Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 1
- First Published: 01 December 2023

In nature, differences in temperature create completely distinguishable landscapes in winter and spring. Similarly, by controlling the reaction temperature, efficient regioselective control of nickel-catalyzed hydrosilylation of conjugated dienes with primary silanes can be achieved, facilitating the divergent synthesis of various homoallylic silanes and allylic silanes under mild conditions. More details are discussed in the article by Zhang et al. on page 13—19.
Inside Cover Picture
Contents
Concise Reports
Nickel-Catalyzed Regioselective Hydrosilylation of Conjugated Dienes
- Pages: 13-19
- First Published: 23 August 2023
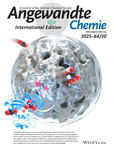
Herein, we developed a Ni-catalyzed regiodivergent hydrosilylation of aromatic conjugated dienes with excellent regioselectivity by adjusting the temperature and ligands. Under low temperature (–30 °C), Ni/t-BuOK can efficiently catalyze the 3,4-anti-Markovnikov hydrosilylation to provide homoallylic silanes without eternal ligands; under room temperature (25 °C), Ni/t-BuOK/PPh3 can catalyze the 3,4-Markovnikov hydrosilylation to produce allylic silanes.
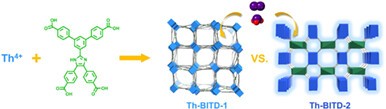
Synthetic Control of Thorium Metal-Organic Frameworks for Sequencing and Sensing of Radioiodine Species
- Pages: 20-28
- First Published: 23 August 2023
Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Markovnikov Hydroalkynylation of Unactivated Terminal Alkenes
- Pages: 29-34
- First Published: 11 September 2023
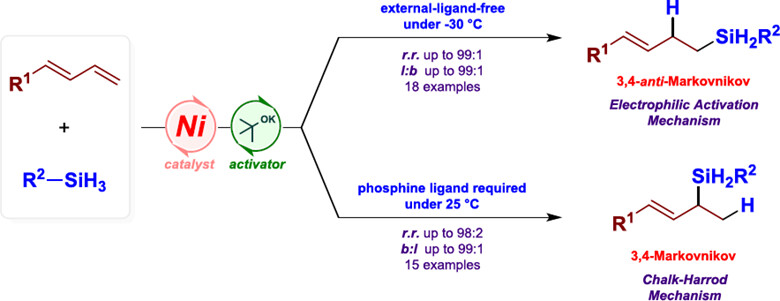
A palladium-catalyzed hydroalkynylation of unactivated terminal alkenes with ethynyl benziodoxolone (EBX) reagents under mild conditions has been developed, which provides an efficient method for the synthesis of branched alkynyl products in moderate to good yields under mild reaction conditions. The reaction features excellent regioselectivity and functional group compatibility.
Dcalycinumines A—E, Alkaloids with Cytotoxic Activities of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells from Daphniphyllum calycinum
- Pages: 35-42
- First Published: 13 September 2023
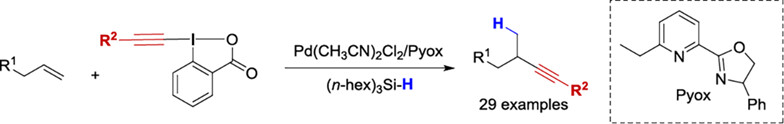
Five novel Daphniphyllum alkaloids, named dcalycinumines A—E (1—4, 6), and eight known Daphniphyllum alkaloids (5, 7—13) were isolated from Daphniphyllum calycinum. Compound 1 showed remarkable antitumor activities, which could inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, and promoted nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells apoptosis.
Rhodium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Heterocyclic Diaryl Ketones: Facile Access to Key Intermediate of Baloxavir
- Pages: 43-47
- First Published: 10 September 2023
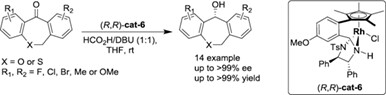
Herein, we have developed a highly practical and enantioselective rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of heterocyclic diaryl ketones, providing the desired product with up to >99 yield and >99% ee. The synthetical potential of the current reaction was demonstrated by the gram-scale synthesis of key intermediate of baloxavir.
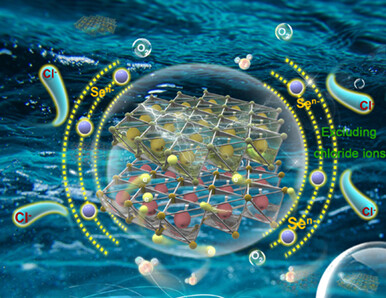
In-situ Generation of Hydroxyl Layers in CoO@FeSe2 Catalyst for High Selectivity Seawater Electrolysis
- Pages: 48-54
- First Published: 04 September 2023
Synergistic Effect of Nitrogen/Phosphorus Co-Doping and Molybdenum Carbide Induced Electron Redistribution of Carbon Layer to Boost Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- Pages: 55-60
- First Published: 10 September 2023
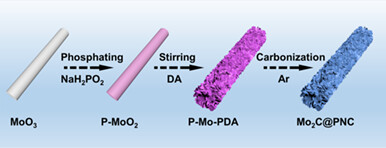
Nitrogen/phosphorus co-doped carbon nanorods encapsulated Mo2C nanoparticles deliver superior HER activity with low overpotential of 104 mV at a current density of 10 mA·cm–2, which has been theoretically demonstrated to originate from the synergistic effect between P doping and Mo2C induced electron redistribution of nitrogen-doped carbon layer.
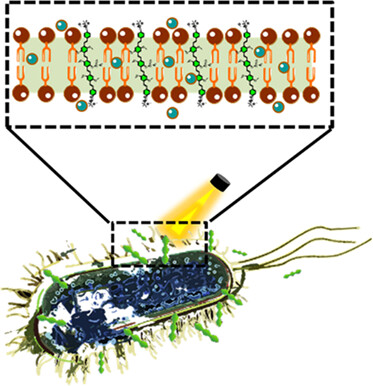
Cationic Conjugated Oligomers for Efficient and Rapid Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy via Both Type I and Type II Pathways
- Pages: 61-66
- First Published: 11 September 2023
Comprehensive Report
Machine Learning-Aided Data Analysis in Single-Protein Conductance Measurement with Electron Tunneling Probes
- Pages: 67-72
- First Published: 14 September 2023
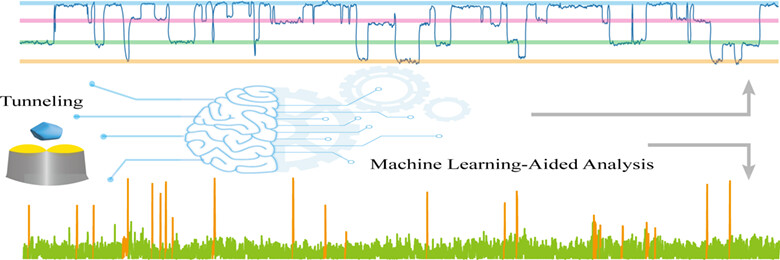
Single-molecule electrical measurements using tunneling sensors have shown remarkable potential because of their numerous advantages. While critical signal information is difficult to gather and analyze due to huge datasets and limited signal-to-noise ratio. We have designed a clustering-based machine learning model, which can calculate signal features with high effectiveness and efficiency.
Critical Reviews
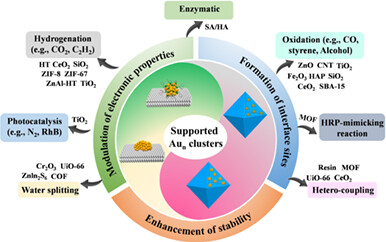
Design of Support Effect in the Catalytic Application of Ligand-Protect Gold Clusters
- Pages: 73-86
- First Published: 24 August 2023
Bioactive Hydrogels with Pro-coagulation Effect for Hemostasis
- Pages: 87-103
- First Published: 23 August 2023
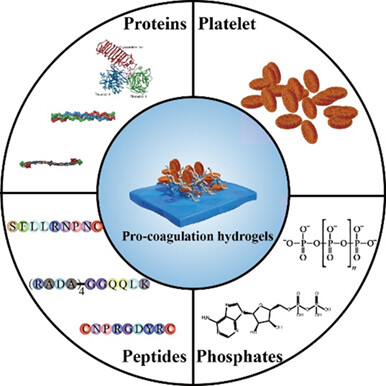
Quanshi Guo and co-workers systematically reviewed the recent progress on bioactive hydrogels with pro-coagulation effect for hemostasis. They outlined the key points in the coagulation process, including the activation of coagulation factors and fibrinogen polymerization, and discussed how to design bioactive hydrogels to accelerate coagulation at these points.
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 107
- First Published: 01 December 2023

Uncontrollable bleeding is like the collapse of heaven for patients, with blood gushing out uncontrollably. Researchers have developed bioactive hydrogels with procoagulant properties to achieve bleeding control as a "heavenly stone" for the defect. These hydrogels can effectively assist in stopping bleeding by activating the coagulation cascade reaction and hold promising prospects for clinical applications as hemostatic materials. More details are given in the article by Mao et al. on page 87—103.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 108
- First Published: 01 December 2023

Hydrogen is a high energy density, clean, and non-polluting energy source and energy carrier. Seawater electrolysis is one of the most promising methods for renewable energy development. CoO@FeSe2/CF catalysts with heterogeneous structures were prepared and showed excellent activity, stability, and selectivity. More details are discussed in the article by Tian et al. on page 48—54.