Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Full Papers
Controlled-release of Avermectin from Organically Modified Hydrotalcite-like Compound Nanohybrids
- Pages: 445-451
- First Published: 02 April 2009
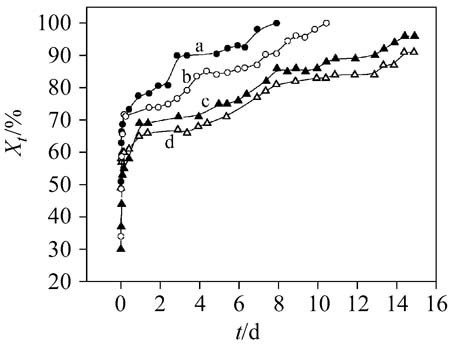
The intercalation of avermectin (AVM) into sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) modified hydrotalcite-like compounds (HTlc) was carried out using an evaporating solvent enhanced intercalation method to obtain AVM-SDS-HTlc nanohybrids. It was found that the nanohybrids could well control the release of avermectin, showing that the nanohybrids are a potential pesticide controlled-release formulation.
A Kinetically Mechanistic Investigation of Oxidation of 1,4-Butanediamine by Ag(III) Complex in Alkaline Medium
- Pages: 452-454
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Theoretical Studies on the Infrared Vibrational Spectra, Thermodynamic Properties and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectra for Polynitro-1,3-bishomopentaprismanes
- Pages: 455-468
- First Published: 02 April 2009
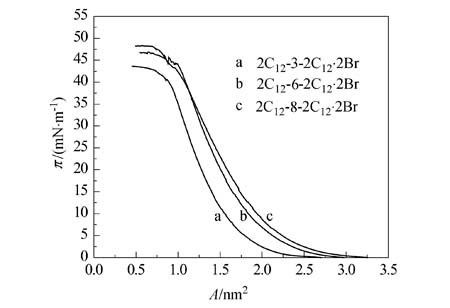
Bending of the Flexible Spacer Chain of Gemini Surfactant Induced by Hydrophobic Interaction
- Pages: 469-471
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Molecular Simulation Study of Hexane Diffusion in Dynamic Metal-Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 472-478
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Synthesis and Structural Characterization of a New 2D Coordination Polymer [Cu(pzta)2]n
- Pages: 479-482
- First Published: 02 April 2009
![Synthesis and Structural Characterization of a New 2D Coordination Polymer [Cu(pzta)2]n](/cms/asset/a8c9af9d-8106-4a35-a616-a9d14214c504/mcontent.jpg)
A new copper(II) tetrazolate coordination polymer [Cu(pzta)2]n (1) (pzta=5-pyrazinyltetrazolate) was prepared from the hydrothermal reaction of Cu(OAc)2·H2O with NaN3 and pyrazinecarbonitrile (pzCN) in the presence of ethanol, and characterized by elemental analysis, IR, TGA and X-ray crystallography. The X-ray diffraction analysis of 1 shows that the compound crystallizes in the monoclinic system with space group P2(1)/c and Cu(II) ion center is six-coordinated by four different pzta ligands. The complex 1 features a 2D tetrazole coordination polymer. The thermal analysis of 1 shows that the decomposition of the complex occurs in two regions.
Catalytic Combustion of Ethyl Acetate over Nanostructure Cobalt Supported ZSM-5 Zeolite Catalysts
- Pages: 483-488
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Gas phase catalytic combustion of ethyl acetate, as one of volatile organic compounds (VOC), was studied on nanostructure ZSM-5, HZSM-5 and Co-ZSM-5 with different cobalt loadings. Nanostructure of ZSM-5 was determined by XRD, SEM and TEM. Catalytic studies were carried out under atmospheric pressure in a fixed bed reactor. Results showed that the Co-ZSM-5 catalysts had better activity than others and at temperatures below 350 °C, amount of Co loading was more effective on catalytic activity. The order of conversion of ethyl acetate over different Co loading is as follows: Co-ZSM-5 (0.75 wt%)<Co-ZSM-5 (1.5 wt%)<Co-ZSM-5 (15 wt%)<Co-ZSM-5 (2.8 wt%). Besides the higher the inlet concentration of ethyl acetate, the lower the conversion yield, and oxygen concentration in catalytic oxidation conditions has not so large influence on conversion. Furthermore, the presence of water vapor in inlet gaseous feed has an inhibitive effect on ethyl acetate conversion and at the temperatures above 400 °C, the effect decreases.
Flame-retardancy of a Cellulosic Fabric by the Application of Synergistic Effect between Ammonium Bromide and Antimony(III) Oxide
- Pages: 489-493
- First Published: 02 April 2009
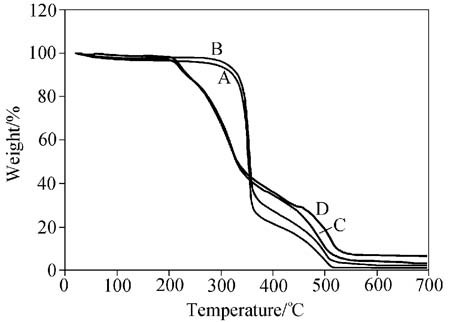
The outcomes of TG curves concerning the flame-retarded supported samples show the similar three stages but with lower decomposition temperatures and mass. The figure also demonstrates TG curve of the flame-retarded cotton fiber and the combined curves respectively. It is obvious that the decomposition temperature of the treated cotton substrate with Sb2O3 is higher compared with untreated one, indicating no influence occurred by using it as a dehydrating agent. Note that both ammonium bromide and its synergy with antimony(III) oxide illustrated a significant role as a dehydrating agent to catalyze the dehydration of the cellulosic substrate, since they lowered the dehydrating temperature around 300 °C.
Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Thermal Behavior of Co(en)3[B4O5(OH)4]Cl·3H2O and [Ni(en)3][B5O6(OH)4]2·2H2O
- Pages: 494-500
- First Published: 02 April 2009
![Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Thermal Behavior of Co(en)3[B4O5(OH)4]Cl·3H2O and [Ni(en)3][B5O6(OH)4]2·2H2O](/cms/asset/567f7e5c-aa15-4087-8932-df4b05a49089/mcontent.jpg)
All components of Co(en)33+, [B4O5(OH)4]2−, Cl− and H2O for Co(en)3- [B4O5(OH)4]Cl·3H2O are linked together to form a 3D supramolecular network through four kinds of hydrogen bonds, O–H···O, O–H···Cl, N–H···Cl and N–H···O and the three crystalline water molecules form a zigzag water-chain through O–H···O.
Synthesis and Crystal Structure of an Unprecedented Supramolecular Complex [Co(µ2-ClO4)2(H2O)2]·2MA
- Pages: 501-504
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Understanding the Effect of Corners: Adsorption of Fluids in Three Different Shapes of Nanopores
- Pages: 505-512
- First Published: 02 April 2009
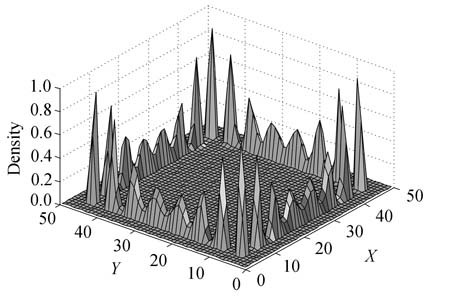
Adsorption of nitrogen, hydrogen and methane in square and rectangular nanopores of various sizes has been studied by grand canonical Monte Carlo simulations (GCMC). By comparison of three kinds of potential models, it was found that the site-site model was more rational, which was therefore used in the work. Adsorption behavior of fluids in square, rectangular and cylindrical pores at T=77 K was compared. Prewetting was found in the corners of the square and rectangular pores, which is absent in the cylindrical pores. Adsorption of hydrogen and methane in the three kinds of pores was compared. Among them, the adsorption uptake of hydrogen in the square pore is highest, especially at low pressures, because the effect of potential superposition in the "corners" makes an important contribution to hydrogen adsorption. The results indicate that the presence of corners has a profound effect upon the adsorption and phase behavior of fluids at low pressures.
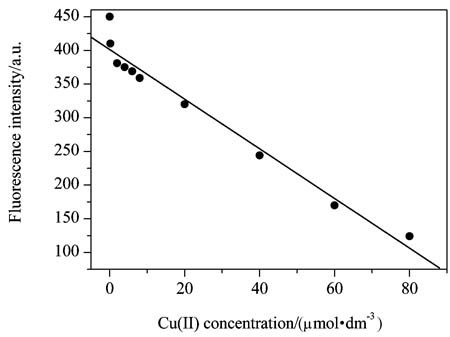
Fluorescence Quenching of Pheophytin-a by Copper(II) Ions
- Pages: 513-517
- First Published: 02 April 2009
A Novel Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Isoniazid Using Cu(II) as Spectroscopic Probe Ion
- Pages: 518-522
- First Published: 02 April 2009

In the presence of SCN−, Cu(II) was reduced to Cu(I) by isoniazid. The resulting Cu(I) reacted with SCN− to develop white emulsion precipitate CuSCN, which was floated on the surface of water when NaNO3 was added into the solution. By determining the amount of residual Cu(II) in the water phase, the amount of isoniazid could be obtained.
Homogeneous DNA Detection Based on Fluorescence Quenching by Nanoparticles in Single-step Format: Target-Induced Configuration Transform
- Pages: 523-528
- First Published: 02 April 2009
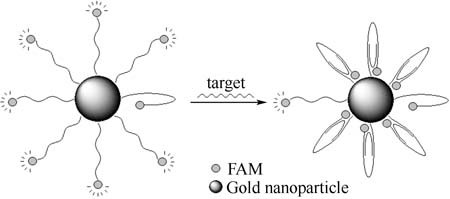
3′ FAM-labeled oligonucleotides were immobilized on the gold nanoparticles via 5′-SH. Specific hybridization with the complementary target makes the probe sequence bend to form an arch-like structure. The fluorophore and gold nanoparticles are brought in close proximity, resulting in fluorescence quenching.
Thermodynamics and Extra-thermodynamics of Bacillus subtilis α-Amylase in Some Chromatographic Systems
- Pages: 529-540
- First Published: 02 April 2009
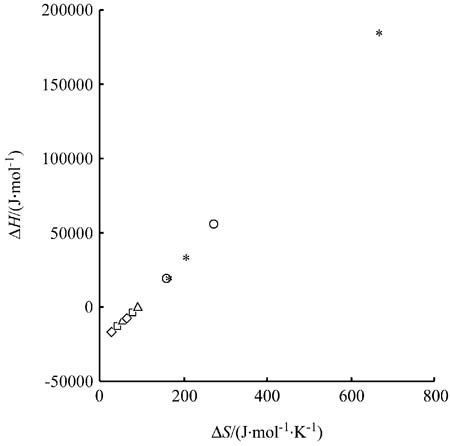
The thermodynamics and extra-thermo- dynamics of Bacillus subtilis α-amylase in some chromatographic systems were studied. It was found that their adsorption procedures were driven by both of the enthalpy change and the entropy change on some chromatographic media, while on some other chromatographic media, their adsorption procedures were driven only by the entropy change; and for α-amylases on a RP-C18 reversed-phase medium (⋄), a Zn-chelated Sepharose fast-flow affinity medium (□), a WCX-1 cation-exchange media (Δ), a PEG-400 hydrophobic medium (◯) and a modified PEG-400 medium (∗︁), their enthalpy-entropy compensation relationships lay on the same straight-line and their enthalpy changes could be compensated only with their entropy changes rising from their conformational change.
Identification of Phenylethanoid Glycosides in Plant Extract of Plantago asiatica L. by Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
- Pages: 541-545
- First Published: 02 April 2009
The present work describes a liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS) method for rapid identification of phenylethanoid glycosides in plant extract from Plantago asiatica L. By using a binary mobile phase system consisting of 0.2% acetic acid and acetonitrile under gradient conditions, a good separation was achieved on a reversed-phase C18 column. The [M–H]− ions, the molecular weights, and the fragment ions of phenylethanoid glycosides were obtained in the negative ion mode using LC-ESI-MS.
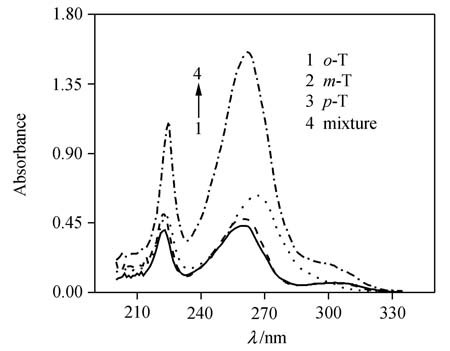
Simultaneous Spectrophotometric Determination of Three Tolualdehyde Isomers by Artificial Neural Networks and Its Comparison with Partial Least Squares
- Pages: 546-550
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Toxicity Effect of Pb(II) on Two Different Kinds of Microbes Measured by Microcalorimetry
- Pages: 551-556
- First Published: 02 April 2009
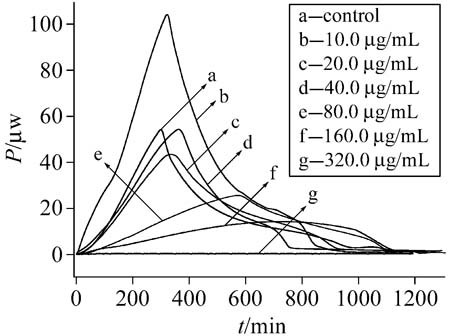
Microcalorimetric was used to analyze the toxic action of Pb2+ on the metabolic activities. Pb2+ has a stimulating effect on Candida humicola and Bacillus subtilis growth at low concentration and an inhibitory influence at high concentration. This investigation aims at evaluating the toxic action of Pb(II) on the Candida humicola and Bacillus subtilis by microcalorimetric technique.
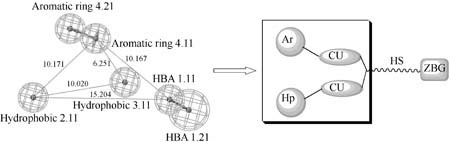
Pharmacophore Identification of Hydroxamate HDAC 1 Inhibitors
- Pages: 557-564
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Synthesis and Biological Activities of Novel Thiophosphoryl Oximates Containing Thiazole and 1,2,3-Triazole Rings
- Pages: 565-568
- First Published: 02 April 2009
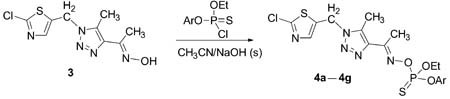
A series of novel thiophosphoryl oximates containing thiazole and 1,2,3-triazole rings 4 were synthesized by the reactions of 1-{1-[(2-chlorothiazol-5-yl)methyl]-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl}ethanone oxime with various asymmetric thiophosphoryl chlorides. The results of preliminary bioassay indicate that some of the title compounds possess moderate insecticidal and fungicidal activities
Application of Heteropolyacids as Heterogeneous and Recyclable Catalysts for One-Pot Synthesis of 3-Cyanopyridine Derivatives
- Pages: 569-572
- First Published: 02 April 2009
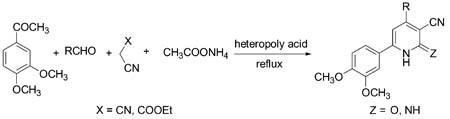
A simple, clean and environmentally benign route to the synthesis of 3-cyanopyridines is described via a one-pot multi-component reaction of 3,4-dimethoxyacetophenone, malonitrile or ethylcyanoacetate, aldehyde and ammonium acetate using heteropolyacids as heterogeneous and recyclable catalysts in very good yields.
Synthesis, Crystal Structures and Electrochemical Properties of O-Chloropropyl and O-Cyanopropyl Resorcinarenes
- Pages: 573-578
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Synthesis, Structure and Biological Activities of Some Novel Anthranilic Acid Esters Containing N-Pyridylpyrazole
- Pages: 579-586
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Ionic liquid-H2O Resulting in a Highly Chemoselective Oxidation of Benzylic Alcohols in the Presence of Aliphatic Analogues Catalyzed by Immobilized TEMPO
- Pages: 587-592
- First Published: 02 April 2009
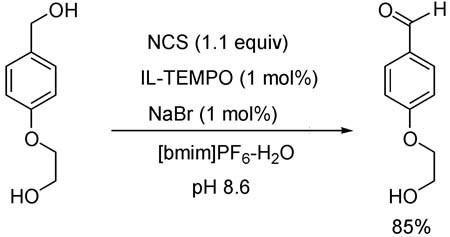
In ionic liquid [bmim][PF6]-H2O, a highly chemoselective oxidation of benzylic alcohols in the presence of aliphatic ones to the corresponding hydroxyl benzyl aldehydes and ketones was allowed in high yields using a facile and effective catalytic oxidation system NCS/NaBr/IL-TEMPO (ionic liquid immobilized TEMPO). The medium, [bmim][PF6], together with the catalyst IL-TEMPO could be easily recycled for ten runs without any influence on the efficacy of the reaction in terms of yield and selectivity of the product.
Synthesis and Antiviral Activities of Chiral Thiourea Derivatives
- Pages: 593-601
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Notes
Experimental and Theoretical Analyses of Complex Bis[2,4-di(p-nitrophenyl)-1,3,5-triazapentadienato]Cu(II) Synthesized in situ
- Pages: 602-606
- First Published: 02 April 2009
Dehydration of Oximes to Nitriles Catalyzed by a Green Heteropolyacid Catalyst: Preyssler's Anion, [NaP5W30O110]14−
- Pages: 607-609
- First Published: 02 April 2009
![Dehydration of Oximes to Nitriles Catalyzed by a Green Heteropolyacid Catalyst: Preyssler's Anion, [NaP5W30O110]14−](/cms/asset/2ebdc3ca-b63a-4651-8fb9-ab90f8584c9a/mcontent.jpg)
A mild, simple, and high yielding procedure for the direct conversion of oximes to nitriles has been developed using heteropolyacid in acetic acid. Aromatic and aliphatic aldoximes were converted to the corresponding nitriles in the presence of Preyssler type heteropolyacid, which could be reused several times without any appreciable loss of activity.
Addition and Correction
Preparation of Magnetic Photocatalyst TiO2 Supported on NiFe2O4 and Effect of Magnetic Carrier on Photocatalytic Activity
- Page: 610
- First Published: 02 April 2009






![Synthesis and Crystal Structure of an Unprecedented Supramolecular Complex [Co(µ2-ClO4)2(H2O)2]·2MA](/cms/asset/48635513-133c-4410-b3bf-89a63b0b3ce4/mcontent.jpg)

![Experimental and Theoretical Analyses of Complex Bis[2,4-di(p-nitrophenyl)-1,3,5-triazapentadienato]Cu(II) Synthesized in situ](/cms/asset/74335a1f-0a60-4ff9-9e1f-e58e0a6f6134/mcontent.jpg)