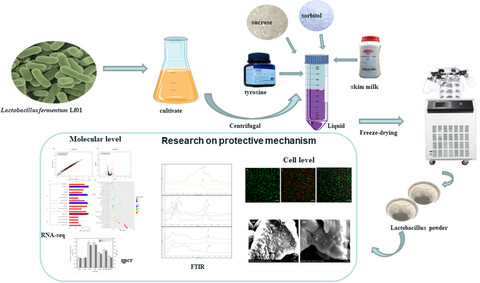
Improving the viability of powdered Lactobacillus fermentum Lf01 with complex lyoprotectants by maintaining cell membrane integrity and regulating related genes
- First Published: 08 April 2022
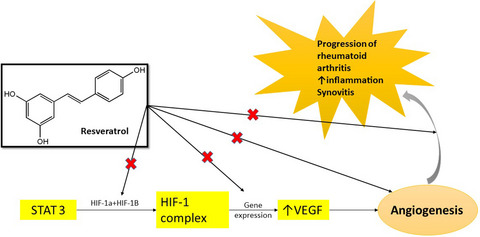
Resveratrol may ameliorate rheumatoid arthritis via the STAT3/HIF-1/VEGF molecular pathway
- First Published: 12 April 2022
Amyloid fibril formation by casein and fatty acid composition in breast milk of mastitis patients
- First Published: 05 April 2022
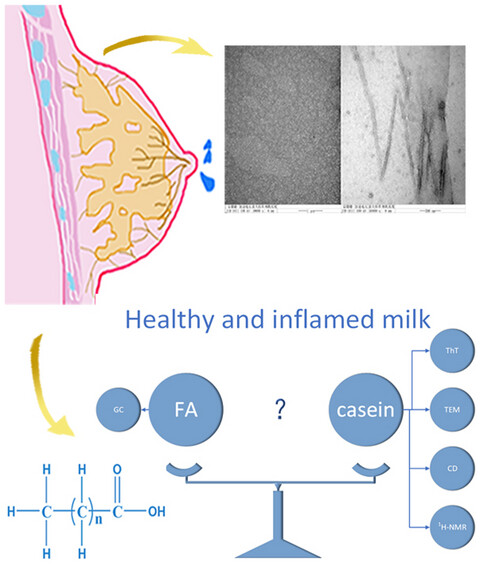
Amyloid fibril in healthy and inflammatory breast milk from women investigated. Healthy milk contained no amyloid fibrils but inflammatory milk did. Fatty acids were significantly different between the two groups. Results clarified the relationship between inflammation, fibrils, and FA in breast milk.
Effect of different cooking times on the fat flavor compounds of pork belly
- First Published: 11 April 2022
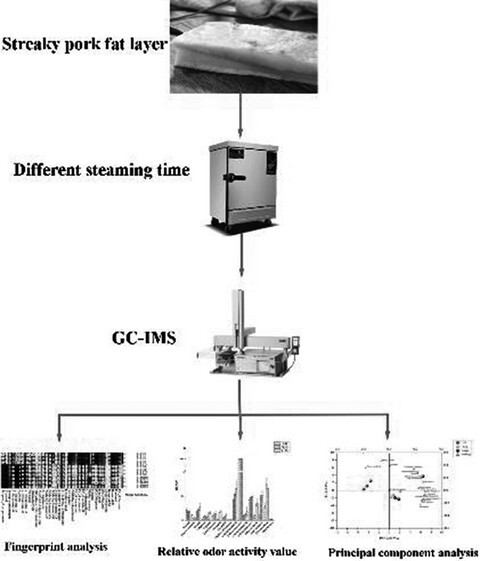
A total of 36 volatile compound were identified in different steamed pork belly fats (F0: fresh pork belly fat; S30: steamed for 30 min; S180: steamed for 180 min). The key volatile compounds heptanal, ethyl hexanoate, 2-methylbutanal-m, 3-methylbutanal, ethyl acetate, and 2,3-butanedione were significantly increased in the steamed fat. Hexanal-d and 1-heptanol imparted fruity and grassy flavors to S30 and S180. 3-Hydroxy-2-butanone imparted milk and fat flavors to S180.
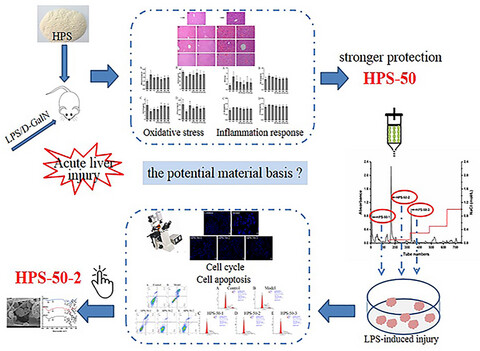
Hepatoprotective effect and structural analysis of Hedysarum polysaccharides in vivo and in vitro
- First Published: 28 April 2022
Epigallocatechin gallate: Phytochemistry, bioavailability, utilization challenges, and strategies
- First Published: 26 April 2022
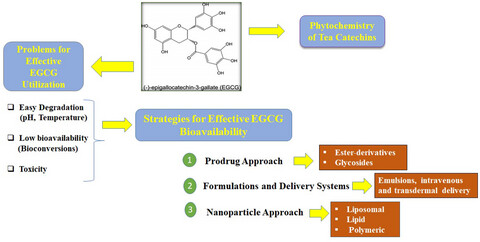
EGCG is a bioactive compound present in green tea. EGCG contains pyrogallol as B-rings while it contains an additional gallate moiety as a D-ring, which increases the number of hydroxyl groups. The EGCG, due to galloyl moieties increasing in their hydroxyl groups, possesses more excellent antioxidant activities than EC and EGC. Considerable challenges in EGCG utilization are the low systemic bioavailability, less stability in alkaline media, temperature, high oxidative degradation, metabolic transformations, as well as toxicity at higher concentrations. Hence, some effective strategies are introduced to overcome its lower bioavailability and stability issues.
Spent coffee grounds: A sustainable approach toward novel perspectives of valorization
- First Published: 12 May 2022
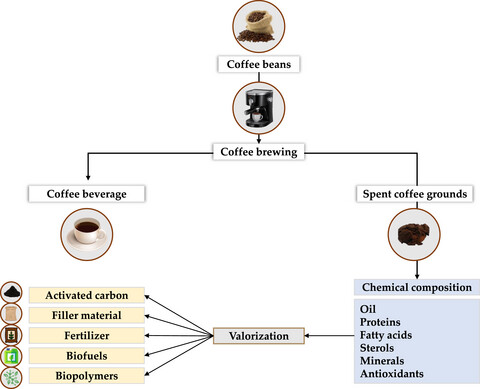
In the graph, coffee consumption generates large quantities of spent coffee grounds, the unused part of the coffee bean that is left after brewing. However, due to its composition, this waste stream has the potentially to be valorized and converted into several valuable bioproducts such as biopolymers, biofuels and filter materials, instead of being discarded in landfills.
Ferula assa-foetida oleo gum resin ethanolic extract alleviated the pancreatic changes and antioxidant status in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: A biochemical, histopathological, and ultrastructural study
- First Published: 26 April 2022
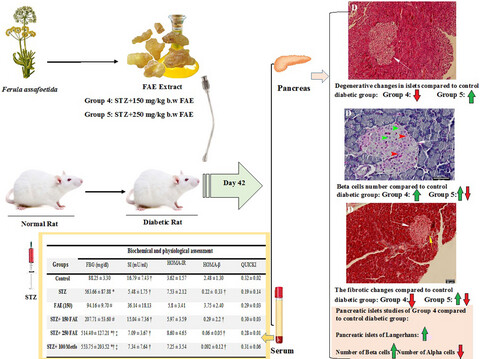
- Ferula assa-foetida gum extract (FAE) has an antidiabetic effect on STZ-induced diabetic rats.
- FAE prevents β cell damage, improves the ultrastructure of these cells, and increases the number of β cells and the secretion of insulin granules.
- FAE is a potential source for the isolation of new oral antidiabetic agent(s).
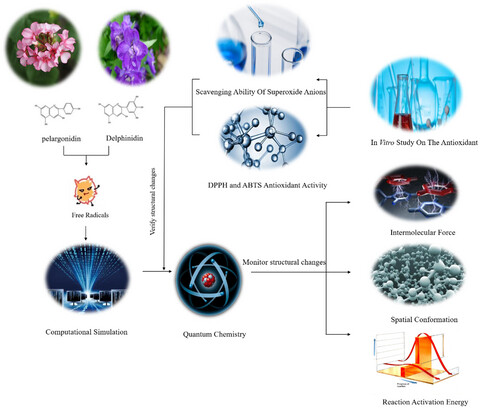
Antioxidant activity of delphinidin and pelargonidin: Theory and practice
- First Published: 28 April 2022
The anticardiac fibrosis of total alkaloids of Plumula nelumbinis by regulating circulating lipidomic profile: In vivo study
- First Published: 02 May 2022
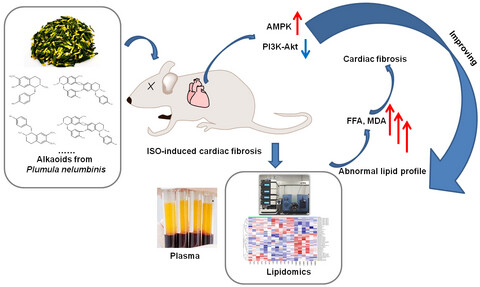
- Total alkaloids of Plumula nelumbinis (TAP) suppressed ISO-induced cardiac fibrosis in mice.
- The lipidomic profiles revealed that TAP improved the lipid disorder in cardiac fibrosis.
- Combining lipidomics, pharmacology network analysis and experimental evaluation, AMPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways were the potential targeted pathways by TAP to regulate lipid metabolism dysfunction.
Hydroalcoholic extract of dill and aerobic training prevents high-fat diet-induced metabolic risk factors by improving miR-33 and miR-223 expression in rat liver
- First Published: 23 April 2022
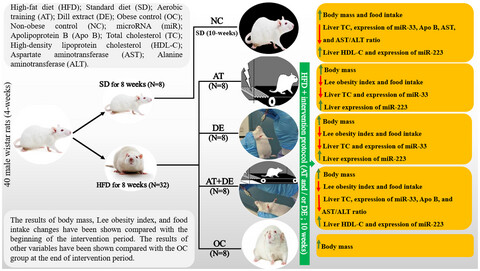
This study aimed to assess the effects of 10 weeks of aerobic training (AT) and dill extract (DE) on miR-33 and miR-223 expression of liver in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese rats. The findings showed that long-term AT combined with the intake of DE may improve the plasma levels of Apo B, and TC and HDL-C levels in the liver, which is probably due to AT and DE positive effects on miR-33 and miR-223 expression in the liver of obese rats.
The synergistic effect of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels and Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. on antioxidant activity and protective ability against cell injury
- First Published: 08 May 2022

Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (DG) and Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. (SDH) can act as neuro protectants. DG-SDH formulated at a ratio of 3:2 (DG-SDH (3:2)) increased content of polysaccharides, polyphenols, and flavonoids and showed the best synergistic effects in scavenging activity of free radicals. DG-SDH (3:2) protected SHSY-5Y cells by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing cell apoptosis, increasing mitochondrial membrane potential and protecting cell morphology.
Mulberry vinegar attenuates lipopolysaccharide and interferon gamma-induced inflammatory responses in C6 glial cells
- First Published: 26 April 2022
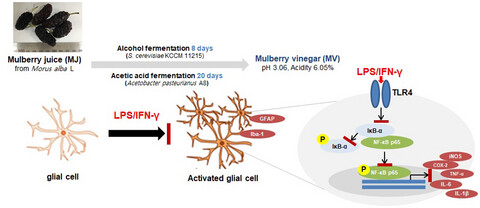
This study investigated the anti-inflammatory property of mulberry vinegar in LPS/IFN-γ-stimulated C6 glial cells. Mulberry vinegar was observed to suppress the LPS/IFN-γ-induced nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species overproduction by regulation of nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway and glial activation.
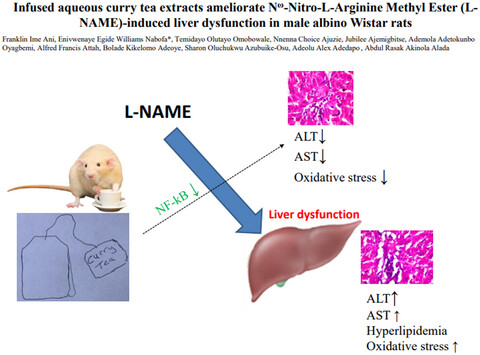
Infused aqueous curry tea extracts ameliorate Nω-Nitro-L-Arginine Methyl Ester-induced liver dysfunction in male albino Wistar rats
- First Published: 24 May 2022
Anti-obesity effect of fermented lemon peel on high-fat diet-induced obese mice by modulating the inflammatory response
- First Published: 28 April 2022
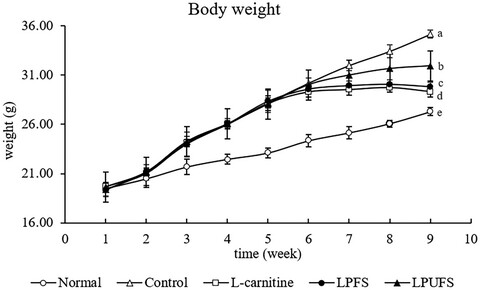
Figure 1. The experimental design of mice. Normal: standard chow diet and 0.1mL/20g (b.w.) 0.9% normal saline; Control: 45% HFD and 0.1mL/20g (b.w.) saline; L-Carnitine: mice treated with 45% HFD and 200 mg/kg (b.w.) L-carnitine; LPFS: mice treated with 45% HFD and 0.1mL/20g (b.w.) lemon peel fermentation supernatant; LPUFS: mice treated with 45% HFD and 0.1mL/20g (b.w.) lemon peel un-fermentation supernatant.
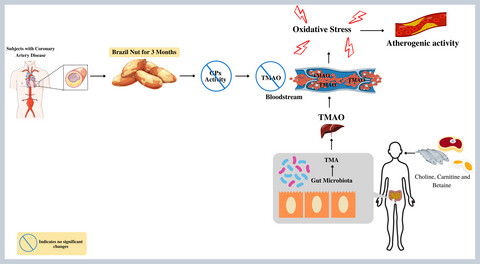
Brazil nut supplementation does not affect trimethylamine-n-oxide plasma levels in patients with coronary artery disease
- First Published: 25 April 2022
The effect of resistance and endurance training with ursolic acid on atrophy-related biomarkers in muscle tissue of diabetic male rats induced by streptozotocin and a high-fat diet
- First Published: 20 May 2022
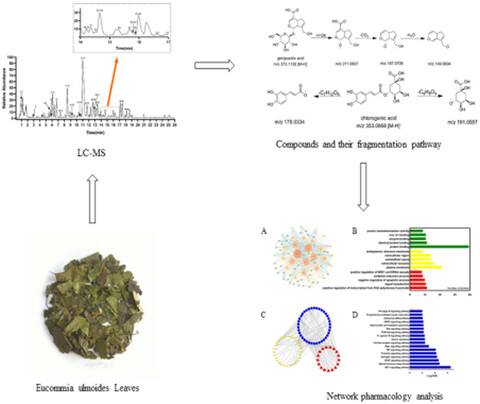
Combination of UHPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap MS and network pharmacology to reveal the mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides leaves in the treatment of osteoarthritis
- First Published: 28 April 2022
Study on the HIF-1α regulated by glycolytic pathways and mitochondrial function in yaks of different altitudes during postmortem aging
- First Published: 02 May 2022
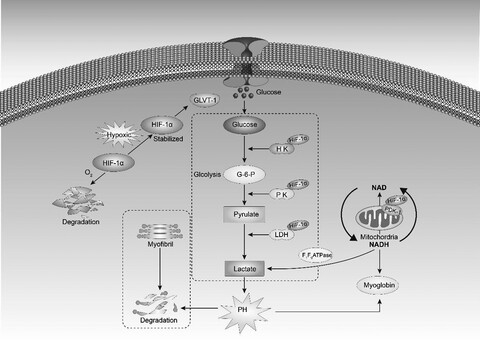
- Effect of HIF-1α on glycolysis pathway in yak meat during the ageing process after death.
- HIF-1α positively regulated activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase in yak meat.
- Glucose transporter is the main downstream target of hypoxia factor.
- HIF-1α was an important factor that slows down mitochondrial respiration to satisfy glycolysis energy.
Diabetic cardiomyopathy was attenuated by cinnamon treatment through the inhibition of fibro-inflammatory response and ventricular hypertrophy in diabetic rats
- First Published: 26 April 2022
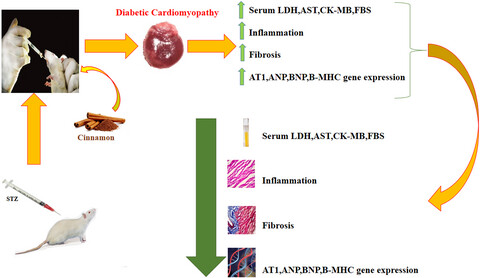
The effects of cinnamon in diabetic cardiomyopathy were evaluated. FBS and cardiac enzyme indicators were reduced in all treated rats. Cinnamon Improved oxidative imbalance in heart tissue of diabetic rats. Inflammation and fibrosis was diminished in treated groups. AT1, ANP, β-MHC, and BNP gene expression were downregulated in treated rats.
Impact of dietary Lactobacillus supplementation on intramuscular fat deposition and meat quality of Sunit sheep
- First Published: 02 May 2022
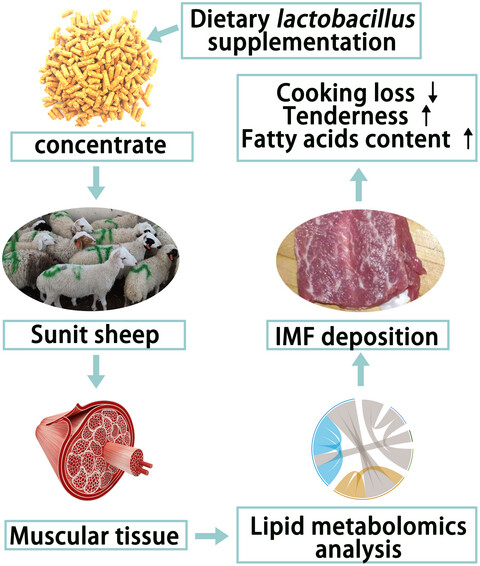
- Lactobacillus dietary supplement can increase the content of intramuscular fat, so that improved meat quality of Sunit sheep;
- Lactobacillus dietary supplement can enrich the quantity of fatty acids in longissimus thoracis of Sunit sheep, especially the functional fatty acids.
- The metabolites and pathways related lipid synthesis in longissimus thoracis were induced by Lactobacillus dietary supplement.
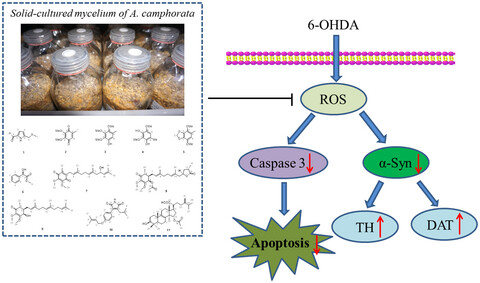
Solid-state-cultured mycelium of Antrodia camphorata exerts potential neuroprotective activities against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced toxicity in PC12 cells
- First Published: 25 April 2022