Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 7/2019
- Page: 1343
- First Published: 19 June 2019

Non-invasive real-time measurement of local heat and mass transfer by application of Rainbow Schlieren Deflectometry. Copyright: JM Schulz@TU Berlin-FGVT
Rainbow Schlieren Deflectometry (RSD) is an optical, non-invasive measuring technique based on the change of refractive index due to differences in temperature, pressure, or concentration. The refractive index gradient is resolved locally with a high spatiotemporal resolution by color-coding the displacement in the filter plane. Integration of the gradient field with respect to the state variable of concern yields, e.g., a spatially resolved real-time measurement of the temperature or concentration field. Due to the integrational character of RSD, the refractive index distribution has to exhibit specific symmetric conditions, e.g., standard rotational symmetry or a tomographic approach is needed. Quantitative validation can be done by measuring local heat transfer from solid test specimen in liquid or gaseous surroundings. Mass transfer measurements are done by visualization of local concentrations, e.g., for jets emitted into a stagnant fluid or liquid-liquid mass transfer in disperse multiphase systems. RSD as well as other optical measurement techniques have seen a rise in popularity, application depth, and measuring precision due to the advances in digital photography in the last decades. Their non-invasive, spatially resolved character in combination with real-time acquisition poses a promising future with deeper insights into highly transient processes and the possibility to match and validate common CFD simulations, e.g., in multiphase systems.
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 7/2019
- Page: 1344
- First Published: 19 June 2019
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 7/2019
- Page: 1345
- First Published: 19 June 2019
Highlights
Editorial
Research Articles
Data-Driven Subgrid-Scale Modeling for Convection-Dominated Concentration Boundary Layers
- Pages: 1349-1356
- First Published: 09 April 2019
Accurate prediction of heat and mass transport is a key step in many engineering applications. Hence, a new approach to model convection-dominated reactive-species boundary layers was developed. Numerical data obtained by solving a substitute problem followed by a statistical analysis were used to train a machine learning model that can approximate the local reactive mass transfer.
Three-Dimensional Observation of Single Air Bubble Breakup in a Stirred Tank
- Pages: 1357-1370
- First Published: 09 April 2019
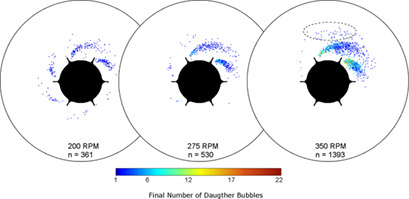
Serial three-dimensional single bubble breakup trajectories were analyzed to gain a better understanding of the breakup process for Rushton turbines in stirred tanks. The experimental breakup positions were linked to the current flow field in the tank, which is highly inhomogeneous over time and space.
Rupture of Wetting Films Formed by Bubbles at a Quartz Surface in Cationic Surfactant Solutions
- Pages: 1371-1380
- First Published: 26 April 2019

The presented unique methodology, allowing precise control over the initial degree of adsorption coverage at the detaching bubble surface, is used to study the kinetics of three-phase contact formation and bubble attachment to quartz surfaces in solutions of cationic surfactant of various concentrations. New evidence confirming different mechanisms of liquid film rupture is provided.
Influence of Liquid Density and Surface Tension on the Pinning of Sliding Droplets on a Triangular Microstructure
- Pages: 1381-1387
- First Published: 17 May 2019
The pinning of sliding droplets on microstructures is a frequently observed phenomenon in nature and industry. Detailed numerical simulations using the Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes equations are performed to research the conditions for the pinning. The physical parameters liquid density and surface tension proved to have a significant impact on the pinning of sliding droplets.
Visualization of Mass Transfer during Droplet Formation
- Pages: 1388-1394
- First Published: 17 May 2019
Liquid-liquid extraction is widely used in chemical processes. The mass transfer behavior is an essential part of understanding the process performance in an extraction apparatus. This research article describes the regimes that are passed through during droplet formation with simultaneous mass transfer.
Numerical Characterization of the Bubble Rise Behavior in Viscoelastic Liquids
- Pages: 1395-1403
- First Published: 17 May 2019
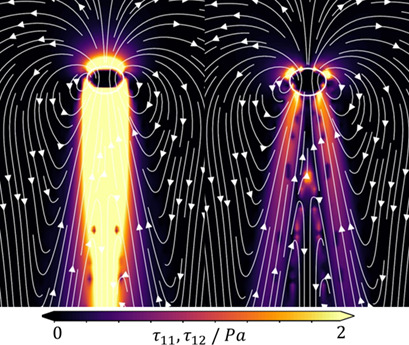
A numerical modelling approach to simulate viscoelastic multiphase flows with moving interfaces is described. The solver is applied to single bubbles rising in viscoelastic liquids and validated against experimental results of the terminal rise velocity and the qualitative shape of the flow field. The stress field is analyzed with respect to the normal and shear components.
Coalescence Modeling for Design of Technical Equipment
- Pages: 1404-1413
- First Published: 17 May 2019
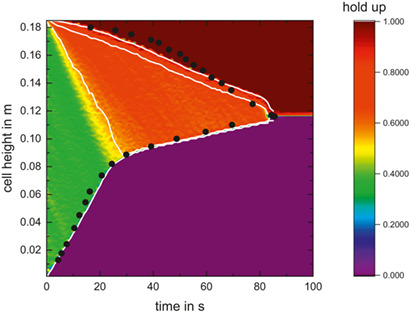
Modeling coalescence is the basis for settler or extraction column design. A coalescence model is presented that builds on generic equations, which describe the fundamental steps of coalescence under various fluid-dynamic conditions, that can easily be adapted to any specific equipment. A quantification of bouncing probability and a consistent description of coalescence probability are included.
Experimental Data on Mutual Mass Diffusivities of Binary Mixtures of Ethanol and [EMIM][DEP]
- Pages: 1414-1420
- First Published: 23 May 2019
![Experimental Data on Mutual Mass Diffusivities of Binary Mixtures of Ethanol and [EMIM][DEP]](/cms/asset/cdcd49b9-6104-486e-8fb9-9ea3317d96ae/ceat201900027-toc-0001-m.jpg)
In most chemical engineering applications, mass transfer is a crucial and determining process, which in turn is dependent on the transport of molecules. The mutual mass diffusivities of binary mixtures of ethanol in an ionic liquid are determined experimentally by means of a diaphragm cell for varying ranges of temperatures and ionic liquid mass fractions.
Communications
How Do Vortex Structures Influence Boundary Layer Dynamics in Gas-Liquid Systems?
- Pages: 1421-1426
- First Published: 02 April 2019

Transport processes near fluidic interfaces play a crucial role in many engineering operations. The influence of vortex structures on momentum and mass transport in gas-liquid flows is studied in a series of experiments. Local mass transfer is strongly influenced by the vortices, whereas global mass transfer is not significantly changed. The theory of boundary layer peeling is introduced.
Editorial
Industrial Crystallization: Increasingly Unavoidable These Days
- Page: 1427
- First Published: 19 June 2019
Research Articles
Estimation of Kinetics for Batch Cooling Crystallization by Focused-Beam Reflectance Measurements
- Pages: 1428-1434
- First Published: 21 March 2019
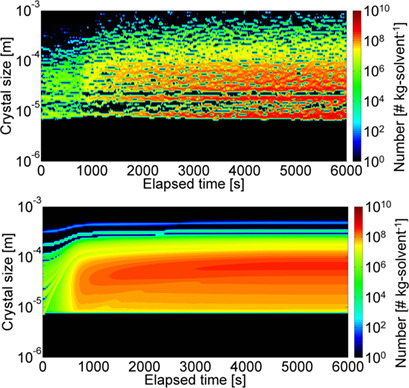
Regulation of crystal size distribution is important in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Seeded batch cooling crystallization of the APIs acetaminophen and L-arginine was monitored by focused-beam reflectance measurements and FTIR spectroscopy and numerically simulated. Simulated values of the mean crystal mass size corresponded reasonably well with the observed values.
Influence of the Solvent Content on the Phase Transformation of Sulfadiazine N-Methyl Pyrrolidone Solvate
- Pages: 1435-1445
- First Published: 25 March 2019
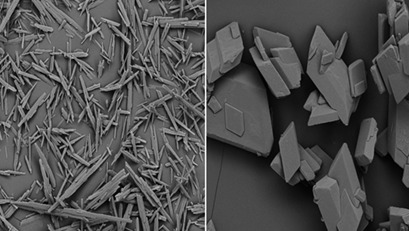
Finer powders of poorly soluble drugs provide better bioavailability and are therefore preferred by the pharmaceutical industry. In the solution-mediated phase transformation of sulfadiazine (SD) N-methyl pyrrolidone (NMP) solvate into SD, the NMP amount influences the crystal structure while higher temperatures and stirring rates accelerate the transformation process, negatively influencing the product quality.
Synthesis and Characterization of Sodium Dithionate and its Dihydrate
- Pages: 1446-1451
- First Published: 21 March 2019
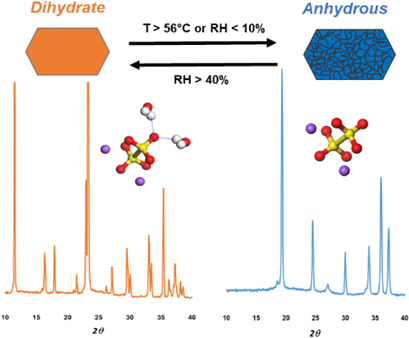
The inorganic compound sodium dithionate has been studied as tailor-made impurity in the literature but its characterization remained unexplored. Solid-state characterization of Na2S2O6 is conducted using complementary experimental tools, allowing to gather data about the mechanism of dehydration/hydration. The important role of water in the dihydrate crystalline structure is highlighted.
Simulation and Empirical Studies of Solvent Evaporation Rates in Vacuum Evaporation Crystallization
- Pages: 1452-1457
- First Published: 28 March 2019

The challenge in evaporation crystallization technologies is to reduce the energy consumption. Mass and energy balance calculations of evaporation crystallization were performed based on thermodynamic modeling with the aid of Aspen Plus simulation as well as experimental work. A deeper understanding of an evaporation crystallization process from aqueous solutions could be achieved.
Modeling and Growth Kinetics of Antisolvent Crystallization Applied to the Pharmaceutical Industry
- Pages: 1458-1465
- First Published: 21 March 2019
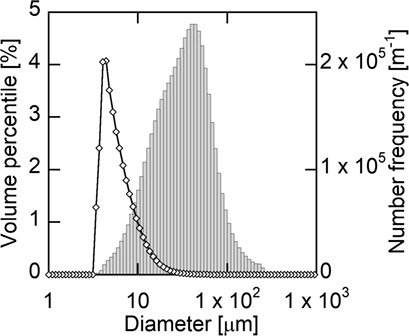
For simulation of the product crystal size in the pharmaceutical industry, a concise antisolvent crystallization model is proposed based on population and mass balances, together with a methodology to determine the growth rate constant and order. The appropriate data treatment of crystal size measured with the laser diffraction/scattering method is discussed.
Ultrasonic Irradiation during the Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate to Dihydrate Transformation Process
- Pages: 1466-1474
- First Published: 20 March 2019
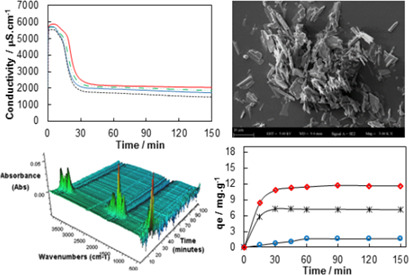
The effects of ultrasonic irradiation combined with mandelic acid as an additive on the transformation process from calcium sulfate hemihydrate to calcium sulfate dihydrate were evaluated. The results provide a better understanding of morphological, physicochemical, filtration and adsorption characteristics during this transformation and serve as a base to further improve this transformation process.
Purification of Nickel Sulfate by Batch Cooling Crystallization
- Pages: 1475-1480
- First Published: 28 March 2019
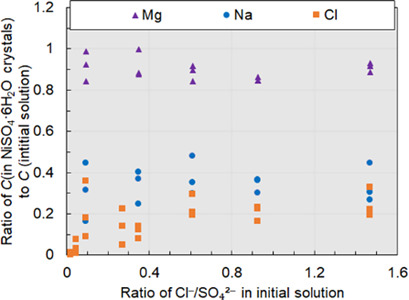
Batch cooling crystallization is successfully applied to recover nickel as NiSO4 crystals from acidic multicomponent solutions that mimic electrowinning downstream process solutions. A high concentration of chloride reduces NiSO4 solubility and decreases the crystal purity. Magnesium persistently remains in the crystals and is harder to remove than the other two impurities: Na and Cl.
Crystallization Mechanisms and Rates of Cyclopentane Hydrates Formation in Brine
- Pages: 1481-1491
- First Published: 28 March 2019
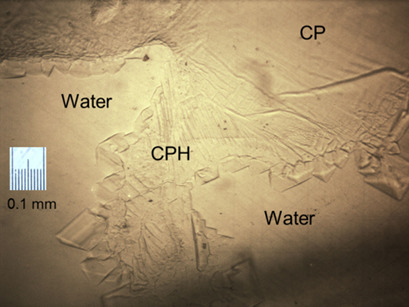
Cyclopentane hydrates are considered to be a candidate for hydrate-based desalination, so the mechanism of cyclopentane hydrate crystallization in pure water and in brine is crucial. Various salts at different concentrations and under three driving forces (subcooling) were considered to explore the phenomenology of hydrate formation by microscopy. The hydrate growth speeds were also determined.
Precipitation of Cobalt Salts for Recovery in Leachates
- Pages: 1492-1499
- First Published: 15 April 2019
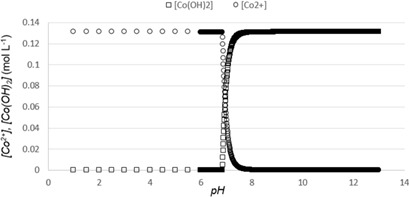
Cobalt is required in many industrial applications and faces the risk of shortage, making research on cobalt recycling highly important for the future. Cobalt is recovered from Li-ion batteries by precipitation from leachates with a yield of 99.8 %. A process is designed allowing selective separation from nickel, manganese, and copper present in solution, with precipitation yields > 99 % for each metal.
Limitations of Preferential Enrichment: A Case Study on Tryptophan Ethyl Ester Hydrochloride
- Pages: 1500-1504
- First Published: 15 April 2019
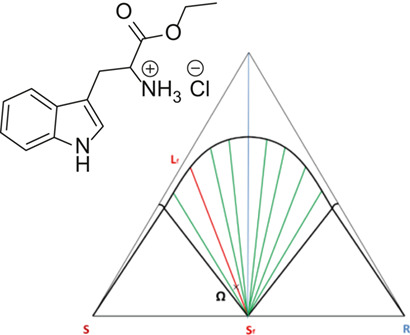
The extension of the scope of preferential enrichment was attempted with tryptophan ethyl ester hydrochloride. This salt possesses one of the most important prerequisites for preferential enrichment in terms of a higher solubility for the pure enantiomers with reference to the racemic compound. Yet, this salt cannot perform preferential enrichment which is due to the absence of a solid solution.
Influence of Solvents on Solution-Mediated Polymorphic Transformation of the Polymorphs of L-Histidine
- Pages: 1505-1511
- First Published: 15 April 2019
Solution-mediated polymorphic transformation of form B into form A of L-histidine via antisolvent crystallization is evaluated. A higher fraction of form A promotes a faster complete transformation. The transformation time increases with higher supersaturation and volume fraction of the antisolvent and is shorter for the transformation in water-acetonitrile solution compared to other solutions.
Crystallization of Cephradine Polymorphs and Hydrates from Mixed Solvents of Methanol and Water
- Pages: 1512-1518
- First Published: 24 April 2019
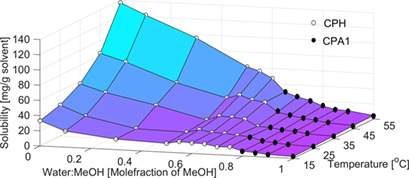
The solubility and relative stability of cephradine anhydrate and monohydrate in various water-methanol mixtures were evaluated at different temperatures. Cephradine monohydrate was crystallized by cooling crystallization from aqueous solutions. It was found that using a slow cooling rate and seeding can improve the particulate properties as well as the filterability of the obtained products.
Unusual Crystal Growth Kinetics of (RS)-Ibuprofen from Ethanolic Solutions
- Pages: 1519-1524
- First Published: 03 May 2019
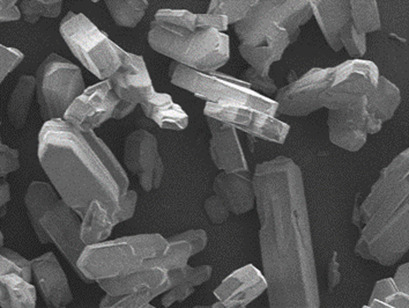
Crystal growth of (RS)-ibuprofen in aqueous ethanol solvent displays significant growth rate dispersion and a large dead zone for slow-growing crystals. The dead zone region is reduced for crystals with average growth rates and does not exist for the fastest growers. These phenomena may be related to differences in thermodynamic stability within the population or to growth pinning effects.
Mineralization of Calcium Carbonate Induced by Egg Substrate and an Electric Field
- Pages: 1525-1532
- First Published: 17 May 2019

CaCO3 biomineralization is strongly influenced by egg substrates. CaCO3 crystals were successfully generated on such substrates. The morphology and polymorphism of CaCO3 are affected by different egg substrates, temperatures, concentrations, and electric fields. Such a rapid calcification process is more suitable for the production of CaCO3 and provides a reference to egg waste recycling.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 7/2019
- Page: 1533
- First Published: 19 June 2019
Letter to the Editor
Corrigendum
Local Mass Transfer Phenomena and Chemical Selectivity of Gas-Liquid Reactions in Capillaries
- Pages: 1536-1537
- First Published: 19 June 2019










