Cationic Conjugated Oligomers for Efficient and Rapid Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy via Both Type I and Type II Pathways
Huan Wang
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shuwen Guo
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorQiong Yuan
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeiqi Li
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yanli Tang
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorHuan Wang
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shuwen Guo
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorQiong Yuan
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeiqi Li
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yanli Tang
Country Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science of Shaanxi Province, Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry, Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710119 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
Recently, photodynamic therapy (PDT) has attracted wide attention due to its less susceptibility to drug resistance, broad-spectrum biocidal activity and biosafety in normal tissues. However, the traditional photosensitizers (PSs) face the disadvantage of poor therapeutic efficacy due to the requirement of an aerobic environment to generate 1O2 through Type ІI pathway. Herein, we designed and synthesized a novel cationic conjugated oligomer oligo(phenylene vinylene) (OPV) and studied its antibacterial photodynamic activity against both Gram-negative Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Gram-positive bacteria methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Importantly, the OPV can rapidly produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) through double pathways, Type I and II mechanism under white light irradiation, and efficiently kill E. coli and MRSA at a nanomolar level. The dual type photosensitizing capability makes OPV promising for enhanced PDT to treat pathogens and tumors in complex environments.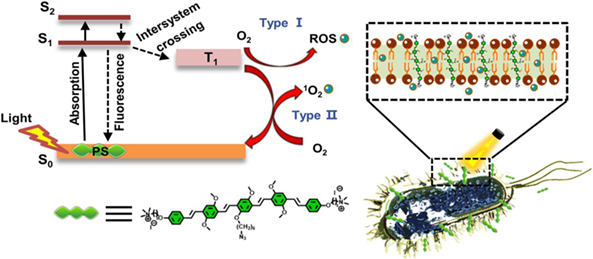
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300447-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.4 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Li, X.; Bai, H.; Yang, Y.; Yoon, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Supramolecular Antibacterial Materials for Combatting Antibiotic Resistance. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805092.
- 2 Yang, X.; Syed, R.; Fang, B.; Zhou, C.-H. A New Discovery towards Novel Skeleton of Benzimidazole-Conjugated Pyrimidinones as Unique Effective Antibacterial Agents. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2642–2654.
- 3 Abdou Mohamed, M. A.; Raeesi, V.; Turner, P. V.; Rebbapragada, A.; Banks, K.; Chan, W. C. W. A versatile plasmonic thermogel for disinfection of antimicrobial resistant bacteria. Biomaterials 2016, 97, 154–163.
- 4 Brown, E. D.; Wright, G. D., Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature 2016, 529, 336–343.
- 5 Ye, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yodsanit, N.; Xie, R.; Gong, S. pH-Responsive Polymer–Drug Conjugate: An Effective Strategy to Combat the Antimicrobial Resistance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002655.
- 6 Jia, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.-X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.-G. Cholesterol-Assisted Bacterial Cell Surface Engineering for Photodynamic Inactivation of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15943–15951.
- 7 Celli, J. P.; Spring, B. Q.; Rizvi, I.; Evans, C. L.; Samkoe, K. S.; Verma, S.; Pogue, B. W.; Hasan, T. Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy: Mechanisms, Monitoring, and Optimization. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2795–2838.
- 8 Zhu, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, N.; Ding, X.; Yu, B.; Xu, F.-J. Polycationic Synergistic Antibacterial Agents with Multiple Functional Components for Efficient Anti-Infective Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706709.
- 9 Shen, Y.; Shuhendler, A. J.; Ye, D.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Two-photon excitation nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6725–6741.
- 10 Sun, J.; Cai, X.; Wang, C.; Du, K.; Chen, W.; Feng, F.; Wang, S. Cascade Reactions by Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Radical for Anti-Hypoxia Photodynamic Therapy Using an Activatable Photosensitizer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 868–878.
- 11 Sun, J.; Du, K.; Diao, J.; Cai, X.; Feng, F.; Wang, S. GSH and H2O2 Co-Activatable Mitochondria-Targeted Photodynamic Therapy under Normoxia and Hypoxia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 12122–12128.
- 12 Whitten, D. G.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Hill, E. H.; Pappas, H. C.; Donabedian, P. L.; Chi, E. Y. A Retrospective: 10 Years of Oligo(phenylene-ethynylene) Electrolytes: Demystifying Nanomaterials. Langmuir 2019, 35, 307–325.
- 13 Shen, Q.; Huang, Y.; Bai, H.; Lv, F.; Wang, S. Polymer Materials Synthesized through Cell-Mediated Polymerization Strategies for Regulation of Biological Functions. Acc. Mater. Res. 2023, 4, 57–70.
- 14 Zhou, L.; Lv, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, S. Water-Soluble Conjugated Organic Molecules as Optical and Electrochemical Materials for Interdisciplinary Biological Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 3211–3222.
- 15 Zhu, C.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Lv, F.; Wang, S. Water-Soluble Conjugated Polymers for Imaging, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4687–4735.
- 16 Gai, P.; Yu, W.; Zhao, H.; Qi, R.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Lv, F.; Wang, S. Solar-Powered Organic Semiconductor–Bacteria Biohybrids for CO2 Reduction into Acetic Acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7224–7229.
- 17 Qi, R.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Dai, N.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, E.; Lv, F.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. In Situ Synthesis of Photoactive Polymers on a Living Cell Surface via Bio-Palladium Catalysis for Modulating Biological Functions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5759–5765.
- 18 Zeng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Qi, R.; Dai, N.; Fu, X.; Zhao, H.; Peng, K.; Yuan, H.; Huang, Y.; Lv, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, S. Photoactive Conjugated Polymer-Based Hybrid Biosystems for Enhancing Cyanobacterial Photosynthesis and Regulating Redox State of Protein. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007814.
- 19 Tang, Y.; Corbitt, T. S.; Parthasarathy, A.; Zhou, Z.; Schanze, K. S.; Whitten, D. G. Light-Induced Antibacterial Activity of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Oligophenylene Ethynylenes. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4956–4962.
- 20 Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y. Enhanced Energy Transfer in a Donor–Acceptor Photosensitizer Triggers Efficient Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38467–38474.
- 21 Bai, H.; Zhang, H.; Hu, R.; Chen, H.; Lv, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, S. Supramolecular Conjugated Polymer Systems with Controlled Antibacterial Activity. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1116–1120.
- 22 Zhou, L.; Lv, F.; Liu, L.; Shen, G.; Yan, X.; Bazan, G. C.; Wang, S. Cross-Linking of Thiolated Paclitaxel–Oligo(p-phenylene vinylene) Conjugates Aggregates inside Tumor Cells Leads to “Chemical Locks” That Increase Drug Efficacy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704888.
- 23 Zheng, L.; Li, J.; Yu, M.; Jia, W.; Duan, S.; Cao, D.; Ding, X.; Yu, B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, F.-J. Molecular Sizes and Antibacterial Performance Relationships of Flexible Ionic Liquid Derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 20257–20269.
- 24 He, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. Substrate-Independent Ag-Nanoparticle-Loaded Hydrogel Coating with Regenerable Bactericidal and Thermoresponsive Antibacterial Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 44782–44791.
- 25 Wang, C.-H.; Xie, X.-R.; Liu, W.-S.; Hou, G.-G.; Sun, J.-F.; Zhao, F.; Cong, W.; Li, H.-J.; Xin, W.-Y. Quaternary ammonium salts substituted by 5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thiol as novel antibacterial agents with low cytotoxicity. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 90, 943–952.
- 26 Qian, Y.; Deng, S.; Cong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Z.; Shao, N.; Bhatti, S. A.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, J.; Gellman, S. H.; Liu, R. Secondary Amine Pendant β-Peptide Polymers Displaying Potent Antibacterial Activity and Promising Therapeutic Potential in Treating MRSA-Induced Wound Infections and Keratitis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1690–1699.
- 27 Zhou, Z.; Ergene, C.; Lee, J. Y.; Shirley, D. J.; Carone, B. R.; Caputo, G. A.; Palermo, E. F. Sequence and Dispersity Are Determinants of Photodynamic Antibacterial Activity Exerted by Peptidomimetic Oligo(thiophene)s. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1896–1906.
- 28 Han, H.; Zhu, J.; Wu, D.-Q.; Li, F.-X.; Wang, X.-L.; Yu, J.-Y.; Qin, X.-H. Inherent Guanidine Nanogels with Durable Antibacterial and Bacterially Antiadhesive Properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806594.
- 29 Hu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wu, X.; Tu, X.; Wang, G.-X. Synthesis and biological evaluation of coumarin derivatives containing imidazole skeleton as potential antibacterial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 958–969.
- 30 Parthasarathy, A.; Pappas, H. C.; Hill, E. H.; Huang, Y.; Whitten, D. G.; Schanze, K. S. Conjugated Polyelectrolytes with Imidazolium Solubilizing Groups. Properties and Application to Photodynamic Inactivation of Bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28027–28034.
- 31 Wang, B.; Feng, G.; Seifrid, M.; Wang, M.; Liu, B.; Bazan, G. C. Antibacterial Narrow-Band-Gap Conjugated Oligoelectrolytes with High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16063–16066.
- 32 Zhu, C.; Yang, Q.; Liu, L.; Lv, F.; Li, S.; Yang, G.; Wang, S. Multifunctional Cationic Poly(p-phenylene vinylene) Polyelectrolytes for Selective Recognition, Imaging, and Killing of Bacteria Over Mammalian Cells. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4805–4810.
- 33 Lu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y. Conjugated Polymers-Based Thermal-Responsive Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Delivery, Tracking, and Synergistic Photodynamic Therapy/Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4485–4492.
- 34 Chen, L.; Bai, H.; Xu, J.-F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Supramolecular Porphyrin Photosensitizers: Controllable Disguise and Photoinduced Activation of Antibacterial Behavior. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13950–13957.
- 35 Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, S.; Yao, C.; Ban, D.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Wang, S. Controllable Targeted Accumulation of Fluorescent Conjugated Polymers on Bacteria Mediated by a Saccharide Bridge. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 438–447.
- 36 Gai, P.; Yu, W.; Zhao, H.; Qi, R.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Lv, F.; Wang, S. Solar-Powered Organic Semiconductor–Bacteria Biohybrids for CO2 Reduction into Acetic Acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7224–7229.




