Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 9/2021
- Page: 1543
- First Published: 19 August 2021

Copyright: Johannes Plenio/Unsplash
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 9/2021
- Page: 1544
- First Published: 19 August 2021
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 9/2021
- Page: 1545
- First Published: 19 August 2021
Highlights
Research Articles
Modeling and Simulation of Hydrodynamics and Filtration in a Membrane-Assisted Stirred Slurry Reactor
- Pages: 1548-1557
- First Published: 14 June 2021
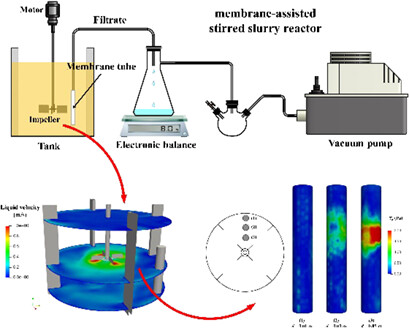
In slurry reactors, separating the fine catalyst particles from liquid products is still a problem. A membrane-assisted stirred slurry reactor was created by coupling membrane filtration with the traditional stirred tank configuration. CFD simulations using combined membrane permeation and particle deposition models resulted in good predictions regarding the hydrodynamics and membrane fouling.
Random Packing Performance in Continuous Foam Fractionation
- Pages: 1558-1566
- First Published: 14 June 2021
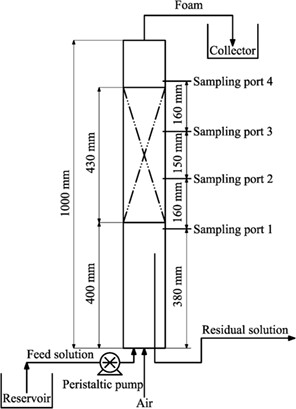
The #25 teller rosette random packing was used to enhance foam drainage in a continuous foam fractionation, thus reducing the liquid holdup and improving the enrichment ratio effectively. The enrichment ratio obtained by the #25 teller rosette column was 1.76 times that obtained by the control column. A new method for graphical illustration of the theoretical stages is presented.
Modeling a Fluidized Bed Dryer through Computational Fluid Dynamics and the Discrete Element Method
- Pages: 1567-1577
- First Published: 21 June 2021
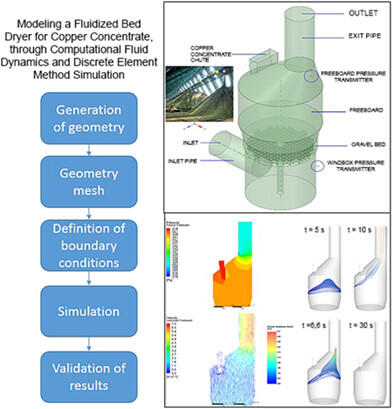
Studying fluid dynamic behavior in a fluidized bed dryer allows a complex process to be simplified with computational tools and acceptable error margins in engineering equipment design. The model proposed herein, based on computational fluid dynamics and the differentiated elements method, can estimate flow size and identify zones with the greatest interaction between drying flow and concentrate.
Extraction on a Robotic Platform – Autonomous Solvent Selection under Economic Evaluation Criteria
- Pages: 1578-1584
- First Published: 21 June 2021
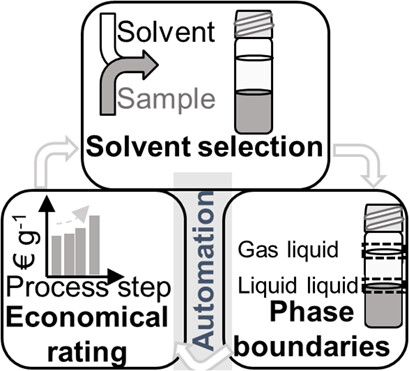
A systematic solvent selection tool was developed based on Hansen solubility parameters. The developed tool, combined with automatic phase boundary detection and key performance indicators for economic rating, led to two suitable solvents for the extraction of progesterone out of a fermentation broth. All experiments necessary were executed autonomously by the robotic platform.
Advanced Evaluation of a Biomass Externally Fired Hydrogen Production Combined Cycle
- Pages: 1585-1595
- First Published: 21 June 2021
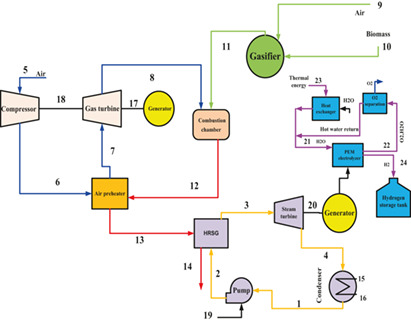
The biomass externally fired hydrogen production combined cycle is assessed with common exergy and exergoeconomic analyses. To attain more realistic results, new exergy and exergoeconomic analyses are applied. With common exergy analysis, the gasifier and the heat recovery steam generator exhibit low exergy efficiencies, but the modified analysis attributes high exergy efficiency to them.
Effect of Liquid Addition on Gas-Solid Fluidization
- Pages: 1596-1603
- First Published: 21 June 2021
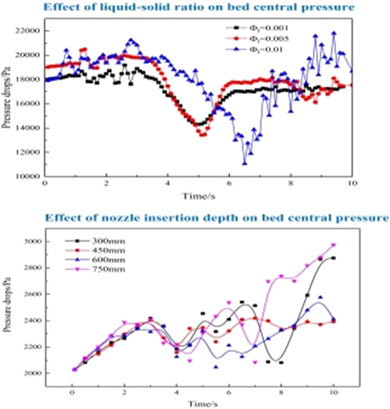
The effect of addition position and quantity of liquid on the evolution rule of flow structure parameters in a fluidized bed was investigated using numerical simulation combined with experiments. The computational fluid dynamics model and liquid bridge force model were coupled to simulate liquid addition in the fluidized bed. The simulation results agreed well with the experimental data.
Effect of Citric Acid and Sodium Chloride on Characteristics of Sunflower Seed Shell-Derived Activated Carbon
- Pages: 1604-1617
- First Published: 21 June 2021

Every year, more than 50 million tons sunflower seeds are produced to feed oil industries which generate an enormous load of noncommercial-value seed shells. Activated carbon with ultrahigh surface area was successfully and effectively synthesized from sunflower seed shells using citric acid and sodium chloride via N2 carbonization followed by KOH activation.
Synthesis of Activated Carbon Using Bagasse and Recycled Carbon Fibers
- Pages: 1618-1622
- First Published: 06 July 2021
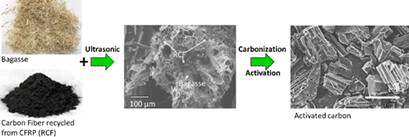
A recycling method for carbon fibers shorter than the critical fiber length is presented, with the aim of producing activated carbon with a high specific surface area and well-developed micropores using bagasse as a raw material with the carbon fiber recycled from carbon fiber reinforced polymer. This method could also be applied to produce activated carbon with lignocellulose as a raw material.
Effects of Zinc and Aluminum on the CuO Crystalline Size for Direct Dimethyl Ether Synthesis from Syngas
- Pages: 1623-1630
- First Published: 08 July 2021
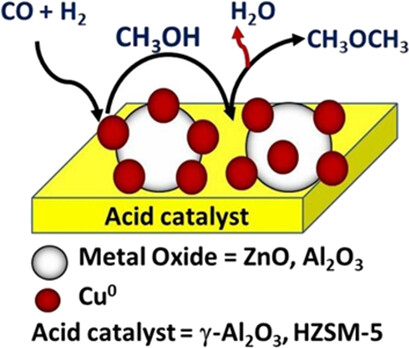
Bifunctional catalysts for direct dimethyl ether synthesis from syngas were prepared by mixing metal oxide catalysts with different acid catalysts. CuO/ZnO/Al2O3 (2:2:1)/γ-Al2O3 is the bifunctional catalyst with the best molar ratio for methanol synthesis as it has the smallest CuO crystal size and the greatest copper dispersion, and γ-Al2O3 has the best acidity for methanol dehydration.
An Efficient Bioaggregate Reactor for Enhanced Denitrification of Sewage with Low Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio
- Pages: 1631-1640
- First Published: 08 July 2021
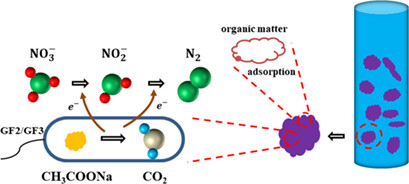
Nitrate in domestic wastewater poses a threat to the environment and human health, but the low C/N ratio of domestic sewage hinders microbial denitrification. A bioaggregate reactor was developed to treat low-C/N wastewater, and the operating parameters were optimized by the response surface method. Almost complete nitrate removal was achieved, with nitrogen gas as final denitrification product.
Continuous Production of Lipid Nanoparticles by Ultrasound-Assisted Microfluidic Antisolvent Precipitation
- Pages: 1641-1650
- First Published: 13 July 2021

In recent studies, nanoparticles for pharmaceutical applications were precipitated in microfluidic systems due to the achievable monodispersity. Such a precipitation process in a microfluidic system increases the fouling and clogging probability, which is a typical issue of microfluidic systems. To precipitate nanoparticles continuously in a microfluidic system, the system was permanently sonicated.
Simulation of a Natural Gas Steam Reforming Plant for Hydrogen Production Optimization
- Pages: 1651-1659
- First Published: 13 July 2021
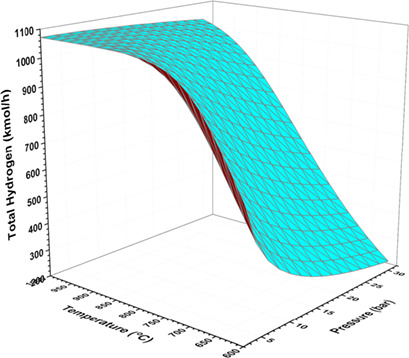
A simulation study is presented for a natural gas steam reforming plant. Simulation results were validated against plant data under steady-state conditions. A simulation tool was developed to identify the optimal operating conditions and predict the plant hydrogen productivity. Optimized conditions for the complete industrial hydrogen plant maximize the added value and minimize the running cost.
Characterization of an Automated Spinning-Band Column as a Module for Laboratory Distillation
- Pages: 1660-1667
- First Published: 13 July 2021
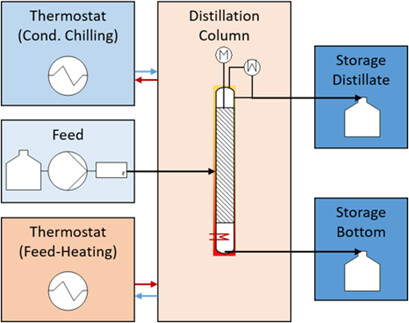
A modular continuously operated spinning-band distillation column for small product amounts is presented and characterized regarding operating window and separation efficiency. The proposed column can be applied either for first product amounts within a small-scale production or as feasibility studies for distillation in a scale-up context with small amounts of resources, energy, and time.
Mass and Heat Transfer Coefficients in a Thermophilic Membrane Distillation Bioreactor
- Pages: 1668-1676
- First Published: 15 July 2021
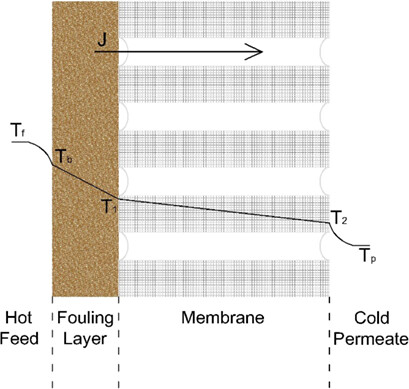
The membrane distillation bioreactor is considered an innovative wastewater treatment process integrating the membrane distillation system with a bioreactor. The heat and mass transfer coefficients of such bioreactor treating raw research hospital wastewater were calculated by using the experimental data obtained from the system. The system proved to be controlled by mass resistance.
Improved Operation of Continuous Ozone Hydrate Production
- Pages: 1677-1685
- First Published: 15 July 2021

In a previous study, forming continuously O3+O2+CO2 hydrate by an experimental system was presented. Further optimization and design parameters of this system are described. The results imply that the cost and time for O3+O2+CO2 hydrate production for industrial applications can be reduced. The overall heat transfer coefficient, a design parameter for scale-up, could be successfully measured.
Development of a Route to the Most Active Nafronyl Stereoisomer by Coupling Asymmetric Synthesis and Chiral Chromatography Separation
- Pages: 1686-1692
- First Published: 15 July 2021
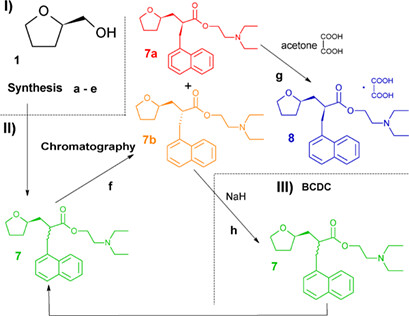
The preparation route of the most active stereoisomer of nafronyl includes three stages: stereoselective synthesis of the binary mixture of nafronyl diastereoisomers from (R)-tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol, chromatographic separation of the mixture obtained, and conversion of the unwanted diastereoisomer to the equimolar mixture of the diastereoisomers by base-catalyzed diastereoisomeric conversion.
Analysis of Hydrocyclone Geometry via Rapid Optimization Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics
- Pages: 1693-1707
- First Published: 16 July 2021
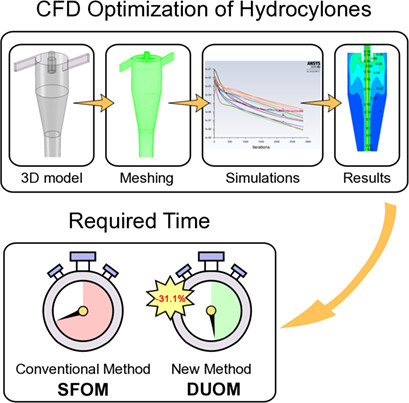
A rapid computational fluid dynamics optimization method (DUOM) for hydrocyclone geometries is presented that can avoid the inevitable repeated modeling, meshing, and simulation steps in the optimization process of traditional methods. Exemplified by the vortex finder length of a hydrocyclone, the DUOM is shown to reduce the operating time of optimization by 31.1 %.
Batch Oxidative Desulfurization of Model Light Gasoil over a Bimetallic Nanocatalyst
- Pages: 1708-1715
- First Published: 16 July 2021

Oxidative desulfurization (ODS) is an alternative to hydrodesulfurization for removing organic sulfur compounds such as dibenzothiophene (DBT) from fuel oils such as diesel fuel to avoid SOx emissions and acid rain. Herein, an AgO/ZnO/HY-zeolite nanocatalyst synthesized by a simple impregnation method showed a high degree of DBT removal in the catalytic ODS of a light gasoil and good reusability.
Design and Control for the Dimethyl Adipate Process with a Side-Reactor Column Configuration
- Pages: 1716-1725
- First Published: 26 July 2021
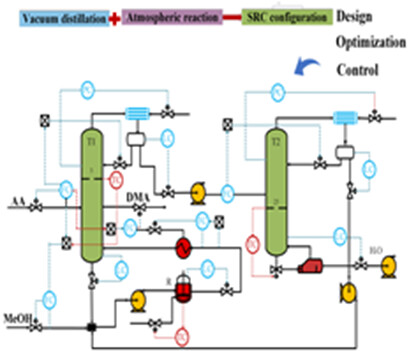
A side-reactor column configuration process for dimethyl adipate production is proposed, which overcomes the limitation of mismatch between reaction and separation conditions in the reactive distillation process. A control strategy which can reject the disturbance of the feed flow rate and composition based on the optimal steady-state conditions is investigated.
Maximizing Propylene Separation from Propane by Extractive Distillation with Aqueous N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone as Separating Agent
- Pages: 1726-1736
- First Published: 15 July 2021
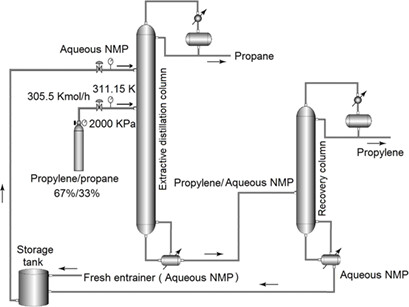
Production of high-purity propylene is important due to its use as feedstock for numerous products. Herein, a simulated extractive distillation process with aqueous N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone as separating agent was used to separate polymer-grade propylene from propane. Compared with the high-pressure binary distillation process, it showed lower energy consumption and 52 % saving in total annual cost.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 9/2021
- Page: 1737
- First Published: 19 August 2021










